Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
The Business Buying Process
Încărcat de
Santanu Roy0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
99 vizualizări4 paginiThe document discusses the 8 stages of the business buying process:
1) Problem recognition, where a company identifies a need for a new product or service.
2) General needs description, where the buying committee determines required product characteristics and alternatives.
3) Product specification, where technical specifications are developed.
4) Supplier search, where potential suppliers are identified.
5) Proposal solicitation, where suppliers submit proposals in response to a Request for Proposal.
6) Supplier selection, where suppliers are evaluated and ranked.
7) Order specification, where final order details are negotiated.
8) Performance review, where the supplier's performance is periodically evaluated.
Descriere originală:
buying process
Drepturi de autor
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentThe document discusses the 8 stages of the business buying process:
1) Problem recognition, where a company identifies a need for a new product or service.
2) General needs description, where the buying committee determines required product characteristics and alternatives.
3) Product specification, where technical specifications are developed.
4) Supplier search, where potential suppliers are identified.
5) Proposal solicitation, where suppliers submit proposals in response to a Request for Proposal.
6) Supplier selection, where suppliers are evaluated and ranked.
7) Order specification, where final order details are negotiated.
8) Performance review, where the supplier's performance is periodically evaluated.
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
99 vizualizări4 paginiThe Business Buying Process
Încărcat de
Santanu RoyThe document discusses the 8 stages of the business buying process:
1) Problem recognition, where a company identifies a need for a new product or service.
2) General needs description, where the buying committee determines required product characteristics and alternatives.
3) Product specification, where technical specifications are developed.
4) Supplier search, where potential suppliers are identified.
5) Proposal solicitation, where suppliers submit proposals in response to a Request for Proposal.
6) Supplier selection, where suppliers are evaluated and ranked.
7) Order specification, where final order details are negotiated.
8) Performance review, where the supplier's performance is periodically evaluated.
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 4
Submitted for I.T.
S Ghaziabad
Submitted To Prof. SWATI SINGH
Submitted By Chanchal dey
PGDM (2012-2014) Section-B
INSTITUTE OF MANAGEMENT & SCIENCE, MOHAN NAGAR GHAZIABAD Date: 17/09/2012
The Business Buying Process
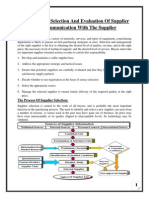
There are 8 stages of business buying process. These are discussed below.
Problem recognition
General needs description
Product specification
Supplier search
Proposal solicitation
Supplier selection
Order-routine specification
Performance review
Business Buying Process
1. Problem recognition:- The buying process start when a
company identifies a need that can be resolved by acquiring a product or service. The company may decide a new product or require new parts on a machine because of the manager unhappy with current product, which is internal. Externally the company gets new idea & solution regarding problem on the product.
2.
General Need Description:-
The buying committee will often
work with e initiator, users, or others to determine the required characteristics and quantity of the product, in addition to researching alternative solutions to fulfill the need.
3. Product Specification:- In this stage the business buying
process in which the company describes the general characteristics and quantity of a needed item. For standard items, this is simple. For complex items the organizational buyer works with specialist and technical experts to define relevant product characteristics such as re liability, durability, or price. The buying organization now develops the items technical specification. Often, the company will assign a product-valueanalysis engineering team to the project. Product value analysis (PVA) is an approach to cost reduction that studies components to determine whether they can be redesigned or standardized or made by cheaper methods of production.
4. Supplier search:- The buying committee identifies and compile
the most suitable qualified suppliers by reviewing trade directories, doing computer search recommend by other companies.
5. Proposal solicitation:- In the next step the buying committee
will require a detailed written proposal and extend an RFP (request for proposal) inviting qualified suppliers to submit proposals. After reviewing the proposals the buyer will invite a few prospective suppliers to make formal presentations in person. At this point it may make sense to stop all other marketing communications directed at this prospect and focus all communication via personal communication between the buying committee and sales person.
6. Supplier selection:-Before choosing a supplier the buying
committee will specify the desired supplier attributes (product and service quality, reputation, on time delivery, ethical corporate behavior, honesty communication and competitive price) and then rank the suppliers based on these attributes to identify the most suitable supplier. As part of the process buyers may even attempt to negotiate with preferred suppliers for better prices and terms before making a final selection In order to position yourself most favorably, take the time to understand the specific buying situation, relative importance of the product attributes and how their prospects determine their valuations.
7. Order-Routine specification:- the buyer now prepare an
order-line specification, after selecting a supplier, the buyer will negotiate the final order by listing the technical specifications, agreed upon price, quantities, expected time of delivery, return policies, warranties and any other terms of negotiation.
8. Performance Review:- The buyer periodically reviews the
performance of the chosen supplier. The buyer may contact user and ask them to rate their satisfaction .The performance review may lead the buyer to continue, modify or end the relationship with the supplier. The sellers job to monitors the same factors used by the buyer to make sure that the seller is giving the expected satisfaction.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- PurchasingmanagementDocument20 paginiPurchasingmanagementlalitha kandikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 009 Installation of Pumps Risk AssessmentDocument2 pagini009 Installation of Pumps Risk Assessmentgangadharan000100% (13)
- The Business Buying ProcessDocument3 paginiThe Business Buying ProcessShakira YasminÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Procurement ManagementDocument30 paginiWhat Is Procurement Managementcompiler&automataÎncă nu există evaluări
- Business Buying ProcessDocument4 paginiBusiness Buying ProcessArIf KarIm AbIr100% (1)
- Lesson Plan: Instructor: Date Topic: Grade Level: Subject ObjectivesDocument5 paginiLesson Plan: Instructor: Date Topic: Grade Level: Subject Objectivesapi-340265930Încă nu există evaluări
- Analyzing Business Markets 7Document21 paginiAnalyzing Business Markets 7Stranger SinhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Procurement Management SummaryDocument9 paginiProcurement Management SummaryHermione OrangutangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch7 Analyzing Business MarketsDocument4 paginiCh7 Analyzing Business MarketsRina Fordan BilogÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industrial MarketingDocument8 paginiIndustrial MarketingHina Jain100% (1)
- Procedure On AskDocument6 paginiProcedure On AskAbdul SaboorkhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steps in The Procurement ProcessDocument5 paginiSteps in The Procurement ProcessSahili SalveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vendor Selection ProcessDocument3 paginiVendor Selection ProcessJay Ramchandani100% (1)
- Vendor SourcingDocument5 paginiVendor SourcingDeepak JettaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Nature of Industrial BuyingDocument40 paginiThe Nature of Industrial Buying99862123780% (1)
- A Project On Shoppers Stop Ltd.Document43 paginiA Project On Shoppers Stop Ltd.NARENz83% (6)
- Industrial Buying Process MbaknolDocument9 paginiIndustrial Buying Process Mbaknolthereald100% (1)
- Chapter 6 - Business Markets and Business Buyer Behavior LETRA GRANDEDocument8 paginiChapter 6 - Business Markets and Business Buyer Behavior LETRA GRANDEwoley37683Încă nu există evaluări
- The Consumer Decision ProcessDocument2 paginiThe Consumer Decision ProcessĐức VũÎncă nu există evaluări
- MarketingDocument9 paginiMarketingashima khadkaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6Document3 paginiChapter 6Anik ChandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Consumer Buying DecisionDocument21 paginiConsumer Buying DecisionShivraj JoshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Source Selection and Vendor DevelopmentDocument23 paginiSource Selection and Vendor DevelopmentVicky Vignesh100% (1)
- Procurement ManagementDocument10 paginiProcurement ManagementAkshatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial 5 6Document2 paginiTutorial 5 6Sha HerÎncă nu există evaluări
- B2B Marketing Unit2Document18 paginiB2B Marketing Unit2mansiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Name: Aman Prakash Enrollment Number: 19BSP0279 Section: B Subject: B2B MarketingDocument4 paginiName: Aman Prakash Enrollment Number: 19BSP0279 Section: B Subject: B2B Marketingmonika sharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sales Management AbhilashDocument17 paginiSales Management AbhilashRaghav LahotiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Purchase Decision Making Process in OrganizationDocument6 paginiPurchase Decision Making Process in OrganizationJowjie TVÎncă nu există evaluări
- B2B TmaDocument15 paginiB2B Tma1990fitsumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6: Business Markets and Business Buyer Behavior The Business Market - It Also Includes Retailing and Wholesaling Firms That Acquire Goods For The PurposeDocument2 paginiChapter 6: Business Markets and Business Buyer Behavior The Business Market - It Also Includes Retailing and Wholesaling Firms That Acquire Goods For The PurposeeliecstlloÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHAPTER SIX Purchase DescriptionDocument13 paginiCHAPTER SIX Purchase DescriptionTessema TeshomeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Procurement ManagementDocument8 paginiProcurement ManagementManoj AgarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles of Marketing Module 3Document2 paginiPrinciples of Marketing Module 3Peter John IntapayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vendor Qualification ProcedureDocument2 paginiVendor Qualification ProceduresamÎncă nu există evaluări
- UNIT-2 (Control On Purchased Product)Document12 paginiUNIT-2 (Control On Purchased Product)monishasingh088Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter No 6 Business Markets and Business Buyer BehaviorDocument15 paginiChapter No 6 Business Markets and Business Buyer BehaviorIrfan AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Purchase Process 8 StepsDocument2 paginiThe Purchase Process 8 StepsTUBUA JULIUSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Materials Mangament Chapter 3 and 4Document138 paginiMaterials Mangament Chapter 3 and 4Abubeker AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comprehensive Discussions AboutDocument30 paginiComprehensive Discussions AboutDimple MontemayorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit-4 Analyzing Marketing: Analyzing Business Markets and Business Buying BehaviorDocument18 paginiUnit-4 Analyzing Marketing: Analyzing Business Markets and Business Buying BehaviorFarrukh KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9 2 2+Session+Summary+Document7 pagini9 2 2+Session+Summary+Poonam VankudreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group 4 Strategic SourcingDocument6 paginiGroup 4 Strategic Sourcingadwiyan0510Încă nu există evaluări
- Presented To:-Presented ByDocument61 paginiPresented To:-Presented Byhitesh tokeÎncă nu există evaluări
- B2B Marketing DiscussionDocument5 paginiB2B Marketing DiscussionLauraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To VendorDocument2 paginiIntroduction To VendorRajesh Kumar KÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Buying Decisions Do Business Buyers MakeDocument9 paginiWhat Buying Decisions Do Business Buyers MakeNaol danielÎncă nu există evaluări
- Factors Affecting Industrial Buying BehaviourDocument6 paginiFactors Affecting Industrial Buying BehaviourSaisrita PradhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Buying Beha 123Document31 paginiBuying Beha 123Prakash VadavadagiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Consumer Buying BehaviorDocument3 paginiConsumer Buying BehaviormohdsabirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shubham QualityDocument12 paginiShubham Qualitysp181119Încă nu există evaluări
- PoM W5 Ch.6 Business Markets and Buyer BehaviorDocument18 paginiPoM W5 Ch.6 Business Markets and Buyer BehaviorMarijon CarpioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Operations Management - Live Session 5 NotesDocument21 paginiOperations Management - Live Session 5 NotesPavan KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marketing Management (Chapter 7) 3Document16 paginiMarketing Management (Chapter 7) 3Salman PreeomÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Do An ABC AnalysisDocument11 paginiHow To Do An ABC AnalysisAdhiraj A. BhaduriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Procurement and Inventory MGTDocument45 paginiIntroduction To Procurement and Inventory MGTEuroline NtombouÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter Three: Purchasing and Materials ManagementDocument22 paginiChapter Three: Purchasing and Materials ManagementVijay BurmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- SCE Assignment CO2Document3 paginiSCE Assignment CO2atul953020Încă nu există evaluări
- BUS5112 - Unit 2 - Understanding Customer Behavior - AssignmentDocument8 paginiBUS5112 - Unit 2 - Understanding Customer Behavior - AssignmentxwereÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 10 Supply Chain ManagementDocument9 paginiChapter 10 Supply Chain ManagementarantonizhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 2 - AssessmentDocument2 paginiTopic 2 - AssessmentJoshua TirambuloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eco-Friendly Packaging in Supply Chain: Suyog DharmadhikariDocument13 paginiEco-Friendly Packaging in Supply Chain: Suyog DharmadhikariSantanu RoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- BUDGET 2013: Fiscal DeficitDocument2 paginiBUDGET 2013: Fiscal DeficitSantanu RoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stick or SwitchDocument9 paginiStick or SwitchSantanu RoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- I.T.S Management & I.T Institute, Mohan Nagar Ghaziabad TIME TABLE FOR: PGDM-III TRIMESTER BATCH 2012-2014, W.E.F:18.02.2013Document2 paginiI.T.S Management & I.T Institute, Mohan Nagar Ghaziabad TIME TABLE FOR: PGDM-III TRIMESTER BATCH 2012-2014, W.E.F:18.02.2013Santanu RoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Corrosion of Iron Lab Writeup Julia GillespieDocument4 paginiCorrosion of Iron Lab Writeup Julia Gillespieapi-344957036Încă nu există evaluări
- Barry Farm Powerpoint SlidesDocument33 paginiBarry Farm Powerpoint SlidessarahÎncă nu există evaluări
- LG 55lw5600 Chassis La12c SMDocument29 paginiLG 55lw5600 Chassis La12c SMwandag2010Încă nu există evaluări
- Manufacturing Technology - Metrology: Dr.B.Ramamoorthy Professor Manufacturing Engg. Section Iitmadras 600 036Document22 paginiManufacturing Technology - Metrology: Dr.B.Ramamoorthy Professor Manufacturing Engg. Section Iitmadras 600 036Ramasubramanian KannanÎncă nu există evaluări
- DataStage Interview QuestionsDocument3 paginiDataStage Interview QuestionsvrkesariÎncă nu există evaluări
- HS ĐỀ CƯƠNG KIỂM TRA GIỮA KỲ I KHOI 10 NH 23 24Document6 paginiHS ĐỀ CƯƠNG KIỂM TRA GIỮA KỲ I KHOI 10 NH 23 24Ngô Hiểu NhiênÎncă nu există evaluări
- Property PalleteDocument5 paginiProperty PalletePranay PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evolution of Management TheoriesDocument20 paginiEvolution of Management TheoriesKanishq BawejaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spirolab IIIDocument1 paginăSpirolab IIIDzenan DelijaÎncă nu există evaluări
- New Text Document 22Document90 paginiNew Text Document 22Marija SerifovskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- INV201 ReadParameterDocument3 paginiINV201 ReadParameterRaul ArbaniesÎncă nu există evaluări
- DSSSSPDocument3 paginiDSSSSPChris BalmacedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gpcdoc Gtds Shell Gadus s3 v460xd 2 (En) TdsDocument2 paginiGpcdoc Gtds Shell Gadus s3 v460xd 2 (En) TdsRoger ObregonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical Means For Energy-Based Analyses of Disproportionate Collapse PotentialDocument13 paginiPractical Means For Energy-Based Analyses of Disproportionate Collapse PotentialNhut NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Henderson 1Document4 paginiHenderson 1danielÎncă nu există evaluări
- BC-2800 Maintenance Manual For EngineersDocument3 paginiBC-2800 Maintenance Manual For EngineersIslam AdelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Leadership Competencies Paper 2Document5 paginiLeadership Competencies Paper 2api-297379255Încă nu există evaluări
- Tcps 2 Final WebDocument218 paginiTcps 2 Final WebBornaGhannadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Numerical Methods - Fixed Point IterationDocument4 paginiNumerical Methods - Fixed Point IterationMizanur RahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vertical Axis Wind Turbine ProjDocument2 paginiVertical Axis Wind Turbine Projmacsan sanchezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Policy Analysis ReportDocument16 paginiPolicy Analysis ReportGhelvin Auriele AguirreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sika Bro - E - Sikadur-Combiflex SG System - High Performance Joint - Crack Waterproofing System (09.2010)Document8 paginiSika Bro - E - Sikadur-Combiflex SG System - High Performance Joint - Crack Waterproofing System (09.2010)Joh SongthamÎncă nu există evaluări
- EZ-FRisk V 7.52 User Manual PDFDocument517 paginiEZ-FRisk V 7.52 User Manual PDFJames IanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research QuestionDocument6 paginiResearch QuestionAlfian Ardhiyana PutraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1981 Albus - Brains, Behavior, and RoboticsDocument362 pagini1981 Albus - Brains, Behavior, and RoboticsmarkmcwilliamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Science Lesson Plan Analysis Instrument For Formative and Summative Program Evaluation of A Teacher Education ProgramDocument31 paginiA Science Lesson Plan Analysis Instrument For Formative and Summative Program Evaluation of A Teacher Education ProgramTiara Kurnia KhoerunnisaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heat Transfer Enhancement Using Nano FluidsDocument17 paginiHeat Transfer Enhancement Using Nano FluidsranjithkrajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Day 11 PDFDocument16 paginiDay 11 PDFჯონ ფრაატეეკÎncă nu există evaluări