Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
English Expo
Încărcat de
Uriel Alejandro Argueta SandovalDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
English Expo
Încărcat de
Uriel Alejandro Argueta SandovalDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Mechanic engineering is a branch or division of engineering that applies physics principles and materials science for design, analysis,
manufacture and maintenance of mechanical systems. The mechanical engineering is not only applied on
Definition
Mechanical engineering is a branch of engineering that applies physics principles and materials analysis for design, analysis, manufacture and maintenance of mechanical systems, such as mechanisms, structures, engines, etc. To make a better understanding of mechanical engineering is imperative the knowledge of core concepts including statics, kinematics, thermodynamics, materials science and structural analysis. Importance
Today, our world is driven by the need to reduce costs in production by improving manufacturing processes or redesigning elements. The application of ME is anywhere a physical effect is applied on an element or junction of elements, a mechanical mechanism. From a water boiler to the design of transportation mean the Mechanical engineering goes further from just automotive mechanics. Behavior of materials
Is imperative to understand the behavior of a material subjected to physical effects, such as load or thermic effects if the creation, modification or maintenance of a mechanical design is needed. For example: Under the predesign step of a billboard, first of all is needed to know the service conditions under which the structure will be subjected, such as wind conditions, weight of the structure, etc. Then with this information is possible to make a design that will support a service period, using a range of values within of which the structure will be on duty. The importance of stress-strain diagrams
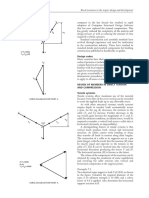
First of all what is a stress-strain diagram. It is a representative curve of the amount of stress absorbed during a deformation process. This curve gives information about how a material reacts to a force that creates stress. This reaction is called deformation. These diagrams are sketched from tensile tests of materials. These curves depict the behavior of brittle and ductile materials.
Application of stress-strain diagrams in structural design, from a general point of view.
A structure is a set or junction of elements bonded together to support the the effects of dynamic or static loads or a combination of both. A static load is a type of load that builds up overtime or has negligible dynamic effects. A dynamic load is a type of load produced by impacts, waves, etc. For instance the effects of wind over a structure are dynamics, because it varies overtime in magnitude and direction.
Where do you apply it?
MI can be applied everywhere from the maintenance of a small refrigerator to the design of a space shuttle. This is because MI is applied physics. How do you apply it? By means of physic principles and material analysis, is possible to understand how a material reacts to an external effect. This information gives the chances of taking a decision between accept or reject an element or a whole system, or even improve them. There are many ways to study the mechanical behavior The importance of stress-yield diagrams Stress-yield diagrams, a characteristic curve of materials behavior under load Application of stress-yield diagrams in design
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- M 004 ExercisesDocument33 paginiM 004 ExercisesKannan MuthusamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wooden Formwork Design Criteria With Calculation Formulas For ConcreteDocument10 paginiWooden Formwork Design Criteria With Calculation Formulas For Concretevenkateswara rao PothinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fundamentals of Structural Design Part of Steel StructuresDocument10 paginiFundamentals of Structural Design Part of Steel StructuresJanice FernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flexural Design of Reinforced Concrete Beam SectionsDocument15 paginiFlexural Design of Reinforced Concrete Beam SectionsAamir HaideriÎncă nu există evaluări
- ISO PLUS Cijevi (Pipes)Document39 paginiISO PLUS Cijevi (Pipes)Gradska toplana - ServisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Development and Validation of Bolted Connection Modeling in LS-DYNA For Large Vehicle ModelsDocument12 paginiDevelopment and Validation of Bolted Connection Modeling in LS-DYNA For Large Vehicle ModelsAmir IskandarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 15.lattice (Cage) Beam Design and Finite Element Analysis of Gantry CraneDocument3 pagini15.lattice (Cage) Beam Design and Finite Element Analysis of Gantry CraneravirajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rebar CalculationDocument8 paginiRebar CalculationEr Pranabesh SenÎncă nu există evaluări
- High Tensile Nuts BoltsDocument10 paginiHigh Tensile Nuts BoltssagarhalappaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Entries M ODocument46 paginiEntries M OXiaohui ChenÎncă nu există evaluări
- #ESTIMATING COSTING (PDF - Io)Document11 pagini#ESTIMATING COSTING (PDF - Io)Poot NarkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hybrid Metal Matrix Composite: Faculty Guide: S. SeralathanDocument9 paginiHybrid Metal Matrix Composite: Faculty Guide: S. SeralathanMECHA ENGINEEERINGÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thompson R. J. and Visser A.T. 1999. Designing and Managing Unpaved Opencast Mine Haul Roads For Optimum PerformanceDocument17 paginiThompson R. J. and Visser A.T. 1999. Designing and Managing Unpaved Opencast Mine Haul Roads For Optimum PerformanceIr Azizul Bin HawariÎncă nu există evaluări
- If P 100N T1 T2 58: Design CodesDocument1 paginăIf P 100N T1 T2 58: Design CodessereÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 22 - Maxwell Stress Tensor PDFDocument10 paginiCH 22 - Maxwell Stress Tensor PDFArtemis KarvounisÎncă nu există evaluări
- RahemiDocument113 paginiRahemiDani SantosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 4 03-02-2024Document20 paginiLecture 4 03-02-2024ahmed11 engyemenÎncă nu există evaluări
- ME G 641 Compre Exam Part A Through Google FormDocument14 paginiME G 641 Compre Exam Part A Through Google Formasish saiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rheology For AllDocument19 paginiRheology For AllHasanAlMonemTanim100% (1)
- Jalcom D 14 09005R2Document57 paginiJalcom D 14 09005R2d_nagarajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Failure Envelope - Meeting September 2021Document46 paginiFailure Envelope - Meeting September 2021Osama AshourÎncă nu există evaluări
- AAA4 - NanothermodynamicsDocument28 paginiAAA4 - Nanothermodynamicsvosongtv100% (1)
- Ejercicio 2 y 3 ANSYSDocument33 paginiEjercicio 2 y 3 ANSYSMiguel Angel Vázquez GayossoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rubber Elasticity PDFDocument25 paginiRubber Elasticity PDFMinhao Zhou100% (1)
- Mechanical Properties of MetalDocument26 paginiMechanical Properties of MetalLuis NunesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Post Tensioned FoundationsDocument27 paginiPost Tensioned FoundationsBogdanBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pressure Vessels (Att. VIII)Document42 paginiPressure Vessels (Att. VIII)Syed M. Imran Ali100% (1)
- R18 Jntu SyllabusDocument31 paginiR18 Jntu SyllabusSnehith SagarÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHYS 3203 - Lab PDFDocument55 paginiPHYS 3203 - Lab PDFTaukeer KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pubb-0589-L-Rock-mass Hydrojacking Risk Related To Pressurized Water TunnelsDocument10 paginiPubb-0589-L-Rock-mass Hydrojacking Risk Related To Pressurized Water Tunnelsinge ocÎncă nu există evaluări