Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Pipe Jacking of CIP Pipes (Kubota)
Încărcat de
Yam Balaoing0%(2)0% au considerat acest document util (2 voturi)
683 vizualizări2 paginiPipe jacking is a trenchless method for installing pipelines underground without excavating a trench. There are different types of pipe jacking methods, including automatic, semi-shield, and hand-mining jacking. For hand-mining jacking, pipes with a diameter of 1000mm or larger are typically used. The pipes are pushed into the ground by hydraulic jacks while workers enter the pipe to remove soil. Ductile iron pipes are commonly used for pipe jacking, and come in push-on or mechanical joint types depending on diameter. The document also provides allowable resistance force values for different diameter ductile iron pipes used in jacking.
Descriere originală:
Ebook
Drepturi de autor
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentPipe jacking is a trenchless method for installing pipelines underground without excavating a trench. There are different types of pipe jacking methods, including automatic, semi-shield, and hand-mining jacking. For hand-mining jacking, pipes with a diameter of 1000mm or larger are typically used. The pipes are pushed into the ground by hydraulic jacks while workers enter the pipe to remove soil. Ductile iron pipes are commonly used for pipe jacking, and come in push-on or mechanical joint types depending on diameter. The document also provides allowable resistance force values for different diameter ductile iron pipes used in jacking.
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0%(2)0% au considerat acest document util (2 voturi)
683 vizualizări2 paginiPipe Jacking of CIP Pipes (Kubota)
Încărcat de
Yam BalaoingPipe jacking is a trenchless method for installing pipelines underground without excavating a trench. There are different types of pipe jacking methods, including automatic, semi-shield, and hand-mining jacking. For hand-mining jacking, pipes with a diameter of 1000mm or larger are typically used. The pipes are pushed into the ground by hydraulic jacks while workers enter the pipe to remove soil. Ductile iron pipes are commonly used for pipe jacking, and come in push-on or mechanical joint types depending on diameter. The document also provides allowable resistance force values for different diameter ductile iron pipes used in jacking.
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 2
Chapter 15-1 Pipe Jacking
15 Piping under Special Conditions
Pipe jacking method can be used to install a pipeline in the ground without trench excavation. This method is applicable for negotiating obstacles such as roads, railways, canals and rivers.
15-1-1 Jacking ductile iron pipe
Body portion of jacking ductile iron pipe is sheathed with reinforced concrete to make the whole outside diameter uniform along the pipe axis. Jacking force is transferred to the socket face through the puddle flange welded on the spigot of the connected pipe. There are two types of joint for jacking ductile iron pipe. They are push-on type (TD type joint) for DN300 to DN1600 and mechanical type (UD type joint) for DN700 to DN2600. Basically jacking ductile iron pipes are manufactured in accordance with Japanese standard (JIS). The nominal pipe outside diameter by Japanese standard is slightly different from that by ISO standard, therefore change collars or change spigots shall be used to connect pipes of these standards. (Refer to Chapter 12) However DN700 to DN1600 jacking ductile iron pipe with push-on joint may be supplied with ISO standard pipe. UD-type jacking ductile iron pipe (DN700 to DN2600)
Fig. 15-1
TD-type jacking ductile iron pipe (DN300 to DN1600)
Fig. 15-2
15-1-2 Jacking method
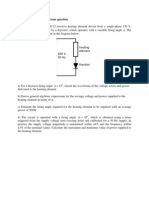
There are some pipe jacking methods such as automatic jacking, semi-shield jacking and hand-mining jacking. Automatic jacking and semi-shield jacking methods employ special jacking machines. In case of hand-mining jacking, pipe is pushed into the ground by hydraulic jacks and persons should enter the pipe to carry out the soil in the pipe. This hand-mining method is recommended to DN1000 and larger pipes. An example of equipment for hand-mining jacking is shown in Fig 15-3.
114
Chapter
15 Piping under Special Conditions
Fig. 15-3
General arrangement of pipe jacking equipment
15-1-3 Allowable resistance force of jacking pipe
Pipes shall be jacked within the allowable resistance force of the jacking pipe given in the below table. Allowable resistance force of jacking ductile iron pipe Table 15-1
Allowable resistance force (kN) Class of pipe by Japanese standard Class of pipe by ISO standard Class 1 Class 2 Class 3 Class K9 Class K10 Class K11 2,060 1,770 2,450 1,770 2,840 2,450 2,160 2,840 2,840 2,450 3,730 3,330 2,840 3,730 3,730 3,730 6,570 5,790 4,810 4,540 5,870 6,570 6,570 6,570 5,790 5,410 6,570 6,570 6,570 6,570 6,570 6,350 6,570 6,570 9,020 9,020 8,040 7,360 9,020 9,020 9,020 9,020 9,020 8,450 9,020 9,020 9,020 9,020 9,020 9,020 9,020 9,020 9,020 9,020 9,020 12,360 12,360 12,360 12,360 12,360 12,360 12,360 12,360 12,360 12,360 12,360 12,360 12,360 12,360 12,360 18,670 18,670 18,670 18,670 18,670 18,670 18,670 18,670 18,670 23,240 23,240 23,240 -
DN 300 350 400 450 500 600 700 800 900 1000 1100 1200 1400 1500 1600 1800 2000 2200 2400 2600
115
Note The above values should be distributed evenly around the circumference of the pipe.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Structural Analysis 1: Statically Determinate StructuresDe la EverandStructural Analysis 1: Statically Determinate StructuresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alec - Mep - Post - Tender - Training 06 - MEP - Val'01 - 25jan'2011: 3 M020 Plastherm PPR PipesDocument2 paginiAlec - Mep - Post - Tender - Training 06 - MEP - Val'01 - 25jan'2011: 3 M020 Plastherm PPR PipesMohamedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rock-Socketed Large Diameter Bored Pile and Geophysical Survey in Cavernous Karst AreaDocument8 paginiRock-Socketed Large Diameter Bored Pile and Geophysical Survey in Cavernous Karst AreaHilary YÎncă nu există evaluări
- Herrenknecht Gripper Illustration enDocument1 paginăHerrenknecht Gripper Illustration enantoniusnoroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ground Treatment For TunnellingDocument22 paginiGround Treatment For Tunnellingthauwui860% (1)
- 1974 - CivilEng - Seminars - Reinforced Concrete PipeDocument52 pagini1974 - CivilEng - Seminars - Reinforced Concrete PipeChen YishengÎncă nu există evaluări
- L2. Closure To Effect of Bentonite Slurry Pressure On Interface Friction of Pipe Jacking by Mucahit Namli and Erol GulerDocument4 paginiL2. Closure To Effect of Bentonite Slurry Pressure On Interface Friction of Pipe Jacking by Mucahit Namli and Erol GulerAna Maria Garcia EscandonÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2012 - Long Distance Pipe Jacking - ExperienceDocument40 pagini2012 - Long Distance Pipe Jacking - ExperienceCheng KimHuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pipe JackingDocument2 paginiPipe JackinghutuguoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pipe Jacking Presentation by HydrochinaDocument23 paginiPipe Jacking Presentation by Hydrochinaأون جهادÎncă nu există evaluări
- TERRATEC Microtunnelling Brochure PDFDocument5 paginiTERRATEC Microtunnelling Brochure PDFKhaled MaddallahÎncă nu există evaluări
- SLS-T Allgemein VMT - JMDocument65 paginiSLS-T Allgemein VMT - JMjmtexla680% (1)
- BSi Jacking PipeDocument56 paginiBSi Jacking PipeJayesh100% (1)
- TBM Basics TUdelftDocument134 paginiTBM Basics TUdelftRamSwaroopÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sheet PileDocument22 paginiSheet PileMuhammad HasifÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earth Pressure Balance (Epb) Machines: Levent Ozdemir Tunneling ConsultantDocument25 paginiEarth Pressure Balance (Epb) Machines: Levent Ozdemir Tunneling ConsultantSérgio BernardesÎncă nu există evaluări
- DSI ALWAG-Systems Pantex Lattice Girders EDocument8 paginiDSI ALWAG-Systems Pantex Lattice Girders Epramods_8Încă nu există evaluări
- AMWLecture 2011-BD2Document32 paginiAMWLecture 2011-BD2ovion_itaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ring Beam Shoring System 25oct06Document14 paginiRing Beam Shoring System 25oct06Seng SiongÎncă nu există evaluări
- SFRC Jacking Pipe Design: Numerical Modelling and Factory TrialsDocument34 paginiSFRC Jacking Pipe Design: Numerical Modelling and Factory Trialsjuan carlos silva ospinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thu Thiem Tunnel Construction - Sequence - Immersed - Tunnel PDFDocument36 paginiThu Thiem Tunnel Construction - Sequence - Immersed - Tunnel PDFThông PhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vertical Shaft Boring MachinesDocument2 paginiVertical Shaft Boring MachinesTony ChanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Document For Pipe Jacking WorksDocument12 paginiDocument For Pipe Jacking WorksRichard YiiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heinke Tunnel Segment GasketsDocument6 paginiHeinke Tunnel Segment GasketsChin Thau WuiÎncă nu există evaluări
- CS5 Shaft Uplift Calculation - 26.02.2018Document9 paginiCS5 Shaft Uplift Calculation - 26.02.2018yadav04_abhishekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cable Anchors: A Prestressed Cable Anchor Is A High Strength Steel Tendon, Fitted With ADocument13 paginiCable Anchors: A Prestressed Cable Anchor Is A High Strength Steel Tendon, Fitted With AAnonymous RBDKAkBPoFÎncă nu există evaluări
- Use of Tremie To Concrete A Pile Under FluidDocument3 paginiUse of Tremie To Concrete A Pile Under FluidAlphaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2009 Microtunnel SuppDocument36 pagini2009 Microtunnel SuppHua Hidari YangÎncă nu există evaluări
- CREG IntroductionDocument47 paginiCREG IntroductionCarlos GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis of Jacking Forces During Microtunnelling in LimestoneDocument15 paginiAnalysis of Jacking Forces During Microtunnelling in Limestonetkm2004Încă nu există evaluări
- TBM DetailsDocument100 paginiTBM DetailswheyfrappeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Excel Pipes Jacking PipesDocument4 paginiExcel Pipes Jacking PipesAli ZarehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Large Diameter Pipe Roof Box Excavation For Passenger Linkway TunnelDocument14 paginiLarge Diameter Pipe Roof Box Excavation For Passenger Linkway TunnelMH Enc Const TrdÎncă nu există evaluări
- 200 Limestones of Jurong Formation Engineering ExperienceDocument9 pagini200 Limestones of Jurong Formation Engineering ExperiencegahsoonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Surge Shaft Concreting by Slip Form MethodDocument4 paginiSurge Shaft Concreting by Slip Form MethodCharumitra Singh YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- 111 - The Design and Construction of Cliffsend UnderpassDocument4 pagini111 - The Design and Construction of Cliffsend UnderpassYash SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- GeoSS Event Seminar 5 Oct 2010 Slides 1Document32 paginiGeoSS Event Seminar 5 Oct 2010 Slides 1freezefreezeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Underpinning For TBM To Under-Cross A Building in Thomson-East Coast Line (TEL) Contract T220Document11 paginiUnderpinning For TBM To Under-Cross A Building in Thomson-East Coast Line (TEL) Contract T220freezefreezeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hume Pipe JackingDocument1 paginăHume Pipe JackingLau Meng YongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Norwegian Standard Road Tunnels 021 - e - 05 - W, 0Document140 paginiNorwegian Standard Road Tunnels 021 - e - 05 - W, 0verxiriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Recommended Rock Testing Methods For Predicting TBM Performance: Focus On The CSM and Ntnu ModelsDocument8 paginiRecommended Rock Testing Methods For Predicting TBM Performance: Focus On The CSM and Ntnu Modelsjack21abÎncă nu există evaluări
- Temporary Excavation Support System For A New Railway Bridge and Highway Underpass in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania by Andrew G. Cushing and Christopher J. LewisDocument8 paginiTemporary Excavation Support System For A New Railway Bridge and Highway Underpass in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania by Andrew G. Cushing and Christopher J. LewisAndrew CushingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curve Jacking - Paper Bangkok T-1ThorenDocument10 paginiCurve Jacking - Paper Bangkok T-1ThorenCheng KimHuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation 03 - 09 - 2020Document29 paginiPresentation 03 - 09 - 2020Rayees AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ismailia Road Tunnel Crossing The Suez Canal PDFDocument8 paginiIsmailia Road Tunnel Crossing The Suez Canal PDFRonald HeijmansÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brosur Concrete PipeDocument20 paginiBrosur Concrete PipegneissetiagrahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design Issues Related To Jet Grouted Slabs at The Base of Excavations, 2000Document6 paginiDesign Issues Related To Jet Grouted Slabs at The Base of Excavations, 2000freezefreezeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alternate To Ghat-Ki-Guni by Construction of Tunnel in Jhalana Hills JaipurDocument46 paginiAlternate To Ghat-Ki-Guni by Construction of Tunnel in Jhalana Hills JaipurDevendra SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Geotechnical Analysis CE 444: PLAXIS Assignment ReportDocument16 paginiAdvanced Geotechnical Analysis CE 444: PLAXIS Assignment ReportShikhar SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tunelling in Soft SoilsDocument14 paginiTunelling in Soft SoilsPiyush BhatiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparison Between 2d and 3d Behaviour of Sheet Piles by Finite Element MethodDocument16 paginiComparison Between 2d and 3d Behaviour of Sheet Piles by Finite Element MethodtavialimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Steel Fibre Reinforced Segmental Lining For The Gold Coast Desal TunnelsDocument8 paginiDesign of Steel Fibre Reinforced Segmental Lining For The Gold Coast Desal Tunnelsrajesh005Încă nu există evaluări
- Manchette Tube SystemDocument4 paginiManchette Tube SystemThanh Khiet Ung100% (1)
- Lubrication Fluids For Micro-Tunnelling & Pipe-JackingDocument6 paginiLubrication Fluids For Micro-Tunnelling & Pipe-JackingEnri05Încă nu există evaluări
- Trenchless TechnologyDocument41 paginiTrenchless TechnologyESAM ALHASHEDIÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Steel Pipe in Trenchless TechnologyDocument8 paginiThe Steel Pipe in Trenchless TechnologyktsnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1729Document52 pagini1729praj24083302Încă nu există evaluări
- Technical SpecificationsDocument6 paginiTechnical Specificationspradeep reddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technical SpecificationDocument12 paginiTechnical SpecificationYousuf KamalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rsa in Etabs With LRB DamperDocument5 paginiRsa in Etabs With LRB DamperSyed Rizwan Saleem100% (1)
- J323 TPTC Erss 01 PDFDocument1 paginăJ323 TPTC Erss 01 PDFYam BalaoingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structural Behaviorofa Guyed MastDocument17 paginiStructural Behaviorofa Guyed MastYam BalaoingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test QuestionDocument6 paginiTest QuestionYam BalaoingÎncă nu există evaluări
- MT PDFDocument65 paginiMT PDFYam BalaoingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yncc GTG - Dynamic - Case 13 at 7455rpm - MassDocument1.985 paginiYncc GTG - Dynamic - Case 13 at 7455rpm - MassYam BalaoingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Foundation Design AssumptionsDocument1 paginăFoundation Design AssumptionsYam BalaoingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sdre14-14 Bol 1-5-1dec17Document6 paginiSdre14-14 Bol 1-5-1dec17Yam BalaoingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maldives Building Design CodeDocument11 paginiMaldives Building Design CodeYam Balaoing0% (1)
- Wind Turbine Footing Design - Page 6 PDFDocument14 paginiWind Turbine Footing Design - Page 6 PDFMaman AsepÎncă nu există evaluări
- Beam ScheduleDocument5 paginiBeam ScheduleYam BalaoingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Beams With CrackDocument1 paginăBeams With CrackYam BalaoingÎncă nu există evaluări
- CPM Critical PathDocument3 paginiCPM Critical PathYam BalaoingÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6.b LTA Standard Bollard Connection CapacityDocument7 pagini6.b LTA Standard Bollard Connection CapacityYam BalaoingÎncă nu există evaluări
- LTA Standard RailingDocument1 paginăLTA Standard RailingYam BalaoingÎncă nu există evaluări
- UndergroundBasementWorks RequirementsDocument38 paginiUndergroundBasementWorks RequirementsYam BalaoingÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02-Rapid Load Tests Practice in Japan PDFDocument71 pagini02-Rapid Load Tests Practice in Japan PDFYam BalaoingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maldives ClimateDocument166 paginiMaldives ClimateYam BalaoingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Submission of Building Plans: Version 1.0 - 1999Document10 paginiSubmission of Building Plans: Version 1.0 - 1999Yam BalaoingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Site Engineer 1 Site Engineer 2Document2 paginiSite Engineer 1 Site Engineer 2Yam BalaoingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter6 - Main Terrain Category 3 in WT PDFDocument56 paginiChapter6 - Main Terrain Category 3 in WT PDFArchie PapÎncă nu există evaluări
- New Doc 2017-12-04Document1 paginăNew Doc 2017-12-04Yam BalaoingÎncă nu există evaluări
- 005 - 1 Typ. One Way SlabDocument5 pagini005 - 1 Typ. One Way SlabYam BalaoingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Autocad ScaleDocument2 paginiAutocad ScaleYam BalaoingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nu-Tie Report 070808mktDocument28 paginiNu-Tie Report 070808mktYam BalaoingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Autocad ScaleDocument2 paginiAutocad ScaleYam BalaoingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Systhethic RainfallDocument2 paginiSysthethic RainfallYam BalaoingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maldives Nationa Building Act 05th July 2010Document89 paginiMaldives Nationa Building Act 05th July 2010Yam BalaoingÎncă nu există evaluări
- PointDocument9 paginiPointYam BalaoingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Demolition Works Presentation 07052017 HCE COMMENT 1Document104 paginiDemolition Works Presentation 07052017 HCE COMMENT 1Yam BalaoingÎncă nu există evaluări
- 942 15Document1 pagină942 15Gia Trish100% (2)
- OPEC PresentationDocument5 paginiOPEC Presentationashish9mehta0% (1)
- Five Points Reg Material SelectionDocument2 paginiFive Points Reg Material Selectionselva_raj215414Încă nu există evaluări
- MVRDV 'S WoZoCo Apartment BuildingDocument10 paginiMVRDV 'S WoZoCo Apartment BuildingJosé SilvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thyristor Control QuestionDocument3 paginiThyristor Control QuestionAnonymous TJRX7CÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydraulics: and The Use of Liquid PressureDocument9 paginiHydraulics: and The Use of Liquid PressurePrarit PatyalÎncă nu există evaluări
- BikoDocument5 paginiBikonathanmaprettyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tourist Attractions From RomaniaDocument3 paginiTourist Attractions From RomaniaDaniel-Catalin HodorogeaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECON2102 Tutorial 5 SolDocument2 paginiECON2102 Tutorial 5 SolErnest TangÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Motors (GM) Decides Smaller Is BetterDocument11 paginiGeneral Motors (GM) Decides Smaller Is BetterSufian TanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Apparel Standards Specification and Quality Control - 1Document116 paginiApparel Standards Specification and Quality Control - 1P. Lakshmanakanth100% (3)
- HLC Vs KWIK CON IIDocument2 paginiHLC Vs KWIK CON IIrajedmaglinteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sss20102011 Slide Otoacoustic EmissionsDocument11 paginiSss20102011 Slide Otoacoustic EmissionsWendi Perd'sÎncă nu există evaluări
- Symbols For Rules - Gears and StuffDocument1 paginăSymbols For Rules - Gears and StuffJanneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Keda's ERPDocument12 paginiKeda's ERPBikash PrasadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Os 096016 PP 08 MW 1 B 10Document2 paginiOs 096016 PP 08 MW 1 B 10Lexndru V LuthorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Integrated Avionics SystemsDocument13 paginiIntegrated Avionics SystemsKoh Shao Ning Joel100% (1)
- Air SpeedsDocument2 paginiAir SpeedsmgskumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activating MP3 BMW E60, E90, E63Document2 paginiActivating MP3 BMW E60, E90, E63OreonoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Etiology of Malocclusion Local FactorsDocument13 paginiEtiology of Malocclusion Local FactorsAshis BiswasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pancreas: Ahmad AminuddinDocument16 paginiPancreas: Ahmad AminuddinWhydia Wedha SutedjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DMT80480T070 18WT DatasheetDocument4 paginiDMT80480T070 18WT DatasheetMatheus Maia Barbosa D. OliveiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- The End of Live or World War 3Document1 paginăThe End of Live or World War 3ShussyLoveDickyÎncă nu există evaluări
- MazdaBiante Pricelist 121113Document2 paginiMazdaBiante Pricelist 121113Ahmad Hamdan Rahman AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- BQ Rmu PlinthDocument3 paginiBQ Rmu Plinthaqeel_al_triniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tripleband Combiner 1Document2 paginiTripleband Combiner 1Bambang NurrahmantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aids Survey QuestionsDocument3 paginiAids Survey QuestionsZoe BradshawÎncă nu există evaluări
- Soal Ujian PraktekDocument3 paginiSoal Ujian PraktekHadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- PancreatitisDocument2 paginiPancreatitisThomcris PatalinghugÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electronic Structure of Atoms and The Periodic Table ExerciseDocument7 paginiElectronic Structure of Atoms and The Periodic Table ExerciseFlorance ChiengÎncă nu există evaluări