Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Tylenol for mild to moderate pain
Încărcat de
Kristi WrayDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Tylenol for mild to moderate pain
Încărcat de
Kristi WrayDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
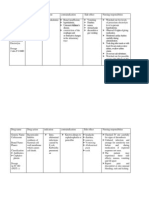
Generic Name Acetaminophen, paracetamol
Trade Name Tylenol
Classification NONNARCOTI C ANALGESIC, ANTIPYRETIC Duration 34 h.
Dose 335mg
Route PO
Time/frequency Q4-6h PRN Pain
Peak 0.52 h.
Normal dosage range Adult: PO 325650 mg q46h (max: 4 g/day) PR 650 mg q46h (max: 4 g/day) Why is your patient getting this medication For IV meds, compatibility with IV drips and/or treatment of vitamin/mineral supplementation during solutions pregnancy/lactation N/A Mechanism of action and indications Nursing Implications (what to focus on) (Why med ordered) Monitor for S&S of: Hepatotoxicity, even with moderate acetaminophen doses, especially in It provides temporary analgesia for mild to moderate individuals with poor nutrition or who have pain. In addition, acetaminophen lowers body ingested alcohol over prolonged periods; poisoning, temperature in individuals with a fever. usually from accidental ingestion or suicide attempts; potential abuse from psychological dependence (withdrawal has been associated with restless and excited responses). Common side effects Body as a Whole: Negligible with recommended dosage; rash. Acute poisoning: Anorexia, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, lethargy, diaphoresis, chills, epigastric or abdominal pain, diarrhea; onset of hepatotoxicity: elevation of serum transaminases (ALT, AST) and bilirubin; hypoglycemia, hepatic coma, acute renal failure (rare). Chronic ingestion: Neutropenia, pancytopenia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenic purpura, hepatotoxicity in alcoholics, renal damage. Interactions with other patient drugs, OTC or Lab value alterations caused by medicine herbal medicines (ask patient specifically) False increases in urinary 5-HIAA (5-hydroxyindoleacetic Drug: Cholestyramine may decrease acid) by-product of serotonin; false decreases in blood acetaminophen absorption. With chronic glucose (by glucose oxidaseperoxidase procedure); false coadministration, BARBITURATES, increases in urinary glucose (with certain instruments in carbamazepine, phenytoin, and rifampin may glucose analyses); and false increases in serum uric acid increase potential for chronic hepatotoxicity. (with phosphotungstate method). High doses or long-term Chronic, excessive ingestion of alcohol will increase therapy: hepatic, renal, and hematopoietic function risk of hepatotoxicity. (periodically).
Onset Unknown
Be sure to teach the patient the following about this medication Do not take other medications (e.g., cold preparations) containing acetaminophen without medical advice; overdosing and chronic use can cause liver damage and other toxic effects. Do not self-medicate adults for pain more than 10 days (5 days in children) without consulting a physician. Do not use this medication without medical direction for: Fever persisting longer than 3 days, fever over 39.5 C (103 F), or recurrent fever. Do not give children more than 5 doses in 24 h unless prescribed by physician.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Paracetamol PODocument3 paginiParacetamol POSheena GallardoÎncă nu există evaluări
- AcetaminophenDocument3 paginiAcetaminophenapi-3797941Încă nu există evaluări
- Gabapentin medication guideDocument15 paginiGabapentin medication guideTyron ChuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adderall medication guideDocument2 paginiAdderall medication guideKristi Wray100% (1)
- Acetaminophen, ParacetamolDocument2 paginiAcetaminophen, ParacetamolAubrey Unique Evangelista100% (2)
- Drug Study: GENERIC NAME: Acetaminophen TRADE NAME: TylenolDocument3 paginiDrug Study: GENERIC NAME: Acetaminophen TRADE NAME: TylenolLinda AdamsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tylenol (Acetaminophen)Document2 paginiTylenol (Acetaminophen)gagandipkSÎncă nu există evaluări
- F&E Drug StudyDocument2 paginiF&E Drug Studychelle_asenjoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paracetamol 500mg Tablets - Summary of Product Characteristics (SMPC) - Print Friendly - (EMC)Document4 paginiParacetamol 500mg Tablets - Summary of Product Characteristics (SMPC) - Print Friendly - (EMC)Ira PuspitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Duplicate Therapy Issues: This Product Contains Acetaminophen, Which May Be A ComponentDocument15 paginiDuplicate Therapy Issues: This Product Contains Acetaminophen, Which May Be A ComponentDevi KusumaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zocor Drug CardDocument1 paginăZocor Drug CardSheri490Încă nu există evaluări
- Calpol Suspension Pi Gds V06Document4 paginiCalpol Suspension Pi Gds V06lelaniaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ibuprofen 150mg + Paracetamol 500mg (Combodex)Document15 paginiIbuprofen 150mg + Paracetamol 500mg (Combodex)ddandan_2Încă nu există evaluări
- (Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsDocument6 pagini(Why Med Ordered) Contraindications/warnings/interactionsJita SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- DRUG STUDY DETAILS FOR CEFLEXIN, MULTIVITAMINS, AND FOLIC ACIDDocument7 paginiDRUG STUDY DETAILS FOR CEFLEXIN, MULTIVITAMINS, AND FOLIC ACIDKrishna BalsarzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paracetamol Use GuideDocument13 paginiParacetamol Use GuideShashiprakash KshatriyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Ferin Plus Pediatric Syrup Chlorpheniramine Maleate Paracetamol Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride Bilim Ilac Sanayi Ve Ticaret AsDocument9 paginiA Ferin Plus Pediatric Syrup Chlorpheniramine Maleate Paracetamol Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride Bilim Ilac Sanayi Ve Ticaret Asaschetefera6Încă nu există evaluări
- Drugs Fall 2014: Pharm ListDocument31 paginiDrugs Fall 2014: Pharm Listashleynorris1403Încă nu există evaluări
- 2b04cfdb-8571-4543-a4c9-b1380e0a92c3Document5 pagini2b04cfdb-8571-4543-a4c9-b1380e0a92c3KirubakaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument13 paginiDrug StudyClarkEstacioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Panadol - Sri - Lanka Medicine Panadol 1000pc Leaflet 500mg (IND 20077761 1)Document2 paginiPanadol - Sri - Lanka Medicine Panadol 1000pc Leaflet 500mg (IND 20077761 1)Abu Mejza'atÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fast Relief from Pain & Fever with FebramolDocument5 paginiFast Relief from Pain & Fever with FebramolDr.2020Încă nu există evaluări
- Ketorolac drug studyDocument2 paginiKetorolac drug studyJacqueline LimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aspirin ASA BayerDocument2 paginiAspirin ASA BayerKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calpol Tablets Oral Suspension and Paediatric DropsDocument13 paginiCalpol Tablets Oral Suspension and Paediatric DropsMiscrit ManÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cases CompilationDocument77 paginiCases CompilationRina S.Încă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudDocument12 paginiDrug StudKhryss Paula BaldonadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aminophylline (Theophylline Ethylenediamine) : TruphyllineDocument4 paginiAminophylline (Theophylline Ethylenediamine) : TruphyllineRosalie SepayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drugs of MineDocument16 paginiDrugs of MineJoan GungobÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ferrous Sulfate: o o o o o o oDocument5 paginiFerrous Sulfate: o o o o o o oLelanie Japitana100% (1)
- Drug Study - TempraDocument3 paginiDrug Study - TempraIzza DeloriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ZafirlukastDocument3 paginiZafirlukastapi-379794167% (3)
- Patient Allergies: Children 1-12y/o-10-20mg/kg/dose q4-6h Prn. Infants - 10-20mg/kg/dose q4-6h Prn. Neonates - 10Document2 paginiPatient Allergies: Children 1-12y/o-10-20mg/kg/dose q4-6h Prn. Infants - 10-20mg/kg/dose q4-6h Prn. Neonates - 10Marlisha D. BrinkleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pantozol Control Epar Product Information - enDocument30 paginiPantozol Control Epar Product Information - enDeKa NineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument16 paginiDrug StudyJhann0% (1)
- Acetaminophen Drug StudyDocument7 paginiAcetaminophen Drug StudyHugh Klied ItuhatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calpol Tablets Oral Suspension and Paediatric DropsDocument15 paginiCalpol Tablets Oral Suspension and Paediatric DropsDIWAKAR MISHRAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug and NCPDocument15 paginiDrug and NCPgeelawlietÎncă nu există evaluări
- SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS Ibuprofen and Codeine 200mg/12.8mg Film-Coated TabletsDocument12 paginiSUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS Ibuprofen and Codeine 200mg/12.8mg Film-Coated TabletsDane WoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rabeprazole SodiumDocument3 paginiRabeprazole Sodiumapi-37979410% (1)
- Drug TylenolDocument1 paginăDrug TylenolSrkocherÎncă nu există evaluări
- PARACETAMOL 120 MG/ 5 ML Pediatric Elixir: Pharmacological PropertiesDocument2 paginiPARACETAMOL 120 MG/ 5 ML Pediatric Elixir: Pharmacological PropertiesKarim FK MalahayatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug CardDocument1 paginăDrug CardDuangkamol UasapwasinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study: History: Hypersensitivity To Any Xanthine or ToDocument2 paginiDrug Study: History: Hypersensitivity To Any Xanthine or ToJean De Vera MelendezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Generic NameDocument2 paginiGeneric NamePerdie Branden ReizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study NewDocument4 paginiDrug Study NewJehannah Dayanara Berdan HayudiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paracetamol PoisoningDocument42 paginiParacetamol PoisoningsnigdhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acetaminophen Complete Drug StudyDocument1 paginăAcetaminophen Complete Drug Studyemi LaxamanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Medication ListDocument181 paginiClinical Medication Listsophia onu100% (2)
- Drugs For ObesityDocument41 paginiDrugs For ObesityBiplav SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- EzetimibeDocument3 paginiEzetimibeapi-3797941Încă nu există evaluări
- Venlafaxine XRDocument2 paginiVenlafaxine XRMichael KuzbytÎncă nu există evaluări
- AcetominophenDocument2 paginiAcetominophenchristine_goodnoÎncă nu există evaluări
- PantoprazoleDocument3 paginiPantoprazoleapi-3797941Încă nu există evaluări
- Drugs StudyDocument35 paginiDrugs StudyMark CapillanesÎncă nu există evaluări
- ZileutonDocument3 paginiZileutonapi-3797941100% (2)
- Manage Acute Asthma in Children Under 2Document9 paginiManage Acute Asthma in Children Under 2Choo YieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcDe la EverandMedical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesDe la EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (2)
- Clopidogrel Bisulfate - PlavixDocument2 paginiClopidogrel Bisulfate - PlavixKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Codiene-Acetaminophen Tylenol 3Document1 paginăCodiene-Acetaminophen Tylenol 3Kristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clonazepam KlonopinDocument3 paginiClonazepam KlonopinKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cefepime MaxipimeDocument2 paginiCefepime MaxipimeKristi Wray100% (1)
- Ciprofloxacin CiproDocument1 paginăCiprofloxacin CiproKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Citalopramhydrobromide CelexaDocument3 paginiCitalopramhydrobromide CelexaKristi Wray100% (1)
- Cefotaxime Drug Class, Uses, Side EffectsDocument3 paginiCefotaxime Drug Class, Uses, Side EffectsKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cefoxitin Sodium MefoxinDocument3 paginiCefoxitin Sodium MefoxinKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aripiprazole AbilifyDocument2 paginiAripiprazole AbilifyKristi Wray100% (2)
- Aspirin ASA BayerDocument2 paginiAspirin ASA BayerKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cefazolin Sodium AncefDocument1 paginăCefazolin Sodium AncefKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Baclofen drug profileDocument2 paginiBaclofen drug profileKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carvedilol KredexDocument2 paginiCarvedilol KredexKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aripiprazole AbilifyDocument2 paginiAripiprazole AbilifyKristi Wray100% (2)
- Amblodipine NorvaseDocument2 paginiAmblodipine NorvaseKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adacel Tdap VaccineDocument1 paginăAdacel Tdap VaccineKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aripiprazole AbilifyDocument2 paginiAripiprazole AbilifyKristi Wray100% (2)
- Aloe Vera - ZanzibarDocument2 paginiAloe Vera - ZanzibarKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alprazolam Dosage, Uses, Side EffectsDocument2 paginiAlprazolam Dosage, Uses, Side EffectsKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Albuterol AccunebDocument2 paginiAlbuterol AccunebKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Albuterol VentolinDocument3 paginiAlbuterol VentolinKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pick The Gender of Your Baby - Free EditionDocument26 paginiPick The Gender of Your Baby - Free EditionAlicia Adrianti0% (1)
- Global Warming Is The Term Used To Describe A Gradual Increase in The Average Temperature of The EarthDocument6 paginiGlobal Warming Is The Term Used To Describe A Gradual Increase in The Average Temperature of The EarthSaswataBhattacharyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Series: Mechanical Style Pressure SwitchDocument15 paginiSeries: Mechanical Style Pressure SwitchPhúc Phan TiếnÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3.1 The Truth About Air TravelDocument14 pagini3.1 The Truth About Air TravelСвітлана Свирид0% (1)
- Paradise Pools Flyer With Price ListDocument5 paginiParadise Pools Flyer With Price ListKhuzaima HussainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Passive Filter vs. Active Filter: DefinitionsDocument3 paginiPassive Filter vs. Active Filter: DefinitionsAmit DebnathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 (CHM 127)Document105 paginiChapter 3 (CHM 127)FiqajasmeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carta Psicrometrica PDFDocument2 paginiCarta Psicrometrica PDFJuliethÎncă nu există evaluări
- DUB01CB Eng PDFDocument4 paginiDUB01CB Eng PDFAnonymous hj273CMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nitration of Methyl BenzoateDocument3 paginiNitration of Methyl BenzoateDaniel McDermottÎncă nu există evaluări
- Porter's Diamond Model Explains Nations' Success in IT CompetitionDocument30 paginiPorter's Diamond Model Explains Nations' Success in IT CompetitionKuthubudeen T MÎncă nu există evaluări
- Turkey ImportDocument14 paginiTurkey ImportMani 1Încă nu există evaluări
- Fault Code 155: Intake Manifold Air Temperature High - CriticalDocument3 paginiFault Code 155: Intake Manifold Air Temperature High - Criticalhamilton miranda100% (1)
- Ex Ophtalmo Eng 1Document4 paginiEx Ophtalmo Eng 1Roxana PascalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diff Types of Transmission Lines Used in CommsDocument9 paginiDiff Types of Transmission Lines Used in CommsLe AndroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Metric Heavy Hex Nuts: ASME B18.2.4.6M-2010Document16 paginiMetric Heavy Hex Nuts: ASME B18.2.4.6M-2010CarlitosÎncă nu există evaluări
- GreyFox Intercom Install GuideDocument12 paginiGreyFox Intercom Install GuideAbdallah HashemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tracking sports training efficiency with surface EMGDocument8 paginiTracking sports training efficiency with surface EMGsdjuknicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Site Master FileDocument51 paginiSite Master FileMilonhg100% (2)
- Purification of Morphologically and Functionally Intact Human Basophils To Near HomogeneityDocument9 paginiPurification of Morphologically and Functionally Intact Human Basophils To Near HomogeneitySinaí GutierrezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Total Tattoo-June 2021Document114 paginiTotal Tattoo-June 2021Comicgek100% (2)
- SXMDocument7 paginiSXMLi NearÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2nd - Science-Second-Quarter-Week-1Document37 pagini2nd - Science-Second-Quarter-Week-1Arlene AranzasoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paguro 06000 Spare Parts Catalogue PDFDocument88 paginiPaguro 06000 Spare Parts Catalogue PDFBoris Sitorus100% (2)
- Datasheet De14h (II) HC 1500v May2019 NTDocument2 paginiDatasheet De14h (II) HC 1500v May2019 NTkrishnakumar paamireddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry How To Make Stuff PDFDocument184 paginiChemistry How To Make Stuff PDF2967449CEEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Approach To Malabsorption (SANJAY)Document58 paginiApproach To Malabsorption (SANJAY)Sanjay KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coley A4Document49 paginiColey A4mfiarkeeaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MICROPAR PPT Group ADocument43 paginiMICROPAR PPT Group AEben Alameda-PalapuzÎncă nu există evaluări
- SB632B Connecting Rod IdentificationDocument20 paginiSB632B Connecting Rod IdentificationLuisCheukoCheuquianÎncă nu există evaluări