Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Aripiprazole Abilify
Încărcat de
Kristi WrayDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Aripiprazole Abilify
Încărcat de
Kristi WrayDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
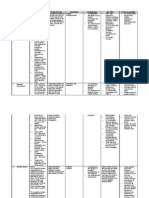
Generic Name aripiprazole
Trade Name Abilify
Classification Atypical antipsychotic
Dose 10mg
Route tab
Time/frequency Morning
Peak 35 h.
Onset 3 hr
Duration 75 h (94 h for metabolite); 146 h (poor metabolizers)
Normal dosage range Schizophrenia Adult: PO 1015 mg once daily, may increase at 2wk intervals to max of 30 mg/day if needed Adolescent/Child (at least 10 y old): PO 2 mg daily, increase to 5 mg after 2 days, increase to 10 mg after 2 more days. Can increase up to 30 mg. Bipolar Mania Adult: PO 1530 mg once daily Adolescent/Child (at least 10 y old): PO 2 mg daily, increase to 5 mg after 2 days, increase to 10 mg after 2 more days. Can increase up to 30 mg. Agitation Associated with Schizophrenia/Bipolar Adult: IM 9.75 mg (range: 5.2515 mg) Adjunct in Major Depression Adult: PO 25 mg daily Pharmacogentic Dosage Adjustment Reduced CYP2D6 expression (i.e., poor metabolizers): Give 70% of normal starting dose For IV meds, compatibility with IV drips and/or solutions N/A
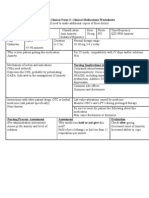
Why is your patient getting this medication Major Depressive Disorder
Mechanism of action and indications (Why would this med be ordered) . Efficacy of aripiprazole may be mediated through a combination of partial agonist activity at D2 and 5-HT1A receptors and antagonist activity at 5-HT2A receptors. Partial dopaminergic agonist property of aripiprazole accounts for antipsychotic treatment of schizophrenic and bipolar individuals.
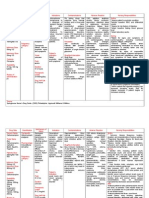
Nursing Implications (what to focus on) Contraindications/warnings/interactions Assessment & Drug Effects Monitor diabetics for loss of glycemic control. Monitor cardiovascular status. Assess for and report orthostatic hypotension. Take BP supine then in sitting position. Report systolic drop of greater than 1520 mm Hg. Patients at increased risk are those who are dehydrated, hypovolemic, or receiving concurrent antihypertensive therapy. Monitor body temperature in situations likely to elevate core temperature (e.g., exercising strenuously, exposure to extreme heat, receiving drugs with anticholinergic activity, or being subject to dehydration). Monitor for and report signs of tardive dyskinesia. Monitor for and immediately report S&S of neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS) that include: Hyperpyrexia, muscle rigidity, altered mental status, irregular pulse or blood pressure, tachycardia, diaphoresis, and cardiac dysrhythmia. Withhold drug if NMS is suspected. Lab tests: Monitor periodically Hct and Hgb. Monitor periodically blood glucose. Monitor for elevated CPK and myoglobinuria if NMS is suspected. Common side effects Body as a Whole: Headache, asthenia, fever, flu-like symptoms, peripheral edema, chest pain, neck pain, neck rigidity. CNS: Anxiety, insomnia, lightheadedness, somnolence, akathisia, tremor, extrapyramidal symptoms, depression, nervousness, increased salivation, hostility, suicidal thought, manic reaction, abnormal gait, confusion, cogwheel rigidity. CV: Hypertension, tachycardia, hypotension, bradycardia. Risk of
stroke in elderly with dementia-related psychosis. GI: Nausea, vomiting, constipation, anorexia. Hematologic: Ecchymosis, anemia. Metabolic: Weight gain, weight loss, hyperglycemia, diabetes mellitus, increased creatine kinase. Musculoskeletal: Muscle cramp. Respiratory: Rhinitis, cough. Skin: Rash. Special Senses: Blurred vision.
Interactions with other patient drugs, OTC or herbal medicines (ask patient specifically) Drug: CYP3A4 inducers ( carbamazepine, phenytoin, etc.) will decrease aripiprazole levels (may need to double aripiprazole dose); use with CYP2D6 or CYP3A4 inhibitors ( ketoconazole, quinidine, fluoxetine, paroxetine, etc.) may increase aripiprazole levels (reduce dose by ); may cause additive sedation with other SEDATIVES (alcohol, tramadol, BARBITURATES, etc.); may enhance effects of ANTIHYPERTENSIVE AGENTS.
Lab value alterations caused by medicine Lab tests: Monitor periodically Hct and Hgb. Monitor periodically blood glucose. Monitor for elevated CPK and myoglobinuria if NMS is suspected.
Be sure to teach the patient the following about this medication Carefully monitor blood glucose levels if diabetic. Do not drive or engage in other potentially hazardous activities until reaction to drug is known. Avoid situations where you are likely to become overheated or Herbal: St. John's wort may decrease aripiprazole levels. dehydrated. Notify physician if you become pregnant or intend to become pregnant Food: High fat meals may delay time to peak plasma levels. while taking this drug. Nursing Process- Assessment Assessment Evaluation (Pre-administration assessment) Why would you hold or not give this med? Check after giving Monitor diabetics for loss of glycemic Monitor periodically Hct and CONTRAINDICATIONS Hypersensitivity to aripiprazole; dementia in control. Hgb. Monitor periodically blood elderly; QT prolongation; lactation. Monitor cardiovascular status. Assess for glucose. Monitor for elevated and report orthostatic hypotension. CPK and myoglobinuria if NMS Take BP supine then in sitting is suspected. position. Report systolic drop of greater than 1520 mm Hg. Patients at increased risk are those who are dehydrated, hypovolemic, or receiving concurrent antihypertensive therapy. Monitor body temperature in situations likely to elevate core temperature (e.g., exercising strenuously, exposure to extreme heat, receiving drugs with anticholinergic activity, or being subject to dehydration). Monitor for and report signs of tardive dyskinesia. Monitor for and immediately report S&S of neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS) that include: Hyperpyrexia, muscle rigidity, altered mental status, irregular pulse or blood pressure, tachycardia, diaphoresis, and cardiac dysrhythmia. Withhold drug if NMS is suspected.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Lamictal (Lamotrigine)Document1 paginăLamictal (Lamotrigine)E100% (1)
- Psych Drug StudyDocument5 paginiPsych Drug StudyLorina Lynne Apelacio100% (4)
- DivalproexDocument2 paginiDivalproexeefrheelÎncă nu există evaluări
- CymbaltaDocument2 paginiCymbaltaEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument2 paginiDrug Studyunkown userÎncă nu există evaluări
- AlprazolamDocument2 paginiAlprazolamRenggaSuhardijantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Citalopramhydrobromide CelexaDocument3 paginiCitalopramhydrobromide CelexaKristi Wray100% (1)
- Bupropion Hydrochloride (Drug Study)Document3 paginiBupropion Hydrochloride (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888100% (1)
- Escitalopram Drug StudyDocument2 paginiEscitalopram Drug StudyLizShermanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lithium CarbonateDocument2 paginiLithium CarbonateArnzz AgbulosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Olanzapine Drug StudyDocument1 paginăOlanzapine Drug StudyJeyser T. Gamutia100% (1)
- Prozac FluoxetineDocument2 paginiProzac FluoxetineEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chlorpromazine Drug StudyDocument7 paginiChlorpromazine Drug Studyjennachristy03100% (3)
- FluoxetineDocument3 paginiFluoxetineArnzz Agbulos100% (1)
- Venlafaxine XRDocument2 paginiVenlafaxine XRMichael KuzbytÎncă nu există evaluări
- Methylphenidate Hydro ChlorideDocument3 paginiMethylphenidate Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941Încă nu există evaluări
- ZopicloneDocument2 paginiZopicloneMichael KuzbytÎncă nu există evaluări
- School of Nursing and Midwifery: Emilio Aguinaldo CollegeDocument3 paginiSchool of Nursing and Midwifery: Emilio Aguinaldo CollegeMiggsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacologic Class: Therapeutic Class: Atypical: Dibenzothiazepine Derivative AntipsychoticDocument2 paginiPharmacologic Class: Therapeutic Class: Atypical: Dibenzothiazepine Derivative AntipsychoticBianca Nicole Gacad Fernandez100% (1)
- AMITRIPTYLINEDocument2 paginiAMITRIPTYLINERPh Krishna Chandra JagritÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study ClonazepamDocument3 paginiDrug Study ClonazepamJohn Rey AbadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument5 paginiDrug StudyLizeth Querubin92% (25)
- ImipramineDocument6 paginiImipramineMuhammed Faruk JambazÎncă nu există evaluări
- DRUG StudyDocument3 paginiDRUG StudyArfe BaquinquitoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument4 paginiDrug StudyYasminGianneDeOcampoBarizoÎncă nu există evaluări
- ChlorpromazineDocument2 paginiChlorpromazineevalyn dane50% (2)
- Librium ChlordiazepoxideDocument2 paginiLibrium ChlordiazepoxideEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oxazepam (Serax)Document1 paginăOxazepam (Serax)CassieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument12 paginiDrug StudyAnneÎncă nu există evaluări
- HaloperidolDocument2 paginiHaloperidolMikz JocomÎncă nu există evaluări
- Divalproex Sodium (Depakote ER)Document1 paginăDivalproex Sodium (Depakote ER)karenmichellelecarozÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument4 paginiDrug StudyTeZza_Enano_2209100% (1)
- Drugs Psych WardDocument4 paginiDrugs Psych WardIris CaberteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lithium Carbonate Drug StudyDocument3 paginiLithium Carbonate Drug StudyJennyLapitan80% (5)
- FluphenazineDocument4 paginiFluphenazineimthebossÎncă nu există evaluări
- DiazepamDocument1 paginăDiazepamStephanie PeÎncă nu există evaluări
- DRUG STUDY PsycheDocument1 paginăDRUG STUDY Psychejulesubayubay5428100% (1)
- Fluoxetine Duloxetine SertralineDocument7 paginiFluoxetine Duloxetine SertralineReneé Camille100% (1)
- Clozapine (Drug Study)Document2 paginiClozapine (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888100% (3)
- Clorazepate Dipotassium (Drug Study)Document2 paginiClorazepate Dipotassium (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888Încă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study (Haloperidol)Document3 paginiDrug Study (Haloperidol)Mae Ann Bueno CastillonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quetiapine - Drug Study - BSN3D BantayDocument4 paginiQuetiapine - Drug Study - BSN3D BantayJAN FEDERICK BANTAYÎncă nu există evaluări
- Risperidone Drug StudyDocument2 paginiRisperidone Drug StudyNajmah Saaban77% (13)
- Drug Study and Mental Health AssessmentDocument8 paginiDrug Study and Mental Health AssessmentVincent Quitoriano100% (1)
- Drug Study ZiprasidoneDocument2 paginiDrug Study ZiprasidoneArnzz Agbulos100% (1)
- Haloperidol DRUG STUDYDocument2 paginiHaloperidol DRUG STUDYaaron tabernaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Requirement Drug Study PsycheDocument6 paginiRequirement Drug Study PsycheRegine Lorenzana Mey-AngÎncă nu există evaluări
- AlprazolamDocument3 paginiAlprazolamapi-3797941100% (1)
- DS HaloperidolDocument3 paginiDS HaloperidolbillyktoubattsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study (Olanzapine)Document1 paginăDrug Study (Olanzapine)Eden Marie Francisco100% (1)
- DRUG SODIUM VALPROATE (Depakote, Epilim, Episenta)Document5 paginiDRUG SODIUM VALPROATE (Depakote, Epilim, Episenta)Pearl Princess Guerrero100% (2)
- Drug Carbidopa LevodopaDocument1 paginăDrug Carbidopa LevodopaSrkocherÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effectiveness Indicated by A Reduction in Psychotic BehaviorDocument4 paginiEffectiveness Indicated by A Reduction in Psychotic BehaviorGwyn RosalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- AripiprazoleDocument4 paginiAripiprazoleAP TOROBX100% (1)
- QuetiapineDocument3 paginiQuetiapineMichael KuzbytÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seroquel (Quetiapine)Document3 paginiSeroquel (Quetiapine)E100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument12 paginiDrug StudyAngeli A EstilloreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychopharmacology in PsychiatryDocument94 paginiPsychopharmacology in PsychiatryOslo SaputraÎncă nu există evaluări
- ANTIPSYCHOTICS Olanzapine (Zyprexa), Aripiprazole (Abilify), Chlorpromazine (Thorazine)Document5 paginiANTIPSYCHOTICS Olanzapine (Zyprexa), Aripiprazole (Abilify), Chlorpromazine (Thorazine)Rhanne BolanteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Propranolol Hydro ChlorideDocument4 paginiPropranolol Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941Încă nu există evaluări
- Citalopramhydrobromide CelexaDocument3 paginiCitalopramhydrobromide CelexaKristi Wray100% (1)
- Ciprofloxacin CiproDocument1 paginăCiprofloxacin CiproKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clopidogrel Bisulfate - PlavixDocument2 paginiClopidogrel Bisulfate - PlavixKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Codiene-Acetaminophen Tylenol 3Document1 paginăCodiene-Acetaminophen Tylenol 3Kristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clonazepam KlonopinDocument3 paginiClonazepam KlonopinKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ceftaroline Teflaro CefotaximeDocument3 paginiCeftaroline Teflaro CefotaximeKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cefoxitin Sodium MefoxinDocument3 paginiCefoxitin Sodium MefoxinKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cefepime MaxipimeDocument2 paginiCefepime MaxipimeKristi Wray100% (1)
- Aspirin ASA BayerDocument2 paginiAspirin ASA BayerKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cefazolin Sodium AncefDocument1 paginăCefazolin Sodium AncefKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Baclofen KemstroDocument2 paginiBaclofen KemstroKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adacel Tdap VaccineDocument1 paginăAdacel Tdap VaccineKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amphetamine AdderallDocument2 paginiAmphetamine AdderallKristi Wray100% (1)
- Albuterol VentolinDocument3 paginiAlbuterol VentolinKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acetaminophen TylenolDocument2 paginiAcetaminophen TylenolKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alprazolam XanaxDocument2 paginiAlprazolam XanaxKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aripiprazole AbilifyDocument2 paginiAripiprazole AbilifyKristi Wray100% (2)
- Chronic Kidney Disease in Dogs and Cats: Joseph W. BartgesDocument24 paginiChronic Kidney Disease in Dogs and Cats: Joseph W. BartgesYader CorredorÎncă nu există evaluări
- OxygenationDocument20 paginiOxygenationKhie-An OcampoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gutiera BruxismDocument3 paginiGutiera BruxismGeorgeIliescuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abdikadir Ali Adan-Research Proposal Revised-1Document4 paginiAbdikadir Ali Adan-Research Proposal Revised-1abdiqadir ali adanÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Frontal Assessment Battery (FAB) Normative Value PDFDocument9 paginiThe Frontal Assessment Battery (FAB) Normative Value PDFIcaroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tinidazole Is An AntiDocument6 paginiTinidazole Is An AntiNoi Maya Anggrita SariÎncă nu există evaluări
- GravolDocument5 paginiGravoldrugcardrefÎncă nu există evaluări
- Risk and Protective Factors in Schizophrenia: Heinz Hafner (Editor)Document322 paginiRisk and Protective Factors in Schizophrenia: Heinz Hafner (Editor)Eva CastanheiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wariskan Keluarga Dengan Kesenangan Dan Kepastian: WarisanplusDocument12 paginiWariskan Keluarga Dengan Kesenangan Dan Kepastian: WarisanplusdinmdpiahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia in The Neonate - UpToDate PDFDocument38 paginiCongenital Diaphragmatic Hernia in The Neonate - UpToDate PDFJosé Abraham Amaya DuarteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Patient Care PDFDocument310 paginiPatient Care PDFCindy BonghanoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sta - Importance of Mental HealthDocument2 paginiSta - Importance of Mental HealthZerah LunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formative Practice Chapter 2 (BI)Document8 paginiFormative Practice Chapter 2 (BI)suraya nazaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Sketch of Indonesia Medicine: Sugma AP, MD, MARSDocument42 paginiThe Sketch of Indonesia Medicine: Sugma AP, MD, MARSRaja Friska YulandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BNF GuidelinesDocument6 paginiBNF Guidelineselhassia elhassiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Examination For ThyroidDocument3 paginiPhysical Examination For ThyroidVincent ChristiansenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Personal Development: Quarter 1 - Module 4Document33 paginiPersonal Development: Quarter 1 - Module 4JulieAnnLucasBagamaspad100% (1)
- Stress Management Objectives Stree Illness and Adaptaion OriginalDocument49 paginiStress Management Objectives Stree Illness and Adaptaion OriginalKhizar AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCQ Cardio 2Document54 paginiMCQ Cardio 2Dian Paramita100% (1)
- The Pathogenesis and Pathophysiology of Type 1 and PDFDocument12 paginiThe Pathogenesis and Pathophysiology of Type 1 and PDFasmawatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument8 paginiDrug StudyMaria Charlene Orpilla0% (1)
- Approach To Patient With Altered Mental Status & ComaDocument38 paginiApproach To Patient With Altered Mental Status & ComaSol Gat ChupataÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathogenic Organisms and Virulence FactorsDocument45 paginiPathogenic Organisms and Virulence FactorsqwertÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transform at Home EbookDocument302 paginiTransform at Home EbookLuckyÎncă nu există evaluări
- EssayDocument2 paginiEssayapi-424561848Încă nu există evaluări
- RCL Employment Medical Examination Form A (New-Returning) Revised 2015-03Document2 paginiRCL Employment Medical Examination Form A (New-Returning) Revised 2015-03Ahmad ShodiqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Thyroid MedicationsDocument3 paginiTypes of Thyroid MedicationsfennarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conditions in Occupational Therapy Effect On Occupational Performance 5th Edition Ebook PDFDocument62 paginiConditions in Occupational Therapy Effect On Occupational Performance 5th Edition Ebook PDFzachary.mellott289100% (46)
- Unit 5: Healing SystemDocument24 paginiUnit 5: Healing SystemSushmita BudhathokiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pengaruh Penyuluhan Kesehatan Terhadap PDocument8 paginiPengaruh Penyuluhan Kesehatan Terhadap PEdith LauraÎncă nu există evaluări