Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Lipids
Încărcat de
Jay Mar TurnoDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Lipids
Încărcat de
Jay Mar TurnoDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
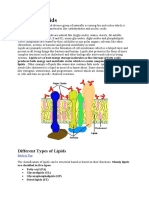
Lipids constitute a group of naturally occurring molecules that include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins
A, D, E, and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, triglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The main biological functions of lipids include energy storage, signaling, and acting as structural components of cell membranes. Lipids may be broadly defined as hydrophobic or amphiphilic small molecules; the amphiphilic nature of some lipids allows them to form structures such as vesicles, liposomes, or membranes in an aqueous environment. Biological lipids originate entirely or in part from two distinct types of biochemical subunits or "building-blocks": ketoacyl and isoprene groups.[4] Using this approach, lipids may be divided into eight categories: fatty acids, glycerolipids, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids, saccharolipids, and polyketides (derived from condensation of ketoacyl subunits); and sterol lipids and prenol lipids (derived from condensation of isoprene subunits). Although the term lipid is sometimes used as a synonym for fats, fats are a subgroup of lipids called triglycerides. Lipids also encompass molecules such as fatty acids and their derivatives (including tri-, di-, monoglycerides, and phospholipids), as well as other sterol-containing metabolites such as cholesterol. [6] Although humans and other mammals use various biosynthetic pathways to both break down and synthesize lipids, some essential lipids cannot be made this way and must be obtained from the diet. Common name Myristoleic acid Palmitoleic acid Sapienic acid Oleic acid Examples of Unsaturated Fatty Acids Chemical structure CH3(CH2)3CH=CH(CH2)7COOH CH3(CH2)5CH=CH(CH2)7COOH CH3(CH2)8CH=CH(CH2)4COOH CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)7COOH cis-9 cis-9 cis-6 cis-9 trans-9 trans-11 cis,cis-9,12 trans,trans9,12 cis,cis,cis9,12,15 cis,cis,cis,cis58,11,14 cis,cis,cis,cis,cis5,8,11,14,17 cis-13 cis,cis,cis,cis,cis, cis4,7,10,13,16, 19 x C: D 14 :1 16 :1 16 :1 18 :1 18 :1 18 :1 18 :2 18 :2 18 :3 20 :4 20 :5 22 :1 22 :6 n x n 5 n 7 n 10 n 9 n 9 n 7 n 6 n 6 n 3 n 6 n 3 n 9 n 3
Elaidic acid CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)7COOH Vaccenic acid Linoleic acid Linoelaidic acid -Linolenic acid Arachidoni c acid Eicosapent aenoic acid Erucic acid Docosahex aenoic acid CH3(CH2)5CH=CH(CH2)9COOH CH3(CH2)4CH=CHCH2CH=CH(CH2)7COOH CH3(CH2)4CH=CHCH2CH=CH(CH2)7COOH CH3CH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CH(CH2)7COOH CH3(CH2)4CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CH(CH2)3 COOHNIST CH3CH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH= CH(CH2)3COOH CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)11COOH CH3CH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH= CHCH2CH=CH(CH2)2COOH
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Lecture Research BiochemDocument16 paginiLecture Research BiochemDianne MaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- CNP 3 LipidsDocument49 paginiCNP 3 LipidsKepa KepaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lipid: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument25 paginiLipid: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediahasimi91Încă nu există evaluări
- LipidDocument97 paginiLipidNasar ullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Glycerolipids: Acid, The Most Abundant Fatty-Acyl Chains of Plant Thylakoid Membranes, Render TheseDocument2 paginiGlycerolipids: Acid, The Most Abundant Fatty-Acyl Chains of Plant Thylakoid Membranes, Render TheseshobhrajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lipids - Definition, Classification and PropertiesDocument41 paginiLipids - Definition, Classification and PropertiesAdityaNugrohoÎncă nu există evaluări
- LipidsDocument141 paginiLipidsabrham sharewÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formal Report of LipidDocument14 paginiFormal Report of LipidSaraSaraswatyÎncă nu există evaluări
- RESEARCHDocument8 paginiRESEARCHbun carÎncă nu există evaluări
- NURS 1012: Basic Biochemistry: Lecture #4: Lipid Structure and FunctionDocument26 paginiNURS 1012: Basic Biochemistry: Lecture #4: Lipid Structure and FunctionqpidjmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Che 473 Presented by - Nishatanjum (0802005) Seefat Farzin (0802011) Turna Barua (0802016)Document30 paginiChe 473 Presented by - Nishatanjum (0802005) Seefat Farzin (0802011) Turna Barua (0802016)asha196Încă nu există evaluări
- 5 LipidDocument32 pagini5 LipidAli HusseinÎncă nu există evaluări
- CholesterolDocument12 paginiCholesterolCrina LupuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 14 BiomoleculesDocument13 paginiChemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 14 Biomoleculesrathi rupaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Metabolism II Notes Reviewed-1Document80 paginiBasic Metabolism II Notes Reviewed-1felixÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diet For Bodybuilder by Guru MannDocument58 paginiDiet For Bodybuilder by Guru MannDhanjayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lipids & Biological MembranesDocument54 paginiLipids & Biological MembranesvictoriousÎncă nu există evaluări
- L8 - Structure Functions of Various LipidsDocument23 paginiL8 - Structure Functions of Various Lipidsbilawal khanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aao Lipid 1Document29 paginiAao Lipid 1api-386303659Încă nu există evaluări
- BCM 202 Quality AssuranceDocument18 paginiBCM 202 Quality AssuranceTeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Classification of Lipids: Bio-Molecules Categorized As Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids and Nucleic Acids LipidsDocument5 paginiClassification of Lipids: Bio-Molecules Categorized As Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids and Nucleic Acids Lipidsjoi orpillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lipids Classification and TypesDocument4 paginiLipids Classification and TypesDesiree Roxanne DiamzonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture No. 4: Lipid ChemistryDocument19 paginiLecture No. 4: Lipid ChemistrySafura IjazÎncă nu există evaluări
- VojoyDocument7 paginiVojoyFerds SalvatierraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fatty Acid MetabolismDocument8 paginiFatty Acid MetabolismJessicaOktavianusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biochemistr Y: Digital Assignment 2Document15 paginiBiochemistr Y: Digital Assignment 2Ann Angella sibyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lipid ChemistryDocument93 paginiLipid ChemistrySanreet RandhawaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy at PhysiologyDocument17 paginiAnatomy at Physiologyagentlara28Încă nu există evaluări
- Common Fatty AcidsDocument2 paginiCommon Fatty AcidsJohnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carbohydrates & Krebs CycleDocument70 paginiCarbohydrates & Krebs CycleShimmering MoonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutritional Biochemistry 1 - LIPIDSDocument62 paginiNutritional Biochemistry 1 - LIPIDSAdnan AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lipid Metabolism - WikipediaDocument31 paginiLipid Metabolism - WikipediaTomiwa AdeshinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lipids 2Document44 paginiLipids 2zubair saeedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lipid Structure and FunctionDocument47 paginiLipid Structure and FunctionMariam ShalabyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lipid: Source: WikipediaDocument1 paginăLipid: Source: WikipediaAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture Notes On LipidsDocument22 paginiLecture Notes On Lipidsofforp211Încă nu există evaluări
- CarbohydrateDocument8 paginiCarbohydrateDhrubo RoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biochemistry: Digital Assignment 2Document14 paginiBiochemistry: Digital Assignment 2Ann Angella sibyÎncă nu există evaluări
- BCM 202 Additional MaterialsDocument16 paginiBCM 202 Additional MaterialsTeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lipid Chemistry: Roselyn G. Dellosa BSMT 3-2Document10 paginiLipid Chemistry: Roselyn G. Dellosa BSMT 3-2Nixon DellosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carbohydrate: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument9 paginiCarbohydrate: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAlmaNukićÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lipid NotesDocument5 paginiLipid NotesGary TeohÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dr. Shyam Babu Prasad: Course Code: ZOOL 4008 (Biochemistry and Metabolism)Document17 paginiDr. Shyam Babu Prasad: Course Code: ZOOL 4008 (Biochemistry and Metabolism)Brama AtmajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lipid MetabolismDocument32 paginiLipid MetabolismNahid HasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- LipidsDocument172 paginiLipidsK V SATHEESHKUMAR MECHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Different Types of LipidsDocument7 paginiDifferent Types of LipidsNESLIHAN ERSOYAKÎncă nu există evaluări
- I. Monosaccharides (Simple Sugars) :: Aldoses KetosesDocument9 paginiI. Monosaccharides (Simple Sugars) :: Aldoses KetosesdenisseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutritional Quality of Milkfat: 1 What's in Milkfat?Document10 paginiNutritional Quality of Milkfat: 1 What's in Milkfat?test testÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lipids: Functions, Applications in Food Industry and OxidationDocument11 paginiLipids: Functions, Applications in Food Industry and OxidationSiti JamilahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carbohydrate Chemistry - by Dr. Naila For Nursing 2 YearDocument14 paginiCarbohydrate Chemistry - by Dr. Naila For Nursing 2 YearsalmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- LipidDocument80 paginiLipidMirza Salman BaigÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 3 BiomoleculesDocument30 paginiModule 3 BiomoleculesAlaine Paul GeronimoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lipids and Its Metabolism ProjectDocument51 paginiLipids and Its Metabolism ProjectJopeter Alicer TinayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group 2 LIPIDS Formal Written ReportDocument7 paginiGroup 2 LIPIDS Formal Written ReportmiallyannaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Metabolism of LipidsDocument38 paginiMetabolism of LipidsВладислав ЯкушевÎncă nu există evaluări
- LipidsDocument4 paginiLipidsKatelyn ValeraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problems LipidsDocument2 paginiProblems LipidsDittha Rieztya Phyramid0% (1)
- Week 7 Biochemistry: Classification of LipidDocument5 paginiWeek 7 Biochemistry: Classification of LipidRiza Dela CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 7chemistry of LipidDocument31 paginiChapter 7chemistry of Lipidbayan.grÎncă nu există evaluări
- SFE - Learning About Chemistry - G B ShulpinDocument235 paginiSFE - Learning About Chemistry - G B ShulpinShiv7_som784100% (2)
- Transition Elements WS (MCQ)Document6 paginiTransition Elements WS (MCQ)Torenku100% (1)
- Catalytic ConverterDocument17 paginiCatalytic ConverterRavi Donga93% (14)
- Esthetic Dentistry and Ceramic Restoration, 1edDocument331 paginiEsthetic Dentistry and Ceramic Restoration, 1edMariana RaduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Classification of AggregatesDocument3 paginiClassification of Aggregatespaddy11234Încă nu există evaluări
- Highly Acidic BINOL-Derived Phosphoramidimidates and Their ApplicationDocument3 paginiHighly Acidic BINOL-Derived Phosphoramidimidates and Their Applicationxuyijing2007comÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper 1Document7 paginiPaper 1Akash Kumar UpadhyayÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHEMISTRY IpeDocument2 paginiCHEMISTRY IpeRam MohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application of IR (Infra-Red) SpectrosDocument8 paginiApplication of IR (Infra-Red) SpectrosRadowan Ahmad100% (1)
- Experiment Vi Photochemical Reduction of Iron (Iii) IonsDocument3 paginiExperiment Vi Photochemical Reduction of Iron (Iii) IonsSafa AnnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chen 2009Document6 paginiChen 2009Татьяна СаенкоÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIOCHEM 1 Cell Biomolecules PDFDocument3 paginiBIOCHEM 1 Cell Biomolecules PDFHarold James AlcantaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Manufacturing Process of LeadDocument10 paginiThe Manufacturing Process of LeadJACKULIN DAFNEEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Workshop Ferrous 2012Document228 paginiWorkshop Ferrous 2012Pramod MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 4 Preprations and Standardisation of Standard SolutionsDocument41 paginiUnit 4 Preprations and Standardisation of Standard SolutionsAnis SayyedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jan, Wang - 2020 - Waste-Water Purification Through A Countercurrent System Driven by Supercritical Carbon Dioxide (SC-CO2) - Part I ExpeDocument10 paginiJan, Wang - 2020 - Waste-Water Purification Through A Countercurrent System Driven by Supercritical Carbon Dioxide (SC-CO2) - Part I ExpeIlireaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Appendix CDocument8 paginiAppendix CJia ChenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Full Length Article: J. Greco-Duarte, E.D. Cavalcanti-Oliveira, J.A.C. Da Silva, R. Fernandez-Lafuente, D.M.G. FreireDocument10 paginiFull Length Article: J. Greco-Duarte, E.D. Cavalcanti-Oliveira, J.A.C. Da Silva, R. Fernandez-Lafuente, D.M.G. FreireAna Cristina CollaçoÎncă nu există evaluări
- GeneralChemistry (Organic Compounds)Document27 paginiGeneralChemistry (Organic Compounds)yen perioles100% (1)
- Hydroxyl Compounds (Alcohols)Document7 paginiHydroxyl Compounds (Alcohols)Nazmul NayeemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carbohydrates: By: Tom Anthony A. Tonguia, RMT, CssoDocument77 paginiCarbohydrates: By: Tom Anthony A. Tonguia, RMT, CssoTom Anthony TonguiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Codex Standard For Cocoa PowdersDocument4 paginiCodex Standard For Cocoa PowdersIdamelis Rodríguez GarcíaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MSDS Colalube 3410Document3 paginiMSDS Colalube 3410mndmattÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analytical Chemistry Notes, Problems PDFDocument32 paginiAnalytical Chemistry Notes, Problems PDFKuo Sarong100% (1)
- Ointments Ms. Wajiha IffatDocument29 paginiOintments Ms. Wajiha Iffatmdsajidaali0% (1)
- Pre Foundation ChemistryDocument68 paginiPre Foundation ChemistryAARYAN SURESH V. X DÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry 2Document38 paginiChemistry 2James Loyed TabasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Method Statement For Site Handling of Concrete Made With GGBSDocument2 paginiMethod Statement For Site Handling of Concrete Made With GGBSabobeedoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0620 s16 QP 42 PDFDocument12 pagini0620 s16 QP 42 PDFAlmeeraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Streptozocin Injection 090325 (ZY)Document2 paginiStreptozocin Injection 090325 (ZY)Shahid pinÎncă nu există evaluări