Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
AC Vector Drives 3 Equations
Încărcat de
leo232Descriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
AC Vector Drives 3 Equations
Încărcat de
leo232Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
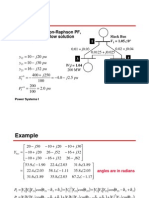
Dynamic Equation of Cage IM - Introduction
S R R R
The 3 stator coils A,B,C can be represented by TWO stationary coils Each stationary coil has resistance and inductance and:
vs = is Rs +
S
d s dt
vs = is Rs +
d s dt
v s = i s Rs +
d s dt
The 3 rotor coils A,B,C can be represented by TWO moving coils Each moving coil has resistance and inductance and: d d d v r = i r Rs + r vr = ir Rs + r vr = ir Rs + r dt dt dt These are the equations of coils moving round at rotor speed
Dynamic Equation of Cage IM Stator
The equations of the TWO coils rotating at r can be written in a coordinate frame rotating with e
v s
d = i s Rs + s dt
j s
x d
v sdq = v s e j i sdq = i s e s
sdq = s e
j s
v s = v sdq e
j s
xq
i s = i sdq e
j s
j s
xd
s
d dt
sdq
sdq
v sdq = i sdq R s +
+ j e sdq
v sdq e j = i sdq e j R s + v sdq e j
d sdq e j dt d sdq j = i sdq e j R s + e + j e sdq e j dt
v sd = i sd R s +
v sq
d sd e sq dt d = i sq R s + sq + e sd dt
Dynamic Equation of Cage IM Rotor
The equations of the TWO coils rotating at r can be written in a coordinate frame rotating with e
0 = i r
d Rr + dt
x d
e
xd
v rdq = v r e j ( r )
v r = v rdq e j ( r )
i rdq = i r e
j( r )
i r = i rdq e
j( r )
xq
-r
j( r ) rdq = re j( r ) r = rdqe
0 = i rd R s +
0 = i rdq R s + d rdq + j sl rdq dt
d rd sl rq dt
0 = i rq R s +
d rq + sl rd dt
Dynamic Equation of Cage IM contd
The stator and rotor fluxes of the two coils in the dq rotating frame are:
sd = Ls isd + Lo ird
rd = Lo isd + Lr ird
rq = Lo isq + Lr irq
sq = Ls isq + Lo irq
These can be used to eliminate ird, irq,sd ,sq
The stator equations Had:
v sdq = i sdq R s +
d dt
sdq
+ j e sdq
In terms of is and r :
v sdq = Rs i sdq + Ls
L d L d i sd + je Ls i sdq + o rdq + je o rdq dt Lr dt Lr L d L d isd e Ls isq + o rd e o rq dt Lr dt Lr L d L d isq + e Ls isd + o rq + e o rd dt Lr dt Lr
vsd = Rs isd + Ls
Comparing real and imaginary terms :
vsq = Rs isq + Ls
These are the stator equations in a rotating dq axis frame
Dynamic Equation of Cage IM contd
The stator and rotor fluxes of the two coils in the dq rotating frame are:
sd = L s isd + Lo ird
rd = Lo isd + Lr ird
rq = Lo isq + Lr irq
sq = L s isq + Lo irq
These can be used to eliminate ird, irq,sd ,sq
The rotor equations
Had:
0 = i rdq R s +
0=
d rdq + j sl rdq dt
In terms of is and r :
L Rr d rdq o Rr i sdq + rdq + jsl rdq Lr Lr dt
Comparing real and imaginary terms :
Lo Rr d 0 = rd Rr isd + rd sl rq Lr Lr dt L R d 0 = r rq o Rr isq + rq + sl rd Lr Lr dt
These are the rotor equations in a rotating dq axis frame
Dynamic Equation of Cage IM
Consider equations in dq rotating frame orientated on rotor flux:
q r is d
rq= ? rq= 0!!
Hence all rq terms go zero
The stator equations under ROTOR FLUX ORIENTATION (RFO)
vsd = Rs isd + Ls vsq = Rs isq + Ls
L d d isd e Ls isq + o rd dt Lr dt L d isq + e Ls isd + e o rd dt Lr
Dynamic Equation of Cage IM
Consider equations in dq rotating frame orientated on rotor flux:
q r is d
rq= 0!!
Hence all rq terms go zero
The rotor equations under ROTOR FLUX ORIENTATION (RFO):
0=
L Rr d rd o Rr isd + rd Lr Lr dt
0=
Lo Rr isq + sl rd Lr
The vector control equations (RFO)
Consider rotor equations under ROTOR FLUX ORIENTATION (RFO)
L R d 0 = r rd o Rr isd + rd Lr Lr dt
Define the magnetising current imrd as:
Lo 0 = Rr isq + sl rd Lr rd = Loimrd
L R d 0 = r Loimrd o Rr isd + Lo imrd Lr Lr dt
Lr d imrd + imrd = isd Rr dt
Rr sl = isq Lr imrd
L 0 = o Rr isq + sl Loimrd Lr
These are often called the vector control equations
Equivalence to DC machine
Consider the d-axis vector control equation:
Lr d imrd + imrd = isd Rr dt
ia
Rf
Vf if Lf
d Vf = Rf i f + Lf i f dt
Comparing terms we see that:
Lf d Vf if + if = R f dt Rf
imrd i f
isd V f / R f
In steady state i.e. under constant field conditions
imrd = isd
isd is really the field forcing current, but is commonly called the field current Be aware of difference between isd and imrd under field weakening conditions
Slip gain and motor torque
Consider the q-axis vector control equation:
Rr sl = isq Lr imrd
Rr sl = isq Lr imrd
sl =
1 isq = ksl isq r imrd
This is true IF and ONLY IF we are orientated on the rotor flux axis Slip is directly proportional to the torque component of stator current The slip gain ksl depends on field level and the rotor time constant r The motor torque was:
T = kisq rd
And if
rd = Loimrd
T = kLoisqimrd
The value of k depends on the convention used for the 3-2 (3-phase to transformation) scaling:
For the 3/2 x peak convention:
2 P Lo k= 3 2 Lr
For the rms convention:
P Lo k =3 2 Lr
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Dyn of Ind MacDocument18 paginiDyn of Ind MacsucinervozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Adaptive Input-Output Feedback Linearization Controller For Doubly-Fed Induction Machine DrivesDocument16 paginiAn Adaptive Input-Output Feedback Linearization Controller For Doubly-Fed Induction Machine Drivesashikhmd4467Încă nu există evaluări
- Generator TorqueDocument34 paginiGenerator TorqueTarun KV100% (1)
- AVR Instruction Set SummaryDocument3 paginiAVR Instruction Set Summarycolea11Încă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 3 VTSDocument42 paginiLecture 3 VTSGanesuni HarishÎncă nu există evaluări
- 05 Instantaneous Axis of RotationDocument14 pagini05 Instantaneous Axis of RotationSupriyo DuttaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Central ForceDocument30 paginiCentral Forcemanish_mehta009_3526Încă nu există evaluări
- Single Phase Induction Motor MODELING AND SIMULATIONDocument3 paginiSingle Phase Induction Motor MODELING AND SIMULATIONMAULANA MALIK IBRAHIMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Induction MotorDocument50 paginiInduction Motorsolo4000100% (1)
- Time ConstantsDocument8 paginiTime ConstantsVishwas Acharya NÎncă nu există evaluări
- Protecciones AyudaDocument13 paginiProtecciones AyudaDiego Javier Ponce AndradeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Equações Mecanicas Do MotoresDocument10 paginiEquações Mecanicas Do MotoresTiago FariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asynchronous MachineDocument15 paginiAsynchronous MachineboumedienÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3.modeling and Analysis of Multi-Phase Inverter Fed Induction MotorDocument8 pagini3.modeling and Analysis of Multi-Phase Inverter Fed Induction MotorRenuka DeviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Machines EPM405A Presentation 06Document18 paginiMachines EPM405A Presentation 06Ibrahim AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- MMA LabDocument31 paginiMMA LabA Naveen KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vortex Motion: - Consider Flow Along A Curved PathDocument19 paginiVortex Motion: - Consider Flow Along A Curved PathAnkit AgrawalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ball and Beam Dynamics - Full ModelDocument9 paginiBall and Beam Dynamics - Full ModelMarco SouzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3.5 y 3.6Document6 pagini3.5 y 3.6Flor Hernandez TiscareñoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gov NS Solver Sandberg PDFDocument8 paginiGov NS Solver Sandberg PDFAnonymous Y9pm84ZpJpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sliding Mode Control of Active and Reactive Powers Generated by A Doubly-Fed Induction Generator (DFIG)Document14 paginiSliding Mode Control of Active and Reactive Powers Generated by A Doubly-Fed Induction Generator (DFIG)marouan86Încă nu există evaluări
- Simulation of Indirect Field-Oriented Induction Motor Drive SystemDocument12 paginiSimulation of Indirect Field-Oriented Induction Motor Drive SystemThinseepÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cap 6Document17 paginiCap 6valentinmullerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Help - Asynchronous Machine - Blocks (SimPowerSystems™) PDFDocument23 paginiHelp - Asynchronous Machine - Blocks (SimPowerSystems™) PDFnmulyonoÎncă nu există evaluări
- DQ TransformationDocument51 paginiDQ TransformationAili LuggymixÎncă nu există evaluări
- DQ TransformationDocument51 paginiDQ Transformationसुमित नेमा50% (2)
- Emtl Unit-1Document85 paginiEmtl Unit-1Naga LakshmaiahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Emt (Ee) PDFDocument55 paginiEmt (Ee) PDFckvirtualize100% (4)
- Simulation of Electric Machines and Drive Systems Using Matlab and SimulinkDocument11 paginiSimulation of Electric Machines and Drive Systems Using Matlab and SimulinkmdpkishoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Robótica: Cinemática Directa + Cinemática InversaDocument46 paginiRobótica: Cinemática Directa + Cinemática InversaJoão CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- NXGDCLSRVX 55327 NXGDCLSRVXDocument26 paginiNXGDCLSRVX 55327 NXGDCLSRVXkprk414Încă nu există evaluări
- D-Q Transformation: J. MccalleyDocument51 paginiD-Q Transformation: J. MccalleyRicardo TironeÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHL231 Fluid Mechanics For Chemical Engineers Formula SheetDocument4 paginiCHL231 Fluid Mechanics For Chemical Engineers Formula SheetGarvit GoelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cdamp TheveninDocument9 paginiCdamp TheveninssyellampalliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Navier PDFDocument2 paginiNavier PDFRickyHerreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Homework: Ideal FlowsDocument15 paginiHomework: Ideal Flowsgaldo2Încă nu există evaluări
- DQ TransformationDocument51 paginiDQ TransformationWGSÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.1 - Equations of The Induction Motor ModelDocument25 pagini1.1 - Equations of The Induction Motor ModelAdithya ChandrasekaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- ATmega16 ATmega32Document9 paginiATmega16 ATmega32binitdubeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transforming Voltage Equations - Term 3: K K I I R R V VDocument11 paginiTransforming Voltage Equations - Term 3: K K I I R R V VGthulasi78Încă nu există evaluări
- 2 Acdc Machines Lecture IDocument58 pagini2 Acdc Machines Lecture IJayjay Rindole BalingbingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture14 16.360Document10 paginiLecture14 16.360kprk414Încă nu există evaluări
- Aircraft Parameters by Ying HuoDocument10 paginiAircraft Parameters by Ying HuoMohtashimAliKazmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Time Constant Inductance/ Resistance X: Time Constants From Equivalent CircuitsDocument154 paginiTime Constant Inductance/ Resistance X: Time Constants From Equivalent Circuitsanoopingle9Încă nu există evaluări
- EE 42/43/100 Introduction To Digital Electronics: Review of Ch. 4-7.3 7/19/13Document43 paginiEE 42/43/100 Introduction To Digital Electronics: Review of Ch. 4-7.3 7/19/13ozanistzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation On Synchronous Machine Model: Tandin Jamtsho STUDENT #3226091Document30 paginiPresentation On Synchronous Machine Model: Tandin Jamtsho STUDENT #3226091Parameswararao BillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Goldstein 18 21 13 14 20Document15 paginiGoldstein 18 21 13 14 20Abdul Shakoor ButtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oct 13 2022 CH 13 (6-7) Kinetics of Particles R-Theta Coordinat SystemDocument22 paginiOct 13 2022 CH 13 (6-7) Kinetics of Particles R-Theta Coordinat SystemArtEEzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electromagnetic TheoryDocument108 paginiElectromagnetic Theorytomica06031969Încă nu există evaluări
- 24gear Notes AGMA 1012 F 90Document7 pagini24gear Notes AGMA 1012 F 90Sezgin BayrakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Letters: Accurate Steady-State Representation of A Doubly Fed Induction MachineDocument6 paginiLetters: Accurate Steady-State Representation of A Doubly Fed Induction MachineAmy Leigh WilliamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atomic OrbitalsDocument21 paginiAtomic Orbitalsjesi5445Încă nu există evaluări
- Robot Manipulators: Modeling, Performance Analysis and ControlDe la EverandRobot Manipulators: Modeling, Performance Analysis and ControlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathematical Tables: Tables of in G [z] for Complex ArgumentDe la EverandMathematical Tables: Tables of in G [z] for Complex ArgumentÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99De la EverandThe Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99Încă nu există evaluări
- (Arjun N. Saxena) Invention of Integrated CircuitsDocument564 pagini(Arjun N. Saxena) Invention of Integrated Circuitsleo232100% (1)
- 331 Frey S Railway Electrification Systems EngineeringDocument145 pagini331 Frey S Railway Electrification Systems Engineeringdanutzughe100% (1)
- A Study of Ferroresonance and Mitigation TechniquesDocument41 paginiA Study of Ferroresonance and Mitigation Techniquesleo232Încă nu există evaluări
- Difference Between Switchgear and SwitchboardDocument5 paginiDifference Between Switchgear and Switchboardleo232Încă nu există evaluări
- Lecture6 The Fast Decoupled MethodDocument25 paginiLecture6 The Fast Decoupled Methodleo232Încă nu există evaluări
- Lecture3-Network Matrices, The Y-Bus Matrix Tap Changing TransformersDocument13 paginiLecture3-Network Matrices, The Y-Bus Matrix Tap Changing Transformersleo232Încă nu există evaluări
- Lecture1-Review of Power System Networks, Complex Power, and Per UnitsDocument29 paginiLecture1-Review of Power System Networks, Complex Power, and Per Unitsleo232Încă nu există evaluări
- PM Drives 2 ModsDocument4 paginiPM Drives 2 Modsleo232Încă nu există evaluări
- Microgrids PDFDocument27 paginiMicrogrids PDFleo232Încă nu există evaluări
- Droop ControlDocument3 paginiDroop Controlleo232100% (1)
- PMdrives Part2Document24 paginiPMdrives Part2leo232Încă nu există evaluări
- FactoringDocument13 paginiFactoringglebe myrtle belnasÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Description 1.6.1 Plate and Shell ElementDocument11 paginiGeneral Description 1.6.1 Plate and Shell Elementsinu21Încă nu există evaluări
- Eee 326 Lecture Notes 1Document38 paginiEee 326 Lecture Notes 1Barış DuranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Planar NonPlanar GraphsDocument23 paginiPlanar NonPlanar GraphsRozygynaga Xavierra LumminaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple Linear RegressionDocument24 paginiSimple Linear Regressionইশতিয়াক হোসেন সিদ্দিকীÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guia Calculo IntegralDocument3 paginiGuia Calculo IntegralLuis ManuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Demidovich Problems in Mathematical AnalysisDocument495 paginiDemidovich Problems in Mathematical Analysisjwcstar7985100% (5)
- Adding Numbers in ExcelDocument3 paginiAdding Numbers in ExcelFafunso AbiodunÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE206 MATLAB FundamentalsDocument43 paginiCE206 MATLAB FundamentalssjrokzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mert Ozbayram Math219 Assignment Week12 Due 08/23/2016 at 11:59pm EESTDocument6 paginiMert Ozbayram Math219 Assignment Week12 Due 08/23/2016 at 11:59pm EESTOrkun AkyolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Section 10.1: Boolean FunctionsDocument23 paginiSection 10.1: Boolean FunctionsOsamah AzamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math 8 QTR 3 Week 4Document10 paginiMath 8 QTR 3 Week 4JillianÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCV4U Derivatives of Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Practice TestDocument6 paginiMCV4U Derivatives of Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Practice TestEmily ChenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wave EquationDocument8 paginiWave EquationaminÎncă nu există evaluări
- 978 3 642 35858 6 - Book - OnlineDocument341 pagini978 3 642 35858 6 - Book - OnlineIvn TznÎncă nu există evaluări
- Accuracy & Precision: Applied ChemistryDocument35 paginiAccuracy & Precision: Applied ChemistryDiana Jean Alo-adÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 13-Compass and Transit RuleDocument4 paginiModule 13-Compass and Transit RuleGerovic ParinasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2020 ADP Nonlinear System Mismatched Disterbances 2Document8 pagini2020 ADP Nonlinear System Mismatched Disterbances 2Khải VũÎncă nu există evaluări
- XT MATHS Grade 11 Functions Parabolas + Lines MemoDocument7 paginiXT MATHS Grade 11 Functions Parabolas + Lines MemoJunaedi SiahaanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math Problem SolvingDocument57 paginiMath Problem SolvingzspiroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Projections Examples of Different Projections Coordinate Systems DatumsDocument53 paginiProjections Examples of Different Projections Coordinate Systems DatumsRajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 9: Center of Gravity and CentroidDocument10 paginiChapter 9: Center of Gravity and CentroidvictorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concrete Code Check Theory EnuDocument117 paginiConcrete Code Check Theory EnuNaida AdemovicÎncă nu există evaluări
- C Programming ProblemsDocument61 paginiC Programming ProblemsRajdeep BharatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Material Downloaded From - 1 / 4Document4 paginiMaterial Downloaded From - 1 / 4Ashmal ShazÎncă nu există evaluări
- IIyear R Mid2 Question BankDocument2 paginiIIyear R Mid2 Question Bankssrkm guptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic - Minima and MaximaDocument11 paginiTopic - Minima and MaximaMike OxlongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Must Solve 100 Programs Part 5 - 10Document11 paginiMust Solve 100 Programs Part 5 - 10Poojith Kodavaluru100% (1)
- CBSE Class 11 Mathematics Worksheet - Conic SectionsDocument5 paginiCBSE Class 11 Mathematics Worksheet - Conic SectionsAnand TripathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- WelfarismDocument28 paginiWelfarismKajal TiwaryÎncă nu există evaluări


















































![Mathematical Tables: Tables of in G [z] for Complex Argument](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/282615796/149x198/febb728e8d/1714993295?v=1)