Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Cefotaxime Drug Class, Uses, Side Effects
Încărcat de
Kristi WrayDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Cefotaxime Drug Class, Uses, Side Effects
Încărcat de
Kristi WrayDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
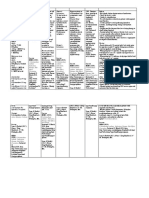
KRISTI WRAY NUR 335 DRUG NAME CLASS/FAMILY MECHANISM OF ACTION
Generic: ceftaroline Trade Name: Teflaro, Cefotaxime BETA-LACTAM ANTIBIOTIC; THIRD-GENERATION CEPHALOSPORIN Broad-spectrum semi-synthetic third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic. Preferentially binds to one or more of the penicillin-binding proteins (PBP) located on cell walls of susceptible organisms. This inhibits third and final stage of bacterial cell wall synthesis, thus killing the bacteria. Generally active against a wide variety of gram-negative bacteria including most of the Enterobacteriaceae. Also active against some organisms resistant to first- and second-generation cephalosporins, and currently available aminoglycoside antibiotics and penicillins. Serious infections of lower respiratory tract, skin and skin structures, bones and joints, CNS (including meningitis and ventriculitis), gynecologic and GU tract infections, including uncomplicated gonococcal infections caused by penicillinase-producing Neisseria gonorrhoeae (PPNG). Also used to treat bacteremia or septicemia, intra-abdominal infections, and for perioperative prophylaxis. Possible infection of surgical incisions IV, IM 600 mg IV BID Moderate to Severe Infections Adult: IV/IM 12 g q812h, up to 2 g q4h (max: 12 g/day) Child: IV/IM 1 wk or younger, 50 mg/kg q12h; 14 wk, 50 g/kg/q8h; 1 mo12 y, 50200 mg/kg/day divided q48h (max: 12 g/24 h) Disseminated Gonorrhea Adult: IV 1 g q8h Surgical Prophylaxis Adult: IV/IM 1 g 3090 min before surgery Renal Impairment Dosage Adjustment CrCl less than 20 mL/min: Give normal dose Hemodialysis Dosage Adjustment: Supplemental dose may be needed Peak: 30 min after IM; 5 min after IV. Intravenous IV administration to neonates, infants, and children: Verify correct IV concentration and rate of infusion with physician. Do not admix cefotaxime with sodium bicarbonate or any fluid with a pH greater than 7.5. Risk of phlebitis may be reduced by use of a small needle in a large vein. Prepare: Direct: Add 10 mL diluent to vial with 1 or 2 g drug providing a solution containing 95 or 180 mg/mL, respectively. Intermittent: To 1 or 2 g drug add 50 or 100 mL D5W, NS, D5/NS, D5/.45% NaCl, LR, or other compatible diluent.
INDICATIONS
WHY IS YOUR PATIENT GETTING THIS MEDICINE ROUTES PATIENT DOSAGE COMMON DOSAGE
ONSET, PEAK, DURATION FOR IV MEDS, COMPATIBILITY WITH IV DRIPS AND OR SOLUTIONS
KRISTI WRAY NUR 335 Continuous: Dilute in 5001000 mL compatible IV solution. Administer: Direct: Give over 35 min. Intermittent: Give over 2030 min, preferably via butterfly or scalp vein-type needles. Continuous: Infuse over 624 h. Incompatibilities: Solution/additive: AMINOGLYCOSIDES, aminophylline. Y-site: Allopurinol, azithromycin, cisatracurium, filgrastim, fluconazole, gemcitabine, hetastarch, pentamidine, vancomycin. Protect from excessive light. Reconstituted solutions may be stored in original containers for 24 h at room temperature; for 10 days under refrigeration at or below 5 C (41 F); or for at least 13 wk in frozen state. May cause falsely elevated serum or urine creatinine values (Jaffe reaction). False-positive reactions for urine glucose have not been reported using copper sulfate reduction methods (e.g., Benedict's, Clinitest); however, since it has occurred with other cephalosporins, it may be advisable to use glucose oxidase tests (Clinistix, TesTape, Diastix). Positive direct antiglobulin (Coombs') test results may interfere with hematologic studies and cross-matching procedures. Hypersensitivity to cefotaxime, cephalosporins and other beta-lactam antibiotics.
LAB VALUE ALTERATIONS CAUSE BY THIS MED
CONTRAINDICATIONS/ PRECAUTIONS
INTERACTIONS ADVERSE/SIDE EFFECTS
IMP NURS RESPONSIBILITIES
Drug: Probenecid decreases renal elimination; alcohol produces disulfiram reaction. Body as a Whole: Fever, nocturnal perspiration, inflammatory reaction at IV site, phlebitis, thrombophlebitis; pain, induration, and tenderness at IM site, superinfections. GI: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, colitis, pseudomembranous colitis, anorexia. Metabolic: Transient increases in serum AST, ALT, LDH, bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase concentrations. Skin: Rash, pruritus. Determine previous hypersensitivity reactions to cephalosporins and penicillins, and history of other allergies, particularly to drugs, before therapy is initiated. Lab tests: Perform culture and sensitivity tests before initiation of therapy. Serum creatinine, creatinine clearance, BUN should be evaluated at regular intervals during therapy and for several months after drug has been discontinued. Perform periodic hematologic studies (including PT and/or PTT) and evaluation of hepatic functions with high doses or prolonged therapy.
KRISTI WRAY NUR 335 PT/FAMILY TEACHING Monitor I&O rates and patterns, especially with higher doses or concurrent aminoglycoside therapy. Report significant changes in I&O. Superinfection due to overgrowth of nonsusceptible organisms may occur, particularly with prolonged therapy. Report onset of diarrhea promptly. Check for fever. If diarrhea is mild, discontinuation of cefotaxime may be sufficient. If diarrhea is severe, suspect antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis, a life-threatening superinfection (may occur in 49 days or as long as 6 wk after cephalosporin therapy is discontinued). Report any early signs or symptoms of superinfection promptly. Superinfections caused by overgrowth of nonsusceptible organisms may occur, particularly during prolonged use. Yogurt or buttermilk, 120 mL (4 oz) of either (if allowed), may serve as a prophylactic against intestinal superinfection by helping to maintain normal intestinal flora. Report loose stools or diarrhea.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Drug study on chemotherapeutic alkylating agentsDocument16 paginiDrug study on chemotherapeutic alkylating agentsPrincess CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study: NCM 106 Pharmacology: Patient MonitoringDocument2 paginiDrug Study: NCM 106 Pharmacology: Patient Monitoringpoleene de leonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study On Gastrointestinal AgentsDocument18 paginiDrug Study On Gastrointestinal AgentsJenica ManuntagÎncă nu există evaluări
- Generic Name: Acute Aspirin ToxicityDocument1 paginăGeneric Name: Acute Aspirin ToxicityShermayne Mallapre HernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluvastatin indications, contraindications, nursing responsibilitiesDocument1 paginăFluvastatin indications, contraindications, nursing responsibilitiesKevin H. MilanesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug AnalysisDocument3 paginiDrug AnalysisAbby BorabienÎncă nu există evaluări
- DS (Calcium + Vit. D)Document6 paginiDS (Calcium + Vit. D)Mary April MendezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vitamin KDocument2 paginiVitamin KMuvs RazonÎncă nu există evaluări
- DRUGS Study OrigDocument17 paginiDRUGS Study OrigKiersten Karen Policarpio Verina100% (1)
- Drug NystatinDocument1 paginăDrug NystatinSrkocherÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tramadol Drug StudyDocument4 paginiTramadol Drug StudyJust A Nsg StudentÎncă nu există evaluări
- MefenamicDocument1 paginăMefenamicChristian Clyde N. ApigoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument21 paginiDrug StudyShyla Garnace JavillonarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lui Sh-Colored Lips and Finger Nails Blur Red VisionDocument1 paginăLui Sh-Colored Lips and Finger Nails Blur Red VisionMagdayao Romamea100% (1)
- Wesleyan: College of Nursing and Allied Medical SciencesDocument2 paginiWesleyan: College of Nursing and Allied Medical SciencesShane Aileen AngelesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study - CefotaximeDocument5 paginiDrug Study - CefotaximeAngel laurestaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aspirin: Generic NameDocument4 paginiAspirin: Generic NameGwww BabababaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Insulin Mechanism of Action and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument7 paginiInsulin Mechanism of Action and Nursing ResponsibilitiesGrape JuiceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study OrthoDocument4 paginiDrug Study OrthoJhessa Curie Pitagan100% (1)
- Cephalexin Nursing GuideDocument2 paginiCephalexin Nursing GuideKatyana Cesar100% (1)
- LOSARTAN (ARBs) Drug Study (GERIATRICS)Document5 paginiLOSARTAN (ARBs) Drug Study (GERIATRICS)CHRISTIE MONTANOÎncă nu există evaluări
- JM DrugDocument3 paginiJM DrugVerdie B. NgayanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument4 paginiDrug StudyHennah ReblandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tramadol Drug StudyDocument2 paginiTramadol Drug StudyTipey Segismundo0% (1)
- Drug Study IsoniazidDocument1 paginăDrug Study IsoniazidEphraim MaravillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ColistinDocument2 paginiColistinGwyn RosalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- CefadroxilDocument2 paginiCefadroxilArvie AlvarezÎncă nu există evaluări
- FINAL Drug StudyDocument2 paginiFINAL Drug StudycasedraftÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug study cilostazol intermittent claudicationDocument2 paginiDrug study cilostazol intermittent claudicationart_mutantÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clindamycin Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument3 paginiClindamycin Nursing ResponsibilitiesDUMANGENG ELLAINE D.100% (1)
- DelavirdineDocument2 paginiDelavirdineRosher Deliman JanoyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aspirin Drug SummDocument2 paginiAspirin Drug SummWarren0% (1)
- Name of Drug Classification of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 paginiName of Drug Classification of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesNemo Del RosarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atracurium BesylateDocument3 paginiAtracurium BesylateAP TOROBXÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ferrous Sulfate - Drug StudyDocument3 paginiFerrous Sulfate - Drug StudyElla Musk100% (1)
- Spinal Anes Drug StudyDocument12 paginiSpinal Anes Drug StudyNicosia Mae FerrerÎncă nu există evaluări
- PrioritizationDocument1 paginăPrioritizationJLAZROÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indications:: Brand Name: Classificati OnDocument1 paginăIndications:: Brand Name: Classificati OnTel SisonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Micromonospora Purpurea. Action IsDocument3 paginiMicromonospora Purpurea. Action IsCarlos H. AcuñaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug AnalysisDocument3 paginiDrug AnalysisAnn Aquino100% (1)
- Omeprazole Drug StudyDocument4 paginiOmeprazole Drug StudyjoanneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study Ceftriaxone SodiumDocument3 paginiDrug Study Ceftriaxone SodiumPrincess Queenie OlarteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Insulin As PartDocument3 paginiInsulin As PartRezaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug SDocument2 paginiDrug SJane CasiquinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Burn - Concept MapDocument1 paginăBurn - Concept MapAaron RafaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study Vitamin C + ZincDocument2 paginiDrug Study Vitamin C + ZincKrizzia FosterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ceftriaxone medication guideDocument3 paginiCeftriaxone medication guideCiera YoungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Verapamil HCLDocument3 paginiVerapamil HCLMae Ann Bueno CastillonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study: Name of PatientDocument1 paginăDrug Study: Name of PatientKaloy KamaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cefpodoxime Proxetil - Print VersionDocument5 paginiCefpodoxime Proxetil - Print Versionchristina_1990Încă nu există evaluări
- Drug Name Classification/ Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindications Side Effects/ Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NameDocument1 paginăDrug Name Classification/ Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindications Side Effects/ Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NameRheza AltimoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dexamethasone and MgSO4Document2 paginiDexamethasone and MgSO4Nasriah MacadatoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cefprozil (Drug Study)Document2 paginiCefprozil (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888Încă nu există evaluări
- Ciprofloxacin Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComDocument3 paginiCiprofloxacin Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComAsterlyn ConiendoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Journal PediaDocument2 paginiJournal PediapeteiroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Azithromycin Dosage Indications Adverse Effects NursingDocument1 paginăAzithromycin Dosage Indications Adverse Effects NursingGrape JuiceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drugstudy OrsdDocument10 paginiDrugstudy OrsdRafmar A. SalundaguitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cefoxitin Sodium MefoxinDocument3 paginiCefoxitin Sodium MefoxinKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cefepime MaxipimeDocument2 paginiCefepime MaxipimeKristi Wray100% (1)
- Amikacin antibiotic for urinary tract infectionsDocument17 paginiAmikacin antibiotic for urinary tract infectionsMc Crister SilangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clonazepam KlonopinDocument3 paginiClonazepam KlonopinKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Codiene-Acetaminophen Tylenol 3Document1 paginăCodiene-Acetaminophen Tylenol 3Kristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clopidogrel Bisulfate - PlavixDocument2 paginiClopidogrel Bisulfate - PlavixKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cefoxitin Sodium MefoxinDocument3 paginiCefoxitin Sodium MefoxinKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ciprofloxacin CiproDocument1 paginăCiprofloxacin CiproKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carvedilol KredexDocument2 paginiCarvedilol KredexKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cefepime MaxipimeDocument2 paginiCefepime MaxipimeKristi Wray100% (1)
- Citalopramhydrobromide CelexaDocument3 paginiCitalopramhydrobromide CelexaKristi Wray100% (1)
- Aripiprazole AbilifyDocument2 paginiAripiprazole AbilifyKristi Wray100% (2)
- Cefazolin Sodium AncefDocument1 paginăCefazolin Sodium AncefKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Baclofen drug profileDocument2 paginiBaclofen drug profileKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Albuterol AccunebDocument2 paginiAlbuterol AccunebKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adderall medication guideDocument2 paginiAdderall medication guideKristi Wray100% (1)
- Aspirin ASA BayerDocument2 paginiAspirin ASA BayerKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aripiprazole AbilifyDocument2 paginiAripiprazole AbilifyKristi Wray100% (2)
- Alprazolam Dosage, Uses, Side EffectsDocument2 paginiAlprazolam Dosage, Uses, Side EffectsKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amblodipine NorvaseDocument2 paginiAmblodipine NorvaseKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adacel Tdap VaccineDocument1 paginăAdacel Tdap VaccineKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Albuterol VentolinDocument3 paginiAlbuterol VentolinKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aloe Vera - ZanzibarDocument2 paginiAloe Vera - ZanzibarKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aripiprazole AbilifyDocument2 paginiAripiprazole AbilifyKristi Wray100% (2)
- Tylenol for mild to moderate painDocument2 paginiTylenol for mild to moderate painKristi WrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pain - SpringerDocument1.175 paginiPain - SpringerGrossl Schorr Fernando100% (1)
- Pharmacist Job ResponsibilitiesDocument2 paginiPharmacist Job ResponsibilitiesLouie G NavaltaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Airway ManagementDocument4 paginiAirway Managementpaveethrah100% (1)
- Nursing Care of Clients Undergoing Eye SurgeryDocument1 paginăNursing Care of Clients Undergoing Eye SurgerySewyel GarburiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laboratory Test: Potassium (K+)Document4 paginiLaboratory Test: Potassium (K+)Amiel Francisco ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Management of Keloids and Hypertrophic ScarsDocument7 paginiManagement of Keloids and Hypertrophic Scarsdonlot lover100% (1)
- Antisocial Personality Disorder and HomeopathyDocument2 paginiAntisocial Personality Disorder and HomeopathyAnonymous dpxYTEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heridas ExtremidadesDocument17 paginiHeridas ExtremidadesEdisson MoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- BronchiectasisDocument20 paginiBronchiectasisOeyi Mutia SatifaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical Injury and Burn ManagementDocument11 paginiMechanical Injury and Burn ManagementAdhe Intan ImaniaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medicinal Mushrooms Their Therapeutic Properties and Current Medical Usage With Special Emphasis On Cancer Treatments 2002Document276 paginiMedicinal Mushrooms Their Therapeutic Properties and Current Medical Usage With Special Emphasis On Cancer Treatments 2002lordraffael100% (1)
- Nexpro Uae FinalDocument13 paginiNexpro Uae Finalamr ahmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- ConjunctivitisDocument6 paginiConjunctivitisAlvin JjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kaplan Spikes 2010Document4 paginiKaplan Spikes 2010Asrini Widya AnomÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acceptance and Commitment Therapy Versus Traditional Cognitive Behavioral Therapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Current Empirical EvidenceDocument25 paginiAcceptance and Commitment Therapy Versus Traditional Cognitive Behavioral Therapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Current Empirical EvidenceErik AlmeidaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacology - Antibiotics Flash CardsDocument20 paginiPharmacology - Antibiotics Flash CardsJamil100% (2)
- Menopause Remedy Folliculinum Differential DiagnosisDocument13 paginiMenopause Remedy Folliculinum Differential Diagnosismapati66100% (2)
- Robert Emmons The Power of GratitudeDocument2 paginiRobert Emmons The Power of GratitudeSajid YasinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Speech & Language Therapy in Practice, Autumn 2006Document32 paginiSpeech & Language Therapy in Practice, Autumn 2006Speech & Language Therapy in PracticeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology and Etiology of PCP: HIV InfectionDocument20 paginiPathophysiology and Etiology of PCP: HIV InfectionJehan Sendix100% (1)
- Natural Benefits of Urine Therapy by Jagdish R. BhuraniDocument60 paginiNatural Benefits of Urine Therapy by Jagdish R. BhuraniAlejandro Yolquiahuitl100% (7)
- Test de Fantus PDFDocument4 paginiTest de Fantus PDFMax George Samame GomezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cerebral Palsy Rehabilitation: Birth-Related Brain InjuryDocument13 paginiCerebral Palsy Rehabilitation: Birth-Related Brain InjuryAnuj GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biko's Case StudyDocument5 paginiBiko's Case StudyMakau Elijah100% (1)
- Concept Analysis of Interdisciplinary PDFDocument11 paginiConcept Analysis of Interdisciplinary PDFCharles JacksonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Obongsan Cultural Village InsightsDocument11 paginiObongsan Cultural Village Insightshey peachÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group Leukemia ProjectDocument12 paginiGroup Leukemia Projectapi-194733693100% (1)
- Cervical Exercise: The Backbone of Spine TreatmentDocument9 paginiCervical Exercise: The Backbone of Spine TreatmentCorina SovieticaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review of Related LiteratureDocument28 paginiReview of Related LiteratureporseenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Man with Fatigue and Abdominal Pain Diagnosed with Iron-Deficiency AnemiaDocument45 paginiMan with Fatigue and Abdominal Pain Diagnosed with Iron-Deficiency AnemiaMark GironÎncă nu există evaluări