Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
The Normal Kidney: Pediatrics 2 The Urinary System and Urinary Tract Infections
Încărcat de
sarguss14Descriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
The Normal Kidney: Pediatrics 2 The Urinary System and Urinary Tract Infections
Încărcat de
sarguss14Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
May.Yvette.Allain.Cristina.Ralph.Sheryl.Bart.Heinrich.Pipoy.KC.Jam.Cecille.Denesse.Mike.Hoops.Ces.Christian.Elaine.Riza.Kristel.Ezra.Goldi.
Buf
f.Mona.AM.Maan.Adi.KC.Peng.Karla.Alphe.Aaron.Kyth.Anne.Eisa.Kring.Candy.Isay.Marco.Joshua.Fars.Rain.Jassie.Mika.Shar.Erika.Macky.Viki.Joan
.Precious.Kate.Katrina.Ams.Hannah. Memay.Pau.Rachelle.Esther.Joel.Glenn.Toni
PEDIATRICS 2 07-july-08
THE URINARY SYSTEM and URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS
Dr. Victor S. Doctor
Trans grUp: Goldie and Her Invisible Frends!!!
THE NORMAL KIDNEY
ANATOMY PHYSIOLOGY
Kidneys of Newborn Infant
Notes from Nelson:
relatively large and can usually be palpated through
the anterior abdominal wall
mean combined weight of both kidneys at birth: Glomerular Filtration - net result of opposing forces across
at 6 mos = 24 grams
the capillary wall. The force for ultrafiltration (glomerular
at 12 mos = 70 grams capillary hydrostatic pressure) is a result of systemic arterial
at 6 y/o = 140 grams pressure, modified by the tone of the afferent and efferent
adult weight approx. 300 grams arterioles. The major force opposing ultrafiltration is the
Nephron glomerular capillary oncotic pressure, which is created by the
structural and functional unit of the renal parenchyma gradient between the high concentration of plasma proteins
within the capillary and the almost protein-free ultrafiltrate in
36 week of gestation, nephrogenesis stops and each
th
Bowman's space. Filtration may be modified by the rate of
kidney has 850,000-1M nephrons
glomerular plasma flow, the hydrostatic pressure within
each nephron consists of a glomerulus and its tubules
Bowman's space, and the permeability of the glomerular
for urine formation, acid-base balance, secretion of
certain substances capillary wall.
each glomerulus is a rete of capillary tufts enclosed The GFR may be estimated by measurement of the serum
in Bowman’s capsule creatinine level. Creatinine is derived from muscle
capillary tufts consist of loops bound together in a metabolism. Its production is relatively constant, and its
central area called Mesangium excretion is primarily through glomerular filtration, although
mesangium is composed of cytoplasmic matrix and tubular secretion may become important in renal insufficiency.
cells (mesangial or capillary); it is usually the FIRST In contrast to the concentration of blood urea nitrogen, which
TO REACT IN THE EVENT OF GLOMERULAR INSULT is affected by state of hydration and nitrogen balance, the
3 Fixed cells of the Glomerulus:
serum creatinine level is primarily influenced by the level of
•endothelial or intracapillary cell
glomerular function. The serum creatinine is of value only in
•mesangial cell
estimating the GFR in the steady state. A patient may have a
•epithelial or extracapillary cell
normal creatinine level without effective renal function very
shortly after the onset of acute renal failure with anuria. In this
Notes from Nelson: clinical setting, serum creatinine may be an insensitive
measure of decreased renal function because its level does not
rise above normal until the GFR falls by 30–40%.
Each kidney contains approximately 1 million
nephrons (glomeruli and associated tubules). In 3 Principal Kidney Functions
humans, formation of nephrons is complete at 1. maintain constancy of internal environment by
birth, but functional maturation with tubular adjusting volume, concentration and composition of
growth and elongation continues during the first body fluids
decade of life. Because new nephrons cannot be 2. elimination of metabolic wastes such as urea &
formed after birth, progressive loss of nephrons creatinine
may lead to renal insufficiency. Decreased 3. elaborate the hormones rennin, erythropoietin,
nephron number at birth may be associated with prostaglandins, kallikrein-kinin
hypertension in adulthood, presumably related to
hyperfiltration and “premature” sclerosis of
overworked nephron units. This provocative Urine Formation
hypothesis, if proven, could identify a major risk 1. initiated by elaboration of a large volume of protein-
factor for hypertension and its associated free plasma ultrainfiltrate thru glomerular filtration
cardiovascular complications in the newborn 2. concentration and alteration of filtrate composition in
the tubules (thru tubular reabsorption of essential
period.
substances and elimination of waste products)
>space< >space< >space< >space< Proximal Tubule
- reabsorbs 80% of filtrate volume and sodium
- all the glucose and amino acids (small portion)
and much of the filtered phosphate, minute amt
of protein that pass thru the glomeruli
- primary active process is sodium reabsorption
May.Yvette.Allain.Cristina.Ralph.Sheryl.Bart.Heinrich.Pipoy.KC.Jam.Cecille.Denesse.Mike.Hoops.Ces.Christian.Elaine.Riza.Kristel.Ezra.Goldi.Buf
f.Mona.AM.Maan.Adi.KC.Peng.Karla.Alphe.Aaron.Kyth.Anne.Eisa.Kring.Candy.Isay.Marco.Joshua.Fars.Rain.Jassie.Mika.Shar.Erika.Macky.Viki.Joan
.Precious.Kate.Katrina.Ams.Hannah. Memay.Pau.Rachelle.Esther.Joel.Glenn.Toni
- followed by passive reabsorption of chloride and there is diluted urine d/t failure to concentrate
water by diffusion glomerulus is not affected so filtration is not affected
- volume is greatly reduced but Na and Cl- not creatinine clearance – for kidney function test
altered
3. Loss of Renal Function
decreased number of nephrons
Loop of Henle
water is reabsorbed in the descending limb nephron hypertrophy early aging
sodium is reabsorbed in the ascending limb hyperfiltration nephrosclerosis eventual
result is an environment in the interstitial tissue of destruction (proteinuria and HPN) renal
insufficiency renal failure
medulla that is hypertonic to plasma thus urine
concentration takes place in the adjacent collecting
4. Necrosis of Renal Parenchyma
ducts
tubule and surrounding intersitium are inflamed
fluid at end of loop is Hypertonic.
destruction of the growth of functional cells (growth
Distal Tubules factors, vit D, erythropoietin, prostaglandins,
hormones)
fluid initially hypotonic to plasma d/t large amt of
sodium reabsorbed in the ascending limb tubule destroyed, glomerulus obliterates
more sodium reabsorbed d/t aldosterone area replaced by non-functional scar TISSUE
potassium is secreted # of nephrons are reduced
acidification takes place remaining nephrons are overworked
Collecting Ducts Notes from Nelson:
- final concentration mediated by vasopressin (ADH)
acting on the lining cells of the duct making them more
permeable to water The 3 basic forms of UTI are pyelonephritis, cystitis, and
asymptomatic bacteriuria.
Now we come to Doctor Doctor’s lecture.. Have fun.. Clinical pyelonephritis is characterized by any or all of the
following: abdominal or flank pain, fever, malaise, nausea,
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS vomiting, and, occasionally, diarrhea. Newborns may show
- there is bacterial invasion and multiplication nonspecific symptoms such as poor feeding, irritability, and weight
- inflammation and host reaction
loss. Pyelonephritis is the most common serious bacterial infection
- loss of normal renal function
in infants <24 mo of age who have fever without a focus. These
- necrosis of renal tissue
symptoms are an indication that there is bacterial involvement of
1. Bacterial Invasion and Multiplication the upper urinary tract. Involvement of the renal parenchyma is
bacteria from stools termed acute pyelonephritis, whereas if there is no parenchymal
proximity of urethra involvement, the condition may be termed pyelitis. Acute
adherence of e.coli that resists urine flow pyelonephritis may result in renal injury, termed pyelonephritic
ascends from urethra to bladder (cystitis; lower UTI) scarring.
ascends from bladder to ureters ( reflux)
ascends from ureters to kidneys (pyelonephritis: Cystitis indicates that there is bladder involvement; symptoms
Upper UTI) include dysuria, urgency, frequency, suprapubic pain, incontinence,
low to negative bacterial growth by culture & and malodorous urine. Cystitis does not cause fever and does not
sensitivity result in renal injury. Malodorous urine, however, is not specific
short bladder time: newborn & infants
for a UTI.Asymptomatic bacteriuria refers to a condition that
acidic urine
results in a positive urine culture without any manifestations of
low dose antibiotics
infection. It is most common in girls. The incidence is 1–2% in
wrong culture media
preschool and school-age girls and 0.03% in boys. The incidence
2. Inflammation and Host Reaction declines with increasing age. This condition is benign and does not
Urethritis – dysuria, burning sensation cause renal injury, except in pregnant women, in whom
asymptomatic bacteriuria, if left untreated, can result in a
Cystitis – dysuria, bladder tenderness, frequent symptomatic UTI. Some girls are mistakenly identified as having
urination with fever; on ultrasound: thickened asymptomatic bacteriuria, whereas they actually are symptomatic,
bladder wall experiencing day or night incontinence or perineal discomfort.
Pyelonephritis – systemic SSx
bladder irritation – hypercontracted bladder wall Normal Urinary Tract
frequent small amt of urine vesicoureteric junction does not allow retrograde
to diagnose bladder infxn: ultrasound will show flow of urine from the bladder to the kidney
bladder walls thickened than normal
Vesico-ureteral Reflux
inflammation edema thickening of walls phenomenon of backward-upward flow of urine
WBC during inflammation
May.Yvette.Allain.Cristina.Ralph.Sheryl.Bart.Heinrich.Pipoy.KC.Jam.Cecille.Denesse.Mike.Hoops.Ces.Christian.Elaine.Riza.Kristel.Ezra.Goldi.Buf
f.Mona.AM.Maan.Adi.KC.Peng.Karla.Alphe.Aaron.Kyth.Anne.Eisa.Kring.Candy.Isay.Marco.Joshua.Fars.Rain.Jassie.Mika.Shar.Erika.Macky.Viki.Joan
.Precious.Kate.Katrina.Ams.Hannah. Memay.Pau.Rachelle.Esther.Joel.Glenn.Toni
permits transport of urine from bladder to the - most common type and most common post-
kidney infectious form
may be unilateral or bilateral - peak age at 7 y/o
demonstrated and graded by Voiding - an immune-complex meadiated dse d/t prior
Cystourethrogram (VCUG) infection with the nephritogenic strains of
Group A beta-hemolytic strep
(post-strep AGN inflamed glomerulus
(immunologic)
*yan po ung part na me example c doc ng past,
present at future..
- low volume urine w/ high sp. gravity
Notes from Nelson: - RBC PREDOMINANCE (gross hematuria)
- tubules unaffected
- glomerulus is congested
Retrograde flow of urine from the bladder to the ureter and - essential elements: edema, oliguria, hematuria,
renal pelvis is referred to as vesicoureteral reflux. The hypertension
ureter normally is attached to the bladder in an oblique - Tx:
direction, perforating the bladder muscle (detrusor) laterally a. anemia from hematuria is insignificant
and proceeding between the bladder mucosa and detrusor b. oliguria / edema – osmotic diuretics;
muscle, creating a flap-valve mechanism that prevents water intake and salt intake
reflux. Reflux occurs when the submucosal tunnel between c. for HPN – rapid-acting anti-HPN
the mucosa and detrusor muscle is short or absent. Reflux
usually is congenital, occurs in families, and affects UTI –
Notes WBC
from Nelson:
approximately 1% of children. NephroticRBC
AGN – syndrome is primarily a pediatric disorder and is
15Nephrotic
times more Syndrome
common in children than adults. The incidence
– urine should not contain WBC nor RBC; no
Reflux predisposes to renal infection (pyelonephritis) by is 2-3/100,000 children per year; and the majority of affected
hematuria; no pyuria
facilitating the transport of bacteria from the bladder to the children will have steroid-sensitive minimal change disease.
– contains massive amount of protein
upper urinary tract. The inflammatory reaction caused by a The characteristic
–
features of nephrotic syndrome are heavy
excessive protein excretion
pyelonephritic infection may result in renal injury or proteinuria (>3.5 g/24 hr in adults or 40 mg/m2/hr in children),
scarring, also termed reflux nephropathy. Extensive renal – hypoalbuminemia
hypoalbuminemia d/t massive
(<2.5 2g/dL), edema, proteinuria
and hyperlipidemia.
scarring impairs renal function and may result in renin- ( > 1 g / m / 24 hrs)
ETIOLOGY: Most children (90%) with nephrotic syndrome
del aMundo
have form of–the
2gidiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Causes of
mediated hypertension. renal insufficiency or end-stage
Harisson – 3.5
idiopathic nephroticg syndrome include minimal change
renal disease, impaired somatic growth, and morbidity
during pregnancy. Reflux nephropathy once accounted for disease (85%), mesangial proliferation (5%), and focal
as much as 15–20% of end-stage renal disease in children segmental glomerulosclerosis (10%). The remaining 10% of
and young adults. With greater attention to the management children with nephrotic syndrome have secondary nephrotic
of urinary tract infections (UTIs) and a better understanding syndrome related to syste-mic ( Table 527-1 ) or glomerular
of reflux, end-stage renal disease secondary to reflux diseases such as membranous nephropathy or
nephropathy is uncommon. Reflux nephropathy remains membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis
one of the most common causes of hypertension in
children. Reflux in the absence of infection or elevated PATHOPHYSIOLOGY: The underlying abnormality in
bladder pressure does not cause renal injury. nephrotic syndrome is an increase in permeability of the
glomerular capillary wall, which leads to massive proteinuria
and hypoalbuminemia. The cause of the increased
Components of Urinalysis permeability is not well understood. In minimal change
• color disease, it is possible that T-cell dysfunction leads to alteration
• volume of cytokines, which causes a loss of negatively charged
• consistency (cloudy or not) glycoproteins within the glomerular capillary wall. In focal
• sp. gravity segmental glomerulosclerosis, a plasma factor, perhaps
• RBCs, WBCs, casts, crystals produced by lymphocytes, may be responsible for the increase
• pH (varies normally with food intake) in capillary wall permeability. Alternately, mutations in
• blood chemistry podocyte proteins (podocin, α-actinin 4) are associated with
• creatinine focal segmental glomerulosclerosis ( Table 527-3 ). Steroid-
• uric acid / other metabolic products
resistant nephrotic syndrome is associated with mutations in
NPHS2 (podocin) and WT1 genes.
if with acidosis, but kidneys are normal
urine will be acidic Although the mechanism of edema formation in nephrotic
if blood is acidic, urine is alkaline syndrome is incompletely understood, it seems likely that, in
kidneys are non-functional most instances, massive urinary protein loss leads to
if with high Na in blood, kidneys are normal hypoalbuminemia, which causes a decrease in the plasma
there will be Na in urine oncotic pressure and transudation of fluid from the
intravascular compartment to the interstitial space. The
Post-Streptococcal Acute Glomerulonephritis (PSAGN) reduction in intravascular volume decreases renal perfusion
pressure, activating the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system,
which stimulates tubular reabsorption of sodium. The reduced
intravascular volume also stimulates the release of antidiuretic
hormone, which enhances the reabsorption of water in the
collecting duct.
May.Yvette.Allain.Cristina.Ralph.Sheryl.Bart.Heinrich.Pipoy.KC.Jam.Cecille.Denesse.Mike.Hoops.Ces.Christian.Elaine.Riza.Kristel.Ezra.Goldi.Buf
f.Mona.AM.Maan.Adi.KC.Peng.Karla.Alphe.Aaron.Kyth.Anne.Eisa.Kring.Candy.Isay.Marco.Joshua.Fars.Rain.Jassie.Mika.Shar.Erika.Macky.Viki.Joan
.Precious.Kate.Katrina.Ams.Hannah. Memay.Pau.Rachelle.Esther.Joel.Glenn.Toni
Assignment ni doc.. kinuha ko n lng ulit sa del Mundo..
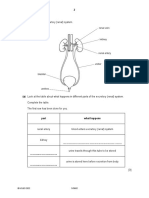
What are the alternative methods for collecting 24-
hr urine? Figure 1: ze urineri zystem
A freshly voided urine specimen collected early in the
morning is preferable for routine urinalysis. The
specimen should be examined immediately to avoid
disintegration of formed elements. Water or softdrinks to
hasten collection of a specimen should be avoided as
these results in dilute urine, red cell lysis, and
undergraded qualitative protein testing.
Methods:
1. PEREZ REFLEX - Stimulation of urination by running
tap water or stroking the spinal column upward or
downward (recommended)
2. Plastic (U- or wee_ bags and sterile vials may be used
to collect samples after proper cleansing of the genitalia
*bags should be discarded and changed if no
urine is voided w/in 3 hrs
3. Aseptic catheterization using French 8 or 10 catheter
(or French 5 C-32 feeding tube) and suprapubic bladder
tap may be done when indicated
Figure 2: zis is e nefron
mga words of wisdom ni doc..
1. if the function of ur legs is to walk and it is severed,
what will happen? answer: you cannot walk.. akalain
mo un, nabago pananaw ko sa buhay dahil dito..
2. Know what is normal… bawal kontrahin to..
PASENSYA NA AT MAGULO UNG TRANS.. CNUBUKAN
NAMIN KUNIN ANG PANIG NI NELSON EH..
UNFORTUNATELY, MAHIRAP CYA ISINGIT SA LEC SO
NAKA BOX NALNG CYA.. SANA MAKATULONG.. LAM KO
KULANG, ALANGAN NAMAN ILAGAY KO LAHAT DB..
HEHE.. ANYWAY, KNG MAY TNUNG, PLS REFER TO THE
FIGURES BELOW.. YAN NA MISMO UNG LEC NATIN.. UH
HUH!! UH HUH!!
Figure 3: This iz e cast
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Gastrointestinal Diseases Part1Document7 paginiGastrointestinal Diseases Part1sarguss14100% (1)
- HerniaDocument5 paginiHerniasarguss14100% (5)
- Small Intestine 01 PDFDocument9 paginiSmall Intestine 01 PDFfadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Breast CancerDocument6 paginiBreast Cancersarguss14Încă nu există evaluări
- Tumour Marker For Medincine ResidentsDocument58 paginiTumour Marker For Medincine ResidentsSandeep NarayananÎncă nu există evaluări
- Osce FlowchartDocument1 paginăOsce FlowchartPeter SongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kidney, Ureter, BladderDocument12 paginiKidney, Ureter, Bladdersarguss14100% (1)
- Respiratory DiseasesDocument2 paginiRespiratory Diseasessarguss14Încă nu există evaluări
- Gyne 2.6 - Benign and Malignant Tumors of The Ovaries and Fallopian TubesDocument8 paginiGyne 2.6 - Benign and Malignant Tumors of The Ovaries and Fallopian TubesVon HippoÎncă nu există evaluări
- PleuraDocument6 paginiPleuraameerabest100% (1)
- Mediastinum and Its ContentsDocument11 paginiMediastinum and Its ContentsPap YeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Internal Medicine Quick TablesDocument276 paginiInternal Medicine Quick Tablesjoey plouffeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kidney Part 1Document5 paginiKidney Part 1sarguss14Încă nu există evaluări
- Dengue Virus: DescriptionDocument12 paginiDengue Virus: Descriptionpedia blue bookÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anemia Type Pathogenesis Clinical Manifestations Diagnosis Peripheral Blood Lab FindingsDocument15 paginiAnemia Type Pathogenesis Clinical Manifestations Diagnosis Peripheral Blood Lab FindingsDanielle FosterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Female Genital TractDocument5 paginiFemale Genital Tractsarguss14100% (1)
- Approach To Pleura LeffusionDocument91 paginiApproach To Pleura Leffusionrodie1050% (1)
- Distal To Ligament of Treitz: CausesDocument8 paginiDistal To Ligament of Treitz: CausesKiara GovenderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Overview of AnaemiaDocument2 paginiOverview of AnaemiaGerardLumÎncă nu există evaluări
- (MED II) 1.05 Emergencies in Cancer PatientsDocument17 pagini(MED II) 1.05 Emergencies in Cancer PatientsJearwin AngelesÎncă nu există evaluări
- PEDIA para 08AMDocument17 paginiPEDIA para 08AMpedia blue bookÎncă nu există evaluări
- Red Vascular: Polygonal Cells Growing in Nests or Cords Lamellae of Dense CollagenDocument3 paginiRed Vascular: Polygonal Cells Growing in Nests or Cords Lamellae of Dense CollagenMaryam FadahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pedia Bacte Table 08amDocument25 paginiPedia Bacte Table 08ampedia blue bookÎncă nu există evaluări
- # Diseases of ConjunctivaDocument4 pagini# Diseases of Conjunctivaameerabest100% (1)
- Acute LeukemiaDocument16 paginiAcute Leukemianouval_iqbalÎncă nu există evaluări
- ENDOCRINE PATHOLOGY WebpathDocument35 paginiENDOCRINE PATHOLOGY Webpathapi-3766657Încă nu există evaluări
- Small BowelDocument4 paginiSmall Bowelsarguss14100% (1)
- Ent Diseases of The Oral and Pharynx Dr. UyDocument7 paginiEnt Diseases of The Oral and Pharynx Dr. UyAileen EmyÎncă nu există evaluări
- History Taking: Item DescriptionDocument22 paginiHistory Taking: Item DescriptionBikash Sah100% (1)
- Lower Limb Motor ExamDocument3 paginiLower Limb Motor ExamAmjaSaudÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medicine OSCE - Common Diseases Ver2Document4 paginiMedicine OSCE - Common Diseases Ver2TrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Skin PathogensDocument4 paginiSkin PathogensEhi EdialeÎncă nu există evaluări
- IKD9 - Radiological Evaluation of Renal CystsDocument26 paginiIKD9 - Radiological Evaluation of Renal CystsRenal Association MauritiusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hem-Onc: AnswerDocument3 paginiHem-Onc: AnswerAman Raj KÎncă nu există evaluări
- GI + Renal OSCE: AMSA Edinburgh X IMU Y4Document41 paginiGI + Renal OSCE: AMSA Edinburgh X IMU Y4Abby LiewÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anemia Flow ChartDocument1 paginăAnemia Flow ChartCynthiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Breech Delivery and Vacuum ExtractionDocument71 paginiBreech Delivery and Vacuum ExtractionRendy Adhitya PratamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- OPTOMED-HW2-Diabetic Retinopathy PDFDocument3 paginiOPTOMED-HW2-Diabetic Retinopathy PDFDanalie SalvadorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Breech PresentationDocument13 paginiBreech PresentationIsrael WoseneÎncă nu există evaluări
- DISC, Drugs, Infection, Thick Basal MembraneDocument5 paginiDISC, Drugs, Infection, Thick Basal MembraneHOPEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Midterm Chapter7Document43 paginiMidterm Chapter7Frances FranciscoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review Slides OphthaDocument14 paginiReview Slides OphthaSUSHMITA MAE ROSE CONTRERASÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kidney AnatomyDocument2 paginiKidney Anatomyameerabest100% (1)
- Diseases of The Female Genital TractDocument4 paginiDiseases of The Female Genital Tractsarguss14Încă nu există evaluări
- Young Stroke Etiology and Clinical ApproachDocument43 paginiYoung Stroke Etiology and Clinical ApproachDr Prakash HarischandraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bleeding Disorders 1 - DR - Kamal MokbelDocument13 paginiBleeding Disorders 1 - DR - Kamal MokbelRawan E. SaeedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tumor Markers: Blood Group AntigenDocument5 paginiTumor Markers: Blood Group AntigenAngela ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Red Blood Cell Disorders Anemia: Anemia Is A Laboratory DiagnosisDocument3 paginiRed Blood Cell Disorders Anemia: Anemia Is A Laboratory DiagnosisAnonymous 8hJAATBÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 PEDIA 8 - Bleeding DisordersDocument5 pagini4 PEDIA 8 - Bleeding DisordersRainy Liony DuhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lec 2 - Blood VesselsDocument12 paginiLec 2 - Blood VesselsJeffrey LübbertÎncă nu există evaluări
- #Chest TraumasDocument4 pagini#Chest Traumasameerabest100% (3)
- Chart - WBC DisordersDocument1 paginăChart - WBC DisordersSamuel RothschildÎncă nu există evaluări
- (MICROA - 2.1) Myeloid Tissue HistologyDocument6 pagini(MICROA - 2.1) Myeloid Tissue HistologyHenryboi CañasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bot Med Final CHARTDocument33 paginiBot Med Final CHARTapi-26938624100% (3)
- Liver & PancreasDocument3 paginiLiver & Pancreasameerabest100% (1)
- Bone TumorsDocument15 paginiBone Tumorssarguss1450% (2)
- A Simple Guide to the Adrenal Gland and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsDe la EverandA Simple Guide to the Adrenal Gland and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adrenal Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDe la EverandAdrenal Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chronic Kidney Disease in Children New Trends in ManagementDocument103 paginiChronic Kidney Disease in Children New Trends in Managementfranklin ifioraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Epidural and Spinal AnesthesiaDocument86 paginiEpidural and Spinal Anesthesiasarguss1471% (7)
- Preoperative EvaluationDocument25 paginiPreoperative Evaluationsarguss14Încă nu există evaluări
- World Gastroenterology Organization Global GuidelineDocument29 paginiWorld Gastroenterology Organization Global GuidelineRizky Rachmania AmandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inhalational Anesthetics: Patigas, Requinta, ResuelloDocument88 paginiInhalational Anesthetics: Patigas, Requinta, Resuellosarguss140% (1)
- Axial Arthritis: Degenerative Annular DiseaseDocument18 paginiAxial Arthritis: Degenerative Annular Diseasesarguss14100% (1)
- Cyanotic Congenital Heart Diseases, Etc.Document12 paginiCyanotic Congenital Heart Diseases, Etc.sarguss14100% (2)
- Small BowelDocument4 paginiSmall Bowelsarguss14100% (1)
- Introduction To RadiologyDocument3 paginiIntroduction To Radiologysarguss14Încă nu există evaluări
- CNS Tumors and Infections Part1Document2 paginiCNS Tumors and Infections Part1sarguss14100% (1)
- Stage 1: Dorsal Induction: Pediatric NeuroradiologyDocument8 paginiStage 1: Dorsal Induction: Pediatric Neuroradiologysarguss14100% (1)
- NeuroradiologyDocument11 paginiNeuroradiologysarguss14100% (2)
- Pediatric GI RadiologyDocument6 paginiPediatric GI Radiologysarguss14Încă nu există evaluări
- Male PelvisDocument8 paginiMale Pelvissarguss14100% (1)
- Kidney, Ureter, BladderDocument12 paginiKidney, Ureter, Bladdersarguss14100% (1)
- Male Genital TractDocument7 paginiMale Genital Tractsarguss14Încă nu există evaluări
- Genitourinary SystemDocument8 paginiGenitourinary Systemsarguss14100% (1)
- From Doc Bandong's Own Words:: Shar 1 of 20Document20 paginiFrom Doc Bandong's Own Words:: Shar 1 of 20sarguss14100% (1)
- CNS Tumors and Infections Part3Document6 paginiCNS Tumors and Infections Part3sarguss14100% (1)
- Gallbladder, Liver, Pancreas and SpleenDocument19 paginiGallbladder, Liver, Pancreas and Spleensarguss14100% (3)
- Cardiac ImagingDocument7 paginiCardiac Imagingsarguss14Încă nu există evaluări
- CNS Tumors and Infections Part2Document2 paginiCNS Tumors and Infections Part2sarguss14Încă nu există evaluări
- Extracerebral Hemorrhage, Etc.Document14 paginiExtracerebral Hemorrhage, Etc.sarguss14Încă nu există evaluări
- Chest RadiologyDocument3 paginiChest Radiologysarguss14Încă nu există evaluări
- NeuroradiologyDocument25 paginiNeuroradiologysarguss14100% (2)
- Introduction To RadiologyDocument3 paginiIntroduction To Radiologysarguss14Încă nu există evaluări
- ArthritisDocument9 paginiArthritissarguss14100% (1)
- Bone TumorsDocument15 paginiBone Tumorssarguss1450% (2)
- Pleura and MediastinumDocument16 paginiPleura and Mediastinumsarguss14100% (1)
- Congenital Cystic Adenomatoid Malformation (CCAM)Document7 paginiCongenital Cystic Adenomatoid Malformation (CCAM)sarguss14Încă nu există evaluări
- Genitourinary SystemDocument8 paginiGenitourinary Systemsarguss14100% (1)
- Medicine June 2009: Fcps Part1 Q BankDocument14 paginiMedicine June 2009: Fcps Part1 Q Bankqudsia_niaziÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Endocrine System: Year 9 Biological ScienceDocument20 paginiThe Endocrine System: Year 9 Biological ScienceSasha VoleskyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1035 Pathway CKDDocument1 pagină1035 Pathway CKDeka pandeÎncă nu există evaluări
- ABDOMEN124Document25 paginiABDOMEN124Ashraf Alamin AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1-4Document11 paginiChapter 1-4Vy ThachÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Stage 9 02 9RP AFP tcm143-639993Document17 paginiScience Stage 9 02 9RP AFP tcm143-639993mal100% (1)
- Peritoneal DialysisDocument12 paginiPeritoneal DialysisSheeba StephenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fetal and Neonatal PhysiologyDocument65 paginiFetal and Neonatal Physiologyahmed mahamedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anemia in CKD: Ppds Sp1 Divisi Ginjal Hipertensi Bagian Ilmu Penyakit Dalam Rsup Dr. Mohammad Hoesin Palembang 2021Document31 paginiAnemia in CKD: Ppds Sp1 Divisi Ginjal Hipertensi Bagian Ilmu Penyakit Dalam Rsup Dr. Mohammad Hoesin Palembang 2021Richard 151289Încă nu există evaluări
- Tumours of KidneyDocument39 paginiTumours of KidneyjabirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument18 paginiChronic Kidney DiseaseAde Cahyo IslamiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASHP Chapter 29 - Medication Dosing in Patients With Renal DysfunctionDocument5 paginiASHP Chapter 29 - Medication Dosing in Patients With Renal DysfunctionTammyÎncă nu există evaluări
- ATI Ebook - Med SurgDocument702 paginiATI Ebook - Med SurgMichelle Villanueva100% (4)
- Blood Pressure RegulationDocument11 paginiBlood Pressure RegulationManuÎncă nu există evaluări
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Nephrotic SyndromeDocument2 paginiNURSING CARE PLAN - Nephrotic Syndromederic80% (45)
- Nephrotic SyndromeDocument17 paginiNephrotic Syndromevishnu0% (1)
- Pathological Anatomy Exam PicturesDocument42 paginiPathological Anatomy Exam PicturesAnonymous AW6ak83qOuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pex 09 06Document4 paginiPex 09 06Illich Ramirez Tanta100% (2)
- Paper 1Document36 paginiPaper 1warnereditsproÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diagnostic Algorithms in Renal Biopsy PDFDocument27 paginiDiagnostic Algorithms in Renal Biopsy PDFRajeev Pareek100% (1)
- Excretory System Worksheet - NephronDocument3 paginiExcretory System Worksheet - NephronDinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Materi Urinary System Bhs InggrisDocument8 paginiMateri Urinary System Bhs InggrisMelany LtrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eating Disorder Manuscript ReportDocument16 paginiEating Disorder Manuscript ReportKeemuel LagriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity 4 Dialysis - Anna Philomena B. FerrerDocument5 paginiActivity 4 Dialysis - Anna Philomena B. FerrerSebs BerebsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Urinalysis and Body Fluids 6th Edition by Susan King Strasinger - Test BankDocument45 paginiUrinalysis and Body Fluids 6th Edition by Susan King Strasinger - Test Bankroseyoung0Încă nu există evaluări
- KrishnamurthyDocument62 paginiKrishnamurthymihaipopescu0100% (1)
- MetamizoleDocument1 paginăMetamizoleOliviaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Olivier Hanon MD - Laure Caillard MD - Edouard Chaussade MD - Intza Hernandorena MD - Clemence Boully MDDocument8 paginiOlivier Hanon MD - Laure Caillard MD - Edouard Chaussade MD - Intza Hernandorena MD - Clemence Boully MDVinh Quy VoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kidney DissectionDocument6 paginiKidney DissectionLucky Diamond Cabayao Montañez100% (1)
- Topic Test: Oxfordaqa International Gcse Biology 9201Document26 paginiTopic Test: Oxfordaqa International Gcse Biology 9201Novanolo Christovori ZebuaÎncă nu există evaluări