Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
QT 2assignment Final
Încărcat de
Ravindra KumarDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
QT 2assignment Final
Încărcat de
Ravindra KumarDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Submitted By:
Quantitative Technique- 2 Assignment
X1
Ravindra Kumar(50034)
X2 X3 X4 X5 The data (X1, X2, X3, X4, X5) are by city. 8 78 284 9.1 109 9.3 68 433 8.7 144 X1 = death rate per 1000 residents 7.5 70 739 7.2 113 8.9 96 1792 8.9 97 X2 = doctor availability per 100,000 residents 10.2 74 477 8.3 206 X3 = hospital availability per 100,000 residents 8.3 111 362 10.9 124 X4 = annual per capita income in thousands of 8.8 77 671 10 152 dollars 8.8 168 636 9.1 162 X5 = population density people per square mile 10.7 82 329 8.7 150 11.7 89 634 7.6 134 Above data for ten city are given. Build a multiple regression for death rate as dependent variable and independent variable as a doctor availability, hospital availability, per capita income, population density and test at a 5% that regression as a whole significantly represents the death rate? SUMMARY OUTPUT Regression Statistics Multiple R 0.537396 R Square 0.288794 Adjusted R Square -0.28017 Standard Error 1.463415 Observations 10 ANOVA df Regression Residual Total 4 5 9 SS MS F 4.348081 1.08702 0.507578 10.70792 2.141583 15.056 Standard Error t Stat P-value 5.29972 1.794783 0.132646 0.017716 -0.11348 0.914066 0.001277 0.142723 0.892082 0.495352 -0.65877 0.539169 0.017385 1.101494 0.320859 Significance F 0.734544
Coefficients Intercept 9.511847 Doctor avail. -0.00201 Hospital avail. 0.000182 per capita -0.32632 Density 0.01915 Regression equation:-
Lower 95% -4.11152 -0.04755 -0.0031 -1.59966 -0.02554
Upper 95% 23.13521 0.043531 0.003466 0.947021 0.06384
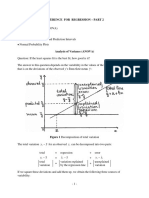
Y hat = 9.511847- 0.00201* Doctor avail + 0.000182* Hospital avail. - 0.32632* per capita. + 0.01915*Density Here equation shows that doctor and per capita income in negative related to y hat and hospital and density are positive related to regression equation it means hospital is not doing their job properly Analysis:R square- It is called the coefficient of multiple determinations and also the proportion of the total variation of Y hat that is explained by the regression plane. In my data the value of R square is
28.88% which is very low .This tells us that 28.88% percent of the total of death rate can be explain by independent variable i.e. number of doctor available, hospital available, per capita income and population density. Standard error- The standard error of estimate is a measure of error of prediction or variability of data point around the regression line. Here standard error is 1.463415which is very high. P-value:-It is the highest value of significance level at which we select the null hypothesis it means it means if significance level is more than prob value then null hypothesis is not accepted here. Here prob value of all independent variable is very high; it means none of the variable is significant at 5% significance level. Hypothesis testing:Ho: B1=B2=B3=B4=0 H1: at least one is not equal to zero Null hypotheses: slopes of the independent variables are zero Alternate hypothesis
Now I have to find out F ratio observed and F ratio critical F ratio is equal to SSR(egression sum of square )/K divided by SSE(error sum of squares)/(N-K-1) where K is number of independent variable and called numerator degree of freedom ,N is number of observation and N-K-1 is called denominator degree of freedom. It is find from F table Here F ratio observed is 0.507578 and F(4,5 5%) is 5.19, which is little more than F ratio observed So null hypothesis is accepted, it means regression plane as a whole is not significant at 5% significance level. The same, we can do by comparing significance F and significance level Here P-value of all the independent variable is higher than significance level so none of the variable is significant at 5% significance level Q. If there is a belief that the slopes of per capita income is -1 then test it at a 10% significance level Solution: - Ho: B = -1 H1: B -1 Null hypothesis slope of per capita income is -1 Alternate Hypothesis-slope is not equal to -1
Now I have to find t observed and t critical Tobs = (coefficient of per capita) (-1) and the whole divided by standard error of per capita income Tobs = (-0.32632 +1)/ 0.495352 =1.36 T cr comes from t table for 5% significance level and degree of freedom of (N-K-1) 5 that is 2.015, which is more than observed value so null hypothesis accepted. It means slope of per capita income is -1 so one additional increment in per capita income decline date rate by one unit. Reference :- Statistics for management by Richard I Levin & David S. Rubin Data source:http://college.cengage.com/mathematics/brase/understandable_statistics/7e/students/datasets/mlr/fram es/frame.html
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Statistics: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideDe la EverandStatistics: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideÎncă nu există evaluări
- SMMDDocument10 paginiSMMDAnuj AgarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ganda KoDocument15 paginiGanda KoDonyell50% (6)
- EViews 10 Users Guide IIDocument1.183 paginiEViews 10 Users Guide IIShanthakumari S SÎncă nu există evaluări
- ML Word To PDFDocument229 paginiML Word To PDFRajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ore Reserve EstimationDocument11 paginiOre Reserve EstimationMijail ACÎncă nu există evaluări
- Impact of Subsidies and Other Transfers On Poverty and Crop ProductionDocument7 paginiImpact of Subsidies and Other Transfers On Poverty and Crop ProductionAfrin TonniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Poisson Regression Analysis 136Document8 paginiPoisson Regression Analysis 136George AdongoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Poisson Regression Analysis 136Document8 paginiPoisson Regression Analysis 136George AdongoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 1Document6 paginiAssignment 1Marko MakobiriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Regression Analysis: Interpretation of Regression ModelDocument22 paginiRegression Analysis: Interpretation of Regression ModelRadith ShakindaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DOM105 Session 20Document10 paginiDOM105 Session 20DevanshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intro To Error AnalysisDocument10 paginiIntro To Error AnalysisTomDenver11Încă nu există evaluări
- Assignment No.2: Jameel Ahmed (8513) To: Sir Arsalan HashmiDocument7 paginiAssignment No.2: Jameel Ahmed (8513) To: Sir Arsalan HashmiAbdul RafayÎncă nu există evaluări
- F, T TestDocument21 paginiF, T TestKamini Satish SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample Size CalculatorDocument5 paginiSample Size CalculatorJalaluddin Rumi PrasadÎncă nu există evaluări
- chm202 Statistics PDFDocument24 paginichm202 Statistics PDFMohammad MouallemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Statistical EstimationDocument31 paginiStatistical EstimationAgung Nuza DwiputraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Probability DistributionsDocument26 paginiProbability DistributionsRajat JadhavÎncă nu există evaluări
- My PartDocument3 paginiMy PartSahrish Jaleel ShaikhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concentrationindex Handout PDFDocument6 paginiConcentrationindex Handout PDFAremy TestarossaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linear Regression ModelDocument15 paginiLinear Regression ModelezambaglioneÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPSS ProjectDocument12 paginiSPSS ProjectRishabh Sethi0% (1)
- BRM Question Bank AnsDocument7 paginiBRM Question Bank Ansharsh hariharnoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Econometric AssignmentDocument12 paginiEconometric Assignmentkizzy McraeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Estimation Techniques: Essential ConceptsDocument4 paginiBasic Estimation Techniques: Essential ConceptsRohit SinhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HW 5, 448Document16 paginiHW 5, 448pdrogos02100% (1)
- ITM Chapter 6 On Testing of HypothesisDocument39 paginiITM Chapter 6 On Testing of HypothesisAnish Kumar SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cfa Level 1 - Quantitative Review: Calculate Mean and Standard Deviation of Expected ReturnsDocument5 paginiCfa Level 1 - Quantitative Review: Calculate Mean and Standard Deviation of Expected ReturnsNoroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Statistics - Own CompilationDocument20 paginiStatistics - Own Compilationbogdan_de_romaniaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Statistics SPSS ProjectDocument12 paginiStatistics SPSS Projectrishabhsethi1990Încă nu există evaluări
- Estimating Population Values PPT at BEC DOMSDocument50 paginiEstimating Population Values PPT at BEC DOMSBabasab Patil (Karrisatte)Încă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 2Document19 paginiAssignment 2Ehsan KarimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Regress Y On X2 and X3 and Report The Results:: ECO 372 Assignment On HeteroscedasticityDocument33 paginiRegress Y On X2 and X3 and Report The Results:: ECO 372 Assignment On HeteroscedasticitySaqif Nayeem KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indicates That It Is Significant and Will Reject The Null Hypothesis and Accept The Alternative Hypothesis Since It Is Lower Than 0.05Document4 paginiIndicates That It Is Significant and Will Reject The Null Hypothesis and Accept The Alternative Hypothesis Since It Is Lower Than 0.05Leilalyn NicolasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Decision - Science AI 2 SelfDocument9 paginiDecision - Science AI 2 SelfTarun Singh PanuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multicollinearity Assignment April 5Document10 paginiMulticollinearity Assignment April 5Zeinm KhenÎncă nu există evaluări
- SDM 1 FormulaDocument9 paginiSDM 1 FormulaANZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hypothesis TestingDocument44 paginiHypothesis TestingRudraksh AgrawalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Confidence Intervals-summer22-Lecture11Document23 paginiConfidence Intervals-summer22-Lecture11Abu Bakar AbbasiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Number of Observations: It: Number of Variables Plus 1'. Here We Want To Estimate For 1 Variable Only, So Number ofDocument3 paginiNumber of Observations: It: Number of Variables Plus 1'. Here We Want To Estimate For 1 Variable Only, So Number ofQuynh Ngoc DangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathematics in Machine LearningDocument83 paginiMathematics in Machine LearningSubha OPÎncă nu există evaluări
- Regression With Categorical Explanatory Variables: Dr. Mine Çetinkaya-Rundel Duke UniversityDocument6 paginiRegression With Categorical Explanatory Variables: Dr. Mine Çetinkaya-Rundel Duke UniversityNiroshani MannaperumaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction On Chi Square DistributionDocument13 paginiIntroduction On Chi Square DistributionMonil GandhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- BS 8 1Document27 paginiBS 8 1Prudhvinadh KopparapuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Malhotra 15Document99 paginiMalhotra 15Satyajeet ChauhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHAPTER 5 - Sampling Distributions Sections: 5.1 & 5.2: AssumptionsDocument9 paginiCHAPTER 5 - Sampling Distributions Sections: 5.1 & 5.2: Assumptionssound05Încă nu există evaluări
- CI For A ProportionDocument24 paginiCI For A ProportionkokleongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Non-Parametric TestDocument12 paginiNon-Parametric Testhansdeep479Încă nu există evaluări
- ECON1203/ECON2292 Business and Economic Statistics: Week 2Document10 paginiECON1203/ECON2292 Business and Economic Statistics: Week 2Jason PanÎncă nu există evaluări
- P1.T2. Quantitative AnalysisDocument23 paginiP1.T2. Quantitative Analysisruthbadoo54Încă nu există evaluări
- Testing of Hypothesis HypothesisDocument32 paginiTesting of Hypothesis HypothesisAbhishek JaiswalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Statistics in Traffic Engineering-1Document14 paginiStatistics in Traffic Engineering-1Zainab A. AbdulstaarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 2Document75 paginiLecture 2Nikoli MajorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hypothesis Statistics-1-1Document35 paginiHypothesis Statistics-1-111- NikunjÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECONOMETRICSDocument4 paginiECONOMETRICSAlix MuratetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Analysis Using Statsdirect A. Investigating ProbabilityDocument8 paginiData Analysis Using Statsdirect A. Investigating Probabilityahmad_nazib_1Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter FourDocument9 paginiChapter FourTadele BekeleÎncă nu există evaluări
- S2 Revision NotesDocument2 paginiS2 Revision NotesimnulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Critical Value: What Is The Formula of Z Score?Document6 paginiCritical Value: What Is The Formula of Z Score?godzillasaurus123Încă nu există evaluări
- 2 by 2 Chi-Square Test (Four-Fold Contingency Table) - StatsDirectDocument3 pagini2 by 2 Chi-Square Test (Four-Fold Contingency Table) - StatsDirectwienslaw5804Încă nu există evaluări
- Relationship Between Inflation and UnemploymentDocument29 paginiRelationship Between Inflation and Unemploymentnits0007Încă nu există evaluări
- The Taj Hotel and Resort. THE TAJ'S PEOPLE PHILOSOPHY AND STARS SYSTEMDocument10 paginiThe Taj Hotel and Resort. THE TAJ'S PEOPLE PHILOSOPHY AND STARS SYSTEMRavindra KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marico Limited Company Analysis by K.N.T Arasu in Marketing Category On ManagementParadiseDocument12 paginiMarico Limited Company Analysis by K.N.T Arasu in Marketing Category On ManagementParadiseRavindra KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cad Dairy MilkDocument10 paginiCad Dairy MilkRavindra KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- LUX-The Beauty Soap: by Group 2:-Anjali Nishita Ravindra VaibhavDocument11 paginiLUX-The Beauty Soap: by Group 2:-Anjali Nishita Ravindra VaibhavRavindra KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Titan Watch Consumer MotivationDocument10 paginiTitan Watch Consumer MotivationRavindra KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Etika Profesi Auditor Dalam Memoderasi Pengaruh Independensi Dan Kompetensi Auditor Atas Kualitas AuditDocument9 paginiEtika Profesi Auditor Dalam Memoderasi Pengaruh Independensi Dan Kompetensi Auditor Atas Kualitas AuditCahya DiningsihÎncă nu există evaluări
- Regresi Data PanelDocument10 paginiRegresi Data PanelN NailyÎncă nu există evaluări
- STA5328 Ramin Shamshiri HW3Document6 paginiSTA5328 Ramin Shamshiri HW3Redmond R. ShamshiriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple Linear Regression Example InfographicDocument1 paginăSimple Linear Regression Example InfographicMiguel Angelo GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6 Sebaran Penarikan ContohDocument15 pagini6 Sebaran Penarikan ContohsudahkuliahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 8 Regression AnalysisDocument22 paginiUnit 8 Regression Analysisshane naigalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pengaruh Personal Selling Terhadap Keputusan Berkunjung Di Jendela AlamDocument8 paginiPengaruh Personal Selling Terhadap Keputusan Berkunjung Di Jendela AlamzainabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Colonial Q10 ExplanationDocument3 paginiColonial Q10 ExplanationDevyani Sanjay BoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1Document17 paginiChapter 1Getasew AsmareÎncă nu există evaluări
- ST102 NotesDocument21 paginiST102 NotesBenjamin Ng0% (1)
- Panel Data Models Stata Program and Output PDFDocument8 paginiPanel Data Models Stata Program and Output PDFcrinix7265Încă nu există evaluări
- ID Pengaruh Human Relation Dan Reward TerhaDocument15 paginiID Pengaruh Human Relation Dan Reward Terhanuraeni agusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Slides On Taming The Factor ZOODocument35 paginiSlides On Taming The Factor ZOOAkshay RaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Econometrics, 5 Edition: Chapter 3: Multiple Regression AnalysisDocument28 paginiIntroduction To Econometrics, 5 Edition: Chapter 3: Multiple Regression AnalysisRamarcha KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 7 Linear Regreation CHP14Document21 paginiTopic 7 Linear Regreation CHP14Natasha Mgt JoharÎncă nu există evaluări
- 19bit0404 VL2020210101940 Ast02Document11 pagini19bit0404 VL2020210101940 Ast02Saji JosephÎncă nu există evaluări
- Logistic Regression in RDocument19 paginiLogistic Regression in RRenukaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Matlab-STATISTICAL MODELS AND METHODS FOR FINANCIAL MARKETSDocument13 paginiMatlab-STATISTICAL MODELS AND METHODS FOR FINANCIAL MARKETSGonzalo SaavedraÎncă nu există evaluări
- U X X X Y: Linear in VariablesDocument22 paginiU X X X Y: Linear in VariablesMedico Nol DelaphanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Participatory Sensing For Localization of A GNSS JammerDocument7 paginiParticipatory Sensing For Localization of A GNSS JammerAaron GalvezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Econometrics Chapter 5 PPT SlidesDocument39 paginiEconometrics Chapter 5 PPT SlidesIsabelleDwight100% (2)
- 5.multiple RegressionDocument17 pagini5.multiple Regressionaiman irfanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 Inference For Regression Part2Document12 pagini10 Inference For Regression Part2Rama DulceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jurnal Kecerdasan EmosionalDocument17 paginiJurnal Kecerdasan EmosionalarisÎncă nu există evaluări
- HeteroscedasticityandHomoscedasticity SAGE Author - NotesDocument3 paginiHeteroscedasticityandHomoscedasticity SAGE Author - Notes6hb47jbtqnÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11 Structural Education ModelingDocument27 pagini11 Structural Education ModelingAC BalioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bayesian Information CriterionDocument3 paginiBayesian Information CriterionDivyashri JainÎncă nu există evaluări