Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Congenital Hip Dislocation
Încărcat de
serpeptumdanaeDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Congenital Hip Dislocation
Încărcat de
serpeptumdanaeDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Trinity University of Asia
St. Lukes College of Nursing
E. Rodriguez Sr. Avenue, Cathedral Heights, Quezon City, Philippines
Congenital Hip Dislocation
Definition: Is an abnormal formation in the hip joint in which the ball at the top of the thigh bone (femoral head) is not stable in the socket (acetabulum). Also, the ligaments of the hip joint may be loose and stretched. In here, although the hip is in the right place, the socket does not grow properly and is too shallow. If the socket is shallow, this may allow the ball to move from the position it should occupy. Furthermore, the head of the femur is usually dislocated post-superiorly. There is complete loss of contact between articular surface of femoral and head and acetabulum. Dislocation may either be partial or complete and may be either be unilateral or bilateral. May develop at any time during fetal life, infancy or childhood. Includes hip that are unstable, sublimated, dislocated, and have malformed acetabulum. Clinical Manifestation: Ortolanis Sign Barlows Sign Asymmetry of gluteal and thigh folds Limited hip abduction, as seen in flexion Alls/Galeazzis Sign Positive trendelenburg Sign (if child is weight bearing) Limping, toe walking, or waddling, duck-like gait
*The Ortolani and Barlow tests are most reliable from birth to 2-3 months of age. Other Signs and Symptoms:
Trinity University of Asia
St. Lukes College of Nursing
E. Rodriguez Sr. Avenue, Cathedral Heights, Quezon City, Philippines
Telescoping Sign-in older infant and child, the affected leg will be shorter than the other Dislocation Maneuvers (useful only in first three months of life) Thigh abduction Thigh extension Relocation Maneuvers Thigh flexion Thigh abduction
Treatment/Management: a) Range of motion exercises b) Orthosis (a force system, involving braces) c) Chiropractic medications for procedures of closed manipulations between 6-18months to reduce the dislocated hip joint d) Pain control e) Functional activities Age Less than 6 months More than 6 months More than 2 years old More than 3 years old More than 4 years old Management Pavlik harness Traction, closed reduction Open reduction: Anterolateral/Smith Petersen Approach Femoral shortening + Hip Spica Cast + Abduction Orthosis Pelvic Osteotomy
Management indicated for hip instability beyond 5 days:
Trinity University of Asia
St. Lukes College of Nursing
E. Rodriguez Sr. Avenue, Cathedral Heights, Quezon City, Philippines
Step 1: Pavlik Harness a) b) indicated as first-line if <6 months old start with harness trial for 3 4 weeks splints hips in flexed and abducted position ultrasound should demonstrate reduction at 3 weeks: Reduced: continue harness for more than 6 weeks Not reduced: Go to step 2
Step 2: Closed Reduction and Casting by Orthopedics. a) Removable protective Abduction Brace- used in children aged more than 6 months. b) Hip Spica casting for 12 weeks ( 6- 18months old) - Positioning confirmed by post-op MRI or CT scan c) Gradual reduction by traction - for approximately 3 weeks d) Abduction splint - Must be maintained if the radiographic evidence of residual dysplasia is still present. e) Plaster Treatment (Frog Cast) - Involves a large plaster around the lower body and both legs, with a hole cut to allow baby to pass urine and empty the bowels. Step 3: Surgical Management Surgical Open Reduction ( if hips are not reducible and is indicated for older children ) Indicated for refractory cases Requires multi-step procedures:
Trinity University of Asia
St. Lukes College of Nursing
E. Rodriguez Sr. Avenue, Cathedral Heights, Quezon City, Philippines
Tendon lengthening Clearing tissues obstructing relocation Tightening hip capsuled. Osteotomy if performed after age 18 month
Diagnostics: 1. Initial examination after birth 2. Radiographic examination/Hip X-ray (in infants than age 4 months and in children)>It is not reliable in early infancy because ossification of the femoral head does not normally take place until the third to six month of life.>evaluated with reference lines drawn over AP x-ray: Hilgenreiners Line.- horizontal line through tri-radiate cartilages) Perkins line- vertical line along lateral acetabulum) Shentons Line- femoral neck medial border; superior border of obturator foramen 3. CT scan is useful to assess the position of the femoral head relative to the acetabulum after closed reduction and casting. 4. Dynamic Hip Ultrasound for infants aged 1 -6 months diagnostic for congenital hip dislocation evaluates for subluxation and reducibility high false positive rate for <6 weeks old
Nursing Care:
Trinity University of Asia
St. Lukes College of Nursing
E. Rodriguez Sr. Avenue, Cathedral Heights, Quezon City, Philippines
1. Teach the parents how to maintain devices, provide nurturing activities to meet the infants need. 2. Prevent skin breakdown by putting undershirt under the chest straps of the pavlik harness and put knee socks under the foot and leg pieces to prevent the straps from rubbing the skin. 3. Check frequently for red areas under the straps and the clothing. 4. Gently massage healthy skin under the straps once a day to stimulate circulation. 5. Avoid lotions and powder they can cake and irritate the skin. * Complications of treatment may include a delay in walking if the child was placed in a body cast. The pavlik harness and other positioning devices may cause skin irritation, and a difference in leg length may remain. A growth disturbance of the upper thigh rarely occurs. The complications of surgical interventions can be re-dislocation and the severe form, osteonecrosis.
Trinity University of Asia
St. Lukes College of Nursing
E. Rodriguez Sr. Avenue, Cathedral Heights, Quezon City, Philippines
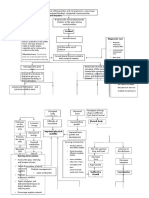
Pathophysiology:
Non Modifiable Factors: Gender: Female Birth order: Firstborn Race: Caucasians Family History Breech Positioning Large infant size Maternal hormone secretion
Modifiable Factors:
Delivery type: CS instead of NSD Postnatal Positioning
Acetabular Dysplasia
Femoral head dislocates from acetabulum
Congenital Hip Dislocation
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- If they could talk about walking again: Canine Cruciate Surgery Rehabilitation Program: A 10 week detailed program of specific approaches, exercises, massage, and restoring balance to get the best results after your pet has undergone surgery for cruciate ligament repair. Tracking sheets for each week.De la EverandIf they could talk about walking again: Canine Cruciate Surgery Rehabilitation Program: A 10 week detailed program of specific approaches, exercises, massage, and restoring balance to get the best results after your pet has undergone surgery for cruciate ligament repair. Tracking sheets for each week.Încă nu există evaluări
- Congenital Hip DislocationDocument6 paginiCongenital Hip DislocationPaola CamainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Congenital Hip DislocationDocument8 paginiCongenital Hip DislocationSpread MushooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pectus Carinatum, (Pigeon Chest) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsDe la EverandPectus Carinatum, (Pigeon Chest) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Congenital Hip DislocationDocument5 paginiCongenital Hip DislocationMonica Aguirre QuilangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mom's Guide to Diastasis Recti: A Program for Preventing and Healing Abdominal Separation Caused by PregnancyDe la EverandMom's Guide to Diastasis Recti: A Program for Preventing and Healing Abdominal Separation Caused by PregnancyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Congenital Hip DysplasiaDocument4 paginiCongenital Hip DysplasiaJustFhamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Congenital Abnormalities MusculoSkeletal SystemDocument116 paginiCongenital Abnormalities MusculoSkeletal SystemVii syilsaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Congenital Hip Dislocation GuideDocument32 paginiCongenital Hip Dislocation GuideLauÎncă nu există evaluări
- Musculoskeletal System Nursing ReviewerDocument11 paginiMusculoskeletal System Nursing Reviewerposh003850% (2)
- Developmental Dysplasia of The Hip (CDH)Document5 paginiDevelopmental Dysplasia of The Hip (CDH)venkata ramakrishnaiahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Congenital Hip DislocationDocument13 paginiCongenital Hip DislocationKei CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Musculoskeletal Disorders: Carah Fe R. Bacus, RNDocument40 paginiMusculoskeletal Disorders: Carah Fe R. Bacus, RNcoosa liquorsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Congenital Hip DislocationDocument8 paginiCongenital Hip DislocationadrianojenfferÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kano State College of Nursing and Midwifery: Club FootDocument20 paginiKano State College of Nursing and Midwifery: Club FootMuhammad Daha SanusiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ScoliosisDocument3 paginiScoliosisYoshizawa MiharuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pediatric OrthopaedicDocument66 paginiPediatric OrthopaedicDhito RodriguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- School of Health and Allied Health Sciences Nursing Department Self-Directed Learning (Nur 146 - Clinical Area)Document5 paginiSchool of Health and Allied Health Sciences Nursing Department Self-Directed Learning (Nur 146 - Clinical Area)Milagros FloritaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4th Jakarta PMR Scientific Forum Clubfoot ManagementDocument31 pagini4th Jakarta PMR Scientific Forum Clubfoot ManagementrachmadyÎncă nu există evaluări
- CastDocument7 paginiCastRegina Nina YoshidaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DDH Developmental Hip DysplasiaDocument67 paginiDDH Developmental Hip DysplasiaGladys MainaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Congenital Disorders of The Skeletal SystemDocument64 paginiCongenital Disorders of The Skeletal SystemLovely CervantesÎncă nu există evaluări
- ClubfootDocument27 paginiClubfootPrashanth K NairÎncă nu există evaluări
- ClubfootDocument27 paginiClubfootJaya Prabha100% (1)
- ClubfootDocument9 paginiClubfootLorebell100% (5)
- Club Foot: Ison, Kevin Christian B. BSN3D1Document27 paginiClub Foot: Ison, Kevin Christian B. BSN3D1Saputro AbdiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adolescent Health Problems and Nursing CareDocument40 paginiAdolescent Health Problems and Nursing CaremilayosoresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Congenital Talipes Equinovarus 222Document10 paginiCongenital Talipes Equinovarus 222jjjj30Încă nu există evaluări
- Congenital Muscular Torticollis and Scapula Elevation LectureDocument102 paginiCongenital Muscular Torticollis and Scapula Elevation LectureFahmi MujahidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Congenital hip dysplasia diagnosis in under 40Document6 paginiCongenital hip dysplasia diagnosis in under 40Bek DiazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clubfoot Written ReportDocument7 paginiClubfoot Written ReportAira Madel ArabaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Developmental Dysplasia of The Hip: Group BDocument24 paginiDevelopmental Dysplasia of The Hip: Group B21.FARHANIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anomalies of Skeletal System-1Document44 paginiAnomalies of Skeletal System-1Meena KoushalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clubfoot Definition, Types, and TreatmentDocument5 paginiClubfoot Definition, Types, and TreatmentcrisolandÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mayank Pushkar. Congenital Talipes Equinovarus (CTEV) SRJI Vol - 2, Issue - 1, Year - 2013Document7 paginiMayank Pushkar. Congenital Talipes Equinovarus (CTEV) SRJI Vol - 2, Issue - 1, Year - 2013Dr. Krishna N. SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sup-ER Orthosis: An Innovative Treatment For Infants With Birth Related Brachial Plexus InjuryDocument6 paginiSup-ER Orthosis: An Innovative Treatment For Infants With Birth Related Brachial Plexus InjuryJuli DeviaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case StudyDocument11 paginiCase StudyAnj TadxÎncă nu există evaluări
- CTEV (Congenital Talipes Equinovarus) 2Document6 paginiCTEV (Congenital Talipes Equinovarus) 2Rahmat Syukur ZebuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Developmental Dysplasia of The Hip, (DDH) Including Femoral and Pelvic OsteotomyDocument16 paginiDevelopmental Dysplasia of The Hip, (DDH) Including Femoral and Pelvic OsteotomyAkbar GazaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Congenital Hip DysplasiaDocument32 paginiCongenital Hip DysplasiaChristine AllonarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Developmental Dysplasia of HipDocument13 paginiDevelopmental Dysplasia of HipIndra Purwanto AkbarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Congenial Hip DysplasiaDocument6 paginiCongenial Hip DysplasiaDrew CabigaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- DevelopmentalDysplasiaoftheHip (DDH) IDocument2 paginiDevelopmentalDysplasiaoftheHip (DDH) Iapi-3822433Încă nu există evaluări
- Pediatric Orthopaedics: Dr. Zairin Noor Helmi, Spot. (K) .MM - FicsDocument53 paginiPediatric Orthopaedics: Dr. Zairin Noor Helmi, Spot. (K) .MM - FicsmegaFitrianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Objectives CLUB FOOTDocument2 paginiObjectives CLUB FOOTAdriano SonnyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathway - Skoliosis GROUPDocument12 paginiPathway - Skoliosis GROUPAnonymous NZTQVgjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clubfoot: Bicol University Tabaco Campus Department of Nursing Tabaco CityDocument5 paginiClubfoot: Bicol University Tabaco Campus Department of Nursing Tabaco CitymikutekiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Care of Patients With Traction TractionDocument5 paginiCare of Patients With Traction TractionMOHAMMAD JABBER M. PAUDACJRÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zabrina Joana DDocument4 paginiZabrina Joana DEmman BalidoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Umbilical Hernia - TPIDocument4 paginiUmbilical Hernia - TPIDeepak CÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Neglected ClubfootDocument3 paginiThe Neglected ClubfootAngelica Mercado SirotÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clubfoot: Lady Diane M. Cabriga Bsn-IiiDocument7 paginiClubfoot: Lady Diane M. Cabriga Bsn-IiiDayan CabrigaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Congenital Hip DysplasiaDocument24 paginiCongenital Hip DysplasiaElizabeth Quiñones100% (1)
- Congenital Anomalies of Skeletal SystemDocument44 paginiCongenital Anomalies of Skeletal SystemMeena Koushal100% (1)
- Congenital Talipes Equinovarus (Clubfoot)Document4 paginiCongenital Talipes Equinovarus (Clubfoot)Julliza Joy PandiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study - AutintoyatsDocument21 paginiCase Study - AutintoyatsMae Jane AuzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medical Management of DDHDocument5 paginiMedical Management of DDHMark Christian CuiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Menejemen Fisioterapi - Conginetal Hip DislocationDocument79 paginiMenejemen Fisioterapi - Conginetal Hip DislocationMufidah AlhadarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clubfoot Care: Nursing Goals for Congenital Talipes EquinovarusDocument10 paginiClubfoot Care: Nursing Goals for Congenital Talipes EquinovarusHazel NialaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Placenta FunctionsDocument46 paginiPlacenta Functionsvenkata sryanamala50% (2)
- Reading Task 1-Breast Cancer and The ElderlyDocument6 paginiReading Task 1-Breast Cancer and The ElderlyJats_Fru_1741100% (5)
- Need To Call To Confirm HoursDocument35 paginiNeed To Call To Confirm HoursRadyusman RajagukgukÎncă nu există evaluări
- Managing Benign Breast ConditionsDocument20 paginiManaging Benign Breast Conditionschristel chadidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Appendicitis and Crohn's Disease GuideDocument11 paginiAppendicitis and Crohn's Disease GuideJa DimasÎncă nu există evaluări
- ThesisDocument5 paginiThesisVictoria ManeboÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steroid Tapering and Supportive Treatment Guidance V1.0 PDFDocument1 paginăSteroid Tapering and Supportive Treatment Guidance V1.0 PDFNthutagaol TrusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Live Donor Liver Transplantation: Caq CornerDocument12 paginiLive Donor Liver Transplantation: Caq CornerBarbara ZabraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Soft Tissue Biology Around Dental ImplantsDocument76 paginiSoft Tissue Biology Around Dental Implantsaakankshakanwar0% (2)
- B.SC Nursing2018Question PapersFirst YearNursing Foundations FR 4firstDocument1 paginăB.SC Nursing2018Question PapersFirst YearNursing Foundations FR 4firstJagdeesh PrasadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anxiety and Depression in TeensDocument2 paginiAnxiety and Depression in TeensHenry Alexander Gerena SalazarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zirconia Crowns Improve Patient SmileDocument4 paginiZirconia Crowns Improve Patient SmileWiwin Nuril FalahÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCMB316 Rle 2-10-7addison's DiseaseDocument4 paginiNCMB316 Rle 2-10-7addison's DiseaseMaica LectanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Greyson 2019Document10 paginiGreyson 2019Ziha Zia Leonita FauziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vastarel MR 35mgDocument1 paginăVastarel MR 35mgPhil Edgar Contreras RNÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clsi 2012Document50 paginiClsi 2012niluh suwasanti100% (1)
- Hensleys Practical Approach To Cardiothoracic Anesthesia Sixth EditionDocument62 paginiHensleys Practical Approach To Cardiothoracic Anesthesia Sixth Editiontimothy.daniels842100% (39)
- HYPETHYROIDISM NURSING CARE PLANDocument6 paginiHYPETHYROIDISM NURSING CARE PLANTrisha Joyce MadriagaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abdominoperineal Resection MilesDocument17 paginiAbdominoperineal Resection MilesHugoÎncă nu există evaluări
- The XbarM Control ProgramDocument7 paginiThe XbarM Control ProgramLaboratório Jofre CohenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Developing Biocompatibility For Medical DevicesDocument30 paginiDeveloping Biocompatibility For Medical DevicesNagula Naresh100% (1)
- Achilles Tendon Conditions Signs and SymptomsDocument1 paginăAchilles Tendon Conditions Signs and SymptomsTessa DagutÎncă nu există evaluări
- CL (Mr. Von) Mathematics (Mr. Ryan) : Trivia QuestionsDocument2 paginiCL (Mr. Von) Mathematics (Mr. Ryan) : Trivia QuestionsRichard Andrew Abratique DandanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sonus CompleteDocument4 paginiSonus CompleteSonusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiovascular DisorderDocument6 paginiCardiovascular DisorderClara De GuzmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abbas Et Al. 2020 - Nature Immunology-2020-Abbas-TomaselloDocument33 paginiAbbas Et Al. 2020 - Nature Immunology-2020-Abbas-TomaselloAchille BroggiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amended Modern Pharmacology Syllabus 051218Document26 paginiAmended Modern Pharmacology Syllabus 051218harshad patelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bipolar and Related Disorder: Recio, Kate M. Far Eastern University - Cavite PSY1831-ADocument20 paginiBipolar and Related Disorder: Recio, Kate M. Far Eastern University - Cavite PSY1831-AKate RecioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmaceutical Assasination (Partial)Document14 paginiPharmaceutical Assasination (Partial)jamie_clark_2100% (2)
- Peyronies DiseaseDocument6 paginiPeyronies Diseaseapi-255601700Încă nu există evaluări
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionDe la EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (402)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessDe la EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (327)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityDe la EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (13)
- The Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesDe la EverandThe Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (34)
- Techniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementDe la EverandTechniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (40)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsDe la EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (3)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeDe la EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedDe la EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (78)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDe la EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityDe la EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsDe la EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossDe la EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (3)
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingDe la EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingDe la EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (4)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingDe la EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (31)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsDe la EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (169)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaDe la EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsDe la EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDe la EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (41)
- The Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossDe la EverandThe Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (4)
- Summary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDe la EverandSummary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (3)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.De la EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (110)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisDe la EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (8)