Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Gastric Outlet Obstruction Pathophysiology
Încărcat de
Tania NovizaTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Gastric Outlet Obstruction Pathophysiology
Încărcat de
Tania NovizaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
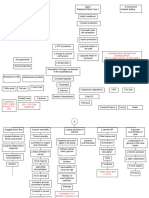
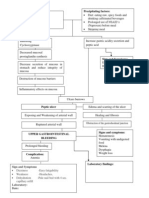
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF GASTRIC OUTLET OBSTRUCTION
Predisposing factors: Non-modifiable: Old age (68 years old) Modifiable: Diet (small serving/ meals) Stress Helicobacter pylori infection Smoking NSAID use Colonoscopy: Nonspecific Colitis; Internal Hemorrhoids Grade 1 UGIE: Diffuse Erosive Gastritis; Hiatal Hernia; Gastroduodenal Reflux Chest PA: Senile Pulmonary Emphysematous changes. Atherosclerotic aorta. Senile Osteoporosis Abdomen Supine Upright There are non-dilated bowel loops with no air fluid level. There is no demonstrable free peritoneal air. The hepatic shadow appears prominent with displacement. of the hepatic flexure inferiorly. No unusual paravertebral density. There is spurring along the margins of the visualized vertebral bodies. There is generalized decrease in osseous density. There is slight rightward deviation of the lumbar spine. The rest of the structures are unremarkable. Obstruction persists for 5-7 days despite intense medical therapy, operation should be considered. (vagotomy and antrectomy with gastroduodenal drainage or truncal vagotomy with drainage; balloon dilation) Precipitating factor: Excess gastric acid production
Acid-peptic injury to the gastroduodenal mucosal barrier Acute ulcer Inflammation and edema and/or muscular spasm epigastric pain
Succession splash, epigastric tenderness abdominal distension, hypoactive bowel sounds
Lumen obstruction Tympanic mass in epigastric area
Inc. WBC, segmenters, lymphocytes
Nausea, vomiting, LBM, fullness relieve by emesis, early satiety, weight lost, lost of appetite, fatigue
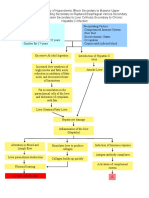
Progressive gastric dilation Malnutrition (protein) Stomach loses contractility Inc. BUN, crea Anemia, dec. S. albumin Loss of fluid, hydrogen, chloride
Intestinal bacterial overgrowth
Accumulation of undigested food
DHN, metabolic, hypokalemic alkalosis TPN (Kombiven ) Severe DHN (kidneys compensate by retaining Na+) Ensure patent line, regulate rate Dec. Na+
Medical therapy is effective in preparing patients for surgery but not proved successful on eliminating need for surgery
Risk for aspiration PNA Monitor CBC, signs of bleeding, albumin, edema, skin turgor
PNA, recurrent or persistent bleeding, ulceration, perforation, or obstruction
postgastrectomy syndromes, such as dumping, alkaline gastritis, and afferent loop syndrome
Stomach decompression, maintain optimum nutritional status
Death
K+ is initially exchanged, but as DHN progresses and K+ stores become depleted, H+ is exchanged for Na+ in the renal tubules
Encourage COMPLIANCE monitor of weight loss Correct the volume, electrolyte, acidbase disturbances Administer Normal Saline FC place (if renal function is adequate) may give K+ Continuous nasogastric suction Decompression of the stomach (placement of large bore NGT) Parenteral administration of H2receptor antagonist/ PPI meds Monitor VS, UO, electrolytes, signs of infection, dehydration Keep patient comfortable in bed Health teachings: avoids acidic drinks
Meds: Omeprazole 40 mg 1 cap BID Moseger 1 tab OD @ HS Ciprofloxacin 500 mg 1 tab BID Colchicine 0.5 mg 1 tab BID Prednisone 1 tab OD x 5 days Mucosta 100 mg 1 tab TID Conzace 1 cap OD Stat/prn meds: Metoclopramide 1 amp prn for comiting Tx: Ensure 3 scoops / 150cc water BID
Recovery
Starvation
Hypoproteinemia and potential Vit, K deficiency
Monitor nutritional status (TPN) and coagulation factors
Anemia
BT, parenteral iron Leads to
LEGEND:
If metabolic alkalosis (blood pH >7.6) either 0.01 N HCl or ammonium chloride solution may be given IV
Inc. clotting time; dec. RCB, hemohlobin, hematocrit Bold letters
Does not lead to S/sx manifested by the patient Laboratory results/ diagnostic findings Nursing Intervention Medical intervention
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Community Acquired Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDe la EverandCommunity Acquired Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Small Bowel ObstructionDocument2 paginiSmall Bowel ObstructionSrividya PushpalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Perforated Gastric UlcerDocument15 paginiPerforated Gastric UlcerNorshahidah IedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathology Polycystic Kidney DiseaseDocument4 paginiPathology Polycystic Kidney DiseaseOnyedika EgbujoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Predisposing Conditions, Management and Prevention of Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument52 paginiPredisposing Conditions, Management and Prevention of Chronic Kidney DiseaseSaad MotawéaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MSU Buug College Nursing Assessment for Abdominal PainDocument30 paginiMSU Buug College Nursing Assessment for Abdominal Painllanelli.graciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hypertension Pathophysiology and Treatment PDFDocument6 paginiHypertension Pathophysiology and Treatment PDFBella TogasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cancer of The ColonDocument8 paginiCancer of The Colonnot your medz duranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anal Canal: Fissure in Ano HaemorrhoidsDocument37 paginiAnal Canal: Fissure in Ano Haemorrhoidsyash shrivastavaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Patent Ductus Arteroisus (PDA)Document2 paginiPathophysiology of Patent Ductus Arteroisus (PDA)Rodel YacasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bladder Cancer Types, Symptoms, Tests & TreatmentDocument1 paginăBladder Cancer Types, Symptoms, Tests & TreatmentCarmina AguilarÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHOLANGITISDocument1 paginăCHOLANGITISKirk Torregosa PañaresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology Cholelithiasis 2Document2 paginiPathophysiology Cholelithiasis 2Jamie HaravataÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pa Tho Physiology of Cad NstemiDocument2 paginiPa Tho Physiology of Cad Nstemianreilegarde100% (1)
- AGE With Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument3 paginiAGE With Pa Tho PhysiologyChichi Licuben OresacamÎncă nu există evaluări
- ConceptMap AMLDocument1 paginăConceptMap AMLnursing concept mapsÎncă nu există evaluări
- PATHOPHYDocument3 paginiPATHOPHYArlly Faena AbadÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Pathophysiology of Peptic UlcerDocument15 paginiThe Pathophysiology of Peptic UlcerKike Meneses100% (1)
- Ulcerative ColitisDocument18 paginiUlcerative ColitisHoussein EL HajjÎncă nu există evaluări
- PericarditisDocument11 paginiPericarditisrbarcellonaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gastric Ulcers: Presented By: Dr. Jawaria Memon & Dr. Deep KumarDocument31 paginiGastric Ulcers: Presented By: Dr. Jawaria Memon & Dr. Deep KumarDeep KhemaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHF PathophysiologyDocument4 paginiCHF PathophysiologyVirtudazo JessaÎncă nu există evaluări
- V. Pathophysiology Modifiable: Non - ModifiableDocument2 paginiV. Pathophysiology Modifiable: Non - ModifiableMary Grace BanezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Non-Modifiable, Partially Modifiable, and Modifiable Risk Factors for Atherothrombotic DiseaseDocument15 paginiNon-Modifiable, Partially Modifiable, and Modifiable Risk Factors for Atherothrombotic DiseaseWiljohn de la CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cholelithiasis Treatment & ManagementDocument8 paginiCholelithiasis Treatment & ManagementRayhanun MardhatillahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology Copd-ChfDocument2 paginiPathophysiology Copd-ChfZaira Batalo100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Heart FailureDocument1 paginăPathophysiology of Heart Failureiz11Încă nu există evaluări
- "Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction, Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, and Community Acquired Pneumonia" Client Centered PathophysiologyDocument3 pagini"Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction, Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, and Community Acquired Pneumonia" Client Centered PathophysiologyCarl Elexer Cuyugan Ano50% (2)
- DB13 - Pathophysiology of AtherosclerosisDocument2 paginiDB13 - Pathophysiology of Atherosclerosisi_vhie03Încă nu există evaluări
- What Is Acute Pancreatitis?Document5 paginiWhat Is Acute Pancreatitis?leonard1971Încă nu există evaluări
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Hospital CaseDocument3 paginiDiabetes Mellitus Type 2 Hospital CaseAngel FiloteoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pernicious Anemia PathophysiologyDocument1 paginăPernicious Anemia PathophysiologyCeline dela cruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Addison'sDocument4 paginiAddison'sKoRnflakesÎncă nu există evaluări
- ABRUPTIO PLACENTAE PathophysiologyDocument3 paginiABRUPTIO PLACENTAE PathophysiologyBarda GulanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case AnalysisDocument12 paginiCase AnalysisFroilan TaracatacÎncă nu există evaluări
- HCVDDocument5 paginiHCVDkhrizaleehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Poststreptococcal Glomerulonephritis - UpToDateDocument21 paginiPoststreptococcal Glomerulonephritis - UpToDateHandre Putra100% (1)
- Schistosomiasis Case StudyDocument5 paginiSchistosomiasis Case Studyapi-318749549Încă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Rheumatic Heart Disease and FeverDocument3 paginiPathophysiology of Rheumatic Heart Disease and FeverDee SarajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of DiarrheaDocument3 paginiPathophysiology of DiarrheaFathur RahmatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of DiseaseDocument7 paginiPathophysiology of DiseaseYannah Mae EspineliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology Diabetic Foot UlcerDocument7 paginiPathophysiology Diabetic Foot UlcerAnnisa ClaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Renal Cell Carcinoma Risk Factors & TypesDocument1 paginăRenal Cell Carcinoma Risk Factors & TypesBobet ReñaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Renal Failure: By: Jonnel Montoya Musngi BSN 4-BDocument1 paginăPathophysiology of Chronic Renal Failure: By: Jonnel Montoya Musngi BSN 4-BKenrick Randell IbanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Malaria: How Parasite Infection Affects the BodyDocument20 paginiPathophysiology of Malaria: How Parasite Infection Affects the Bodymelia100% (1)
- PathoDocument7 paginiPathoAnonymous 87fNoO2fhVÎncă nu există evaluări
- Schistosomiasis (From Anatomy To Pathophysiology)Document10 paginiSchistosomiasis (From Anatomy To Pathophysiology)Tiger Knee100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of HyperthyroidismDocument4 paginiPathophysiology of HyperthyroidismKitty YuffieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study Acute Lymphoid LeukemiaDocument1 paginăCase Study Acute Lymphoid Leukemia2literÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bladder TumorDocument32 paginiBladder TumorAngelynChristabellaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Iron Deficiency AnemiaDocument11 paginiCase Iron Deficiency AnemiaNur Amaleeza Abdul MananÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bacls PDFDocument23 paginiBacls PDFAngelo Domingo0% (1)
- Case 052: Biliary ColicDocument4 paginiCase 052: Biliary ColicZauzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Causes and Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure (CHFDocument1 paginăCauses and Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure (CHFLance MarquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prostate CancerDocument6 paginiProstate CancerfheisanzÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 LiverDocument10 pagini1 LiverAlbino Fulgencio Santos III100% (1)
- Biliary AtresiaDocument8 paginiBiliary AtresiaBrooke MauriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Age Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat IntakeDocument3 paginiAge Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat Intakenursing concept mapsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology-Kni Ns PLZZZDocument8 paginiPathophysiology-Kni Ns PLZZZAnna Lira Manluyang MungcalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysio CRF RevisedDocument2 paginiPathophysio CRF Revisedroseanne18Încă nu există evaluări
- The Nurse Is Discharging A Client With Essential Thrombocytosis. Which of The FF Should The Nurse Include in The Discharge Instructions?Document10 paginiThe Nurse Is Discharging A Client With Essential Thrombocytosis. Which of The FF Should The Nurse Include in The Discharge Instructions?Tania NovizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DiazepamDocument2 paginiDiazepamTania NovizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hemoptysis Focal Ischemia Petechiae Hematuria: A) B) C) D)Document4 paginiHemoptysis Focal Ischemia Petechiae Hematuria: A) B) C) D)Tania NovizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Care: Nursing Students' Perspective". Please Do Not Leave Anything UnansweredDocument2 paginiCare: Nursing Students' Perspective". Please Do Not Leave Anything UnansweredTania NovizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Caring for a Child with Chronic Kidney FailureDocument23 paginiCaring for a Child with Chronic Kidney FailureTania NovizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Homework On Nursing Elective 2Document15 paginiHomework On Nursing Elective 2Tania NovizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ArtDocument5 paginiArtTania NovizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Airforce Group Y: Previous Y Ear P AperDocument14 paginiAirforce Group Y: Previous Y Ear P Aperajay16duni8Încă nu există evaluări
- Simple Future Vs Future Continuous Vs Future PerfectDocument6 paginiSimple Future Vs Future Continuous Vs Future PerfectJocelynÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evaluation of Evidence-Based Practices in Online Learning: A Meta-Analysis and Review of Online Learning StudiesDocument93 paginiEvaluation of Evidence-Based Practices in Online Learning: A Meta-Analysis and Review of Online Learning Studiesmario100% (3)
- Common Application FormDocument5 paginiCommon Application FormKiranchand SamantarayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plo Slide Chapter 16 Organizational Change and DevelopmentDocument22 paginiPlo Slide Chapter 16 Organizational Change and DevelopmentkrystelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lucy Wang Signature Cocktail List: 1. Passion Martini (Old Card)Document5 paginiLucy Wang Signature Cocktail List: 1. Passion Martini (Old Card)Daca KloseÎncă nu există evaluări
- TOPIC - 1 - Intro To Tourism PDFDocument16 paginiTOPIC - 1 - Intro To Tourism PDFdevvy anneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shakespeare's Sonnets Portray a Deeper Understanding of Authentic Love Compared to Marlowe's Idealistic PerspectiveDocument3 paginiShakespeare's Sonnets Portray a Deeper Understanding of Authentic Love Compared to Marlowe's Idealistic Perspectivemaria blascosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transportation ProblemDocument12 paginiTransportation ProblemSourav SahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ! Sco Global Impex 25.06.20Document7 pagini! Sco Global Impex 25.06.20Houssam Eddine MimouneÎncă nu există evaluări
- SCIENCE 5 PPT Q3 W6 - Parts of An Electric CircuitDocument24 paginiSCIENCE 5 PPT Q3 W6 - Parts of An Electric CircuitDexter Sagarino100% (1)
- Bias in TurnoutDocument2 paginiBias in TurnoutDardo CurtiÎncă nu există evaluări
- CSEC Geography June 2014 P1Document14 paginiCSEC Geography June 2014 P1Josh Hassanali100% (1)
- World War 2 Soldier Stories - Ryan JenkinsDocument72 paginiWorld War 2 Soldier Stories - Ryan JenkinsTaharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ax 397Document2 paginiAx 397Yingyot JitjackÎncă nu există evaluări
- Platform Tests Forj Udging Quality of MilkDocument10 paginiPlatform Tests Forj Udging Quality of MilkAbubaker IbrahimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Virtuoso 2011Document424 paginiVirtuoso 2011rraaccÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Types: Plant and Animal TissuesDocument40 paginiCell Types: Plant and Animal TissuesMARY ANN PANGANÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Butterfly Effect movie review and favorite scenesDocument3 paginiThe Butterfly Effect movie review and favorite scenesMax Craiven Rulz LeonÎncă nu există evaluări
- HRU Stowage and Float-free ArrangementDocument268 paginiHRU Stowage and Float-free ArrangementAgung HidayatullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- CARET Programme1 Bennett-1Document10 paginiCARET Programme1 Bennett-1TerraVault100% (3)
- The Free Little Book of Tea and CoffeeDocument83 paginiThe Free Little Book of Tea and CoffeeNgopi YukÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biomass Characterization Course Provides Overview of Biomass Energy SourcesDocument9 paginiBiomass Characterization Course Provides Overview of Biomass Energy SourcesAna Elisa AchilesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Canyon Colorado Electrical Body Builders Manual Service Manual 2015 en USDocument717 paginiCanyon Colorado Electrical Body Builders Manual Service Manual 2015 en USAlbertiniCongoraAsto100% (1)
- Khandelwal Intern ReportDocument64 paginiKhandelwal Intern ReporttusgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study Habits Guide for Busy StudentsDocument18 paginiStudy Habits Guide for Busy StudentsJoel Alejandro Castro CasaresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adam Smith Abso Theory - PDF Swati AgarwalDocument3 paginiAdam Smith Abso Theory - PDF Swati AgarwalSagarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simptww S-1105Document3 paginiSimptww S-1105Vijay RajaindranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Puberty and The Tanner StagesDocument2 paginiPuberty and The Tanner StagesPramedicaPerdanaPutraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Forouzan MCQ in Error Detection and CorrectionDocument14 paginiForouzan MCQ in Error Detection and CorrectionFroyd WessÎncă nu există evaluări