Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Intussusception
Încărcat de
bladimer_riaDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Intussusception
Încărcat de
bladimer_riaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Intussusception
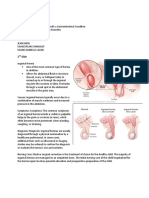
Is a condition that develops when one part of the intestine folds into itself like a telescope. It most commonly occurs between the lower part of the small intestine and the beginning of the large intestine. The cause may be idiopathic (cause is unknown), although some viral and bacterial infections of the intestine may possibly contribute to intussusception in infancy. In older children and adults, the causes are believed to be due to polyps or tumors. It occurs commonly in infant ages 5 to 10 months and rarely in older children and adults. Boys develop the condition two times more often than girls. Assessment: 1. Recurring episodes of severe abdominal pain; legs drawn up, child is inconsolable. 2. Blood in stool or later currant jelly stools containing sloughed mucosa, blood, and mucus. 3. Vomiting 4. Dances sign sausage like mass palpable in abdomen. 5. Abdominal distention, bowel sound diminished absent or high pitch. Diagnostic evaluation 1. X-ray of abdomen 2. Barium enema 3. Ultrasonogram/ultrasound 4. Color Doppler sonography. Nursing intervention 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Monitor IV fluids. Be alert for respiratory distress. Monitor vital signs, urine output, pain, and distention preoperatively and postoperatively. Observe infants behavior. Explain to the parents the cause of pain. Administer analgesic as prescribed. Maintain NPO status as ordered. Insert NGT if ordered. Continually reassess condition. After reduction by hydrostatic enema, monitor vital signs and general condition. Encourage follow up care. Provide anticipatory guidance for developmental age of child.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Dysphagia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsDe la EverandDysphagia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- IntussusceptionDocument4 paginiIntussusceptionlovethestarÎncă nu există evaluări
- HirschsprungDocument4 paginiHirschsprungMrmonstrosityÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intussusception PresentationDocument9 paginiIntussusception PresentationAme NasokiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SCRIPT FOR INTUSSUSCEPTIONDocument5 paginiSCRIPT FOR INTUSSUSCEPTIONRAZELLE JOY CATIAN RODRIGUEZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intussuseption and Hirschprung's DiseaseDocument5 paginiIntussuseption and Hirschprung's DiseaseAris Magallanes100% (2)
- Maternal Finals ReportDocument21 paginiMaternal Finals ReportLaude Sebastian DanÎncă nu există evaluări
- INTUSSUSCEPTIONDocument3 paginiINTUSSUSCEPTIONJanine Karla OrcaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Meeting IHPS 2017-10-30Document28 paginiMeeting IHPS 2017-10-30wawa chenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter X.4. Intussusception: Case Based Pediatrics For Medical Students and ResidentsDocument5 paginiChapter X.4. Intussusception: Case Based Pediatrics For Medical Students and ResidentsNawaf Rahi AlshammariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Key signs and symptoms of infantile pyloric stenosisDocument6 paginiKey signs and symptoms of infantile pyloric stenosisNeil AlviarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Abdominal Pain in ChildrenDocument6 paginiAcute Abdominal Pain in ChildrenDeving Arias RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute appendicitis in children: Key differences from adultsDocument6 paginiAcute appendicitis in children: Key differences from adultsLidiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ROUNDWORM, WHIPWORM, HOOKWORM AND PINWORM: CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS, DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENTDocument6 paginiROUNDWORM, WHIPWORM, HOOKWORM AND PINWORM: CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS, DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENTKrystal Jane SalinasÎncă nu există evaluări
- IntussusceptionDocument60 paginiIntussusceptionAhmad Abu KushÎncă nu există evaluări
- AppendicitisDocument4 paginiAppendicitisFebriyana SalehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Congenital AnomaliesDocument10 paginiCongenital Anomaliesربيع ضياء ربيعÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Abdominal Pain InInfants and ChildrenDocument14 paginiAcute Abdominal Pain InInfants and Childrenemergency.fumcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Afrisya Bimo Siwendro Marisha Yadian Putri Preceptor: DR - Liza Nursanty, Spb. FinacsDocument32 paginiAfrisya Bimo Siwendro Marisha Yadian Putri Preceptor: DR - Liza Nursanty, Spb. FinacsirmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- What is amniotic fluid and its importanceDocument8 paginiWhat is amniotic fluid and its importancetuhinsubhra1Încă nu există evaluări
- Intus Su CeptionDocument26 paginiIntus Su Ceptiongallegomarjorie16Încă nu există evaluări
- In Partial Fulfillment For The Requirements in R.L.E: Submitted By: Elaine Blanche R. GonzalezDocument6 paginiIn Partial Fulfillment For The Requirements in R.L.E: Submitted By: Elaine Blanche R. GonzalezBlanche GonzalezÎncă nu există evaluări
- INTUSSUSCEPTION2Document3 paginiINTUSSUSCEPTION2Jade RubyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gastroschisis - ClinicalKeyDocument33 paginiGastroschisis - ClinicalKeyjpma2197Încă nu există evaluări
- Gastric DisordersDocument135 paginiGastric DisordersEsmareldah Henry SirueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Causes, Types, Symptoms and Treatment of PeritonitisDocument22 paginiCauses, Types, Symptoms and Treatment of Peritonitis28 manan patelÎncă nu există evaluări
- IntussusceptionDocument24 paginiIntussusceptionOjambo Flavia100% (1)
- Abdominal Pain in ChildrenDocument65 paginiAbdominal Pain in ChildrenizeanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aklan State University Nursing Readings on Pyloric StenosisDocument5 paginiAklan State University Nursing Readings on Pyloric Stenosisensoooooooooo100% (1)
- Acute Appendicitis PaedsDocument5 paginiAcute Appendicitis PaedsemmaazizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Constipation in Childhood. An Update On Evaluation and ManagementDocument9 paginiConstipation in Childhood. An Update On Evaluation and ManagementResiden KardiologiÎncă nu există evaluări
- About IntussusceptionDocument6 paginiAbout IntussusceptionErwin OcampoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study of Ruptured Appendicitis With Localize Peritonitis (Final)Document76 paginiCase Study of Ruptured Appendicitis With Localize Peritonitis (Final)DRJC82% (22)
- Case Presentation: Ascariasis: Mrs. Lailanie Evangelista DotimasDocument10 paginiCase Presentation: Ascariasis: Mrs. Lailanie Evangelista DotimasRodelen MarañoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Appendicitis in Children - Children's Health Issues - MSD Manual Consumer VersionDocument4 paginiAppendicitis in Children - Children's Health Issues - MSD Manual Consumer Version2110053Încă nu există evaluări
- Activity # 2 - Santos, Aira Kristelle M.Document9 paginiActivity # 2 - Santos, Aira Kristelle M.Ai MendozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Omphalocele: 1 Baskaran NDocument5 paginiOmphalocele: 1 Baskaran Nதாசன் தமிழன்Încă nu există evaluări
- MiniOSCE Surgery 1Document329 paginiMiniOSCE Surgery 1Mohammad BanisalmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hirschsprung DiseaseDocument14 paginiHirschsprung DiseaseFlordelyn Anuales100% (2)
- Oesophageal Atresia by GabriellaDocument7 paginiOesophageal Atresia by GabriellaGabrielleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dr. Lilia Dewiyanti, Spa, Msi - MedDocument12 paginiDr. Lilia Dewiyanti, Spa, Msi - MedLa Ode RinaldiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Process For A Client With Molar Pregnancy (H-Mole)Document24 paginiNursing Process For A Client With Molar Pregnancy (H-Mole)api-370148995% (19)
- Pedia GiDocument10 paginiPedia GiCam IbardolasaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project 101Document70 paginiProject 101Joanne Bernadette AguilarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indirect Inguinal Hernia FINALDocument6 paginiIndirect Inguinal Hernia FINALJonalyn TumanguilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bishaw Assigment of GI DisorderDocument98 paginiBishaw Assigment of GI DisorderRas Siko SafoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Urinary Tract Infection: Mentor DR - SaralaDocument53 paginiUrinary Tract Infection: Mentor DR - SaralaMimi Suhaini SudinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tugas Mata Kuliah Bahasa Inggris: Dosen Pembimbing: A. M. Aziz, M. PDDocument4 paginiTugas Mata Kuliah Bahasa Inggris: Dosen Pembimbing: A. M. Aziz, M. PDMega Safira MahardiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pediatric and Adolescent Gynecologic Emergencies 2023Document13 paginiPediatric and Adolescent Gynecologic Emergencies 2023Paola LecuonaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Congenital Diseases: Name: Bernadette Anonoy Date: February 3, 2012 Year and Group: IV - Einstein RatingDocument7 paginiCongenital Diseases: Name: Bernadette Anonoy Date: February 3, 2012 Year and Group: IV - Einstein RatingBernadette Bithao AnonoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bovine Abortion Causes and DiagnosisDocument11 paginiBovine Abortion Causes and DiagnosisDio DvmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mal RotationDocument13 paginiMal RotationkavyarkrnagarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pyloric StenosisDocument16 paginiPyloric StenosisHelen McClintockÎncă nu există evaluări
- GI Bleeding PDFDocument9 paginiGI Bleeding PDFTia Amalia Puti RenaeryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digestive DiseasesDocument10 paginiDigestive Diseaseskate_5182178Încă nu există evaluări
- Bedah - Prekas AppendisitisDocument15 paginiBedah - Prekas AppendisitisALfianca Yudha RachmandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute AppendicitisDocument9 paginiAcute AppendicitisSyarafina AzmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- DR NITA MARIANA SPBA IntussusceptionDocument50 paginiDR NITA MARIANA SPBA IntussusceptionHenny Apriani ARÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vomiting in The Newborn InfantDocument5 paginiVomiting in The Newborn Infantdoctordilafroza100% (1)
- IntussusceptionDocument1 paginăIntussusceptionbladimer_riaÎncă nu există evaluări
- LEPROSY Research PaperDocument7 paginiLEPROSY Research Paperbladimer_riaÎncă nu există evaluări
- LeprosyDocument13 paginiLeprosybladimer_riaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course Descriptions - Nursing: NUR3000WI Introduction To Professional NursingDocument5 paginiCourse Descriptions - Nursing: NUR3000WI Introduction To Professional Nursingbladimer_riaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Ethical PrinciplesDocument5 paginiBasic Ethical Principlesbladimer_riaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Exam Template FormatDocument2 paginiPhysical Exam Template Formatbladimer_ria100% (1)
- Principles in BioethicsDocument2 paginiPrinciples in Bioethicsbladimer_riaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Competency StandardsDocument8 paginiCompetency Standardsbladimer_riaÎncă nu există evaluări
- EPI Vaccines HandoutsDocument14 paginiEPI Vaccines HandoutsBurhan uddin100% (11)
- Final PRC Evaluation ToolDocument9 paginiFinal PRC Evaluation Toolbladimer_riaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application LetterDocument3 paginiApplication Letterbladimer_riaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study of Illness Condition Assessment Organ Involved Normal Function Pathophysiology AnalysisDocument2 paginiStudy of Illness Condition Assessment Organ Involved Normal Function Pathophysiology Analysisbladimer_riaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ParentingDocument4 paginiParentingbladimer_riaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Common Instruments in ORDocument3 paginiCommon Instruments in ORbladimer_ria100% (1)
- Saran ADocument4 paginiSaran Abladimer_riaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Myocardial Infarction (MI)Document10 paginiMyocardial Infarction (MI)bladimer_riaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gordon's 11 Functional Health PatternDocument3 paginiGordon's 11 Functional Health Patternbladimer_ria100% (3)
- Gordons - SampleDocument2 paginiGordons - Samplebladimer_riaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of HeadacheDocument16 paginiTypes of Headachebladimer_riaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1896 (Cry Freedom) - Aurelio S. AlveroDocument1 pagină1896 (Cry Freedom) - Aurelio S. Alverobladimer_ria78% (18)
- Ectopic Pregnanc Y Ectopic Pregnanc YDocument26 paginiEctopic Pregnanc Y Ectopic Pregnanc Ybladimer_riaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Health Teaching Plan - New FormatDocument1 paginăHealth Teaching Plan - New Formatbladimer_riaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ectopic Pregnanc Y Ectopic Pregnanc YDocument26 paginiEctopic Pregnanc Y Ectopic Pregnanc Ybladimer_riaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Survey Tool - WmsuDocument3 paginiSurvey Tool - Wmsubladimer_riaÎncă nu există evaluări