Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Ultrasound Flash
Încărcat de
Muh IqbalDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Ultrasound Flash
Încărcat de
Muh IqbalDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Distinguishing AMLs characteristics tend to have between acousticAMLs shadowing. and hyperechoic Hyperechoic RCCs?
RCCs may have cystic elements, calcifications, or hypoechoic Caudate lobe IVC drains via small into veins what separate vein? from hepatic veins. Caudate veins function as collaterals in Budd-Chiari syndrome. Distinguishing Fluid ultrasound collections features displace ofand peritoneal distort fluid adjacent collections structures. versus Ascites simple conforms ascites?to adjacent structures. Causes of fatty Obesity. liver infiltration? Alcohol abuse. TPN. Diabetes. Malnutrition. Steroid use. Hepatic toxins. Chemotherapy. Usefull clueParathyroid in located parathyroid adenomas are adenomas medial and to carotid lympharteries. nodes? Lymph nodes are usually lateral to carotids. Baker's cyst, Neck most that characteristic extends between diagnostic medial feature head at of Ultrasound? gastrocnemius and semimembranosus tendon. Syndrome caused Kasaback-Merritt by hepatic hemangioma syndrome. that sequesters platelets? What markers Pseudocyst are elevated aspirate in a pancreatic elevated amylase. pseudocyst Neoplastic aspirate aspirate compared elevated to a pancreatic carcinoembryonic cystic neoplasm antigen.aspirate? Funiculocele, Spermatic what is it? cord hydrocele. Difference between Replaced: a Artery replaced arises andfrom an accessory an anomalous artery? source (1 anomalous artery). Accessory: one of atleast two arteries ar Which gallstones Cholesterol can float? stones can float in high specific gravity bile. What patient's Symptomatic benefit from patients an carotid with stenosis endarterectomy? >70%. Best study to Sulfur identify colloid a splenule? scan or heat-damaged tagged RBC scan. Reversed flow Central in the venous internal obstruction mammary veins indicates? Solid renal neoplasms? RCC. TCC. Renal medullary carcinoma. Renal sarcoma. Metastases. Lymphoma. Sickle cell trait Renal and medullary solid renal carcinoma. neoplasm? When do hematomas Hematoma: and Immediately lymphoceles after appear transplant in renal Lymphocele: transplant patients? 1 to 2 months posttransplant Most common Metastases. cause of calcified liver tumor? Morton neuroma? Benign mass of plantar digital nerves of the foot. Which side Left. is subclavian steal more common on? What is normal 20 cm/s. portal vein velocity? Pancreatic neoplasm Macrocystic almost neoplasm. exclusively seen in women? RCC stage when At least tumor IIIa invades renal vein or IVC? 2 common liver Preportal. locations Anterior for focal left fatty lobe adjacent infiltration? to ligamentum teres. Resistive index RI = (RI) (S-D)/S formula? Parenchymal <0.7 organ normal resistive index (RI)? Midline prostate Utricle cysts? cyst. Mullerian cyst. What replaced Replaced arteryleft canhepatic be seen artery. coursing through the ligamentum venosum? Mucinous macrocystic Body and tail pancreatic of pancreas. neoplasm, common locations? Distinguish Classic: between > classic 5 microliths and limited on 1 view. microlithiasis Limited: less of testis? than 5 on 1 view. Multilocular Young cysticboys nephroma, (3 months population? - 4 years). Adult women (>30 years old). 2 most common Ganglion masses cyst. in Giant the hand? cell tumor. Does a giant No, cell ittumor arrised move fromwith the tendon the associated sheath not tendon? the tendon. TCC, most common Bladder > anatomy renal pelvis involved? > ureter. Pheochromocytoma's 10% malignant. 10% rule? 10% extra-adrenal. 10% bilateral. 10% associated with MEN. Vascular pattern Spokewheel of FNH pattern. at ultrasound? Most definitive Sulfur means colloid of scanning. diagnosing FNH? Chronic calcific Alcoholic pancreatitis abuse, is not caused gallstones. by? Focal fatty sparing Aroundwithin the gallbladder. the liver commonly At portal bifurcation. occurs where? What is Page Renal kidney? subcapsular hematoma causing hypertension. Effect of renal Normal vein thrombosis to increased on RI. resistive index (RI) of renal artery? Horseshoe kidney Urinary predispositions? obstruction. Stone formation. Rrenal trauma. Questionable increase risk of Wilm's tumor. Upper limit 180-200 of normal cm/s. renal artery velocity? Bile duct blood Hepatic supply? artery. In liver transplant hepatic artery thrombosis bile ducts may form strictures due to ischemia. Common factors Lver metastases. that render Peripancreatic pancreatic cancers vessel nonresectable? invasion. Peritoneal spread. Ultrasound Blunt signs of tendon complete tip (longitudinal tendon rupture? view). Mass (transverse view). Refractive shadowing. Nonvisualization. Loss of fibril Sonographic Anechoic signs of full-thickness or hypoechoic rotator defect.cuff Focal tear? superficial contour abnormality. Compressibility. Nonvisualization.
Characteristics Complex of pseudoaneurysms fluid collection. on Single ultrasound? of multiple loculations. Visible pulsations on gray-scale imaging. Internal luminal fl Characteristics Usually of iatrogenic located below arteriovenous femoral artery fistulas bifurcation. at ultrasound? Perivascular tissue vibration. Low-resistance flow in supplying ar Extremity artery High-resistance waveform? flow. Typically triphasic waveform: Antegrade systole, retrograde early diastole, antegrade in mid Extremity venous Respiratory waveform? phasicity. Variable cardiac related pulsatility. Factors thatExtratesticular. decrease chance Nonpalpable. of scrotal malignancy? Simple cystic appearance. No detectable vascularity. Factors thatIntratesticular. increase chance Palpable. of scrotal Solid malignancy? or complex cyst. Detectable internal vascularity. Germ cell tumor Seminoma. list? Embryonal cell carcinoma. Teratoma. Choriocarcinoma. Yolk sac. Mixed germ cell. Stromal testicular Leydig tumors? cell tumor. Sertoli cell tumor. Other non-germ Lymphyoma/leukemia. cell and non-stromal Metastases. testicular Epidermoid neoplasms? cyst. Testicular lesions Focal orchitis. mimicking Focal tumors? atrophy/fibrosis. Infarcts. Abscess. Hematoma. Contusion. Sarcoid. Tuberculosis. Adrenal rest Causes of enlarged Orchitis.hypoechoic Torsion. Lymphoma. testis? Seminoma. Of the four Increased causes of enlarged flow: Orchitis. hypoechoic Lymphoma. testes, Seminoma. which have Decreased increased/decreased (torsion). blood flow? Primary neoplasms TCC. Adenocarcinoma. of the bladder?SCC. Pheochromocytoma. Causes of bladder Rectum. wall Prostate. lesions Cervix. from adjacent Uterus. neoplasms? Causes of bladder Diverticulitis. wall lesions Crohn's from disease. inflammation PID. Appendicitis. from adjacent organs? Other bladder Ureteroceles. wall lesions? Urachal cyst. Cystitis cystica. Endometriomas. Fistulas. Malakoplakia. Leukoplakia. Tuberculosis. Shis Frequency of Peripheral prostate zone cancer 75%. perTransitional anatomical zone? zone 20%. Central zone 5% Percentage Hypoechoic of prostate cancers 70%. Hyperechoic/mixed that are hypoechoic? 30%. Sonographic Homogeneous characteristics and of seminoma? hypoechoic. Most common Spermatocele. scrotal mass? Causes of hydroceles? Idiopathic (most common). Tumors. Torsion. Inflammatory disorders. Trauma. Varicocele percentage Left-sided 85%. on the Right-sided left? 15%. Scrotal mass Epidermoid with peripheral cyst. calcification and/or onion peel appearance? Testicular microlithiasis Isolated microlithiasis and germ increases cell tumor risk relevance? of germ cell cancer. Annual physical exam recommended. Besides absent Enlarged bloodhypoechoic flow, othertestis. signs of Torsion testicular knot. torsion? Reactive hydrocele. Scrotal wall thickening. Distinguishing Blood characteristic clot is mobile. of blood clot from bladder cancer on ultrasound? After injection 35 m/s of vasoactive substance, normal penile Doppler should have a deep cavernosal velocity that exceeds? Plaque formation Peyronie's in the disease. tunica albuginea of the corpora cavernosa? Sonographic Decreased signs of acute or heterogeneous pancreatitis? pancreatic echogenicity. Pancreatic enlargement. Peripancreatic fluid collection. Per Complications Pseudocyst of Pancreatitis? formation. Bile duct obstruction. Pancreatic abscess. Venous thrombosis. Pseudoaneurysm. Causes of solid Carcinoma. hypoechoic Focal pancreatic Pancreatitis. masses? Lymphoma. Metastases. Islet cell tumors. Thrombosed aneurysm. Pancreatic cystic Pseudocyst. lesions? Macrocystic (mucinous) tumor. Microcystic (serous) tumor. Intraductal papillary mucinous tumor. So Normal pancreatic Less than duct or should equal to mearsure? 3 mm, but can enlarge with age. Sonographic Pancreatic signs of chronic calcification. pancreatitis? Ductal dilation. Ductal irregularity. Parenchymal atrophy. Pancreatic and TRUE islet cell tumors are generally hypoechoic. T/F? Pancreatic neoplasm Microcystic that adenoma. contains serous fluid, consists of multiple small cystic elements, and is benign? Pancreatic neoplasm Macrocystic that tumors. contains mucinous fluid, large cystic elelements, thick septations, solid elements, and can be malign Solid spleenHemangiomas. lesions? Hamartomas. Lymphomas. Metastases. Infarcts. Abscesses. Sarcoidosis. Granulomas. Extramedull Causes of splenomegaly? Heart failure. Portal hypertension. Leukemia. Lymphoma. Hepatitis. Mononucleosis. Generalized infections. Hemo Lymphoma Focal. and leukemia Multifocal. sonographic Diffuse. Almost appearance always inhypoechoic. the spleen? Multiple small Granulomatous calcificationsdisease. within the Histoplasmosis. spleen? Tuberculosis. The age of pregnancy 1st day of LMP/ definition? When is theGestational earliest, onsac TV 5 US, wks. that Yolk gestational sac 5.5 wks. sac,Embryo yolk sac, 6 and wks. embryo can be seen? What structure, Yolk sac. if seen, can confirm a IUP even before the embryo is identified? What is better 1st at trimester estimating CRLgestational (crown rump age length). than LMP? 2nd trimester biparietal diameter (+/- 1 wk) LMP (+/- 2 wks) Normal gestational Correct positioning sac characteristics within uterus. on US? Double decidual sac DDS. Continuous hyperechoic rim > 2mm. Spherical or ovoi 2 hyperechoic DDS, lines Double surrounding decidual asign hypoechoic closed endometrial canal?
How does seeing Its absence a DDSis help more in suggestive 1st trimester of US? miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy. Does not exclude IUP. At what CRL 5is mm. heart activity expected? By 5 wks the > embryonic 120. heart rate should be? After 3 wks 120 the embryonic - 180 heart rate should be? At what Beta-hCG 2000 IU/L level should an intra-uterine gestation sack be seen on TV US? In early pregnancy Every 2 the days. Beta-hCG level should double how often? Differential IUP. diagnosis Miscarriage. of positive Ectopic pregnancy pregnancy. test? Risk factorsAbnormal for ectopic fallopian pregnancy? tubes. Previous ectopic pregnancy. IUD. Fertility medication. In-vitro fertilization. Beta-hCG level Slower. in an ectopic pregnancy patients increases slower or faster than an IUP? Where can an Cornua. ectopic Cervix. pregnancy occur within the uterus? Define an heterotopic Concomitant pregnancy? intrauterine and extrauterine pregnancy. What is a pseudogestational Collection of fluidsac? or decidual cast within endometrial canal or thickened endometrium in an ectopic pregnancy. With a positive Gestation pregnancy sac in test, ectopic give position 5 findings Adnexal that have mass positive with yolk predictive sac or embryo. value for Tubal ectopic ring pregnancy? appearing as an empty gestatio Common causes Inflammation. of bowel Infection. wall thickening? Neoplasm. Ischemia. Edema. Hemorrhage. Sonographic Diameter signs of appendicitis? greater than 6 mm. Lack of compressibility. Inflamed, echogenic periappendiceal fat. Hyperemia. Appen Causes of peritoneal Metastases. masses? Tuberculosis. Mesothelioma. Pseudomyxoma peritonei. Omental infarct. Causes of abdominal Metastases. wall Lipoma. masses? Hernia. Hematoma. Abscess. Seroma. Desmoid. Endometriosis. Sarcoma. Lymphoma. Features of 95% Abdominal infrarenal. Aortic Majority Aneurysms? are fusiform. Mural thrombus common with large aneurysm. Surgery considered when > Common causes Adenoma. of adrenal Metastases. masses? Pheochromocytomas. Primary carcinoma. Lymphoma. Myelolipoma. Hemorrhage. Pseudokidney Extensive sign? mesenteric adenopathy. Distinguishing Tumor feature thrombus of tumor has thrombus internal vascularity. from blood clot? Ultrasound Myelolipomas. is not good at characterizing most adrenal masses, except for? Benign characteristics Cystic elements. of thyroid Hyper nodules? or isoechoic. Eggshell calcification. Inspissated colloid. Malignant characteristics Entirely solid. Hypoechoic. of thyroid nodules? Microcalcifications. Associated cervical adenopathy. Characteristics Solid. of Hypoechoic. parathyroid adenomas Oval shape. on Hypervascular. ultrasound? Posterior to thyroid. Medial to carotid. Locations of Low ectopic neck. parathyroid Mediastinum. adenomas? Retrotracheal/retroesophageal. Carotid sheath. Intrathryoidal. Characteristics Obliteration of Neoplastic of echogenic Neck Lymph hilum. Nodes? Long-axis to short-axis ration less than 1.5. Cystic changes. Microcalcifications. Differences ICA: between Larger. ICA Posterolateral and ECA? location. No branches. Low resistance wavefore. Negative temporal tap. ECA: Smaller ICA peak systolic Normal velocities less than and 125cm/s. associated 50-69% stenoses? stenosis 125-230 cm/s. >70% stenosis >230 cm/s. Near occlusion variable. Com Midline complex Thyroglossal lesions duct that are cyst. usually intimately associated with the hyoid bone? Most common Parathyroid cause of adenoma. hyperparathyroidism? Carotid artery >50% flow stenosis. velocities and ratios start to increase at what stenotic level? Sonographic Heterogenous characteristics plaques of unstable with focal carotid hypoechoic artery plaques? regions. Causes of polyhydramnios? Idiopathic. Maternal (diabetes). Fetal (Anomalies, Hydrops). Findings in anencephaly Absence of normal calvarium and brain above orbits. Residual dysmorphic brain may be seen, called angiomatous Moderate to CNS. marked GI. Fetal polyhydramnios hydrops. is often associated with what fetal anomalies? Fetal head measurements Within 1.2 weeks (BPD up and to 24 HC) weeks. are accurate Accuracy for decreases gestational in third age until trimester. when? Fetal lateralMeasured ventrical evaluation at atria. Less and than measurement? or equal to 10 mm. Choroid plexus occupying 60%. Small or dangling choroid plexus m Regardless of Thin hydrocephaly cortical mantle. severity Hydrancephaly there is always maya mimic this but instead is destroyed brain. Holoprosencephaly Midline developmental anomaly, three forms (alobar, semilobar, lobar). Relatively common Ethmoidal anterior sinus region. cephalocele Banana shaped Neural cerebellum? tube defect with downward displacement of cerebellum. Enlarged cisterna Dandy-Walker magna with abnormality. splaying of cerebellar hemispheres and a vermian defect? A nuchal fold 6 mm. measurement above _____ is a marker for trisomy 21? Choroid plexus Normal cyst or possibilities? other chromosomal abnormalities such as trisomy 18. Secondary abnormalities Lemon sign (least of the specific). skull that Banana occursign. withHydrocephalus. spinal defects? Large aorta Tetralogy in fetal ultrasound? of Fallot. Truncus arteriosus.
Small aorta Coarctation. in fetal ultrasound? Hypoplastic left heart. Small pulmonary Hypoplastic artery right in fetal heart. ultrasound? Ebstein's anomaly with pulmonary hypoplasia. Fetal hydrops Immune generalities and nonimmune causes. Excessive fetal body water. Fluid in serous cavities, skin thickening, placental en Fetal pericardial 2 mm effusions in thickness. are normal if isolated and measure less than ____? Fetal cystic Bochdalek thoracic masses congenital diaphragmatic hernias. Type I and II cystic adenomatoid malformations. Bronchogenic cysts Fetal solid thoracic Morgagni masses and some Bochdalek congenital diaphragmatic hernias. type III CAMs. Bronchopulmonary sequestration Most common CDH, fetal Left-sided intrathoracic, posterolateral extracardiac hernia abnormality (Bochdalek). Enlarged hyperechoic Laryngeal atresia. fetal lungs, a finding for this rare entity Most common Hydrops cause and of enlarged infections. fetal liver? Most common Growth cause restriction of small fetal liver? Fetal pseudoascites? Hypoechoic band in upper abdomen Umbilical vein Normal varix outcome implications? or fetal hydrops. Structural abnormalities. Aneuploidy. Intrauterine demise. Fetal meconium Impaction ileus?of thick meconium within terminal ileum. Proximal bowel dilation may not occur until 3rd trimester. Ca Fetal meconium Intraperitoneal peritonitis calcifications. findings Meconium pseudocysts. Bowel dilation. Ascites. Polydyramnios. Hyperechoic If fetal equal bowel to or greater than bone brightness it may be abnormal. Associations: Cystic fibrosis. Chromosomal abnor Most common Omphalocele. fetal anterior Gastroschisis. wall defects Elevated alpha-fetoprotein. Fetal omphaloceles Defects of mid abdomen. Covered by thin amnioperitoneal membrane. Large type contains liver, usually stomach Fetal gastroschisis Paraumbilical, usually right lower quadrant. No covering membrane. Protruding bowel floats freely in amniotic flu Fetal cystic Mesenteric abdominal masses cyst. Duplication cyst. Urachal cysts. Ovarian (female). Common third Spontaneous trimester cause rupture ofof oligohydramnios membranes. Common second Bilateral trimester renal abnormalit. causes of oligohydramnios Urinary bladder obstruction (posterior urethral valves). Keyhole fetal Dilated bladder bladder configuration and proximal urethra due to posterior urethral valves. Enlarged hyperechoic Infantile polycystic fetal kidneys kidney with disease oligohydramnios? (ARPKD). Bilateral fetal Urethral renal abnormalities? obstruction (posterior urethral valves). Renal agenesis. Infantile polycystic kidney disease. Bilateral UPJ o Distinguishes Doppler dilated distinguishes fetal ureter from from bowel blood and vessel. blood Real vessel? time imaging distinguishes bowel (peristalsis). Fetal renal dysplasia Increasedfindings renal cortex echogenicity (greater than liver). Subcortical cysts Common fetal Multicystic unilateral dysplastic renal anomalies? kidney. Reflux. UPJ obstruction. If obstruction Duplicated is identified kidney in upper with ectopic but not uretrerocele lower pole offrom kidney, upper what pole should moiety. be considered? Four major Heterozygous fetal skeletal anomalies, achondroplasia. whichOsteogenesis account for 2/3 imperfecta. or all dysplasias? Achondrogenesis. Thanatophoric dysplasia Heterozygous Femur achondroplasia length falls below fetal US 10th findings? percentile before 28 weeks' gestation. Osteogenesis Skeletal imperfecta deformities fetal US (fractures findings?and abnormal bowing) or demineralization. Achondrogenesis Severe fetal shortening US major of finding? limbs (micromelic pattern). Varying degrees of demineralization and chest narrowing. Thanatophoric Normal dysplasia bone fetal brightness. US findings? Severe limb shortening and chest narrowing. Pronounced polyhydramnios. Amniotic band Skeletal syndrome deformities at fetal are US? asymmetric and atypical in appearance compared to skeletal dysplasias. Subchorionic Uncomplicated versus retroplacental subchorionic hemorrhages, hemorrhages prognosis? are usually benign. Retroplacental hemorrhages can cause considerabl Placenta previa Low-lying classification? (near). Marginal (touching). Complete (covering cervical os). Vasa previa? Presence of fetal (not placental) blood vessels that cross the internal cervical os (marginal or velamentous cord in Cervical incompetence Shortening of USendocervical findings? length to less than 2.5 cm, with or without cervical funneling. Complete (classic) Noninvasive hydatidiform (85%). Locally mole features? invasive (13%). Metastatic (choriocarcinoma 2%). Enlarged uterus filled with hyperecho
ents, calcifications, or hypoechoic halo. erals in Budd-Chiari syndrome. jacent structures. Chemotherapy. ateral to carotids.
ryonic antigen.
ory: one of atleast two arteries arises from an anomalous source (2 arteries present, 1 artery anomalous).
of Wilm's tumor. strictures due to ischemia.
ng. Nonvisualization. Loss of fibrillar architecture. Fluid collection. sibility. Nonvisualization.
y-scale imaging. Internal luminal flow on color Doppler. To and fro flow in the neck. ow-resistance flow in supplying artery near fistula. High-velocity flow at site of communication. Turbulent and/or arterialized flow in drain e early diastole, antegrade in mid diastole, absent flow in end diastole.
xed germ cell.
arcoid. Tuberculosis. Adrenal rest tissue.
kia. Leukoplakia. Tuberculosis. Shistosomiasis.
ecommended.
Peripancreatic fluid collection. Perivascular fluid collection. Periduodenal fluid collection. Perirenal fluid collection. bosis. Pseudoaneurysm. bosed aneurysm. ctal papillary mucinous tumor. Solid and papillary epithelial neoplasm. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. von Hippel-Lindau
oidosis. Granulomas. Extramedullary hematopoiesis. osis. Generalized infections. Hemolytic anemias. Glycogen storage disease. Malaria. Myelofibrosis.
wk) LMP (+/- 2 wks) hoic rim > 2mm. Spherical or ovoid shape. Growth of > 1.2 mm/day.
In-vitro fertilization.
etrium in an ectopic pregnancy. ng appearing as an empty gestation sac. Complex or solid adnexal mass. Moderate amount of intraperitoneal fluid.
ppendiceal fat. Hyperemia. Appendicolith. Adjacent fluid collection.
osis. Sarcoma. Lymphoma. rysm. Surgery considered when >5 cm. AP diameter measured on sagittal images. Transverse diameter measured on coronal images. Myelolipoma. Hemorrhage.
ic changes. Microcalcifications. gative temporal tap. ECA: Smaller. Anteriomedial location. Branches. High resistance waveform. Positive temoral tap. cm/s. Near occlusion variable. Complete occlusion no flow.
may be seen, called angiomatous stroma.
Small or dangling choroid plexus may indicate ventriculomegaly.
vities, skin thickening, placental enlargement, polyhydramnios.
alformations. Bronchogenic cysts. Duplication cysts. Pulmonary sequestration. Bronchopulmonary sequestration.
erine demise. y not occur until 3rd trimester. Causes: Mechanical intestinal obstruction. Cystic fibrosis. olydyramnios. ystic fibrosis. Chromosomal abnormalities. Growth restriction. Swallowed blood. Perinatal death.
pe contains liver, usually stomach and bowel. Small type contains only bowel located at the base of umbilical cord. Associations: Structur bowel floats freely in amniotic fluid. No associated anomalies or abnormal karyotype.
stic kidney disease. Bilateral UPJ obstruction. (peristalsis).
atophoric dysplasia
ation and chest narrowing. ed polyhydramnios. eletal dysplasias. morrhages can cause considerable fetal and, infrequently, maternal problems.
(marginal or velamentous cord insertions or with succenturiate lobes).
arged uterus filled with hyperechoic tissue (multiple cysts). No fetus present.
nt and/or arterialized flow in draining vein near fistula.
idney disease. von Hippel-Lindau disease. Cystic fibrosis. Aneurysm/pseudoaneurysm.
oneal fluid.
measured on coronal images.
e temoral tap.
bilical cord. Associations: Structural abnormalities and chromosomal abnormalities.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- Magnesium L Threonate For Depression and Anxiety PDFDocument6 paginiMagnesium L Threonate For Depression and Anxiety PDFRocco LamponeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answers To Competency Assessment SectionDocument16 paginiAnswers To Competency Assessment Sectionapi-209542414100% (1)
- YuzurtDocument2 paginiYuzurtFranco Ascari100% (1)
- Pulverizers: By: G. RamachandranDocument140 paginiPulverizers: By: G. Ramachandranshivshankar prajapatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heat Shrink CoatingDocument5 paginiHeat Shrink CoatingMekhmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiovascular Molecular MR ImagingDocument14 paginiCardiovascular Molecular MR ImagingMuh IqbalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acceleration Deceleration Sport RelatedDocument4 paginiAcceleration Deceleration Sport RelatedMuh IqbalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acceleration Deceleration Sport RelatedDocument4 paginiAcceleration Deceleration Sport RelatedMuh IqbalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mid Face Fractures 1Document12 paginiMid Face Fractures 1Muh IqbalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Use of Three Dimensional Computerized Tomography Reconstruction in Complex Facial TraumaDocument7 paginiUse of Three Dimensional Computerized Tomography Reconstruction in Complex Facial TraumaMuh IqbalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparison of Ultrasonography and ConventionalDocument6 paginiComparison of Ultrasonography and ConventionalMuh IqbalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ultrasound To Detect HaemothoraxDocument2 paginiUltrasound To Detect HaemothoraxMuh IqbalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guidelines For The Diagnosis and Treatment of Thoracic TraumatismDocument9 paginiGuidelines For The Diagnosis and Treatment of Thoracic TraumatismMuh IqbalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jeremy Fernando (2011) : ST NDDocument2 paginiJeremy Fernando (2011) : ST NDMuh IqbalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fatal Postoperative Pulmonary Edema : Pathogenesis and Literature ReviewDocument7 paginiFatal Postoperative Pulmonary Edema : Pathogenesis and Literature ReviewMuh IqbalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Poster ARFI Siemens TSADocument1 paginăPoster ARFI Siemens TSAMuh IqbalÎncă nu există evaluări
- AAA V Edgardo SalazarDocument2 paginiAAA V Edgardo SalazarNiajhan PalattaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Business OwnershipDocument2 paginiTypes of Business Ownershipprelovedseller bnÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2457-Article Text-14907-2-10-20120724Document6 pagini2457-Article Text-14907-2-10-20120724desi meleniaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The D - Block ElementsDocument30 paginiThe D - Block ElementsNandya AristaÎncă nu există evaluări
- From Crème Fraîche To Sour Cream: What's The Difference?Document14 paginiFrom Crème Fraîche To Sour Cream: What's The Difference?Maricel BautistaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lithium Battery Handling RegulationDocument11 paginiLithium Battery Handling RegulationFan Man ChungÎncă nu există evaluări
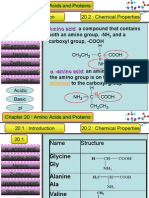
- Matriculation Chemistry Amino Acids-Part-1Document24 paginiMatriculation Chemistry Amino Acids-Part-1iki292Încă nu există evaluări
- Cell Organelles 2Document13 paginiCell Organelles 2Sadeeq ur RahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hand-Pallet Truck - NewDocument2 paginiHand-Pallet Truck - NewAkhilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bubba - S Food MS-CDocument2 paginiBubba - S Food MS-CDũng Trần QuốcÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Aerobic Exercise?Document27 paginiWhat Is Aerobic Exercise?Zedy GullesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unipole Multipole-973098Document225 paginiUnipole Multipole-973098Medes GraciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genomics and Crop ImprovementDocument56 paginiGenomics and Crop Improvementsenguvelan100% (6)
- Calamity and Disaster Preparedness Chapter IXDocument34 paginiCalamity and Disaster Preparedness Chapter IXANGEL ALBERTÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clack 2983 WS1EE Twin Valve LDocument2 paginiClack 2983 WS1EE Twin Valve Lmohamed boufasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Goat AnatomyDocument8 paginiGoat AnatomyLochi GmÎncă nu există evaluări
- SM Electrical Guidelines: General Notes:: Site HereDocument1 paginăSM Electrical Guidelines: General Notes:: Site HereNathaniel DreuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Translating Child Development Research Into Practice - Can Teachers Foster Children's Theory of Mind in Primary SchoolDocument14 paginiTranslating Child Development Research Into Practice - Can Teachers Foster Children's Theory of Mind in Primary SchoolpecescdÎncă nu există evaluări
- UAW-FCA Hourly Contract SummaryDocument20 paginiUAW-FCA Hourly Contract SummaryClickon DetroitÎncă nu există evaluări
- LISD LetterDocument2 paginiLISD LetterAnonymous Pb39klJ100% (1)
- Carapace DigitalDocument15 paginiCarapace DigitalVillain ChatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Instructions For UseDocument14 paginiInstructions For UseEddie UnivoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Crew Resource Management Phil O'DonnellDocument39 paginiCrew Resource Management Phil O'DonnellMostafaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Robodrill 01Document298 paginiRobodrill 01vuchinhvdcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Health and Illness Answer-8Document2 paginiHealth and Illness Answer-8June DumdumayaÎncă nu există evaluări