Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
ECM 216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 2.5 Lift and Elevator
Încărcat de
AZUAN BIN AHMAD FAUZIDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
ECM 216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 2.5 Lift and Elevator
Încărcat de
AZUAN BIN AHMAD FAUZIDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
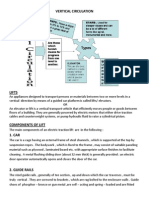
LIFT AND ELEVATOR Introduction Lift has been used widely to building that has more than 4 story.
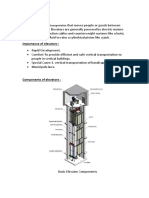
. We know that lift is a machine that provides comfort to people where it provides vertical transportation in a building with ease and fast. Lift can be categorized as a sophisticated machine which applies on various system. Fortunately, in these modern days the lift has been upgraded technically on by program devices, safety practices and even on its regulation. Several main components helps the lift works efficiently which will be discuss on this presentation. All of these components should also be exposed to civil engineering field to give the idea to them on what event about this machine and how they can apply it to their work. Not only about the lift itself, the regulations that has to be followed by the owner of the lift and engineers. How does the lift work?? The lift car moves in a specially constructed vertical chamber within a building. The lift car is driven up and down along guide rails by a drive machine which is connected to an electric motor. The direction in which the lift car moves is controlled by a drive controller. The drive controller determines the direction of the car movement according to the position of the car, the call button and the floor button pressed by the user When the lift car arrives at a floor where a stop is required, the sensing circuits will inform the drive controller to stop the car there. After the lift car is stopped, the car door and the landing door open together automatically. One lift car can transport up to about 20 passengers from one floor to any other floor at one time. They are suitable for high-rise buildings.
Requirement for lifts installation Necessary in all buildings over three stories high. Essential in all buildings over a single story if they are accessed by the elderly or disabled. Minimum standard-one lift per four story Floor space and lift car capacity can be estimated at 0.2m2 per person. TYPE CAR SPEED (M/S) 0.2- 1 0.3-0.8 0.8-1.2 1.2-1.5 1.5-1.7 <0.4
Good ( Electric or Hydraulic Electric passenger <4 floor <4-6 floors <6-9 floors <9-15 floors paternoster
TYPES OF LIFT SYSTEM 1. Traction lift is powered by an electric motor (AC or DC) which is coupled to the hoisting mechanism through a reduction (worm) gear. The motion of the car is obtained through traction between the suspension ropes and the driving sheave. Otherwise known as a cable lift. 2. Hydraulic lift is driven by a pump which raises or lowers the lift car by varying the oil pressure in a ram. The pump is driven by an electric motor.
EDITED BY AZUAN AHMAD FAUZI 2011803188 UITM PULAU PINANG MAC 2013
TYPES OF ELECTRIC TRACTION LIFT (1) Geared: The car is supported in a hoistway by steel hoist ropes, a sheave, and a counterweight. The car and counterweight ride along vertical guide rails. In a geared machine, the drive sheave is connected to the motor shaft through gears in a gearbox. This equipment is designed for mid-rise applications of five or more floors requiring typical speeds up to 350 feet per minute. (2) Gearless: The car is supported in a hoistway by steel hoist ropes, sheaves,and a counterweight. The car, counterweight and guide rails operate like those in a geared system. The gearless machine has a motor that connects directly to the shaft of the drive sheave. The equipment is designed for high-rise applications of 10 or more floors requiring typical speeds of 500 or more feet2-3 per minute.
EDITED BY AZUAN AHMAD FAUZI 2011803188 UITM PULAU PINANG MAC 2013
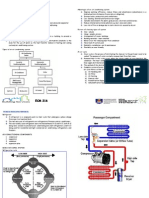
HYDRAULIC LIFTS Hydraulic elevators are one of the two types of elevator which are used in the modern world; the other being the rope-system elevator. Hydraulic elevators work on the simple system of a hydraulic ram. This ram, which incidentally gives the type of lift its name, has a fluid-driven piston mounted inside its outer cylinder. This cylinder is connected to a fluid pumping system. This incompressible fluid is generally oil but other variations are sometimes found (although these are much rarer). The fluid is pumped into a pipe leading to the cylinder, and, after various mechanical happenings, the fluid ultimately begins to collect in the cylinder and this begins to push the piston up; this is what moves the elevator car which has the passengers inside. To lower the elevator car, the reverse happens and the fluid is slowly leaked out; this causes the car to slowly descend and, when the elevator has reached its destination, the valve is closed and the fluid level stays constant. Type of hydraulic lift (1) Direct plunger: A car is connected to the top of a single section piston, that moves up and down in a cylinder, which is below ground level. The car moves up when hydraulic fluid is pumped into the cylinder from a reservoir, raising the piston. Hydraulic systems are used primarily in low-rise installations where moderate car speed is required, up to 150 feet per minute. The typical extent of travel is 40 feet (12192 mm), do not exceed a maximum travel length of 44 feet (13411 mm) or a maximum building height of four floors for (2) Holeless: The car is connected on each side with a single section piston that moves up and down in a cylinder, which is mounted on top of the pit floor. The car moves up when hydraulic fluid is pumped into the cylinder from a reservoir, raising the piston. Car speed up to 125 feet per minute (38.1 meters per minute) is attained and maximum travel length is 12 feet (3658 mm). (3) Roped: The car is supported by steel hoist ropes and sheave, which are moved up and down by a holeless single section piston in a cylinder. Car speed up to 150 feet per minute is attained and maximum travel length is 48 feet (14630 mm). The use of roped hydraulic elevators
Paternoster A paternoster or paternoster lift is a passenger elevator which consists of a chain of open compartments (each usually designed for two persons) that move slowly in a loop up and down inside a building without stopping. Passengers can step on or off at any floor they like.
EDITED BY AZUAN AHMAD FAUZI 2011803188 UITM PULAU PINANG MAC 2013
ESCALATOR AND TRAVELATOR ESCALATOR is a conveyor transport device for transporting people, consisting of a staircase whose steps move up or down on tracks that keep the surfaces of the individual steps horizontal. Most escalators have moving handrails that approximately keep pace with the movement of the steps. The direction of movement (up or down) can be permanently the same, or be controlled by personnel according to the time of day, or automatically be controlled by whomever arrives first, whether at the bottom or at the top. In low to medium rise buildings they will compete favorably with lift, even though they only move at between 0.5-0.65m/s. In high-rise buildings the space will not be justified and the modern high speed lift provides a superior service. Where large number of people are anticipated, such as airports and railway terminals. The angle of indication is normally 30o and can increased to 35o if the vertical rise does not exceed 6m and the sped is limited to 0.5m/s. Designs Modern escalators have metal steps in a continuous loop that move on tracks. Escalators are typically used in pairs with one going up and the other going down. Some modern escalators in stores and shopping malls have glass sides that reveal their workings. Most escalators are straight, some shopping malls use curved versions. Various arrangement of escalator: 1. Single bank traffic in one direction 2. Double bank traffic in two direction 3. Criss-cross 4. Parallel 5. Spiral
EDITED BY AZUAN AHMAD FAUZI 2011803188 UITM PULAU PINANG MAC 2013
TRAVELATOR A moving walkway, moving sidewalk, travelator is a slow conveyor belt that transports people horizontally or on an incline in a similar manner to an escalator. In both cases, riders can walk or stand. The walkways are often supplied in pairs, one for each direction
RAMP
An inclined plane is not a machine that does not move. Many devices based on the principles of the inclined plane allow expending less force to achieve a task. Ramps enable accessing heights that would be too difficult to scale vertically. Ramps allow heavy objects to ascend to, and descend safely from, a high-level bridge.
Designs Moving walkways are built in one of two basic styles: Pallet type a continuous series of flat metal plates join together to form a walkway. Most have a metal surface, though some models have a rubber surface for extra traction. Moving belt these are generally built with mesh metal belts or rubber walking surfaces over metal rollers. The walking surface may have a solid feel or a "bouncy" feel. Both types of moving walkway have a grooved surface to mesh with comb plates at the ends. Also, nearly all moving walkways are built with moving handrails similar to those on escalators. Pallet-types consists of one-piece, die-cast aluminium pallets. Example dimensions are: widths (between balustrades): between 32 inches (800 mm) and 56 inches (1200 mm), with a speed of 100 feet per minute (.5 meters per second), powered by an AC induction motor
EDITED BY AZUAN AHMAD FAUZI 2011803188 UITM PULAU PINANG MAC 2013
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Vertical Transportation SystemDocument14 paginiVertical Transportation Systempassionpropel100% (3)
- Functional Requirements of 8 Transportation Systems in A Building.Document40 paginiFunctional Requirements of 8 Transportation Systems in A Building.Umar Faruq AfokeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carunungan, Marie Util-313Document38 paginiCarunungan, Marie Util-313Marie Holgado CarununganÎncă nu există evaluări
- VerticalDocument26 paginiVerticalArt IjbÎncă nu există evaluări
- LIFTDocument28 paginiLIFTBirla RajasekarÎncă nu există evaluări
- ElevatorsDocument11 paginiElevatorsDalia M-aÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conveying Systems - PDFXDocument32 paginiConveying Systems - PDFXjjÎncă nu există evaluări
- BMC - Escalator, ElevatorDocument23 paginiBMC - Escalator, ElevatorJisniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1Document30 paginiUnit 1Navya chowdaryÎncă nu există evaluări
- BCT Unit 3Document26 paginiBCT Unit 3IqRa JaVedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical System ReportDocument9 paginiMechanical System ReportLea MaligsayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bu 1Document120 paginiBu 1Chi De LeonÎncă nu există evaluări
- TOPIC 4 Mechanical ConveyorsDocument40 paginiTOPIC 4 Mechanical Conveyorsروسيده بت محمد سعد100% (1)
- BU02 Reporting Topic 5Document3 paginiBU02 Reporting Topic 5Katherine GamayotÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 Week NotesDocument39 pagini10 Week Notescharusri74Încă nu există evaluări
- Elevator RescueDocument30 paginiElevator RescueHumberto Arturo AgudeloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 1 BUILDING UTILITIES 2 Transportation SystemsDocument135 paginiLecture 1 BUILDING UTILITIES 2 Transportation SystemsNicole Dizon0% (1)
- Elevators and Escalators Design PDFDocument13 paginiElevators and Escalators Design PDFAmble LamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 10 Tutorial 1Document12 paginiWeek 10 Tutorial 1sonukumarmarchadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elevators and Escalators Design PDFDocument10 paginiElevators and Escalators Design PDFdanokrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elevators and Escalators Design PDFDocument10 paginiElevators and Escalators Design PDFdanokrayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic4b Building TransportationDocument71 paginiTopic4b Building Transportationelleyashahari100% (2)
- Elevators and Escalators DesignDocument10 paginiElevators and Escalators DesignNiong DavidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lift NotesDocument28 paginiLift NotesParzival100% (1)
- Vertical Transportation (Lifts N EsclatorsDocument48 paginiVertical Transportation (Lifts N Esclatorsप्रणव प्रकाश100% (2)
- Lift22 PDFDocument21 paginiLift22 PDFSejal MengajiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ElevatorsDocument27 paginiElevatorsshelmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- As Unit 1 PDFDocument89 paginiAs Unit 1 PDFsaahasitha 14Încă nu există evaluări
- p2 Lift SystemDocument10 paginip2 Lift SystemZikri RosliÎncă nu există evaluări
- PPTXDocument18 paginiPPTXHubert John TabogocÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Elevator / Lift?: How Does A Lift Work?Document8 paginiWhat Is Elevator / Lift?: How Does A Lift Work?ankitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transportation in Buildings: 1. Vertical 2. Inclined 3. HorizontalDocument104 paginiTransportation in Buildings: 1. Vertical 2. Inclined 3. HorizontalManoj JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Construction Methods and Materials Conveying SystemsDocument46 paginiConstruction Methods and Materials Conveying SystemsJuliet MartinÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Is An Elevator MadeDocument7 paginiHow Is An Elevator MadeHyderabadReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic4b Building Transportation PDFDocument71 paginiTopic4b Building Transportation PDFFrancis TiehÎncă nu există evaluări
- So How Do Elevators or Lifts WorkDocument12 paginiSo How Do Elevators or Lifts WorkAyesha MAhmoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 5 LiftsDocument30 paginiUnit 5 LiftsRagul ganeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elevators and Shafts: Qurat-Ul-Ain 103 4th YrDocument5 paginiElevators and Shafts: Qurat-Ul-Ain 103 4th Yraini zahidÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02 Building Finishing 2020 2021 Elevators Escalatros Group RevisedDocument84 pagini02 Building Finishing 2020 2021 Elevators Escalatros Group RevisedRama AlzabenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Escalators&ConveyorsDocument25 paginiEscalators&ConveyorssowmyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- TransportationDocument38 paginiTransportationJarul Zahari0% (1)
- Selection of Drives and Control Systems For LiftsDocument4 paginiSelection of Drives and Control Systems For LiftsSaikat ChakrabortyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit III - VERTICAL TRANSPORTDocument74 paginiUnit III - VERTICAL TRANSPORTAbi GovindÎncă nu există evaluări
- ELEVATORSDocument5 paginiELEVATORSGulienne Randee Mickhaela ZamoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Term Paper 2 MENGR 3100Document5 paginiTerm Paper 2 MENGR 3100caytonericazoeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Building ServicesDocument57 paginiBuilding Servicessofiya0% (1)
- Elevators and EscalatorsDocument24 paginiElevators and EscalatorsarchiammuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Components of ElevatorDocument3 paginiComponents of ElevatorJuri JurieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical Works and Systems: Bistal, Dillera, Dolorito, JunioDocument43 paginiMechanical Works and Systems: Bistal, Dillera, Dolorito, JunioJC DoloritoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design ELEVDocument30 paginiDesign ELEVShiella Barroga LorenzoÎncă nu există evaluări
- LiftDocument43 paginiLiftalyajimmy11Încă nu există evaluări
- Elevators: TransportationDocument5 paginiElevators: TransportationMaram M HaseebaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ElevatorDocument4 paginiElevatormikko intalÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11 A Basic Principles in Building Conveying SystemsDocument59 pagini11 A Basic Principles in Building Conveying SystemsAcademia Account100% (1)
- Transportation SystemsDocument136 paginiTransportation SystemsKaren Dela Torre100% (1)
- Lifts & EscalatorsDocument37 paginiLifts & EscalatorsNikita SalunkheÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 7 - Mechanical Transportation - Module 3 - ElevatorsDocument21 paginiLecture 7 - Mechanical Transportation - Module 3 - ElevatorsShubhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 3Document11 paginiUnit 3SingarayyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sustainable DevelopmentDocument1 paginăSustainable DevelopmentAZUAN BIN AHMAD FAUZIÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECM216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 2.2.1 Phychrometric ChartDocument3 paginiECM216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 2.2.1 Phychrometric ChartAZUAN BIN AHMAD FAUZIÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECM 216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 2.4 Fire FighthingDocument9 paginiECM 216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 2.4 Fire FighthingAZUAN BIN AHMAD FAUZIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ecm 216 Building Services Bab 3.2 Water Supply PDFDocument6 paginiEcm 216 Building Services Bab 3.2 Water Supply PDFAZUAN BIN AHMAD FAUZI100% (8)
- ECM216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 3.3 Gas SupplyDocument3 paginiECM216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 3.3 Gas SupplyAZUAN BIN AHMAD FAUZI67% (3)
- Sustainable Development On SocialDocument4 paginiSustainable Development On SocialAZUAN BIN AHMAD FAUZIÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECM 216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 3.1 Sanitary Piping SystemDocument6 paginiECM 216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 3.1 Sanitary Piping SystemAZUAN BIN AHMAD FAUZI100% (1)
- ECM 216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 2.3 Ahu, Chiller and Cooling TowerDocument3 paginiECM 216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 2.3 Ahu, Chiller and Cooling TowerAZUAN BIN AHMAD FAUZI100% (1)
- ECM216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 1.8 LightingDocument3 paginiECM216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 1.8 LightingAZUAN BIN AHMAD FAUZIÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECM216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 1.6 LightningDocument1 paginăECM216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 1.6 LightningAZUAN BIN AHMAD FAUZIÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECM216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 2.2 Air ConditioningDocument8 paginiECM216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 2.2 Air ConditioningAZUAN BIN AHMAD FAUZI100% (3)
- ECM216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 1.7 Diversity FactorDocument1 paginăECM216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 1.7 Diversity FactorAZUAN BIN AHMAD FAUZIÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECM216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 2.1 Ventilation SystemDocument4 paginiECM216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 2.1 Ventilation SystemAZUAN BIN AHMAD FAUZIÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECM216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 1.4 Star and Delta ConnectionDocument2 paginiECM216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 1.4 Star and Delta ConnectionAZUAN BIN AHMAD FAUZIÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECM 206 CHAPTER 4 TimberDocument8 paginiECM 206 CHAPTER 4 TimberAZUAN BIN AHMAD FAUZI100% (1)
- Ecm216 Building Services Bab 1.5 CableDocument3 paginiEcm216 Building Services Bab 1.5 CableAZUAN BIN AHMAD FAUZI100% (1)
- ECM216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 1.2 Electrical Power SystemDocument4 paginiECM216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 1.2 Electrical Power SystemAZUAN BIN AHMAD FAUZIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ecm216 Building Services Bab 1.1 Generation of ElectricDocument7 paginiEcm216 Building Services Bab 1.1 Generation of ElectricAZUAN BIN AHMAD FAUZIÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECM 206 CHAPTER 2 Fresh ConcreteDocument4 paginiECM 206 CHAPTER 2 Fresh ConcreteAZUAN BIN AHMAD FAUZIÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECM216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 1.3 Generator and AlternatorDocument5 paginiECM216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 1.3 Generator and AlternatorAZUAN BIN AHMAD FAUZIÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECM 206 CHAPTER 6 Bitumen and TarDocument4 paginiECM 206 CHAPTER 6 Bitumen and TarAZUAN BIN AHMAD FAUZI100% (1)
- ECM 206 CHAPTER 3 SteelsDocument11 paginiECM 206 CHAPTER 3 SteelsAZUAN BIN AHMAD FAUZIÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECM 206 CHAPTER 5 Bricks and Masonry Concrete BricksDocument12 paginiECM 206 CHAPTER 5 Bricks and Masonry Concrete BricksAZUAN BIN AHMAD FAUZIÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECM 206 CHAPTER 2 Hardened ConcreteDocument8 paginiECM 206 CHAPTER 2 Hardened ConcreteAZUAN BIN AHMAD FAUZIÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECM 206 CHAPTER 2 AggregatesDocument7 paginiECM 206 CHAPTER 2 AggregatesAZUAN BIN AHMAD FAUZIÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECM 206 CHAPTER 2 CementDocument11 paginiECM 206 CHAPTER 2 CementAZUAN BIN AHMAD FAUZIÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECM 206 CHAPTER 2 Water Used in ConcreteDocument3 paginiECM 206 CHAPTER 2 Water Used in ConcreteAZUAN BIN AHMAD FAUZIÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECM 206 CHAPTER 2 AdmixtureDocument5 paginiECM 206 CHAPTER 2 AdmixtureAZUAN BIN AHMAD FAUZIÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECM 206 CHAPTER 2 ConcreteDocument3 paginiECM 206 CHAPTER 2 ConcreteAZUAN BIN AHMAD FAUZIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lifts, Elevators, Escalators and Moving Walkways-TravelatorsDocument375 paginiLifts, Elevators, Escalators and Moving Walkways-Travelatorsjimmydomingojr94% (17)
- Moving Walkway DESIGNDocument8 paginiMoving Walkway DESIGNChania BhatiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5 - RY PDFDocument72 paginiChapter 5 - RY PDFMuhammad AizatÎncă nu există evaluări
- MP Lifts Catalogue - ENDocument116 paginiMP Lifts Catalogue - ENLe Huynh Long100% (1)
- PPT-T2 VHTDocument31 paginiPPT-T2 VHTBarath RonaldoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lift Escalator and Passenger Conveyor Regulations PDFDocument8 paginiLift Escalator and Passenger Conveyor Regulations PDFANKUSHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Building ServicesDocument57 paginiBuilding Servicessofiya0% (1)
- EN115Document64 paginiEN115Ahmed Yousri Ahmed100% (13)
- R02-Escalators and Its Design CriteriaDocument27 paginiR02-Escalators and Its Design CriteriaRahul PallipamulaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6 Building Transportation PDFDocument53 paginiChapter 6 Building Transportation PDFazmieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lifts Elevators Escalators and Moving Walkways Travelators 1DE2Document207 paginiLifts Elevators Escalators and Moving Walkways Travelators 1DE2jvicec8260Încă nu există evaluări
- Definition of EscalatorDocument31 paginiDefinition of EscalatorkhaimatsahÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECM 216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 2.5 Lift and ElevatorDocument5 paginiECM 216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 2.5 Lift and ElevatorAZUAN BIN AHMAD FAUZIÎncă nu există evaluări
- FIN Escalator 2022Document32 paginiFIN Escalator 2022MARICAR SIGUEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic4b Building Transportation PDFDocument71 paginiTopic4b Building Transportation PDFFrancis TiehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Walk AlatorDocument11 paginiWalk AlatorVanny Gimotea BaluyutÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lift and Escalators: Basic Principles and Design: MECH3005 - Building Services GDocument30 paginiLift and Escalators: Basic Principles and Design: MECH3005 - Building Services GHaris Altaf BhattiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elevator NotesDocument33 paginiElevator NotesLakshmi NarayananÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lifts & Escalators: (Transportation System in Buildings)Document102 paginiLifts & Escalators: (Transportation System in Buildings)Urja ShresthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BS Iii - Unit 4 - EscalatorDocument33 paginiBS Iii - Unit 4 - EscalatorGowthaman Maruthamuthu100% (1)
- Karnataka LEP Rules, 2015 PDFDocument45 paginiKarnataka LEP Rules, 2015 PDFpmbhatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drafting q4 Mr.-TalattadDocument17 paginiDrafting q4 Mr.-TalattadJoven AddatuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ramps, Escalators & Elevators: Prof Vineetkothari Civil Engineeringdepartment NirmauniveristyDocument23 paginiRamps, Escalators & Elevators: Prof Vineetkothari Civil Engineeringdepartment NirmauniveristyrehanmaazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical System ReportDocument9 paginiMechanical System ReportLea MaligsayÎncă nu există evaluări
- KoyoDocument14 paginiKoyoRaul FelipeÎncă nu există evaluări
- EscalatorsDocument9 paginiEscalatorsOdetteGenovaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Mechanical and HVAC SystemsDocument29 paginiBasic Mechanical and HVAC Systemsวรศิษฐ์ อ๋องÎncă nu există evaluări
- Karnataka LEP ACT, 2012Document8 paginiKarnataka LEP ACT, 2012vaibhav_nautiyalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Building Services: Assignment - Ii (PART 2)Document11 paginiBuilding Services: Assignment - Ii (PART 2)Shadowdare VirkÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6.0 Transportation System in High-Rise Building: PSMZA Course Note (Chapter 6)Document25 pagini6.0 Transportation System in High-Rise Building: PSMZA Course Note (Chapter 6)syakirohÎncă nu există evaluări