Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
9C. GSM - Roaming and Switching
Încărcat de
Hồ ThôngDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
9C. GSM - Roaming and Switching
Încărcat de
Hồ ThôngDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
ROAMING AND SWITCHING
Mobile Application Part (MAP) Interface
Key thing in GSM is that subscribers can be called globally. This is because of roaming or mobility functions
These rely mostly on GSM extensions of SS#7
Mobile Application Part procedures relevant to roaming are: Location Registration/update, IMSI Attach/Detach, requesting subscriber data for call se-up, and paging. Additionally in MAP: functions for supplementary services and handover, subscriber management, IMEI management, authentication/identification management, data transfer for SMS
Mobile Application Part (MAP) Interface
MAP entities for roaming services are in MSC, HLR and VLR. At subscriber interface MAP functions correspond to functions of Mobility management (MM) Most important functions Location registration and location update enables to route the calls where the subscriber is
Overview of Location Registration
Before mobile user can get GSM services the MS has t be registered to the network Registration can happen in Home Network (Home PLMN) or to a visited network provided there is roaming agreement between the network operators New registration needed when user changes network and a TMSI has not been issued yet. In this case the user has to report to the network using IMSI and receives TMSI when doing location registration The registration data is stored to the SIM card. So after power up only location update is needed if uses stays within same network A5 = encryption algorithm in air interface, TMSI is transmission is encrypted
Overview of Location Registration
Location Update
MS already has TMSI in the current network. This and LAI identify the user. User also has encryption key Kc. After authentication new TMSI is generated, and it is transmitted in encrypted form (Kc). After the process the new: 3-tuple RAND, SRES, Kc also called SIM-Triplet are updated to VLR and consumed old ones are deleted. Authentication center usually has pre-calculated triplets available to make process faster.
Location Update
Location Update After Changing VLR Area
In this case user changes to a new VLR area, and in location update the new VLR has to ask registration parameters (IMSI, RAND, SRES, Kc) from old VLR. In case user data (TMSI etc.) is lost from database, the authentication needs to be done by using IMSI. After that a new TMSI is assigned and it is now transferred in encrypted form.
Location Update After Changing VLR Area
Routing Call to MS
Due to mobility users cannot be called directly. In location update The MS obtains temporary routing number MSRN according to which MS is reachable. In case of incoming call from outside the MS is dialed by MSISDN. Call is routed to Gateway switch GMSC based by MSISDN. GMSC interrogates the MSRN from HLR. GMSC routes the call using MSRN. MSC then searches corresponding TMSI from VLR and routes the call to destination
Routing Call to MS
Call Routing Variants for National MSISDN
Call Routing Variants for International MSISDN
Routing Through GSMC for International MSISDN
Outgoing Call Setup
Interrogating of Routing Information for Incoming Call
Incoming Call Setup
Mobile Initiated Call Termination
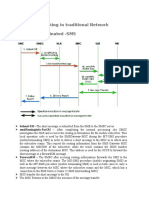
Forwarding Short Message
In the air interface a connectionless protocol (Short Message Transfer Protocol, SM-TP) used for transfer short messages Short messages are transferred using signaling channels (SACCH or SDCCH). Messages are stored in Short Message Center (SMS-SC) and delivered by store and forwarded basis (transmission when receiver available)
Forwarding Short Message
Incoming message
Arrives from Short message Center SMS-SC to a Short Message Gateway MSC (SMS-GMSC). Location MS need to be determined, then authentication etc. MAP procedures used for transfer. Success / failure reported to SMS-GMSC (MAP message Forward Acknowledgement / Error Indication). GMSC then informs SMS-SC. SMS from MS is straightforward sins SMS-GMSC is know to all MSC, os message can be immediately passed to SMS-GMSC
Outgoing message
Forwarding Short Message
Handover
Handover is the process where the connection is set to a new base station as signal goes too low. This ensures continuous communication despite of user movement. Several possibilities depending on location at the network. Controlled by protocols and algorithms based on measurement data.
Handover
Internal and External Handover
Signaling for Intra MSC Handover
Handover Decision
Handover Causes and Threshold
Handover is based on measurements. When predefined limits are exceeded handover is commanded. Limits can be fine-tuned by operator to optimize network
Handover Causes and Threshold
Handover Causes and Threshold
Detection of Mandatory Handover
Typical situations for a mandatory handover
The received signal level in the uplink or downlink (RXLEVEL_UP / RXLEVEL_DL) drops below the respective handover threshold value (L_RXLEVEL_UP_H / L_RXLEVEL_DL_H) and power control range has been exhausted, i.e. MS or BSS have reached their maximal transmitted power The bit error rate ratio as a measure of signal quality in uplink and/or downlink (RXQUAL_UP / RXQUAL_DL) exceeds the respective handover threshold value (L_RXQUAL_UP_H / L_RXQUAL_DL_H) while at the same time the received signal level drops into the neighbourhood of threshold value The maximum distance to the base station (MAX_MS_RANGE) has been reach
Detection of Mandatory Handover
Handover
Basic Handover Between Two MSCs
Subsequent Handover (Handback) MSC-A MSC-B
Subsequent Handover MSC-B MSC-B
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- SPLK-1002 Splunk Core Certified Power User DumpsDocument11 paginiSPLK-1002 Splunk Core Certified Power User Dumpskevin jackyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blue Paper 1 1Document6 paginiBlue Paper 1 1Washington Examiner100% (4)
- 01-SS7 Signaling SystemDocument128 pagini01-SS7 Signaling SystemadeepcdmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Signaling ProtocolsDocument41 paginiSignaling ProtocolsSalim Khan100% (2)
- Digit AnalysisDocument50 paginiDigit Analysisesther_kakani2029100% (1)
- 1 Diameter Base Protocol (8-13)Document107 pagini1 Diameter Base Protocol (8-13)Mohammed F. ShehataÎncă nu există evaluări
- Common Rail Fuel Injection SystemDocument56 paginiCommon Rail Fuel Injection SystemMarcos Maciel100% (1)
- Telecom Operations A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionDe la EverandTelecom Operations A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Service Manual 'B' SC Vac 16 L. AL2Document71 paginiService Manual 'B' SC Vac 16 L. AL2Anwar Dheen67% (3)
- SS7 Protocol LayersDocument3 paginiSS7 Protocol Layerspnvsridhar86Încă nu există evaluări
- Sigtran Connectuon by CiscoDocument75 paginiSigtran Connectuon by CiscoKomunitasGerakanCintaJagapuraÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSM Signaling and Protocol Analysis The Core Network - v1.000 TOC PDFDocument4 paginiGSM Signaling and Protocol Analysis The Core Network - v1.000 TOC PDFmeysamRajabiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Signaling SolutionDocument55 paginiSignaling SolutiongaborkÎncă nu există evaluări
- F5 5G WP BuildingBetter5GSecurity Final 120720Document14 paginiF5 5G WP BuildingBetter5GSecurity Final 120720Jussein TorresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diameter ProxyDocument8 paginiDiameter ProxyIain McIlwaineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Camel Protocol Call FlowDocument9 paginiCamel Protocol Call Flowahmed mohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unrestricted: GSM Association Official Document: IR.52Document24 paginiUnrestricted: GSM Association Official Document: IR.52Senthil Mannan100% (1)
- Camel PPSDocument82 paginiCamel PPSmugeshpv90Încă nu există evaluări
- Navigator Huawei Optix Osn Equipment Command Line Introduction 20080628 ADocument48 paginiNavigator Huawei Optix Osn Equipment Command Line Introduction 20080628 AAlceuCarneiro50% (2)
- Pubate Satienpoch: SCCP: Signaling Connection Control PartDocument23 paginiPubate Satienpoch: SCCP: Signaling Connection Control PartAnuj NayakÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSM Call Path CourseDocument75 paginiGSM Call Path CourseHeraa FarooqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Use Cases Roaming TestingDocument5 paginiUse Cases Roaming TestingFrensel PetronaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intelligent Networks (In) and CAMELDocument11 paginiIntelligent Networks (In) and CAMELnaggu1983Încă nu există evaluări
- Arduino Starter Kit Manual v1.6Document38 paginiArduino Starter Kit Manual v1.6SeunOlubunmi100% (1)
- Home Location RegisterDocument30 paginiHome Location RegistermushishinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- RoamingDocument2 paginiRoamingIppolito GregoÎncă nu există evaluări
- International Mobile Roaming Charging in The OECD AreaDocument109 paginiInternational Mobile Roaming Charging in The OECD AreaICTdocs100% (2)
- Telecom Overview PresentationDocument61 paginiTelecom Overview PresentationPrabh Preet SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Camel Profile 26 Oct 2011Document14 paginiCamel Profile 26 Oct 2011awaisyarÎncă nu există evaluări
- SS7 ProtocolBasicsDocument22 paginiSS7 ProtocolBasicsAbhay MukewarÎncă nu există evaluări
- SS7 in Mobile Communication NetworkingDocument5 paginiSS7 in Mobile Communication Networkinggunasekaran.subramani3879Încă nu există evaluări
- Learn SoRDocument8 paginiLearn SoRRasheedKhouliÎncă nu există evaluări
- BW SANetworkServerModule5 R120Document72 paginiBW SANetworkServerModule5 R120Ochie RomeroÎncă nu există evaluări
- International Roaming StrategiesDocument10 paginiInternational Roaming StrategiesBrent BrownellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study Theme 3 CamelDocument47 paginiStudy Theme 3 CamelMohammed AnwarÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSM System Overview Slides Day - JDocument135 paginiGSM System Overview Slides Day - JnamayeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- VOIP SIP PardeepDocument85 paginiVOIP SIP PardeepViswanathÎncă nu există evaluări
- BroadSoft Business EbookDocument19 paginiBroadSoft Business EbooksagrennÎncă nu există evaluări
- International Roaming User Guide PDFDocument27 paginiInternational Roaming User Guide PDFgosalaprasadÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSM Protocol Architecture: Shariful Hasan ShaikotDocument44 paginiGSM Protocol Architecture: Shariful Hasan Shaikotabdelilahbendani2162Încă nu există evaluări
- UssdDocument3 paginiUssdAbhinav ChittibommaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intelligent Traffic SteeringDocument2 paginiIntelligent Traffic SteeringmuradghaziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Missed Call SolutionDocument2 paginiMissed Call Solutionsuman_123Încă nu există evaluări
- What Is SS7 Protocol - Telecommunication InformationDocument2 paginiWhat Is SS7 Protocol - Telecommunication InformationlllollooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diameter Base Protocol Feature Guide For Subscriber ManagementDocument124 paginiDiameter Base Protocol Feature Guide For Subscriber ManagementChakravarthi ChittajalluÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sigtran Openss7Document150 paginiSigtran Openss7Jesus Bazan100% (1)
- SS7 User's Guide (IBM)Document180 paginiSS7 User's Guide (IBM)hostdonganhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Signalling Training IuPs v4Document51 paginiSignalling Training IuPs v4mainmemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Broadsoft Solutions Guide For Vvx1500Document24 paginiBroadsoft Solutions Guide For Vvx1500Vinod Kumar DhimanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1-Gsm Architecture & InterfacesDocument13 paginiUnit 1-Gsm Architecture & InterfacesJovita Lasrado0% (1)
- Signaling System 7Document31 paginiSignaling System 7thutiheheÎncă nu există evaluări
- Icnd1 CramDocument64 paginiIcnd1 CramJuan SmithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diameter User Guide CCNDocument22 paginiDiameter User Guide CCNLeonardo CalleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Voice Over Internet Protocol: Corvit SystemsDocument16 paginiVoice Over Internet Protocol: Corvit Systemsapi-19663123Încă nu există evaluări
- Call Flow at MNP ScenarioDocument22 paginiCall Flow at MNP Scenariosayan_choudhury8193Încă nu există evaluări
- 1.SMS Interworking in Traditional Network 1.1.mobile Originated - SMSDocument7 pagini1.SMS Interworking in Traditional Network 1.1.mobile Originated - SMSdilipsharma04Încă nu există evaluări
- CDG 117 Inter Standard Roaming White Paper Ver2.0Document49 paginiCDG 117 Inter Standard Roaming White Paper Ver2.0Clarence W HayesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Telecom Signalling Basics - CAS&CCS (SS7)Document47 paginiTelecom Signalling Basics - CAS&CCS (SS7)Rahul BambhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSMA AP LTE Roaming SyniverseDocument19 paginiGSMA AP LTE Roaming Syniversenishant19777Încă nu există evaluări
- SIP Extensions For The IP Multimedia Subsystem A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDe la EverandSIP Extensions For The IP Multimedia Subsystem A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionÎncă nu există evaluări
- PARKER Instrument TubingDocument10 paginiPARKER Instrument TubingDaniel MarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acs BD Schematic Most CurrentDocument8 paginiAcs BD Schematic Most CurrentgregfortkampÎncă nu există evaluări
- Low Voltage Alternator - 4 Pole: 70 To 200 kVA - 50 HZ / 88 To 250 kVA - 60 HZ Electrical and Mechanical DataDocument16 paginiLow Voltage Alternator - 4 Pole: 70 To 200 kVA - 50 HZ / 88 To 250 kVA - 60 HZ Electrical and Mechanical DataAsif ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Delivery Cost SAP PDFDocument7 paginiDelivery Cost SAP PDFsappz3545448Încă nu există evaluări
- Medical Devices Training For Medical StaffDocument3 paginiMedical Devices Training For Medical StafffatematareefÎncă nu există evaluări
- UNIT-1 Basic Elements of AutomationDocument18 paginiUNIT-1 Basic Elements of AutomationSudhanshu PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Materials System SpecificationDocument4 paginiMaterials System SpecificationAjeetKumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Forcepoint ONE CASB DatasheetDocument6 paginiForcepoint ONE CASB DatasheetP BarreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- TM 35100 TM-35100: 31.7 Metric Ton Capacity (35 US Ton) Hydraulic CraneDocument11 paginiTM 35100 TM-35100: 31.7 Metric Ton Capacity (35 US Ton) Hydraulic CraneEder Rodriguez GonzalezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simplification of WCS and ED Syllabus of Max 40 Hours Each and Merging With Trade TheoryDocument415 paginiSimplification of WCS and ED Syllabus of Max 40 Hours Each and Merging With Trade TheorySourav ChowdhuryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Symbol Table Symbol Table:: Possible Implementations TechniquesDocument7 paginiSymbol Table Symbol Table:: Possible Implementations TechniquesMilad AkbariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Women SafetyDocument6 paginiWomen Safetyanon_318625233Încă nu există evaluări
- Dhomesb Basic Configuration PT Practice SBADocument2 paginiDhomesb Basic Configuration PT Practice SBAHeather SmithÎncă nu există evaluări
- SRAM Cell: Six Transistors Regenerative Feedback Information Held Is StableDocument28 paginiSRAM Cell: Six Transistors Regenerative Feedback Information Held Is StableBittu BharathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Red Networks ProfileDocument4 paginiRed Networks Profileanand.srajuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Apollo Fire Safety in Healthcare Buildings UK CPDDocument1 paginăApollo Fire Safety in Healthcare Buildings UK CPDFernando KatayamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technology For Success: Computer Concepts: NetworkingDocument16 paginiTechnology For Success: Computer Concepts: NetworkingVishwa NirmalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lg02/Olg02 Lora Gateway User Manual: Document Version: 1.6.1Document64 paginiLg02/Olg02 Lora Gateway User Manual: Document Version: 1.6.1121234 datajktÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maintenance Hydraulics QuizDocument11 paginiMaintenance Hydraulics QuizArshad MullaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Animation Bridge Rectifier NonidealDocument24 paginiAnimation Bridge Rectifier NonidealAla'a HusseinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ocbc Plus Partnership FaqsDocument9 paginiOcbc Plus Partnership FaqsLim Ming JianÎncă nu există evaluări
- VerificationDocument49 paginiVerificationMatt ThompsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Noakhali Gold Foods LTD.: 153,154 Tejgoan Industrial Area Dhaka-1208Document4 paginiNoakhali Gold Foods LTD.: 153,154 Tejgoan Industrial Area Dhaka-1208farjana khatunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elektor Mag Summer 2023Document33 paginiElektor Mag Summer 2023Ludo Bagman100% (3)