Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Cell Revision
Încărcat de
rileyevansDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Cell Revision
Încărcat de
rileyevansDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Cell Revision
There are two main types of cells, Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells DO NOT have a nucleus, they are simple cells and their nucleic acids are found in the cytoplasm. They DO NOT have mitochondrion. An example of one is bacterium.
Eukaryotic cells however DO have a nucleus. They are more complex cells, they also have mitochondrion. *An example of a eukaryotic cell is a plant or animal cell. There are certain differences between plant and animal cells. They both contain some things which the other one doesnt. Plant cells contain chloroplasts, a cell wall, a vacuole and cellulose whilst animal cells dont and an animal cell contains glycogen granules. Cells tissue organ organ system organism
Eukaryotic cells contain: Endoplasmic reticulum. Smooth ER is used for transporting Lipids. Rough ER (containing ribosomes) is used for transporting proteins.
made.
Ribosomes, found attached to ER or in the cytoplasm, it is where proteins are
Cell wall. It surrounds PLANT CELLS, it acts as support. Plasma membrane. Its found in both plant and animal cells, it is made of both proteins and lipids and it regulates movement in and out of cell. It contains a lipid bilayer. It is also known as a fluid mosaic model due to the proteins embedded in it.
The nucleus. Its surrounded by a nuclear membrane containing pores. It contains chromatins and a nucleolus. It contains the genetic material of the cell. The nucleolus makes RNA.
A lysosome. Its a round organelle, it contains digestive enzymes it is used to destroy or digest invading cells.
Golgi apparatus. A group of SER containing flattened sacs with vesicles. It packages substances that are produced by the cell it also makes lysosomes.
cell.
Microtubule. Made from tubulin, acts as a guide to moving organelles in the
Mitochondrion. They have a DOUBLE MEMBRANE, the inner one forms cristae. Inside is the matrix which contains enzymes for respiration. It is also where ATP is produced.
Chloroplast. Found only in plant cells. It has a double membrane and is the site where photosynthesis takes place.
Centriole. Seen in animal cells during cell division, it is involved with the chromosomes during said division. Intrinsic proteins completely span the membrane from inside to outside. They are used
in active transport or facilitated diffusion. Extrinsic proteins only partly span the membrane. They are either located in the outer phospholipid layer or the inner phospholipid layer. They are used in cell recognition. Transport across cell membranes. There are four main ways. Diffusion: Is the passive movement of particles. The particles will gradually move from a highly concentrated area to a lowly concentrated area. It can occur across cell membranes, no energy is required for it to occur. Its affected by the concentration gradient and temperature.
Osmosis: Is when WATER molecules ONLY diffuse through a partially permeable membrane. It doesnt require ATP. Water molecules will move both ways through the membrane but the net movement will be towards the area with a lower concentration of water molecules.
Water potential is the ability for water molecules to move, it is represented by this symbol (), it is measured in Kilopascals KPa. Pure water has the highest water potential with 0; all other water potentials are NEGATIVE.
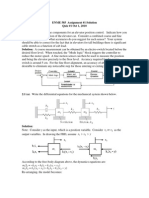
It can be found out using this equation:
Water potential () =solute potential (s) + pressure potential (p)
Solutions can be: Isotonic: same water potential (same concentration) Hypertonic: lower water potential (higher concentrated) Hypotonic: Higher water potential (less concentrated) Facilitated Diffusion: It uses carrier proteins and channel proteins. Some larger molecules e.g. sodium ions cant diffuse through the cell membrane themselves. Instead they use carrier proteins or channel proteins.
Active transport. This REQUIRES ATP and occurs against a concentration gradient. Molecules attach to carrier proteins, then molecules of ATP use energy to change their shape, where they then pass through the cell membrane.
Endocytosis takes materials INTO the cell. The material is surrounded by a small vesicle and then absorbed into the cell. There are two types,
phagocytosis and pinocytosis. Phagocytosis is where SOLIDS are taken into the cell. Pinocytosis is where LIQUIDS are absorbed.
Exocytosis removes materials from the cell. The materials to be removed move through the ER towards the Golgi where they are pinched off by vesicles. The vesicles then secrete then outside the cell.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5795)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Box Transport MechanismDocument36 paginiBox Transport MechanismInzi Gardezi81% (16)
- Curriculum Vitae: Mobile No: +917019900128 E-MailDocument5 paginiCurriculum Vitae: Mobile No: +917019900128 E-MailJay MÎncă nu există evaluări
- Orchid Group of Companies Company ProfileDocument3 paginiOrchid Group of Companies Company ProfileAngelica Nicole TamayoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data StreamDocument256 paginiData Streamy suresh babuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tle7 Ict TD M2 V3Document28 paginiTle7 Ict TD M2 V3Rowemar Corpuz100% (1)
- Hypertension ESC 2013 PDFDocument32 paginiHypertension ESC 2013 PDFNar RungrojanarakÎncă nu există evaluări
- CS 2400 - 2500 BrochureDocument8 paginiCS 2400 - 2500 BrochureOo Kenx OoÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Install Mesa (OpenGL) On Linux Mint - 6 StepsDocument2 paginiHow To Install Mesa (OpenGL) On Linux Mint - 6 Stepsankitfrnd45Încă nu există evaluări
- InflammationDocument44 paginiInflammationramsiyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prishusingh Blogspot Com 2024 03 Digital-Marketing-Course HTMLDocument12 paginiPrishusingh Blogspot Com 2024 03 Digital-Marketing-Course HTMLsudharaj86038Încă nu există evaluări
- Network Tools and Protocols Lab 2: Introduction To Iperf3Document17 paginiNetwork Tools and Protocols Lab 2: Introduction To Iperf3Fabio MenesesÎncă nu există evaluări
- UX-driven Heuristics For Every Designer: OutlineDocument7 paginiUX-driven Heuristics For Every Designer: OutlinemuhammadsabirinhadisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calling An Oracle Stored Proc in JasperDocument10 paginiCalling An Oracle Stored Proc in Jasperlorenzofranchi6371Încă nu există evaluări
- A. in What Way Is Khatri A Surplus Unit?Document5 paginiA. in What Way Is Khatri A Surplus Unit?Aakriti SanjelÎncă nu există evaluări
- 34P S4hana1909 BPD en UsDocument18 pagini34P S4hana1909 BPD en UsBiji RoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cutting Conics AsDocument3 paginiCutting Conics Asbabe09Încă nu există evaluări
- Oxford Math AA SL Exam Practise Additional ResourcesDocument172 paginiOxford Math AA SL Exam Practise Additional ResourcesSıla DenizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pipe Support Reference 8-29-14Document108 paginiPipe Support Reference 8-29-14HITESHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subject-Verb AgreementDocument10 paginiSubject-Verb AgreementLouie Jay Cañada AbarquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- GlobalisationDocument8 paginiGlobalisationdummy12345Încă nu există evaluări
- BIO SCI OsmosisDocument10 paginiBIO SCI OsmosisJoy FernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter - 1 - Digital - Systems - and - Binary - Numbers EE228 15-16Document81 paginiChapter - 1 - Digital - Systems - and - Binary - Numbers EE228 15-16mohamed hemdanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iraqi Portal of Knowledge and Heritage With Format Edits - 11-21-2023Document6 paginiIraqi Portal of Knowledge and Heritage With Format Edits - 11-21-2023محمد الكربلائيÎncă nu există evaluări
- SolutionsManual NewDocument123 paginiSolutionsManual NewManoj SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Japanese Mythology: 2 Kuniumi and KamiumiDocument12 paginiJapanese Mythology: 2 Kuniumi and KamiumipdekraaijÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 1 SolutionDocument11 paginiAssignment 1 SolutionKash TorabiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECE3073 P4 Bus Interfacing Answers PDFDocument3 paginiECE3073 P4 Bus Interfacing Answers PDFkewancamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample Minutes of MeetingDocument3 paginiSample Minutes of MeetingMohamad AzmeerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subordination, Non - Disturbance and Attornment AgreementDocument7 paginiSubordination, Non - Disturbance and Attornment AgreementDavid CromwellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Board Resolution On Assigning Signatories in The Voucher ProgramDocument2 paginiBoard Resolution On Assigning Signatories in The Voucher ProgramavinmanzanoÎncă nu există evaluări