Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Safety
Încărcat de
Paul James ThadhaniDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Safety
Încărcat de
Paul James ThadhaniDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
SAFETY Within the limitation offered by other design criteria, the designer should ensure maximum safety of the
driver, the passenger & other road uses. Thus the vehicle should not be designed to withstand safety collision with on obstacle or another vehicle at high speed but should be designed to reduce the effects of collision. Design of body for safety: The kinetic energy designed during collision may be expressed as E= (m-m) v2/2 Where m total mass of vehicle m movable mass (passenger or load etc.) v Velocity The above energy is absorbed by work done on material by elastic deformation. (i.e) (m-m)v2/2 = pds = (2/2E)AL Where p force generated during collision s distance travelled during collision local stress in material A cross sectioned area L deformation length in cm From above generated is inversely proportional to distance travelled in coming to rest and inversely proportional to youngs modulus of the material. So bumper and collision absorbing materials should be of light alloys aluminum and rubber.
Graph of deceleration of the passenger compartment as a function of time for a collision with stationary obstacles passenger car travelled at a speed of 50 km/hr. Deceleration measured in the passenger compartment of a normal car is usually large, even though only 20% of the maximum retardation is felt in the passenger compartment.
Fig shows the results of except to measure the value of retardation at the extreme points of a vehicle and the passenger compartment. When accident occurs between 2 vehicles, decelerations involved are less then when colliding with a solid obstacle. Fig shows this relation and clearly indicates the importance of the larger distance over within the force travel before the vehicles comes to rest.
Thus long energy absorbing distance should be provided in vehicle design and parts of the structure used for this purpose should have lower stiffness then central section or the passenger compartment of the vehicle. Fig indicates the deceleration generated during impact in the car of a collision between vehicles a solid wall.
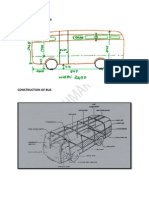
Thus the response time of a human being doesnt allow him to prepare for an impact of short duration and thus safety belt must be used. For a side impact a designer may be able to improve the collision properties of the vehicle by choosing substantial side rails with some elasticity in the lateral direction especially on buses & commercial vehicles. To ensure passenger safety in a case of overturning, a stiff roof constriction most be used or if thus is not possible local reinforcement or antiroll bars may be used. Various safety features are: 1) The bumper design: The bumper should be designed to absorb more energy. Big shock absorbers may be used behind the bumper In some design semi-circular shape is adopted. This avoids direct collision and tilt of the vehicle. The height of the bumper should be such that if it hits the pedestrian below the knee he will fall on the vehicle hence less danger. 2) Ignition switch should be connected with door lock that ignition can be Switched on only when all four doors are perfectly locked. 3) Air bags & safety belts have to be used. 4) Herlomatic flash or horn (peep sound) for every 1m. If the driver doesnt put off, then ignition will be automatically switched off. 5) Use of collapsible or telescopic steering column. 6) Heat toughened or zone toughened glass have to be used.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- ElasticityDocument38 paginiElasticityPaul James ThadhaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stress and StrainDocument42 paginiStress and StrainPaul James Thadhani100% (5)
- Wind TunnelDocument4 paginiWind TunnelPaul James ThadhaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Construction of Passenger CarDocument3 paginiConstruction of Passenger CarPaul James Thadhani100% (1)
- Bus BasicsDocument3 paginiBus BasicsPaul James ThadhaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aero DynamicsDocument18 paginiAero DynamicsPaul James Thadhani0% (1)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- HURDCO International SchoolDocument3 paginiHURDCO International SchoolWakif Khan PrantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE133 Final-Examination MauhayDocument8 paginiEE133 Final-Examination MauhayJohn Zyrus MauhayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cap 8 Livro PDFDocument36 paginiCap 8 Livro PDFDiogo FonaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Post Task - Edwin RojasDocument8 paginiPost Task - Edwin RojasKaren Gordillo RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- PWOG HZL 6033 PR CAL 001 - New Dust Collector Design and DatasheetDocument3 paginiPWOG HZL 6033 PR CAL 001 - New Dust Collector Design and DatasheetpavanÎncă nu există evaluări
- ABB Instrument Transformers: Current Transformer TheoryDocument54 paginiABB Instrument Transformers: Current Transformer TheoryFidel Moreno100% (1)
- Analysis and Calculation 1.1 AnalysisDocument2 paginiAnalysis and Calculation 1.1 AnalysisAmalia FatinÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7.stellar AstrophysicsDocument23 pagini7.stellar AstrophysicsYousra MashkoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Borrow Pit VolumesDocument10 paginiBorrow Pit VolumesShafiullah KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Magnetic Particle Testing: Basic ConceptsDocument3 paginiIntroduction To Magnetic Particle Testing: Basic ConceptsAshfaq KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- E102 KinematicsDocument8 paginiE102 KinematicsKenneth PeraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Code AsterDocument16 paginiCode AsterStefano MilaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Volume 3Document370 paginiPhysics Volume 3Sunilkumar Dubey100% (1)
- 1983-Vibration Studies and Tests of Liquid Storage TanksDocument28 pagini1983-Vibration Studies and Tests of Liquid Storage TanksbehzadÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11 Chemistry Chapter 2 Assignment 1Document1 pagină11 Chemistry Chapter 2 Assignment 1Harman Singh0% (1)
- Six Easy Steps That Explain The Radiation of Rectangular Patch AntennaDocument7 paginiSix Easy Steps That Explain The Radiation of Rectangular Patch AntennaRamya RÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCQ For Module6Document3 paginiMCQ For Module6Ijaz TalibÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9.theories of Elastic FailureDocument6 pagini9.theories of Elastic FailureRohit KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Section7.1, 7.2Document32 paginiSection7.1, 7.2mamdudurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solutions Manual For Reliability Engineering by Singiresu S Rao 0136015727Document36 paginiSolutions Manual For Reliability Engineering by Singiresu S Rao 0136015727eet.rutin1gld4100% (48)
- Land Vs Water StudentDocument4 paginiLand Vs Water Studentwackowacky 97Încă nu există evaluări
- 3 Synchronous PDFDocument16 pagini3 Synchronous PDFASHOK P R kceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chap 4 Nodal & Mesh AnalysisDocument2 paginiChap 4 Nodal & Mesh AnalysisIrtaza Nasir ßhattiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bate and Mueller Astrophysics Homework 5 SolutionsDocument2 paginiBate and Mueller Astrophysics Homework 5 SolutionsAliÎncă nu există evaluări
- O Syllabus Outline: BS. Applied Geology 2 Professional (Morning)Document13 paginiO Syllabus Outline: BS. Applied Geology 2 Professional (Morning)Pak DesireÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transformer Electrical TestsDocument2 paginiTransformer Electrical Testsganesamoorthy1987Încă nu există evaluări
- Postlab 2 Gas AbsorptionDocument7 paginiPostlab 2 Gas AbsorptionDean Joyce AlborotoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Moment Distribution Method: Prof - Kodali SrinivasDocument9 paginiMoment Distribution Method: Prof - Kodali SrinivasprakashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Syllabus Civil KuDocument148 paginiSyllabus Civil KubashuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Syllabus Advanced Dynamics 2018Document5 paginiSyllabus Advanced Dynamics 2018mikeÎncă nu există evaluări