Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
DON'T MISS THESE Important Instructions:: Assignment # 02
Încărcat de
Syed Muhammad Ashfaq AshrafTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
DON'T MISS THESE Important Instructions:: Assignment # 02
Încărcat de
Syed Muhammad Ashfaq AshrafDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Assignment # 02
MTH401 (Spring 2012) Total marks: 30 Lecture # 12-18 Due date: 08-05-2012
DONT MISS THESE Important instructions:
Upload assignments properly through LMS only, (No Assignment will be accepted through email). All students are directed to use the font and style of text as is used in this document. In order to attempt this assignment you should have full command on Lecture # 12 to Lecture # 18. This is an individual assignment, not group assignment, so keep in mind that you are supposed to submit your own, self made & different assignment even if you discuss the questions with your class fellows. All similar assignments (even with some meaningless modifications) will be awarded zero marks and no excuse will be accepted. This is your responsibility to keep your assignment safe from others. Above all instructions are for all assignments so may not be mentioned in future.
Solve the assignment on MS word document and upload your word (.doc) files only. Do not solve the assignment on MS excel. If we get any assignment on MS excel or any format other than word file then it will not be graded.
Assignments through e-mail are not acceptable after due date (If there is any problem in submitting your assignment through LMS, you can send your solution file through email with in due date). You are advised to upload your assignment at least two days before Due date.
Question#1
Marks 10
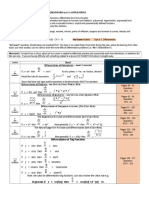
In the following differential equation the indicated function y1 ( x ) is a solution of the associated homogeneous equation. Use the method of reduction of order to find a second solution y2 ( x ) of the homogeneous equation and a particular solution of the given nonhomogeneous equation using method of undetermined coefficients-superposition approach. d2y 4 y = 2 ; y1 = e 2 x 2 dx Question#2 Solve the following initial value problem.
dy + p ( x ) y = 0 ; y ( 0) = 1 dx
Marks 20
Where 2 p ( x) = 1 0 x 1 x >1
Hint:
Linear differential equations sometimes occur in which the function p ( x ) have
jump discontinuities. If x 0 is such a point of discontinuity, then it is necessary to solve the equation separately for x < x 0 and x > x 0 . Afterwards, the two solutions are matched so that the function y ( x ) is continuous at x 0 ; this is accomplished by a proper choice of the arbitrary constants. In the given differential equation p ( x ) has a jump discontinuity at x 0 = 1 , then it is necessary for all of you to solve the equation separately for x < 1 and x > 1 .
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Sample 7394Document11 paginiSample 7394insan100% (1)
- ServiceNow DiscoveryDocument92 paginiServiceNow DiscoveryRaghu ram100% (1)
- l3 DifferentiationDocument4 paginil3 Differentiationapi-287224366100% (2)
- All Clear Kl7 Unit2 Basic Test BDocument3 paginiAll Clear Kl7 Unit2 Basic Test BKatarzyna Agata Krzyczmonik50% (2)
- Wall StreetDocument382 paginiWall Streetpaul-hodorogea-8456100% (2)
- Engineering Mathematics Differential EquationsDocument39 paginiEngineering Mathematics Differential EquationsDhany SSatÎncă nu există evaluări
- UVM Harness WhitepaperDocument12 paginiUVM Harness WhitepaperSujith Paul VargheseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Qualitative Data AnalysisDocument15 paginiQualitative Data Analysisvvijayaraj100% (4)
- Limits and Continuity (Calculus) Engineering Entrance Exams Question BankDe la EverandLimits and Continuity (Calculus) Engineering Entrance Exams Question BankÎncă nu există evaluări
- Editavel Gregory R Andrews - Concurrent Programming - Principles and Practice-The Benjamin - Cummings (1991)Document656 paginiEditavel Gregory R Andrews - Concurrent Programming - Principles and Practice-The Benjamin - Cummings (1991)Tiago Martins100% (1)
- Soft Computing and Signal Processing: Jiacun Wang G. Ram Mohana Reddy V. Kamakshi Prasad V. Sivakumar Reddy EditorsDocument765 paginiSoft Computing and Signal Processing: Jiacun Wang G. Ram Mohana Reddy V. Kamakshi Prasad V. Sivakumar Reddy Editorsopenaloza9150Încă nu există evaluări
- DON'T MISS THESE Important Instructions:: Assignment No.01Document2 paginiDON'T MISS THESE Important Instructions:: Assignment No.01Syed Muhammad Ashfaq AshrafÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spring 2021 - MTH301 - 2Document2 paginiSpring 2021 - MTH301 - 2Engr TA Lha ShEikhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spring 2021 - MTH301 - 1Document2 paginiSpring 2021 - MTH301 - 1Muhammad ZeeshanÎncă nu există evaluări
- DON'T MISS THESE Important Instructions:: Assignment # 1Document2 paginiDON'T MISS THESE Important Instructions:: Assignment # 1komfarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fall 2022 - MTH101 - 1 - SOLDocument2 paginiFall 2022 - MTH101 - 1 - SOLIrtiza ChohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Instructions: Assignment 01 (MTH401) (Differential Equation)Document2 paginiInstructions: Assignment 01 (MTH401) (Differential Equation)Syed Muhammad Ashfaq AshrafÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solution MTH1011Document2 paginiSolution MTH1011Raja MuzammilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fall 2022 - MTH001 - 2Document2 paginiFall 2022 - MTH001 - 2Urwa ButtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fall 2022 - MTH501 - 1Document2 paginiFall 2022 - MTH501 - 1Nimi RasoolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fall 2022 - MTH100 - 1Document1 paginăFall 2022 - MTH100 - 1AR khakwaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fall 2020 - MTH301 - 1Document2 paginiFall 2020 - MTH301 - 1Massi AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fall 2022 - MTH101 - 2Document1 paginăFall 2022 - MTH101 - 2muhammad niazÎncă nu există evaluări
- APM2611 Activity 1 Methods of Solutions To DEs 18Document2 paginiAPM2611 Activity 1 Methods of Solutions To DEs 18JapoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem 1: This Is A Self-Graded and Self-Reported Quiz, Based On The Rubric Given HereDocument2 paginiProblem 1: This Is A Self-Graded and Self-Reported Quiz, Based On The Rubric Given HeremorbidlarueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arooba Fatima MTH201 AssignmenDocument2 paginiArooba Fatima MTH201 AssignmenIsha NasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spring 2022 - MTH301 - 1Document2 paginiSpring 2022 - MTH301 - 1Arslan AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Due Date: 29-12-2021: Fall 2021 MTH104: Sets and Logic Assignment No. 1 (Lectures # 16 To 18) Total Marks: 10Document3 paginiDue Date: 29-12-2021: Fall 2021 MTH104: Sets and Logic Assignment No. 1 (Lectures # 16 To 18) Total Marks: 10manzoor ahmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pauls Online Notes - Differ..Document6 paginiPauls Online Notes - Differ..Fawwad Qureshi0% (1)
- MATH 2170: Differential Equations IDocument3 paginiMATH 2170: Differential Equations IDhruv DharamshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 04 2nd Order ODE - The D OperatorDocument18 pagini04 2nd Order ODE - The D OperatorOlabode EgbinolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fall 2022 - MTH201 - 1Document1 paginăFall 2022 - MTH201 - 1mariam buttÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment # 1 MTH100 (SPRING 2018) : Maximum Marks: 20 Due Date: 15 - 05-2018Document1 paginăAssignment # 1 MTH100 (SPRING 2018) : Maximum Marks: 20 Due Date: 15 - 05-2018Syed Abdul Mussaver ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment # 1 MTH100 (SPRING 2018) : Maximum Marks: 20 Due Date: 15 - 05-2018Document1 paginăAssignment # 1 MTH100 (SPRING 2018) : Maximum Marks: 20 Due Date: 15 - 05-2018Syed Abdul Mussaver ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment # 1 MTH100 (SPRING 2018) : Maximum Marks: 20 Due Date: 15 - 05-2018Document1 paginăAssignment # 1 MTH100 (SPRING 2018) : Maximum Marks: 20 Due Date: 15 - 05-2018Syed Abdul Mussaver ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment No 2 MTH501 (Spring 2021)Document2 paginiAssignment No 2 MTH501 (Spring 2021)Amir BhinderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment No 2 MTH501 (Spring 2021)Document2 paginiAssignment No 2 MTH501 (Spring 2021)Amir BhinderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fall 2020 - MTH101 - 2Document1 paginăFall 2020 - MTH101 - 2Unknown PersonÎncă nu există evaluări
- DON'T MISS THESE Important Instructions:: Solution of Assignment # 2Document6 paginiDON'T MISS THESE Important Instructions:: Solution of Assignment # 2Syed Muhammad Ashfaq AshrafÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spring 2023 MTH501 Section Saima Shafi Assignment 1Document2 paginiSpring 2023 MTH501 Section Saima Shafi Assignment 1Angel Of The GuardianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Day 1: Long Division of Polynomials: Module Info Attachments Pages Others QtyDocument11 paginiDay 1: Long Division of Polynomials: Module Info Attachments Pages Others QtyJazlyn Andria JarafaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fall 2022 - MTH101 - 1Document1 paginăFall 2022 - MTH101 - 1Laiba AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spring 2022 - MTH301 - 1Document1 paginăSpring 2022 - MTH301 - 1HumaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4038T2Su2010 SolutionsDocument5 pagini4038T2Su2010 SolutionsMohammed Waleed SuleimanÎncă nu există evaluări
- ME 201/MTH 281/ME 400/CHE 400 Assignment #1 2009: Lecture Schedule and ReadingDocument2 paginiME 201/MTH 281/ME 400/CHE 400 Assignment #1 2009: Lecture Schedule and Readingsoccerrocker808Încă nu există evaluări
- Assignment#1 Fall 2018: Before Attempting The Solution of This AssignmentDocument1 paginăAssignment#1 Fall 2018: Before Attempting The Solution of This AssignmentSyed Abdul Mussaver ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spring 2019 - MTH632 - 1Document2 paginiSpring 2019 - MTH632 - 1AatifÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment No 1 (MTH 202) : Maximum Marks: 10 Due Date: 28 November, 2018Document2 paginiAssignment No 1 (MTH 202) : Maximum Marks: 10 Due Date: 28 November, 2018Abdul Muqeet KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- FE Exam Preparation - MathematicsDocument4 paginiFE Exam Preparation - MathematicssaurabhsubhuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fall 2022 - MTH101 - 2Document1 paginăFall 2022 - MTH101 - 2Ali ShanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Calculus Q3 Module 8Document25 paginiBasic Calculus Q3 Module 8Rubyrose CorreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fall 2022 - MTH001 - 1Document2 paginiFall 2022 - MTH001 - 1Urwa ButtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spring 2023 - MTH404 - 1Document1 paginăSpring 2023 - MTH404 - 1Isha NasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Differential Equations ReviewDocument31 paginiDifferential Equations ReviewAnonymous cUjriaHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Legal 2 - 220904 - 201318Document17 paginiLegal 2 - 220904 - 201318Surajit RoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spring 2023 - MTH621 - 1Document1 paginăSpring 2023 - MTH621 - 1AneesaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment#1 Spring 2021: Before Attempting The Solution of This AssignmentDocument2 paginiAssignment#1 Spring 2021: Before Attempting The Solution of This Assignmentm umairÎncă nu există evaluări
- Appendix - ODE ReviewDocument11 paginiAppendix - ODE ReviewAriana Ribeiro LameirinhasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Screening Task ILK10 - ReviewerDocument5 paginiScreening Task ILK10 - ReviewerVandana GariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- June 2013 MS - C4 EdexcelDocument28 paginiJune 2013 MS - C4 EdexcelMomen YasserÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spring 2022 - MTH101 - 2Document3 paginiSpring 2022 - MTH101 - 2AhmeddedÎncă nu există evaluări
- First Order OdeDocument49 paginiFirst Order OdeKuma Ravelu100% (1)
- Def Assesed CWDocument2 paginiDef Assesed CWSumeer BoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fall 2022 - MTH202 - 2Document2 paginiFall 2022 - MTH202 - 2MUHAMMAD NABEEL SHAHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 - Part 1Document7 paginiChapter 1 - Part 1Philimond SegieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 3Document2 paginiAssignment 3Mowahhid ShakeelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lec 3 MathDocument6 paginiLec 3 Mathowronrawan74Încă nu există evaluări
- Fall 2022 - MTH101 - 2 - SOLDocument2 paginiFall 2022 - MTH101 - 2 - SOLPumped KicksÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ict Generic Brochure PDFDocument28 paginiIct Generic Brochure PDFSyed Muhammad Ashfaq AshrafÎncă nu există evaluări
- My QuotesDocument1 paginăMy QuotesSyed Muhammad Ashfaq AshrafÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elon Musk Asks Overlooked Engineers To Tweet Him Directly For Jobs at NeuralinkDocument5 paginiElon Musk Asks Overlooked Engineers To Tweet Him Directly For Jobs at NeuralinkSyed Muhammad Ashfaq AshrafÎncă nu există evaluări
- NewportDartmouthThesis PDFDocument27 paginiNewportDartmouthThesis PDFSyed Muhammad Ashfaq AshrafÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Guide To MarkingDocument3 paginiA Guide To MarkingSyed Muhammad Ashfaq AshrafÎncă nu există evaluări
- CieDocument1 paginăCieSyed Muhammad Ashfaq AshrafÎncă nu există evaluări
- Monlymisspelledmisusedwords 2Document1 paginăMonlymisspelledmisusedwords 2Syed Muhammad Ashfaq AshrafÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5.4 Exercise 2 - Complex IonsDocument1 pagină5.4 Exercise 2 - Complex IonsSyed Muhammad Ashfaq AshrafÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4.7 Exercise 1 - AminesDocument1 pagină4.7 Exercise 1 - AminesSyed Muhammad Ashfaq AshrafÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microsoft Project Management Software Book Excerpt 3Document40 paginiMicrosoft Project Management Software Book Excerpt 3Mohamed Darwish MohamedÎncă nu există evaluări
- BL 202Document1 paginăBL 202Syed Muhammad Ashfaq AshrafÎncă nu există evaluări
- Links 31 July 2015Document1 paginăLinks 31 July 2015Syed Muhammad Ashfaq AshrafÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Guide To GradingDocument5 paginiA Guide To GradingSyed Muhammad Ashfaq AshrafÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answers To 4.2 ExercisesDocument1 paginăAnswers To 4.2 ExercisesSyed Muhammad Ashfaq AshrafÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4.4 Exercise 2 - IsomerismDocument1 pagină4.4 Exercise 2 - IsomerismMai Chi0% (1)
- ChemEqbm Exercise1 KCDocument2 paginiChemEqbm Exercise1 KCheretolearnscienceÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5.4 Exercise 2 - Complex IonsDocument1 pagină5.4 Exercise 2 - Complex IonsSyed Muhammad Ashfaq AshrafÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4.3 Exercise 1 - Bronsted-Lowry TheoryDocument1 pagină4.3 Exercise 1 - Bronsted-Lowry TheoryShamala NadarajuÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4.6 Exercise 1 - Aromatic ChemistryDocument1 pagină4.6 Exercise 1 - Aromatic Chemistrynecromancer2412Încă nu există evaluări
- Answers To 4.7 ExercisesDocument2 paginiAnswers To 4.7 ExercisesSyed Muhammad Ashfaq AshrafÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4.3 Answers To ExercisesDocument2 pagini4.3 Answers To ExercisesSyed Muhammad Ashfaq AshrafÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4.1 Answers To ExercisesDocument1 pagină4.1 Answers To ExercisesridithaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4.1 Exercise 1Document2 pagini4.1 Exercise 1ridithaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4.1 Exercise 2 - Changing The Rate of A ReactionDocument1 pagină4.1 Exercise 2 - Changing The Rate of A ReactionSyed Muhammad Ashfaq AshrafÎncă nu există evaluări
- ANSWERS To 4.11 ExercisesDocument2 paginiANSWERS To 4.11 ExercisesSyed Muhammad Ashfaq AshrafÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4.1 Exercise 1Document2 pagini4.1 Exercise 1ridithaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2channelbluetoothrelaymodulev6 1Document24 pagini2channelbluetoothrelaymodulev6 1Syed Muhammad Ashfaq AshrafÎncă nu există evaluări
- BGP Soft Reset Enhancement: Feature OverviewDocument14 paginiBGP Soft Reset Enhancement: Feature OverviewTIBUS145Încă nu există evaluări
- OssecDocument123 paginiOssecSrinivasarao KasiÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIM Implementation - Global StrategiesDocument11 paginiBIM Implementation - Global StrategiesEleazar MendezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iexpenses Overview 1Document48 paginiIexpenses Overview 1rcp.generalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Enterpreneur Interview: BY K.Pramila BBA-2 YearDocument18 paginiEnterpreneur Interview: BY K.Pramila BBA-2 YearbhuvaneswariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Live 4992 9623 JairDocument76 paginiLive 4992 9623 JairAntonio MarcegagliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adobe Scan 29-Dec-2023Document1 paginăAdobe Scan 29-Dec-2023kanishkakhanna.inboxÎncă nu există evaluări
- HNMUN 2020 Guide To RegistrationDocument2 paginiHNMUN 2020 Guide To Registrationahmad zulfikarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Excavation Sequence Layout Drawing R1Document2 paginiExcavation Sequence Layout Drawing R1MrCuong .utcÎncă nu există evaluări
- HS-MATH-PC4 - Answer and Reference Section Back CoverDocument83 paginiHS-MATH-PC4 - Answer and Reference Section Back Cover임민수Încă nu există evaluări
- PSpice9.1 TutorialDocument25 paginiPSpice9.1 TutorialJethro Exequiel SibayanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 魏秀参 Usbm@A?2M Q1Av: ?Iit,Ffhk/Xmdmx2/Mx+Mfr2BtbfDocument178 pagini魏秀参 Usbm@A?2M Q1Av: ?Iit,Ffhk/Xmdmx2/Mx+Mfr2Btbf杨乔Încă nu există evaluări
- 37 Tips and Tricks Using HD2Document4 pagini37 Tips and Tricks Using HD2Nafisa MeisaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Uninformed SearchDocument41 pagini2 Uninformed SearchPratyushÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ppa CVDocument3 paginiPpa CVRashid Mahmood JaatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Milling ProgramDocument20 paginiMilling ProgramSudeep Kumar SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transmission Request FormDocument1 paginăTransmission Request FormDesikanÎncă nu există evaluări
- IBM DS3200 System Storage PDFDocument144 paginiIBM DS3200 System Storage PDFelbaronrojo2008Încă nu există evaluări
- SamsungDocument11 paginiSamsungAvramescu DanielÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To MicroprocessorDocument31 paginiIntroduction To MicroprocessorMuhammad DawoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- DbaDocument29 paginiDbadbareddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- BRKACI-2006 Intergration of Hypervisors and L4-7 Service Into ACI PDFDocument83 paginiBRKACI-2006 Intergration of Hypervisors and L4-7 Service Into ACI PDFDat PhamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bind Variables and Execute ImmediateDocument2 paginiBind Variables and Execute ImmediateSukh VirÎncă nu există evaluări