Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Co Efficient Expansion
Încărcat de
rt1973Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Co Efficient Expansion
Încărcat de
rt1973Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Table 3: Expansion Characteristics of Steel Conduit and Tubing Coefficient of Thermal Expansion = 6.50 x 10 -6 in./in.
/ F* Temperature Length Change Temperature Length Change Temperature Length Change Temperature Length Change Changes in Steel Conduit Changes in Steel Conduit Changes in Steel Conduit Changes in Steel Conduit Degrees F in./100 feet Degrees F in./100 feet Degrees F in./100 feet Degrees F in./100 feet 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 0.04 0.08 0.12 0.16 0.20 0.23 0.27 0.31 0.35 0.39 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100
0.44 0.47 0.51 0.55 0.59 0.62 0.66 0.70 0.74 0.78
105 110 115 120 125 130 135 140 145 150
0.82 0.86 0.90 0.94 0.98 1.01 1.05 1.09 1.13 1.17
155 160 165 170 175 180 185 190 195 200
1.21 1.25 1.29 1.33 1.37 1.40 1.44 1.48 1.52 1.56
*A Fine Print Note in Section 300.7(B) of the NEC refers the user to the Expansion Characteristics of PVC ,Table 352.44(A) for Rigid Nonmetallic Conduit and suggests multiplying the lengths in that table by 0.20 in order to obtain a nominal number for steel conduit. Since the coefficient of steel conduit is between 2-3 times less than that of PVC conduit you would need more expansion fittings for PVC conduit, for a given temperature and length than for steel conduit. We have used the coefficient of expansion of steel, rather than the 0.20 multiplier, to calculate the exact length of change figures in Table 3.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Pressure Drop of Air through Schedule 40 Steel PipeDocument1 paginăPressure Drop of Air through Schedule 40 Steel PipeAzariah ThiraviamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid Pipping - 21-30Document10 paginiFluid Pipping - 21-30andytuorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Description Pipe Size: Cooling Water PipingDocument3 paginiDescription Pipe Size: Cooling Water PipingSuresh ChÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bronze Ball Valves: 600 PSI/41.4 Bar Non-Shock Cold Working Pressure 150 PSI/10.3 Bar Saturated SteamuDocument1 paginăBronze Ball Valves: 600 PSI/41.4 Bar Non-Shock Cold Working Pressure 150 PSI/10.3 Bar Saturated SteamuRuben AranaÎncă nu există evaluări
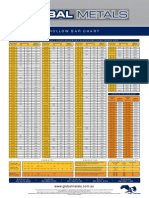
- Hollow Bar ChartDocument1 paginăHollow Bar Charthornet121Încă nu există evaluări
- PVC Cables FinolexDocument8 paginiPVC Cables FinolexMaria DenetÎncă nu există evaluări
- ANSI PIPE SCHEDULES wall thickness and weight chartDocument2 paginiANSI PIPE SCHEDULES wall thickness and weight chartNagesh KhandareÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sarthak Dadkar PIIAL-Practical-6 PDFDocument7 paginiSarthak Dadkar PIIAL-Practical-6 PDFAjuba AbujaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Metric/Imperial/AWG Conductor Equivalents TableDocument1 paginăMetric/Imperial/AWG Conductor Equivalents TableMuhammad Amin HunzaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Galian TimbunanDocument2 paginiGalian TimbunanDenti Rakhael D PanjaitanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Recommended insulation thickness chart for controlling heat gain and condensationDocument1 paginăRecommended insulation thickness chart for controlling heat gain and condensationSteven TrigoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Civil Construction ActivitiesDocument3 paginiCivil Construction ActivitiessreeluÎncă nu există evaluări
- SDM Pipe Calculations (SI)Document23 paginiSDM Pipe Calculations (SI)Mohsen AghaeiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Measuring Cutting and Joining PipesDocument23 paginiMeasuring Cutting and Joining PipesJosue Carubio Ricalde Jr.Încă nu există evaluări
- Specification of Steel BarDocument1 paginăSpecification of Steel BarsutrisnoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1E ThermocableDocument12 pagini1E ThermocableCarlos Enrique Sánchez CáceresÎncă nu există evaluări
- RBL Precision Ansi RollerDocument8 paginiRBL Precision Ansi RollerRingball_GusÎncă nu există evaluări
- NSF61Document12 paginiNSF61Congson Jeff100% (1)
- SVL606 Stainless Steel Safety Valve: DescriptionDocument4 paginiSVL606 Stainless Steel Safety Valve: DescriptionalejjavierdelgadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Piping Wall Thickness / ScheduleDocument3 paginiPiping Wall Thickness / ScheduleGanesh AdityaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steel Bars, Carbon, Hot-Wrought, Special Quality: Standard Specification ForDocument6 paginiSteel Bars, Carbon, Hot-Wrought, Special Quality: Standard Specification ForIngrid Tatiana RojasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Sheet for Steel Flanges and Pipe FittingsDocument2 paginiData Sheet for Steel Flanges and Pipe FittingsgarrybieberÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pds Flange Data SheetDocument2 paginiPds Flange Data Sheetabhaysharma99Încă nu există evaluări
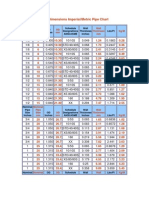
- Pipe Dimensions ImperialDocument7 paginiPipe Dimensions ImperialJason PoulinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bao Gia Ebara Italy NS 1-6-2014 Sao VietDocument6 paginiBao Gia Ebara Italy NS 1-6-2014 Sao Vietjackyt09Încă nu există evaluări
- King Scientific CatalogueDocument694 paginiKing Scientific Catalogue0j1u9nmkv534vw9v100% (1)
- A Complete Guide To Pipe SizesDocument25 paginiA Complete Guide To Pipe SizesahmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manufacturers of Vibration Control Products and Pipe Accessories Data SheetDocument2 paginiManufacturers of Vibration Control Products and Pipe Accessories Data Sheetbman0051401Încă nu există evaluări
- Practical Data HandbookDocument120 paginiPractical Data Handbookjtamminga100% (18)
- Orrcon Steel PFCDocument1 paginăOrrcon Steel PFCmjscarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tuberia Fibra de VidrioDocument0 paginiTuberia Fibra de VidrioFernando Reyes GomezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drain PumpDocument36 paginiDrain Pumpapi-224604257Încă nu există evaluări
- Hex Head Bolts, Steel: Maryland MetricsDocument2 paginiHex Head Bolts, Steel: Maryland MetricsEva Ibáñez Ramos100% (1)
- Ansi Pipe ScheduleDocument1 paginăAnsi Pipe ScheduleRameshBMÎncă nu există evaluări
- MS SAIL TolerancesDocument30 paginiMS SAIL TolerancesAmirthasubash Rajendran100% (1)
- ASTM E 11-01 Standard Specification For Wire Cloth and Sieves For Testing PurposesDocument5 paginiASTM E 11-01 Standard Specification For Wire Cloth and Sieves For Testing PurposesPablo Antonio Valcárcel VargasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Generation Boiler Tubes GuideDocument12 paginiPower Generation Boiler Tubes GuidewalitedisonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Astm A29Document22 paginiAstm A29jangaswathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bars & Rods: All Dimensions in Mm. Cat L - 2008 Jindal Aluminium Ltd. I - 1 All Dimensions in MMDocument8 paginiBars & Rods: All Dimensions in Mm. Cat L - 2008 Jindal Aluminium Ltd. I - 1 All Dimensions in MMnadaf2Încă nu există evaluări
- Grip Type U-BoltsDocument1 paginăGrip Type U-BoltsPaul QueenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Working of Breather Valve Working On TanksDocument4 paginiWorking of Breather Valve Working On Tanks54045114Încă nu există evaluări
- KTY Silicon Sensors GuideDocument2 paginiKTY Silicon Sensors GuideHarpreet SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pipe Schedule PDFDocument1 paginăPipe Schedule PDFSrinivasan SeenuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermal Expansion DataDocument4 paginiThermal Expansion DataMajid MoradiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heating Systems Troubleshooting & Repair: Maintenance Tips and Forensic ObservationsDe la EverandHeating Systems Troubleshooting & Repair: Maintenance Tips and Forensic ObservationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pipeline Rules of Thumb Handbook: A Manual of Quick, Accurate Solutions to Everyday Pipeline Engineering ProblemsDe la EverandPipeline Rules of Thumb Handbook: A Manual of Quick, Accurate Solutions to Everyday Pipeline Engineering ProblemsEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (10)
- All-in-One Manual of Industrial Piping Practice and MaintenanceDe la EverandAll-in-One Manual of Industrial Piping Practice and MaintenanceEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Ceramic Materials for Energy Applications V: A Collection of Papers Presented at the 39th International Conference on Advanced Ceramics and CompositesDe la EverandCeramic Materials for Energy Applications V: A Collection of Papers Presented at the 39th International Conference on Advanced Ceramics and CompositesJosef MatyášÎncă nu există evaluări
- Enhanced Oil Recovery: Resonance Macro- and Micro-Mechanics of Petroleum ReservoirsDe la EverandEnhanced Oil Recovery: Resonance Macro- and Micro-Mechanics of Petroleum ReservoirsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Advances in Solid Oxide Fuel Cells XDe la EverandAdvances in Solid Oxide Fuel Cells XMihails KusnezoffÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical Properties and Performance of Engineering Ceramics and Composites XIDe la EverandMechanical Properties and Performance of Engineering Ceramics and Composites XIJonathan SalemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Friction Stir Welding of High Strength 7XXX Aluminum AlloysDe la EverandFriction Stir Welding of High Strength 7XXX Aluminum AlloysÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heat Exchanger Equipment Field Manual: Common Operating Problems and Practical SolutionsDe la EverandHeat Exchanger Equipment Field Manual: Common Operating Problems and Practical SolutionsEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (6)
- Process Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersDe la EverandProcess Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transactions of the American Society of Civil Engineers, vol. LXX, Dec. 1910 Tests of Creosoted Timber, Paper No. 1168De la EverandTransactions of the American Society of Civil Engineers, vol. LXX, Dec. 1910 Tests of Creosoted Timber, Paper No. 1168Încă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Processing and Manufacturing Technologies for Nanostructured and Multifunctional Materials IIDe la EverandAdvanced Processing and Manufacturing Technologies for Nanostructured and Multifunctional Materials IITatsuki OhjiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermal Insulation Handbook for the Oil, Gas, and Petrochemical IndustriesDe la EverandThermal Insulation Handbook for the Oil, Gas, and Petrochemical IndustriesEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (3)
- 1Document13 pagini1cherif yahyaouiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Designing Eletricalfor For Fire PumpsDocument6 paginiDesigning Eletricalfor For Fire Pumpsrt1973Încă nu există evaluări
- M. Dwelling UnitDocument5 paginiM. Dwelling Unitrt1973Încă nu există evaluări
- Vigi Module Selection PDFDocument1 paginăVigi Module Selection PDFrt1973Încă nu există evaluări
- Inspection and Test Record For Electric Motor - Cage-Induction Type (Including Control Unit)Document3 paginiInspection and Test Record For Electric Motor - Cage-Induction Type (Including Control Unit)karthik_egclÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Quality Basics 4Document1 paginăPower Quality Basics 4rt1973Încă nu există evaluări
- MCA & MOP of CircuitsDocument7 paginiMCA & MOP of CircuitsMiko QuijanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Applying Demand & Diversity FactorDocument5 paginiApplying Demand & Diversity Factoranchak99100% (1)
- Digital Earth Resistance Tester Measures Grounding InstallationsDocument1 paginăDigital Earth Resistance Tester Measures Grounding Installationsrt1973Încă nu există evaluări
- Power Quality Basics 3Document1 paginăPower Quality Basics 3rt1973Încă nu există evaluări
- Clamp MeterDocument1 paginăClamp Meterrt1973Încă nu există evaluări
- UPS Setup and TroubleshootDocument1 paginăUPS Setup and TroubleshootAbner SumalgyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curve 19-S1A8147600Document1 paginăCurve 19-S1A8147600Jose Luis Rodriguez RezaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Correcting Unbalanced Voltage Situations - EC&M 3 PDFDocument1 paginăCorrecting Unbalanced Voltage Situations - EC&M 3 PDFrt1973Încă nu există evaluări
- Correcting Unbalanced Voltage Situations - EC&M 2Document1 paginăCorrecting Unbalanced Voltage Situations - EC&M 2rt1973Încă nu există evaluări
- Insulation Tester 5KVDocument2 paginiInsulation Tester 5KVrt1973Încă nu există evaluări
- Power Quality Basics 1Document1 paginăPower Quality Basics 1rt1973Încă nu există evaluări
- Correcting Unbalanced Voltage Situations - EC&MDocument3 paginiCorrecting Unbalanced Voltage Situations - EC&Mrt1973Încă nu există evaluări
- Correcting Unbalanced Voltage Situations - EC&M 1Document1 paginăCorrecting Unbalanced Voltage Situations - EC&M 1rt1973Încă nu există evaluări
- Power Quality Basics 2Document1 paginăPower Quality Basics 2rt1973Încă nu există evaluări
- Amerec 1Document17 paginiAmerec 1rt1973Încă nu există evaluări
- Cs 09Document1 paginăCs 09rt1973Încă nu există evaluări
- Micrologic Setup GuideDocument4 paginiMicrologic Setup Guide322399mk7086Încă nu există evaluări
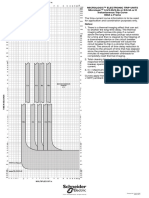
- Micrologic 5.0/6.0 A/P/H TRIP UNIT Characteristic Trip Curve No. 613-5Document1 paginăMicrologic 5.0/6.0 A/P/H TRIP UNIT Characteristic Trip Curve No. 613-5rt1973Încă nu există evaluări
- 610 5Document1 pagină610 5rt1973Încă nu există evaluări
- 613 03 PDFDocument1 pagină613 03 PDFrt1973Încă nu există evaluări
- 613 01Document1 pagină613 01rt1973Încă nu există evaluări
- 610 5Document1 pagină610 5rt1973Încă nu există evaluări
- 613 01Document1 pagină613 01rt1973Încă nu există evaluări
- All NEIS StandardsDocument2 paginiAll NEIS Standardsdelmar02Încă nu există evaluări