Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Pdfa2 7
Încărcat de
aizatDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Pdfa2 7
Încărcat de
aizatDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Chapter 2
Transparency
12
Forces And Motion
The Effects Of A Force
A force acting on an object Types of force
can change its • Frictional force • Gravitational force
• speed • shape • Mechanical force • Electrical force
• direction • size • Nuclear force • Magnetic force
Balanced Forces Unbalanced Forces
The forces on the person are balanced. The forces acting on the book are not balanced.
R The floor pushes The friction between the
upwards on the table/book surfaces exerts
person. a leftward force upon the R The table pushes
rightward-moving book. upwards on the book.
mg = R F
Gravity pulls
downwards on Gravity pulls
the person.
mg = R mg downwards on
mg the book.
Newtonʼs Second Law Of Motion
Force is directly proportional to the rate of change of momentum and it occurs in the
direction of the force.
mv – mu v–u F = ma F = ma
F∝ t = m ( t ) = ma
F
F = kma
F = ma (k = 1) The same force exerted on a larger
mass produces a correspondingly
Force of 1 N = 1 kg m s–2 F smaller acceleration
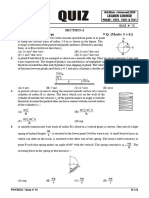
Question The figure shows that one end of a string is attached to a 3 kg load and
the other end is attached to a 2 kg load that is placed on a smooth table.
What is the tension of the string? (Acceleration due to gravity = 10 m s–2)
Solution a
For 2 kg mass, T = m1a ……... (1) T
m1 = 2 kg
For 3 kg mass, m2g – T = m2a …...… (2) T
(1) + (2), m2g = m1a + m2a a m2 = 3 kg
= (m1 + m2)a
m2g m2g
Acceleration a = = 3 × 10 = 6 m s–2
m1 + m2 2+3
Substitute a into (1), Tension of string T = 2 × 6 = 12 N
© Marshall Cavendish ( Malaysia ) Sdn. Bhd.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pagini6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pagini6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Power Factor Testing of Power Distribution TransformersDocument8 paginiPower Factor Testing of Power Distribution TransformersfvicunaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Basics of Insulation TestingDocument6 paginiThe Basics of Insulation TestingbhpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Interview QuestionDocument118 paginiElectrical Interview QuestionMumtaj Khan0% (1)
- ANSYS NCode DesignLife - Usergroups 2011 RADDocument31 paginiANSYS NCode DesignLife - Usergroups 2011 RADSunil SainiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Statics: Vector Mechanics For EngineersDocument28 paginiStatics: Vector Mechanics For EngineersAgus KusnayatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compliance Evaluation of BTS ICNIRP Guidelines.: As PerDocument27 paginiCompliance Evaluation of BTS ICNIRP Guidelines.: As Persyrish2622Încă nu există evaluări
- Energy Elastic Strain EnergyDocument14 paginiEnergy Elastic Strain EnergyamirwmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Small Transmitting Loop Antennas Aa5tbDocument14 paginiSmall Transmitting Loop Antennas Aa5tbDiego García MedinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Explicit Dynamics Chapter 9 Material Models PDFDocument54 paginiExplicit Dynamics Chapter 9 Material Models PDFSaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 400kv SubstationDocument38 pagini400kv SubstationVenkata Suresh Mandava75% (4)
- Engineering Mechanics: StaticsDocument31 paginiEngineering Mechanics: Statics재인디디Încă nu există evaluări
- Moment of A Force: ObjectivesDocument32 paginiMoment of A Force: ObjectivesMohamaadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 8Document48 paginiLecture 8riganÎncă nu există evaluări
- WB-Mech 120 Ch07 BucklingDocument18 paginiWB-Mech 120 Ch07 BucklinghebiyongÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Axial LoadingDocument43 pagini2 Axial LoadingWagih AlfakihÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hooke's Law and The Spring ConstantDocument4 paginiHooke's Law and The Spring ConstantJuan Carlos Mejia Macias0% (1)
- How To Find The Suitable Size of Cable & Wire - ExamplesDocument7 paginiHow To Find The Suitable Size of Cable & Wire - ExamplesShyamraj ArunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mosfet Chapter - 4Document42 paginiMosfet Chapter - 4田佳生100% (1)
- Module Chapter 3-Gravitation2020 PDFDocument20 paginiModule Chapter 3-Gravitation2020 PDFNoorleha Mohd Yusoff100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Torsion PDFDocument30 paginiChapter 4 Torsion PDFadlinasir67% (3)
- Pdfa2 8Document1 paginăPdfa2 8aizatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pdfa2 14Document1 paginăPdfa2 14aizatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pdfa2 12Document1 paginăPdfa2 12aizatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pdfa2 16Document1 paginăPdfa2 16aizat100% (1)
- Pdfa2 13Document1 paginăPdfa2 13aizatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pdfa4 3Document1 paginăPdfa4 3aizatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Specific Latent Heat (I) : Heating Ice To Form VapourDocument1 paginăSpecific Latent Heat (I) : Heating Ice To Form VapouraizatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pdfa4 1Document1 paginăPdfa4 1aizatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical Intro 17.0 WS06.2 JointsDocument15 paginiMechanical Intro 17.0 WS06.2 JointsInventor SolidworksÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mech Intro 18.0 M01 Lecture Slides IntroductionDocument73 paginiMech Intro 18.0 M01 Lecture Slides IntroductionJorge KfaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mesh-Intro 17.0 M05 Mesh Quality and Advanced TopicsDocument39 paginiMesh-Intro 17.0 M05 Mesh Quality and Advanced Topicsjust randomÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 10Document34 paginiChapter 10Gia BaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- A FEM IntroductionDocument18 paginiA FEM IntroductionAnonymous Bdt0OGh100% (1)
- Me 2353 - Finite Element AnalysisDocument4 paginiMe 2353 - Finite Element AnalysiscprabhakaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch3 Contact StiffnessDocument16 paginiCh3 Contact Stiffnessanilmavi100% (1)
- Mechanical Intro 17.0 M03 Structural Analysis PDFDocument49 paginiMechanical Intro 17.0 M03 Structural Analysis PDFFedericaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Finite Element Method-Elements of Elasticity: BY ANJALI A (1211108) JEYAGOMATHI (1211136)Document23 paginiFinite Element Method-Elements of Elasticity: BY ANJALI A (1211108) JEYAGOMATHI (1211136)Makesh Kumar100% (1)
- Simcenter 3D 2020.1 - Structures - What's NewDocument27 paginiSimcenter 3D 2020.1 - Structures - What's NewThanakorn VichiensamuthÎncă nu există evaluări
- SCDM-Intro 17.0 Module04 FEA ModelingDocument29 paginiSCDM-Intro 17.0 Module04 FEA Modelingmarcosandia1974Încă nu există evaluări
- Intro To FemDocument28 paginiIntro To FemcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ce8395 Notes PDFDocument75 paginiCe8395 Notes PDFSisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pdfa4 6Document1 paginăPdfa4 6aizatÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10.1038@s42254 019 0068 9 PDFDocument2 pagini10.1038@s42254 019 0068 9 PDFLeonardo de AraujoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pdfa3 1Document1 paginăPdfa3 1aizatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5b Crystal Imperfections DislocationsDocument94 paginiChapter 5b Crystal Imperfections DislocationsSayantan DexÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mech Nonlin Connections 14.5 L02 Interface TreatmentsDocument32 paginiMech Nonlin Connections 14.5 L02 Interface TreatmentsGanesh R NavadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Department of Mechanical Engineering: National Institute of TechnologyDocument38 paginiDepartment of Mechanical Engineering: National Institute of TechnologyRK ZazzyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pdfa3 3Document1 paginăPdfa3 3aizatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Finite Element FormulationDocument38 paginiFinite Element FormulationntrjnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Statics: Vector Mechanics For EngineersDocument28 paginiStatics: Vector Mechanics For EngineersNidushan NethsaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coupled Field AnalysisDocument12 paginiCoupled Field AnalysisAnonymous 5pwc6LxvHVÎncă nu există evaluări
- Navier StokesDocument6 paginiNavier StokesanjunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Statics Notes: Chap1 Page 1 of 7Document7 paginiStatics Notes: Chap1 Page 1 of 7Hussain Mohammad ImranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture # 1: "Engineering Mechanics"Document18 paginiLecture # 1: "Engineering Mechanics"Razaq Khan MandokhailÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10.2 GravityDocument9 pagini10.2 GravityGeorge AmoateyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gravitation Re TheoryDocument20 paginiGravitation Re TheoryYash MehraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gravation PDFDocument10 paginiGravation PDFJayant AshishÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 Newton's Law of Motion: 3.1 The Important StuffDocument19 paginiChapter 3 Newton's Law of Motion: 3.1 The Important StuffNoppadol EGATÎncă nu există evaluări
- GravitationDocument12 paginiGravitationdav borlÎncă nu există evaluări
- GravitationDocument10 paginiGravitationarhaanhafeez00Încă nu există evaluări
- GraviDocument52 paginiGraviUJJVAL GAHOIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Revision NotesDocument19 paginiClass 9 Science Chapter 10 Revision Notesrupu singhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture No. 6 - Linear Momentum and Tension in A StringDocument9 paginiLecture No. 6 - Linear Momentum and Tension in A StringAli AbbasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5.work Energy and PowerExercise STEMDocument46 pagini5.work Energy and PowerExercise STEMAssem HefnyÎncă nu există evaluări
- GravitylessonDocument15 paginiGravitylessonVishavjit ButtarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Force Summary NoteDocument4 paginiScience Force Summary NotedenyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dynamics of MotionDocument8 paginiDynamics of Motionjulianne sanchezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pdfa5 2Document1 paginăPdfa5 2aizatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pdfa4 7Document1 paginăPdfa4 7aizatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pdfa5 3Document1 paginăPdfa5 3aizatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pdfa5 3Document1 paginăPdfa5 3aizatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pdfa4 8Document1 paginăPdfa4 8aizatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pdfa4 6Document1 paginăPdfa4 6aizatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pdfa4 5Document1 paginăPdfa4 5aizatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pdfa5 1Document1 paginăPdfa5 1aizatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pdfa4 2Document1 paginăPdfa4 2aizatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pdfa3 2Document1 paginăPdfa3 2aizatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pdfa4 1Document1 paginăPdfa4 1aizatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pdfa3 7Document1 paginăPdfa3 7aizatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pdfa3 5Document1 paginăPdfa3 5aizatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pdfa4 3Document1 paginăPdfa4 3aizatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Specific Latent Heat (I) : Heating Ice To Form VapourDocument1 paginăSpecific Latent Heat (I) : Heating Ice To Form VapouraizatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pdfa3 4Document1 paginăPdfa3 4aizatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pdfa3 6Document1 paginăPdfa3 6aizatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pdfa3 1Document1 paginăPdfa3 1aizatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pdfa3 3Document1 paginăPdfa3 3aizatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pdfa2 15Document1 paginăPdfa2 15aizatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pdfa2 10Document1 paginăPdfa2 10aizatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pdfa2 9Document1 paginăPdfa2 9aizat100% (1)
- Pdfa2 11Document1 paginăPdfa2 11aizatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Process Mechanism of EDM ProcessDocument9 paginiProcess Mechanism of EDM ProcessdongreganeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 11 Science Seminar Paper Part 2 2020Document14 paginiGrade 11 Science Seminar Paper Part 2 2020My WorksÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modelling and Control of CCM Boost PFC Using K-Factor MethodDocument1 paginăModelling and Control of CCM Boost PFC Using K-Factor Methoddivya k sÎncă nu există evaluări
- Non-Isolated Buck APFC LED Driver Description FeaturesDocument9 paginiNon-Isolated Buck APFC LED Driver Description FeaturesRisoSilvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- B.Sc. I Semester Physics:: Paper I Mechanics and Oscillations:: Imp QuestionsDocument2 paginiB.Sc. I Semester Physics:: Paper I Mechanics and Oscillations:: Imp QuestionsReddyvari VenugopalÎncă nu există evaluări
- GIS RC Voltage DividerDocument6 paginiGIS RC Voltage DividerEldin EnggÎncă nu există evaluări
- GZM00214 - Gen DataDocument8 paginiGZM00214 - Gen Datatua aggrekoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fixed Bed (Difference Between Fixed and Fluidized Bed) Burke-Plummer Equation by Torrecillas Martínez IsaacDocument3 paginiFixed Bed (Difference Between Fixed and Fluidized Bed) Burke-Plummer Equation by Torrecillas Martínez Isaacmauricio ortegaÎncă nu există evaluări
- EPM-GL-PI-CLC-0004 - Rev 0 - Slug Flow Force CalculationDocument4 paginiEPM-GL-PI-CLC-0004 - Rev 0 - Slug Flow Force CalculationHernán DazaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Natural Mode of Synchronous Operation. It Implies ThatDocument20 paginiNatural Mode of Synchronous Operation. It Implies ThatTana AzeezÎncă nu există evaluări
- LQuiz (TOV1) # 12 (Eng)Document4 paginiLQuiz (TOV1) # 12 (Eng)PkrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Modeling of Sheet Piles Behavior To Improve Their Numerical Modeling and DesignDocument12 paginiPhysical Modeling of Sheet Piles Behavior To Improve Their Numerical Modeling and DesignAhmed RamadanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Circuit Lab: Nai Soknov E20170539Document6 paginiElectrical Circuit Lab: Nai Soknov E20170539SokNov NaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 VS Ac194 DSDocument1 pagină1 VS Ac194 DSYesenia Jaime RoaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electric Circuit Chapter 7 PDFDocument52 paginiElectric Circuit Chapter 7 PDFasdy811224Încă nu există evaluări
- Computing Capacitance: Created in COMSOL Multiphysics 5.5Document16 paginiComputing Capacitance: Created in COMSOL Multiphysics 5.5Adnen Guedria100% (1)
- Up Mech WavesDocument21 paginiUp Mech WavescjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manual HRN-43 43NDocument2 paginiManual HRN-43 43NArtem MarchenkoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Generating Shock AbsorberDocument14 paginiPower Generating Shock Absorbertejas chikhlikar100% (1)
- What Is Charging by Induction and How Does It Occur? How Can The Results of Charging by Induction Be Predicted and Explained?Document2 paginiWhat Is Charging by Induction and How Does It Occur? How Can The Results of Charging by Induction Be Predicted and Explained?Mico James TrillesÎncă nu există evaluări