Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Settings Transfer Utilities PDF
Încărcat de
sajedarefinTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Settings Transfer Utilities PDF
Încărcat de
sajedarefinDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
CAPE Series
Settings Transfer Utilities
May 2005
Electrocon International, Inc. Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA
Copyright 1990, 2005 by Electrocon International, Inc. All rights reserved This document is the sole property of Electrocon International, Inc. It may not be supplied to any third party, or copied or reproduced in any form, without the express written permission of Electrocon International, Inc. All copies and reproductions shall be the property of Electrocon International, Inc. and must bear this ownership statement in its entirety.
Contents
Overview Section 1 Section 2 Section 3 Appendix Exporting Settings to a Neutral Interface Database Importing Settings from a Neutral Interface Database Editing a Neutral Interface Database with the Client Access Program Neutral Interface Reference
ii
Overview
Overview of Settings Transfer Utilities
Comparison and Upload Program (CUP) Neutral Interface Tables
Database Editor
Client Access Program (CAP) for Relay Test Engineers Third-party Software
CAPE Database
Functional Organization of Settings Transfer Utilities As the CAPE database evolved into the master database it was designed to be for its users, it became clear that its contents were too important to be limited to CAPE itself. Requests to share the data, particularly protective device settings, increased. While the CAPE database design has been open (i.e. documented and freely available) since its inception, the efficient fourth order normal design of the data structures made it difficult for an outsider to fathom. Further, those data structures had to be free to grow as new features and enhancements were implemented. It is very difficult for a third party to maintain an interface to a moving target. The proverbial last straw occurred when widespread adoption of digital relays made paper transmittal of long lists of settings inefficient, error-prone, and generally unacceptable. Electronic transmittal was the wave of the future. Our solution to this challenge is centered on a small number of data tables, simplified in design, implemented in a near-universal database product (Microsoft Access), and collectively known as the Neutral Interface. Neutral really means product neutral. Almost anyone can write software to link to an Access database file. We have done it with the Setting Transfer Utilities and you or any vendor can do it too. You can share relay settings of all kinds with whomever you wish.
Overview In summary, the objectives and benefits of the CAPE Neutral Interface are: Promote utilization of CAPE protection data elsewhere in the company Simplify electronic transmittal of protective device settings Give safe, controlled access to settings for relay testing Be a stable format for interchange with third-party software, e.g. asset management and GIS systems
There are three components of the Settings Transfer Utilities: 1. Creation of a Neutral Interface (NI) database. This function is performed by the Database Editor and is available to all CAPE users. The electronic file produced is a simple Microsoft Access .mdb file. It may contain as little as the settings for a single relay and as many as your entire database. You may make as many such NI files as you like. 2. Field access to the settings. A field engineer or technician has full access to the settings in an NI file through the CAPE Client Access Program (CAP). CAP is an easy-to-use mini database editor. Settings may be viewed, annotated, and modified. For some digital relays (SEL primarily), CAP will connect to the database of a relay manufacturers product (e.g. SEL 5010 and 5030) for direct settings transfer, export or import. 3. Synchronization with the CAPE database. Typically, field personnel will return NI files to the protection engineering group. The annotations, testers initials, and dates are valuable information that belongs back in the CAPE database. It may not be typical, but setting adjustments may have been made. This data cannot be blindly returned to the CAPE database; it ought to be reviewed first. This is the function of the Comparison and Upload Program (CUP), in concert with a protection engineer. The engineer selects a relay from the NI and CUP highlights all changes for review and possible correction prior to optional upload.
Exporting Settings
I. Exporting Settings to a Neutral Interface Database
Anyone with access to the Database Editor can generate a Neutral Interface file of relay settings. As is obvious from the picture above, you just click Tools | Neutral Interface I/O. To create a NI file, you need a file we have delivered with the STU program to serve as a template. That file is NeutralStarter.mdb, a template Microsoft Access database containing the table and field definitions for a Neutral Interface database. The STU installation program places it by default in \Program Files\Electrocon\CAP. When creating a new NI file, this template is copied and given a new file name, then populated with data. A. Export to One NI Database
Exporting Settings
i. Create a new NI file for export The Create New button will first prompt you for the location of the template database, then for the location and name of the file you want to create. The template database will be copied to a file of the new name specified. Once you have created a new file it can be populated with data. Note: If you copy the template database manually, be sure to clear the read-only file attribute of your new file. This attribute is set on the template database to prevent it from being accidentally modified. ii. Export to an existing NI file The Browse button allows you to select an existing NI database file into which you may export data. A NI database file can contain as little as one relay, or as much as every relay in your CAPE database. A typical file may contain all relays in a substation, or a comparable amount. iii. Selecting data to export Once you have created or specified the NI database file, you are ready to populate it with data. The checkboxes under Cascading Export Options and the checkbox Use Export Filter are relevant, and are explained below. Click the Select Data To Export button. This button leads to a search form very much like the Database Editor system search.
Exporting Settings On this search form, select the data you would like to export and click the Export button below that column. Selecting a substation to export will export all LZOPs in that substation if the box Substation => LZOP is checked. Selecting an LZOP to export will export all devices in that LZOP if the box LZOP => Device is checked. Selecting a device to export will export all settings groups within that device unless the box Use Export Filter is checked. Selecting a settings group to export will export only that one settings group.
If you have the Use Export Filter box checked on the previous form, the device must pass the filter test or it will not be exported. The filter may be used to limit export to only the active setting group, to a date that must fit between the In Service and Out of Service dates, and/or to one or more settings groups.
Exporting Settings
B. Export to Many NI Databases This option allows you to quickly export a large amount of data to many different NI files. One NI file will be created for each substation, and all relays in that substation will be exported to the file.
You must specify the template database, and the directory where the new NI files should be created. Clicking Select Substations To Export leads to this substation search form. Here you can select one or more substations to export. Clicking the Export button will initiate the data transfer.
Exporting Settings C. Export Library This option allows you to export relay and/or recloser library information only. This is not required, as required library information is automatically exported along with system information. However, pre-populating a NI database with library information provides two advantages: 1. Using a NI database which already contains library information as the template database allows the data export to run slightly faster since the library information does not need to be exported. 2. In a normal export, only required library information is exported. By manually exporting additional library information, field technicians may be able to correct relay style assignments by selecting the correct style from the NI database. (The field technician must use the Admin login to change relay styles.) If the correct style is not available in the NI file, the field technician can only make a note of the problem, and a CAPE user would need to correct it himself.
Importing Settings
II. Importing Settings from a Neutral Interface Database
Often you will often want to import data back from the Neutral Interface to synchronize your CAPE database with the annotations and possible setting changes that may have been made in the field. No one would do this blindly. You first want to see what changes were made and then decide whether to upload them into CAPE, usually on a relay-by-relay basis. The Comparison and Upload Program (CUP) makes this task relatively easy. To run CUP, click Tools | Neutral Interface I/O in the DBE. In the form above, choose the radio button Import From NI Database. Note: You will see the Import From NI Database option only if you have purchased the STU module.
Importing Settings
A. Selecting Data to Import Clicking the Select Data To Import button will lead to a search form very much like the Database Editor system search form. However, this search form shows data from the specified NI database file.
On the search form, select the data you would like to import and click the Add to Review Queue button below that column. Selecting a substation to import will add all LZOPs in that substation to the review queue, if the box under Cascading Import Options labeled Substation => LZOP is checked. Selecting an LZOP to import will add all devices in that LZOP to the review queue, if LZOP => Device is checked. Selecting a device to import will add all settings groups within that device to the review queue, if Device => All Groups is checked. Selecting a settings group to import will add only that one group to the review queue.
Importing Settings
B. The Comparison and Upload Program (CUP) Screen
The Comparison and Upload Program screen consists of three parts: the Review Queue, the Comparison Area, and the Upload Queue. Normally, you interact with the form in that order. i. Review Queue The review queue is a list of devices in the NI database that have been selected for review although not necessarily for upload to your CAPE database. A device is defined here as a relay or distribution recloser and one of its setting groups. It offers an Explorer-like tree of those devices from which you can choose one to review. It offers four buttons. Add Devices To Queue This button leads to a search form for the NI database which allows selecting more devices to add to the review queue.
10
Importing Settings Remove from Queue This button removes the selected device from the review queue. Review Selected This button populates the comparison area. The device selected in the review queue is shown in the Data From NI column. If the same device is located in the CAPE database, it will be shown in the Existing CAPE Data column. Move To Upload Queue This button will move a selected device from the review queue directly to the upload queue, bypassing the comparison area. ii. Comparison Area The Comparison Area displays a device from the NI database alongside a device from the CAPE database. Any differences in data can easily be seen in green highlight. Modifications can be made to the data before moving to the upload queue. The Show All Settings checkbox toggles between showing a complete list of settings and only those that are different. You can perform three operations here. Compare with different CAPE device When you select a device in the review queue and click Review Selected, the program automatically tries to find the same device in the CAPE database for comparison. Sometimes this is not possible (due to changes in the key identifiers), or perhaps you just want to see a comparison with a different device. Clicking Compare with different CAPE device allows you to select any device in the CAPE database for comparison with the device in the NI database. Upload As New Relay Clicking Upload As New Relay will move the relay that is in the comparison area from the Review Queue to the Upload Queue. When uploaded, it will be added as a new device, regardless of whether that relay came from the database originally or not. Note: The Upload As New Relay button will only be active if the four key identifiers (Substation, LZOP Name, Device Name, Settings Group) do not exactly match an existing device in the CAPE database. If a match exists you can not create a new device with identical keys. 11
Importing Settings
Replace Existing CAPE Relay Clicking Replace Existing CAPE Relay will move the relay that is in the comparison area from the Review Queue to the Upload Queue. When uploaded, it will replace the device shown in the Existing CAPE Data column. iii. Upload Queue The Upload Queue is the final holding area for devices to be uploaded from the NI database. Devices in this list may have come directly from the Review Queue (via Move To Upload Queue button) or from the Comparison Area. Regardless of how they got there, devices in this list are ready to be uploaded to the CAPE database. Remove from Queue Clicking the Remove from Queue button will remove a device from the upload queue. Upload Selected Clicking the Upload Selected button will upload the selected device to the CAPE database.
12
Editing Settings
III. Editing Settings with the Client Access Program
The Client Access Program (CAP) is a mini Database Editor, used to view and edit data in a Neutral Interface database. A. Login screen
When the CAP program starts, you must fill in your user name on the login screen. You can use any user name you like (except Admin) and no password is required. The Admin login requires a password. This login is not for security. It merely allows the program to differentiate between a normal user and an Admin user. Data in a NI database is linked to data in a CAPE database through the substation name, LZOP name, device name, and settings group name. Only the Admin user can change the values in these name fields. This restriction helps prevent undesired changes in data, which would lead to difficulties during an upload to a CAPE database. Also, when a non-Admin user modifies a relay or recloser device record, the tested_by and tested_date fields are automatically populated with the user name and todays date. The login screen also allows you to select the NI database with which you wish to work. Once the correct database has been specified, click Open to bring up the search screen.
13
Editing Settings
B. Search screen
The search form looks very much like the System Search form of the CAPE Database Editor. To view data, search to the desired record, then click View Data at the bottom of the column. While it is not commonly done, you may click Add Record to add a new piece of data. C. Substation
The substation form allows editing the substation name (if you are logged in as Admin) and provides easy access to all devices in the substation.
14
Editing Settings
D. LZOP
The LZOP form allows editing the Voltage and Comments fields. If you are logged in as Admin, you may also change the Substation ID and the LZOP name. E. Relay Device
15
Editing Settings
The relay device data form allows editing relay information and settings, except for the Device Name and Setting Group Name. You must be logged in as Admin to modify these. F. Recloser Device
The recloser device data form allows editing recloser information and settings except for the Device Name and the Setting Group Name, for which you must be logged in as Admin.
16
Neutral Interface Reference
Appendix A. Neutral Interface Reference
Table name: SUBSTATION_DATA
Each entry corresponds to a unique substation in CAPE. KEY field: SUBSTATION_ID; SUBSTATION_NAME Database Field Name Definition SUBSTATION_ID A unique identifier for this record. SUBSTATION_STRING Name of this substation Constraints Required Required Field Type Long Integer Char(35)
Table name: LOCATION_DATA
Each entry corresponds to a unique LZOP (relay panel) in CAPE. KEY field: LOCATION_ID; SUBSTATION_ID, LZOP_NAME Database Field Name Definition LOCATION_ID A unique identifier for this record. SUBSTATION_ID Foreign key into SUBSTATION_DATA LZOP_NAME Name of this relay panel. VOLTAGE COMMENTS The nominal base kV of the equipment protected by this LZOP. General description of the relay panel. Constraints Required Required Required; Unique within substation. Field Type Long Integer Long Integer Char(40) Char(10) Memo
Table name: PROTECTIVE_DEVICE_DATA
Each entry corresponds to a protective device, i.e. relay, recloser, or fuse. KEY: DEVICE_ID; LOCATION_ID, DEVICE_NAME Database Field Name Definition DEVICE_ID A unique identifier for this record. LOCATION_ID Foreign key into LOCATION_DATA. DEVICE_NAME A user-specified name for this device. DEVICE_TYPE ACTIVE_GROUP DEVICE_RANK COMMENTS The type of protective device this record represents. Valid values are RELAY, RECL, and FUSE. The name of the settings group that is currently active. Order of the device within LZOP General description of the device Constraints Required Required Required; Unique within location. Required Field Type Long Integer Long Integer Char(20) Char(5) Char(30) Float Memo
Table name: RELAY_DEVICE_DATA
Each entry corresponds to a setting group for a protective relay. Similar tables will support reclosers and fuses. KEY: DEVICE_ID, SETTINGS_GROUP; RELAY_TAG Database Field Name Definition Constraints Field Type RELAY_TAG A unique identifier for this record. Provides a Required Long Integer direct link to the corresponding record in the CAPE database. DEVICE_ID Foreign key into PROTECTIVE_DEVICE_DATA. Required Long Integer. SETTINGS_GROUP Name of settings group this record represents. Required; Unique Char(30) within protective device. STYLE Manufacturer given style no; Ex: 12IAC51A801A Required Char(20) PANEL_NUMBER Identifier for panel where relay is located. Char(20) DRAWING_NUMBER Char(40) RELAY_LABEL Alternative name for this relay Char(20)
17
Neutral Interface Reference
PROTECTION_SCHEME Protection scheme designation; Ex: Primary, Secondary, Tertiary, Primary_Pilot, Secondary_Pilot, Tertiary_Pilot, Primary_Nonpilot, Secondary_Nonpilot, Tertiary_Nonpilot Designation of targets, if any. ANSI functional number of relay. A flag to indicate if the Relay is a part of a Pilot Scheme; "Y" if the relay belongs to a pilot scheme and N if it does not. Number of physical relays. Since the relay on each phase was not explicitly modeled in the original CAPE database, this field has been used to indicate the actual number of relays used to cover all the phases in the case of "phase" protection. The number is usually 2 or 3. For "ground" protection, it is typically 1. A utility-generated serial number for tracking a piece of equipment (transformer, breaker, relay, etc.) Name of department whose responsibility is to install and maintain the device. A code to indicate the type of protective device failure. Ratio (to one) of the current transformer Ratio (to one) of the voltage transformer Ratio (to one) of the neutral current transformer. Voltage at which this relay is used. Amp tap setting of the target. In-Service Date for Relay Settings Out-of-Service Date for Relay Settings Description of relay features (Ex: Supervising, Fault Detector, etc. and notes about relay settings. Textual description of failure history Textual description of reliability related information Textual description of operations history Customized Test Schedule for the Relay. In-Service Date for the Relay Out-of-Service Date for the Relay. Date of installation Initials of the testing personnel. Most recent test date. Initials of person(s) checking the setting calculations. Date when settings are checked. Initials of person(s) performing the setting calculations. Date of calculation of settings. Initials of person(s) approving the setting calculations. Date when settings are approved. Initials of person(s) issuing the settings. Date when settings are issued Char(20)
TARGET_DESIGNATION ANSI_FUNCTIONAL_NO PILOT_FLAG NUMBER_OF_RELAYS
Char(20) Char(10) Char(1) Integer
UTILITY_ID_NO DEPARTMENT FAILURE_CODE CT_RATIO PT_RATIO N_CT_RATIO BUS_VOLTAGE TARGET_TAP_SET SETTINGS_IN_SERVICE_DATE SETTINGS_OUT_DATE RELAY_DESCRIPTION FAILURE_INFO RELIABILITY_INFO OPERATIONS_HISTORY CUSTOM_TEST_SCHEDULE RELAY_IN_SERVICE_DATE RELAY_OUT_DATE INSTALL_DATE TESTERS_INITIALS TEST_DATE SETTINGS_CHECKED_BY SETTINGS_CHECKED_DATE SETTINGS_CALCULATED_BY SETTINGS_CALCULATION_DATE SETTINGS_APPROVED_BY SETTINGS_APPROVED_DATE SETTINGS_ISSUED_BY SETTINGS_ISSUED_DATE
Char(20) Char(20) Char(10) Float Float Float Char(5) Float Date Date Memo Memo Memo Memo Memo Date Date Date Char(10) Date Char(10) Date Char(10) Date Char(10) Date Char(10) Date
18
Neutral Interface Reference Table name: RELAY_SETTINGS
Each entry corresponds to one tap for one settings group for a relay. KEY: RELAY_TAG, TAP_ID Database Field Name Definition RELAY_TAG Foreign key into RELAY_DEVICE_DATA. TAP_ID Foreign key into STYLE_TAPS NUMERIC_SETTING The setting for this tap, if it is a numeric tap. TEXT_SETTING The setting for this tap, if it is a text tap. Constraints Required Required Data Type Long Integer Long Integer Float Char(100)
Table name: RECLOSER_DEVICE_DATA
Each entry corresponds to a setting group for a protective recloser. KEY: DEVICE_ID, SETTINGS_GROUP; RECLOSER_ID Database Field Name Definition RECLOSER_ID A unique identifier for this record. DEVICE_ID Foreign key into PROTECTIVE_DEVICE_DATA. SETTINGS_GROUP Name of settings group this record represents. Constraints Required Required Required; Unique within protective device. Required Field Type Long Integer Long Integer. Char(30)
STYLE DEVICE_MODEL UTILITY_ID_NO DEPARTMENT FAILURE_CODE INSTALL_DATE FAILURE_INFO RELIABILITY_INFO OPERATIONS_HISTORY IN_SERVICE_DATE OUT_DATE SETTINGS_IN_SERVICE_DATE SETTINGS_OUT_DATE TESTERS_INITIALS TEST_DATE SETTINGS_APPROVED_BY SETTINGS_APPROVED_DATE SETTINGS_CALCULATED_BY SETTINGS_CALCULATION_DATE SETTINGS_CHECKED_BY SETTINGS_CHECKED_DATE
Manufacturer given style no. Foreign key into table RECLOSER_STYLES. A utility-generated serial number for tracking a piece of equipment (transformer, breaker, relay, etc.) Name of department whose responsibility is to install and maintain the device. A code to indicate the type of protective device failure. Date of installation Textual description of failure history Textual description of reliability related information Textual description of operations history In-Service Date for the Recloser. Out-of-Service Date for the recloser. In-Service Date for recloser settings Out-of-Service Date for recloser settings Initials of the testing personnel. Most recent test date. Initials of person(s) approving the setting calculations. Date when settings are approved. Initials of person(s) performing the setting calculations. Date of calculation of settings. Initials of person(s) checking the setting calculations. Date when settings are checked.
Char(20) Char(20) Char(20) Char(20) Char(10) Date Memo Memo Memo Date Date Date Date Char(10) Date Char(10) Date Char(10) Date Char(10) Date
19
Neutral Interface Reference Table name: RECLOSER_SETTINGS
Each entry corresponds to one tap for one settings group for a recloser. KEY: RECLOSER_ID, TAP_ID Database Field Name Definition RECLOSER_ID Foreign key into RECLOSER_DEVICE_DATA. TAP_ID Foreign key into RECLOSER_STYLES NUMERIC_SETTING The setting for this tap, if it is a numeric tap. TEXT_SETTING The setting for this tap, if it is a text tap. Constraints Required Required Data Type Long Integer Long Integer Float Char(100)
Table name: RELAY_STYLES Library
Each entry corresponds to one style of relay. KEY: STYLE_ID; STYLE Database Field Name Definition STYLE_ID A unique identifier for this record. STYLE The manufacturer-given style number for this relay. MANUFACTURER The manufacturer for this style of relay. MODEL The model name for this style of relay. INST_MANUAL_NO The instruction manual number for this style of relay. Constraints Required Required Data Type Long Integer Char(20) Char(20) Char(20) Char(20)
Table name: STYLE_TAPS Library
Each entry corresponds to one tap for one relay style. KEY: TAP_ID; STYLE, ELEMENT_CODE, ELEMENT_DESIGNATION, ZONE_UNIT_NUMBER, SETTING_NAME Database Field Name Definition Constraints Data Type TAP_ID A unique identifier for this record. Required Long Integer STYLE_ID Foreign key into table RELAY_STYLES Required Long Integer ELEMENT_CODE The type of element in CAPE this tap is used on. Valid Required Char(10) values are: IOC Instantaneous Overcurrent TOC Time Overcurrent DIR Directional DIST Distance (unit 1) DIST_[name] Distance (unit [name]) TIMER Timer VOLT Voltage (over or under) TAP relay common tap ELEMENT_DESIGNATION Required Char(20) ZONE_UNIT_NUMBER The zone number (for distance elements) or unit Required Char(2) number (for timer elements) of the element this setting corresponds to. SETTING_NAME The name of this setting. Required Char(30) NUMERIC_RANGE_ID Foreign key into table NUMERIC_TAP_RANGES Long Integer TEXT_RANGE_ID Foreign key into table TEXT_TAP_RANGES Long Integer
Table name: RECLOSER_STYLES Library
Each entry corresponds to one style of recloser. KEY: STYLE_ID; STYLE Database Field Name Definition STYLE_ID A unique identifier for this record. STYLE The manufacturer-given style number for this recloser. MANUFACTURER The manufacturer for this style of recloser. MODEL The model name for this style of recloser. INST_MANUAL_NO The instruction manual number for this style of recloser. Constraints Required Required Data Type Long Integer Char(20) Char(20) Char(20) Char(20)
20
Neutral Interface Reference
Table name: RECLOSER_TAPS Library
Each entry corresponds to one tap for one recloser style. KEY: TAP_ID; STYLE, SETTING_NAME Database Field Name Definition TAP_ID A unique identifier for this record. STYLE_ID Foreign key into table RECLOSER_STYLES SETTING_NAME The name of this setting. NUMERIC_RANGE_ID Foreign key into table NUMERIC_TAP_RANGES TEXT_RANGE_ID Foreign key into table TEXT_TAP_RANGES Constraints Required Required Required Data Type Long Integer Long Integer Char(30) Long Integer Long Integer
Table name: NUMERIC_TAP_RANGES Library
Each entry corresponds to one tap range description. Several taps can reference the same description. KEY: RANGE_ID; MODEL, RANGE_TYPE, RANGE_DESCRIPTION Database Field Name Definition Constraints RANGE_ID A unique identifier for this record. Required MODEL The manufacturer-given model name Required RANGE_TYPE The type of tap setting this range is used for. Values should generally match the STYLE_TAPS.ELEMENT_CODE field. RANGE_DESCRIPTION A textual description of the range TAP_VARIATION C = Continuous S = Stepped D = Discrete MIN_TAP Miminum tap setting allowed. MAX_TAP Maximum tap setting allowed. STEP_SIZE Step size, for stepped taps. Data Type Long Integer Char(20) Char(5) Char(20) Char(1) Float Float Float
Table name: TEXT_TAP_RANGES Library
Each entry corresponds to one tap range description. Several taps can reference the same description. KEY: RANGE_ID; MODEL, RANGE_TYPE, RANGE_DESCRIPTION Database Field Name Definition Constraints RANGE_ID A unique identifier for this record. Required MODEL The manufacturer-given model name Required RANGE_TYPE The type of tap setting this range is used for. Values should generally match the STYLE_TAPS.ELEMENT_CODE field. RANGE_DESCRIPTION A textual description of the range Data Type Long Integer Char(20) Char(5) Char(20)
21
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- Short Circuit Calculations in 60 SecondsDocument5 paginiShort Circuit Calculations in 60 Secondscoolcreative100% (3)
- Differential ProtectionDocument30 paginiDifferential ProtectioncalecaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- A330-200 CommunicationsDocument42 paginiA330-200 CommunicationsTarik BenzinebÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solucionario Statistics For Business and Economics - David R. Anderson, Dennis J. Sweeney - 8edDocument8 paginiSolucionario Statistics For Business and Economics - David R. Anderson, Dennis J. Sweeney - 8edTukumaneriko Filiponditoniko0% (1)
- Presentation On Basic Sub-Station Automation SystemDocument13 paginiPresentation On Basic Sub-Station Automation Systemsajedarefin100% (1)
- Transformer Differential Relay Test ReportDocument3 paginiTransformer Differential Relay Test Reportsajedarefin0% (2)
- Hyperion Essbase 6 - 5 Bootcamp - Basic TrainingDocument659 paginiHyperion Essbase 6 - 5 Bootcamp - Basic Trainingrams08Încă nu există evaluări
- Ice Rink: Name OriginsDocument6 paginiIce Rink: Name Originsmichol2014Încă nu există evaluări
- V1 001 PDFDocument20 paginiV1 001 PDFG100% (2)
- Seismic Data AcquisitionDocument14 paginiSeismic Data Acquisitionjoao kiala100% (1)
- Data CenterDocument108 paginiData CenterKhanh Nato100% (5)
- Current Transformer Requirements For Reyrolle Protection RelaysDocument15 paginiCurrent Transformer Requirements For Reyrolle Protection RelayssajedarefinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Overview of Insulation CoordinationDocument8 paginiOverview of Insulation CoordinationsajedarefinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power System Protection SlidesDocument59 paginiPower System Protection SlidessajedarefinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pest Analysis of Telecom IndustryDocument6 paginiPest Analysis of Telecom IndustryAymanCheema70% (10)
- Electrical Substation TypesDocument2 paginiElectrical Substation TypessajedarefinÎncă nu există evaluări
- As The Names ImplyDocument1 paginăAs The Names ImplysajedarefinÎncă nu există evaluări
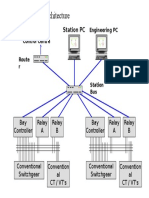
- Traditional SAS ArchitectureDocument1 paginăTraditional SAS ArchitecturesajedarefinÎncă nu există evaluări
- MicroTrip Notes PDFDocument8 paginiMicroTrip Notes PDFsajedarefinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Device NameDocument6 paginiDevice NamesajedarefinÎncă nu există evaluări
- NULEC CAPM4 Notes PDFDocument7 paginiNULEC CAPM4 Notes PDFsajedarefinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Breaker Duty User Guide PDFDocument79 paginiBreaker Duty User Guide PDFsajedarefinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Training On Ester MeterDocument12 paginiTraining On Ester MetersajedarefinÎncă nu există evaluări
- WinEVE ManualDocument12 paginiWinEVE ManualsajedarefinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dxwe VK DG©: Mzzvi MV - BX Pi Cökœ Jvi Dëi W'B ( Mvcyxqzv I V Kiv N E)Document2 paginiDxwe VK DG©: Mzzvi MV - BX Pi Cökœ Jvi Dëi W'B ( Mvcyxqzv I V Kiv N E)sajedarefinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evaluation PaperDocument2 paginiEvaluation PapersajedarefinÎncă nu există evaluări
- SSR HVDCDocument8 paginiSSR HVDCsajedarefinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zero Flux CTDocument2 paginiZero Flux CTsajedarefinÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 CombiflameDocument8 pagini5 CombiflamenitantharaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Article 17 Ijaet Volii Issue IV Oct Dec 2011Document10 paginiArticle 17 Ijaet Volii Issue IV Oct Dec 2011Mustapha Maiz Hadj AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2018 Academic Sector Annual Report PDFDocument213 pagini2018 Academic Sector Annual Report PDFEsperanza ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trial On CompresorDocument3 paginiTrial On CompresorA JÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9500MPR - MEF8 Circuit Emulation ServicesDocument5 pagini9500MPR - MEF8 Circuit Emulation ServicesedderjpÎncă nu există evaluări
- PROSIS Part Information: Date: Image Id: Catalogue: ModelDocument2 paginiPROSIS Part Information: Date: Image Id: Catalogue: ModelAMIT SINGHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eurotherm 2604 PDFDocument2 paginiEurotherm 2604 PDFLorena100% (1)
- CatalogDocument42 paginiCatalogOnerom LeuhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Masterprotect 190: A Two Component Solvent Free High Build Flexible Epoxy Polyurethane Resin Coating SystemDocument3 paginiMasterprotect 190: A Two Component Solvent Free High Build Flexible Epoxy Polyurethane Resin Coating SystemEngTamer100% (1)
- Forensics Plastics and Burn TestsDocument2 paginiForensics Plastics and Burn TestsTrishaÎncă nu există evaluări
- LIVING IN THE IT ERA (Introduction)Document9 paginiLIVING IN THE IT ERA (Introduction)johnnyboy.galvanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Calibrating The Venturi Meter and Orifice MeterDocument5 pagini1 Calibrating The Venturi Meter and Orifice MeterRaghavanÎncă nu există evaluări
- DELTA - IA-HMI - Danfoss VLT 2800 - FC Protocol - CM - EN - 20111122Document4 paginiDELTA - IA-HMI - Danfoss VLT 2800 - FC Protocol - CM - EN - 20111122Ronnie Ayala SandovalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guide To Linux+ (2 Edition) ISBN 0-619-21621-2 End of Chapter Solutions Chapter 4 SolutionsDocument8 paginiGuide To Linux+ (2 Edition) ISBN 0-619-21621-2 End of Chapter Solutions Chapter 4 SolutionsNorhasimaSulaimanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Congelador - Frigidaire GLFC1326FW1 - Man - Eng - PartsDocument7 paginiCongelador - Frigidaire GLFC1326FW1 - Man - Eng - Partsfelix bazanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Euro Guard BrochureDocument28 paginiEuro Guard BrochureNazia SodawalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- E85005-0126 - FireShield Plus Conventional Fire Alarm Systems PDFDocument8 paginiE85005-0126 - FireShield Plus Conventional Fire Alarm Systems PDFLuis TovarÎncă nu există evaluări
- RFQ - Tank DemuckingDocument12 paginiRFQ - Tank Demuckingmuhamadrafie1975100% (1)
- Lynx ROMdisassemblyDocument156 paginiLynx ROMdisassemblyMark LoomisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bhopal Gas TragedyDocument25 paginiBhopal Gas TragedyHarry AroraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Awareness and Application of Ms Iec - Iso 31010 - 2011 Risk Assessment Techniques1 PDFDocument21 paginiAwareness and Application of Ms Iec - Iso 31010 - 2011 Risk Assessment Techniques1 PDFasushk0% (1)
- Seguridad en Reactores de Investigación PDFDocument152 paginiSeguridad en Reactores de Investigación PDFJorge PáezÎncă nu există evaluări