Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide
Încărcat de
bournvilleeaterDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide
Încărcat de
bournvilleeaterDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Vasoactive intestinal peptide
Vasoactive intestinal peptide also known as the vasoactive intestinal polypeptide or VIP is a peptide hormone containing 29 amino acid residues that is produced in many tissues of vertebrates including the gut, pancreas and suprachiasmatic nuclei of the hypothalamus in the brain. In humans, the vasoactive intestinal peptide is encoded by the VIP gene. VIP has a half-life (t) in the blood of about two minutes. Function 1. With respect to the digestive system, VIP seems to induce smooth muscle relaxation (lower esophageal sphincter, stomach, gallbladder), stimulate secretion of water into pancreatic juice and bile, and cause inhibition of gastric acid secretion and absorption from the intestinal lumen. Its role in the intestine is to greatly stimulate secretion of water and electrolytes, as well as stimulating contraction of enteric smooth muscle, dilating peripheral blood vessels, stimulating pancreatic bicarbonate secretion, and inhibiting gastrin-stimulated gastric acid secretion. These effects work together to increase motility. 2. It also has the function of stimulating pepsinogen secretion by chief cells. 3. It is also found in the brain and some autonomic nerves. One region of the brain includes a specific area of the suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN), the location of the 'master circadian pacemaker'. The SCN coordinates daily timekeeping in the body and VIP plays a key role in communication between individual brain cells within this region. Further, VIP is also involved in synchronising the timing of SCN function with the environmental lightdark cycle. Combined, these roles in the SCN make VIP a crucial component of the mammalian circadian timekeeping machinery. 4. VIP helps to regulate prolactin secretion 5. It is also found in the heart and has significant effects on the cardiovascular system. It causes coronary vasodilation as well as having a positive inotropic and chronotropic effect. Research is being performed to see if it may have a beneficial role in the treatment of heart failure. 6. VIP provokes vaginal lubrication in normal women, doubling the total volume of lubrication produced in one study. 7. GH-RH is a member of the VIP family and stimulates Growth Hormone secretion in the anterior pituitary gland. 8. VIP has potent vascular and airway dilatory actions, potent anti-inflammatory actions, improving blood circulation to the heart and lung, and modulation of airway secretions. Vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor
There are two known receptors for the vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) termed VPAC1 and VPAC2. These receptors bind both VIP and pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP) to some degree. Both receptors are members of the 7 transmembrane G protein-coupled receptor family. VPAC1 is distributed widely in the CNS, liver, lung, intestine and T-lymphocytes. VPAC2 is found in the CNS, pancreas, skeletal muscle, heart, kidney, adipose tissue, testis, and stomach. Pathology VIP is overproduced in VIPoma. Can be associated with Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 1 (Pituitary, parathyroid and pancreatic tumors). Symptoms are typically:Profuse nonbloody/non-mucoid diarrhea (3L+) causing dehydration and the associated electrolyte disturbances such as hypokalemia and contraction metabolic alkalosis. VIP also implicated in cancer. Clinical significance VIP has emerged as a promising drug candidate for the treatment of several diseases. A number of clinical applications of VIP or its derivatives have been developed; however, VIPbased drugs are not yet in clinical use, possibly because of mainly two serious problems: (1) poor metabolic stability and (2) poor penetration to the desired site of action. Activation of VPAC2R, but not VPAC1R, reduced the loss of skeletal muscle mass and force during conditions of skeletal muscle atrophy resulting from corticosteroid administration, denervation, casting-induced disuse, increased skeletal muscle mass, and force of nonatrophying muscles. Helodermin, and helospectin are selective for the human VIP2 receptor subtypes.VPAC2R agonists may have utility for the treatment of skeletal musclewasting diseases. VIP analogues are being evaluated for treatment of heart failure. They enhance Ca mediated intracardiac neuroexcitability. Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) is widely expressed throughout the cardiopulmonary system and exerts a variety of biological actions, including potent vascular and airway dilatory actions, potent anti-inflammatory actions, improving blood circulation to the heart and lung, and modulation of airway secretions.The development of long-acting VIP analogues, in combination with appropriate drug delivery systems, may provide clinically useful agents for the treatment of PAH, asthma, and COPD.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Metabolic Syndrome: Underlying Mechanisms and Drug TherapiesDe la EverandMetabolic Syndrome: Underlying Mechanisms and Drug TherapiesMinghan WangÎncă nu există evaluări
- UNIT-V PharmacologyofDrugsactingonRenalsystem AntidiuerticsDocument10 paginiUNIT-V PharmacologyofDrugsactingonRenalsystem AntidiuerticsMisganaw Abate AbateÎncă nu există evaluări
- Endocrine SystemDocument22 paginiEndocrine SystemLen Len Ochinang OchinangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Endo Lect - Post PituDocument23 paginiEndo Lect - Post PitudoctorrfarrukhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Downsi 6 PDFDocument11 paginiDownsi 6 PDFmutimutimutiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vasopressin Is A Nonapeptide Antidiuretic Hormone Involved in Modulating Various Physiological ProcessesDocument7 paginiVasopressin Is A Nonapeptide Antidiuretic Hormone Involved in Modulating Various Physiological ProcessesyoungjbÎncă nu există evaluări
- Posteria Pituitary 2023 PDFDocument51 paginiPosteria Pituitary 2023 PDFMpho MosehlaÎncă nu există evaluări
- VasopressinDocument7 paginiVasopressindrlokeshreddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uso de ACUPUNTURA E ERVAS/FITOTERAPIA CHINESA No Tratamento de Insuficiência Renal CrônicaDocument6 paginiUso de ACUPUNTURA E ERVAS/FITOTERAPIA CHINESA No Tratamento de Insuficiência Renal CrônicaDaniel Mendes NettoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacology Test 3 ReviewDocument6 paginiPharmacology Test 3 ReviewNatalia BortellÎncă nu există evaluări
- My FinalDocument33 paginiMy FinalBhoj RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiovascular Effects and Molecular Targets of ResveratrolDocument10 paginiCardiovascular Effects and Molecular Targets of ResveratrolvinothÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vasopressin: Its Current Role in Anesthetic Practice: Jayanta K. Mitra Jayeeta Roy Saikat SenguptaDocument13 paginiVasopressin: Its Current Role in Anesthetic Practice: Jayanta K. Mitra Jayeeta Roy Saikat SenguptarimhenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Endocrine NursingDocument16 paginiEndocrine NursingFreeNursingNotes100% (18)
- Antidiuretic HormoneDocument16 paginiAntidiuretic HormoneNo NameÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study Guide For NURS 320 Exam 2Document15 paginiStudy Guide For NURS 320 Exam 2Anthony Del RioÎncă nu există evaluări
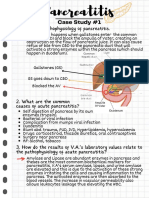
- Ornopia - MS 2 PancreatitisDocument3 paginiOrnopia - MS 2 PancreatitisORNOPIA, JOUELLA ANNE C.Încă nu există evaluări
- Hypothalamus - Anterior Pituitary and Their HormonesDocument138 paginiHypothalamus - Anterior Pituitary and Their HormonesML Rodriguez100% (1)
- Parathyroid & Posterior Pituitary Hormones PDFDocument21 paginiParathyroid & Posterior Pituitary Hormones PDFJeng CaritativoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nucleotide and CHO Metabolism ActivityDocument3 paginiNucleotide and CHO Metabolism ActivityJanson SarmientoÎncă nu există evaluări
- EndocrineDocument34 paginiEndocrineBahareh SanabakhshÎncă nu există evaluări
- M.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, Ph.D.Research ScholarDocument32 paginiM.Prasad Naidu MSC Medical Biochemistry, Ph.D.Research ScholarM.PRASAD NAIDUÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pituitary Gland and Its Relation To The HypothalamusDocument34 paginiPituitary Gland and Its Relation To The HypothalamusAnonymous lsnDTjv100% (1)
- CHAPTER 30 - Pituitary DrugsDocument3 paginiCHAPTER 30 - Pituitary DrugsBre BistanyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structure and Function of The Endocrine and Metabolic SystemDocument21 paginiStructure and Function of The Endocrine and Metabolic Systemcoy008Încă nu există evaluări
- Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDocument38 paginiChemical Coordination and IntegrationSajeev S Chadayamangalam SajÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 - Hypothalmus - Post PituitaryDocument21 pagini4 - Hypothalmus - Post PituitaryAbboodÎncă nu există evaluări
- LEARNING MODULE IN NCM 106 Final Peroid 2Document30 paginiLEARNING MODULE IN NCM 106 Final Peroid 2Threcia RotaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basics in Diseases of Adrenal GlandsDocument7 paginiBasics in Diseases of Adrenal GlandsFrancis ChegeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Endocrine Pharmacology PDFDocument45 paginiEndocrine Pharmacology PDFNur TzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physiology, Posterior Pituitary - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument4 paginiPhysiology, Posterior Pituitary - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfSayan DeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 76 Pituitary Hormones and Their Control of by The HypothalamusDocument5 pagini76 Pituitary Hormones and Their Control of by The Hypothalamusmanjitashet4049Încă nu există evaluări
- AUTACOIDSDocument29 paginiAUTACOIDSStrange eeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Autacoid Pharmacology: Reading AssignmentDocument41 paginiAutacoid Pharmacology: Reading AssignmentTesfahun TekleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hepatitis. POWERDocument66 paginiHepatitis. POWERريام الموسويÎncă nu există evaluări
- MODULE 2 Disorders of The Pituitary GlandDocument24 paginiMODULE 2 Disorders of The Pituitary GlandLorraine GambitoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liver Cirrhosis Marking KeyDocument5 paginiLiver Cirrhosis Marking KeyChristone “Zuluzulu” ZuluÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pituitary Hormones and Their Control by The HypothalamusDocument26 paginiPituitary Hormones and Their Control by The HypothalamusDr. AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathogenesis of Delayed Gastric Emptying - UpToDateDocument25 paginiPathogenesis of Delayed Gastric Emptying - UpToDatemayteveronica1000Încă nu există evaluări
- Antidiuretic HormoneDocument13 paginiAntidiuretic Hormonesadia ahmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- ChoiDocument19 paginiChoiLuciana RafaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nej MR A 2216691Document15 paginiNej MR A 2216691lakshminivas PingaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hormone and Nervous System BioloveDocument28 paginiHormone and Nervous System BioloveOrkid FazzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Renal FailureDocument35 paginiAcute Renal FailureKaelyn Bello Giray100% (1)
- Gi Hormones: Dr. Sharon M. PDocument50 paginiGi Hormones: Dr. Sharon M. PAleenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Endocrine SystemDocument31 paginiEndocrine SystemPreeti ChouhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class 11 Bio Notes CH 3Document7 paginiClass 11 Bio Notes CH 3VinayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gastrointestinal HormonesDocument3 paginiGastrointestinal HormonesDr Sanjeeb Kumar Dey BaidyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interpretation of Liver Function Test in Ayurveda-2Document4 paginiInterpretation of Liver Function Test in Ayurveda-2tasmitadas9101Încă nu există evaluări
- Anti DiureticsDocument26 paginiAnti DiureticsAhaisibwe GordonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reviewer in PharmaDocument10 paginiReviewer in Pharmark24zsyfmxÎncă nu există evaluări
- HHHHHDocument15 paginiHHHHHHamza JubranÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 22 PDFDocument8 pagini11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 22 PDFSaurav SoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemical Co - OrdinationDocument21 paginiChemical Co - OrdinationManinder KaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liver and Its Clinical SignificanceDocument59 paginiLiver and Its Clinical SignificanceazizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pituitary GlandDocument5 paginiPituitary Glandearly birdÎncă nu există evaluări
- HIF in CKD NKF RecDocument10 paginiHIF in CKD NKF Recdiego.cedamanosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gastointestinal Diseases and Its DrugDocument38 paginiGastointestinal Diseases and Its DrugNicole EncinaresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Treatment: Visceral Leishmaniasis: Visceral Leishmaniasis (VL), Also Known As Kala-Azar, Black Fever, and Dumdum FeverDocument3 paginiTreatment: Visceral Leishmaniasis: Visceral Leishmaniasis (VL), Also Known As Kala-Azar, Black Fever, and Dumdum FeverbournvilleeaterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drugeluting StentDocument2 paginiDrugeluting StentbournvilleeaterÎncă nu există evaluări
- WHO-UMC Causality CategoriesDocument2 paginiWHO-UMC Causality CategoriesbournvilleeaterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Creatinine ClearanceDocument2 paginiCreatinine ClearancebournvilleeaterÎncă nu există evaluări
- The HPV Virus and TypesDocument8 paginiThe HPV Virus and TypesbournvilleeaterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Standard Treatment GuidelinesDocument5 paginiStandard Treatment Guidelinesbournvilleeater100% (1)
- Antimicrobial ProphylaxisDocument2 paginiAntimicrobial ProphylaxisbournvilleeaterÎncă nu există evaluări
- NONlinear PKDocument5 paginiNONlinear PKbournvilleeaterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prefrontal Engrams Pain MemoryDocument33 paginiPrefrontal Engrams Pain MemoryDa CuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maternal Behavior in PigsDocument8 paginiMaternal Behavior in PigsThu Y 2007Încă nu există evaluări
- Orchestrating Time: Arrangements of The Brain Circadian ClockDocument7 paginiOrchestrating Time: Arrangements of The Brain Circadian ClockAhmad Haikal Ahmad MochtarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gastrointestinal Physiology MOSBYDocument309 paginiGastrointestinal Physiology MOSBYUlquiorra SchifferÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cellular and Molecular Bases of Biological Clocks - Models and Mechanisms For Circadian Timekeeping PDFDocument512 paginiCellular and Molecular Bases of Biological Clocks - Models and Mechanisms For Circadian Timekeeping PDFLeoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Git Physiology Compiled by Umah, Umah VictorDocument43 paginiGit Physiology Compiled by Umah, Umah VictorNwaoha Chibuzor AnthonyÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of Human HormonesDocument7 paginiList of Human HormonesKeerthana BathojuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psikiatri Biologi - Dr. Depree An SPKJDocument33 paginiPsikiatri Biologi - Dr. Depree An SPKJCaesaria Sarah SellecaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human Physiology-McqDocument2 paginiHuman Physiology-Mcqaryan kothambiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ono Et Al 2021 Frontiers in NeuroscienceDocument8 paginiOno Et Al 2021 Frontiers in NeuroscienceDaisuke OnoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dibner Et Al 2010Document36 paginiDibner Et Al 2010SAMARAH SANTOSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vasoactive Intestinal PeptideDocument2 paginiVasoactive Intestinal PeptidebournvilleeaterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hormone Regulation 1Document20 paginiHormone Regulation 1Manila MedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fase CefalicaDocument16 paginiFase CefalicaDenisseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gastrointestinal Physiology, JohnsonDocument310 paginiGastrointestinal Physiology, JohnsonSubhajit Chakraborty80% (5)
- Colocalisation of Neuropeptides, Nitric Oxide Synthase and Immunomarkers For Catecholamines in Nerve Fibres of The Adult Human Vas DeferensDocument9 paginiColocalisation of Neuropeptides, Nitric Oxide Synthase and Immunomarkers For Catecholamines in Nerve Fibres of The Adult Human Vas DeferensFlavia DinizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Embryonic Expression of Pituitary Adenylate Cyclase-Activating Polypeptide in Sensory and Autonomic Ganglia and in Spinal Cord of The RatDocument13 paginiEmbryonic Expression of Pituitary Adenylate Cyclase-Activating Polypeptide in Sensory and Autonomic Ganglia and in Spinal Cord of The RatLeandro RodriguesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hidrasec Adults 9-11-07Document81 paginiHidrasec Adults 9-11-07Christian Gallardo, MD100% (1)
- Light and Immunomodulation: Joan E. RobertsDocument11 paginiLight and Immunomodulation: Joan E. RobertsBhavani U KulkarniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bai Bao KH 2016-2020 (51-82)Document283 paginiBai Bao KH 2016-2020 (51-82)thanh le minhÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Healthy Ageing and Longevity, 18) Anita Jagota - Sleep and Clocks in Aging and Longevity-Springer (2023)Document552 pagini(Healthy Ageing and Longevity, 18) Anita Jagota - Sleep and Clocks in Aging and Longevity-Springer (2023)amrjano.ajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutrition in Clinical Practice: Dumping Syndrome: Pathophysiology and TreatmentDocument10 paginiNutrition in Clinical Practice: Dumping Syndrome: Pathophysiology and TreatmentInomy ClaudiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ultimate Peptide GuideDocument23 paginiUltimate Peptide GuideMarzena KarmecckaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Package Insert - 07325 - Prolactina - en - 30410 PDFDocument7 paginiPackage Insert - 07325 - Prolactina - en - 30410 PDFadybaila4680Încă nu există evaluări
- American Dream Essay Great GatsbyDocument43 paginiAmerican Dream Essay Great Gatsbyb725c62jÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sanki BiliardDocument31 paginiSanki Biliardalabala alabalaÎncă nu există evaluări