Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Design and Analysis of Buried Composite Fiberglass Pipeline
Încărcat de
Vinh Do ThanhDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Design and Analysis of Buried Composite Fiberglass Pipeline
Încărcat de
Vinh Do ThanhDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Design and Analysis of Burried fiberglass Pipeline based on "Fiberglass Pipe Design Manual M-45 Standard"
This guidline is intended to provide the design and system engineers with the general scheme of designing and analysing the burried GRP composite pipning system. It is only a general guidline as proposed by AWWA M-45 manual.
Design Methodalogy for Buried GRP Composite Pipe lines
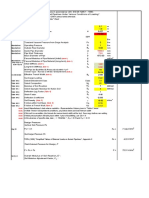
1. Determining the soil load acting on the pipe at minimum and maximum burial depth 2. Determining the live (trafic) load exerted on the pipe at minimum and maximum burial depth. 3. Calculate the predicted pipe deflaction. Compare the prdicted value with the maximum allowable deflection of the Faratec GRP pipe to ensure that predicted deflection is less than the maximum allowable deflection. 4. Verify that the working pressure is less or equal to the nominal pressure (PN).
5. 6. 7. 8. 9.
Verify that the surge pressure is less than allowable limit. (1.4*PN) Calculate the hoop tensile strain at working pressure Calculate the bending strain at th the maximum allowed deflection Calculate the bending strain. Verify that the combined loading conditions are satisfied for pressure as influenced by bending and bending as influenced by pressure. 10. Calculate critical buckling pressure at minmum and maximum bur burial depth 11. Verify that buckling safety factor is satisfied for both normal and for trafic conditions
Equtions Used For Design and Analysis for Buried GRP Composite Pipe lines
Soil load Calculations Wc= (dens) * H Where: Wc = soil load - N / m^2 dens = soil density - N / m^3 H = burial depth m Traffic Load Calculation
Typical Pipe Stiffness
Wl = (P) * (If) / (L1 * L2) Load width parallel to travel L1 = 0.253 + 1.75 * H If = 1 for H => 0.91 If = 1.1 for H < 0.91 Where: Wl = traffic load - N / m^2
Load width perpendicular to travel for H < 0.756 m L2 = 0.509 + 1.75 *H for H => 0.756 m
L1 = width parallel - m L2 = width perpend. - m P = load - N If = impact factor Deflaction Calculation dD/D = kx * ( Wl + Dl * Wc) ----------------------------- * 100 8*SN + 0.061 * E'b * Sc
Where: dD = deflection - % SN = stiffness - N /m^2 E'b = backfill modulus - N / m^2 Dl = deflection lag factor ( For genereal analysis purposes a value of 1.5 is reasonable assumption. Sc = soil support combining factor (function of diameter and trench width) kx = bedding coefficient NOTE: dD/D must be greater or equal to the dDmax ( maximum allowed deflection %) Working Pressure Pw < = PN Where: Pw = working pressure - bars PN = rated pressure bars Surge Pressure Pw + Ps < = 1.4 * PN Where: Pw = working pressure - bars PN = rated pressure bars Ps = surge pressure bars Pressure Strain Calculation Pw * ( OD - t) Ep = ------------------------- * 100 2 * Eht * tr Where: Pw = working pressure - bars * 100000 (Mpa) OD = pipe outside diameter - mm t = pipe wall thickness - mm
Eht = hoop tensile modulus - Gpa tr = reinforced wall thickness - mm ep = pressure strain - % Bending Strain at max deflection Calculation Df * t * dDmax ebmax = ----------------------------------(OD - t) Where: Df = shape factor - dimensionless dDmax = max allowed long term deflection -% t = wall thickness mm OD = pipe outside diameter - mm ebmax = bending strain at max deflection - % Rerounded bending strain Calculation eb = Rc * ebmax Where: Rc = 1 - PN / 30 (rerounding coefficient dimensionless) Combined Loading Calculation Pressure influenced by bending ep / HDB < = 1 - eb / Sb -------------------------1.8
Bending influenced by pressure 1 - eb / Sb -------------------------1.8
ep / HDB < =
Where: HDB = hydrostatic design basis - % strain eb = rerounded bending strain - % strain ep = pressure strain - % strain Sb = long term ring bending strain - % strain Note: 1.8 and 1.5 values are the maximum safety factor for pressure and for bending
Critical Buckling Pressure Calculation qc = ( 32 * Rw * B' * SN * E' * Sc ) ^0.5 Where: qc = critical buckling pressure - N / m^2 E'b = backfill modulus - N / m^2 Sc = soil support combining factor - dimensionless Rw = 1 - 0.33 *( H - hw) / H (water buouancy factor dimensionless) H = burial depth - meters hw = height of ground water over pipe meters
B =
1 -------------------------1 + 4 0.213 H
coefficient of elastic support - dimensionless
Buckling Safety Factors Calculation q c / q = > 2.5 a. typical conditions q = Wc + Ww + Wv b. traffic conditions q = Wc + Ww + Wl Where: q = actual pressure - N / m^2 qc = 2.5 is minimum safety factor (critical buckling pressure - N / m^2) Wc = Soils load - N /m^2 Ww = 9800 * hw - N / m^2 (Water load - N / m^2) Wv = vacuum load - N / m^2 Wl = traffice load - N /m^2
TABLES NOTE: Some values preseneted in these tables are typical valuse intended for general use for exact values contact Farassan Man. & Ind. Compnaay
Table 1: Modulus of Soil Reaction (E'n) for Native Soils (Mpa)
Native Soil Group
Blow Counts (1)
E' values (psi) (MPa)
Non-Cohesive Soils Friction Description Angle (degrees) very, very loose very loose very loose loose slight compact compact
Cohesive Soils Description Unconfined Compr. Strength (tsf) very,very soft very soft soft medium stiff very stiff 0 - 0.125 0.125 - 0.25 0.25 - 0.50 0.50 -1.0 1.0 - 2.0 2.0 - 4.0 (kPa) 0 - 12 12 - 24 24 - 48 48 - 96 96 - 192 192 - 384
6 5 4 3 2 1
0-1 1-2 2-4 4-8 8 - 15 >15
50 200 700 1,500 3,000 5,000
0.34 1.4 4.8 10.3 20.7 34.5
28 28 28 29 30 33
Table 2: Modulus of Soil Reaction (E'b) For Pipe Zone Backfills (Mpa)
Backfil l Soil Type
Description of backfill soils
Table of non-saturated E' values (MPa) Relative Compaction (% max. Std. Proctor Density) 90 80% 85% % 95% 16 7 6 3 3 3 18 11 9 6 6 6 20 16 14 9 9 9 22 19 17 10
1
Table of saturated E' values (MPa) Relative Compaction (% max. Std. Proctor Density) 80 % 85% 90% 95% 12 5 2 1.7 1
2
A B C D E F
Crushed stone , 12% fines Sand, <12% fines Silty sand, 12 - 35% fines Silty, clayey sand, 35 - 50% fines Sandy, clayey silt, 50 - 70% fines, LL<40% Low plasticity fine grained soil, LL<40%
13 7 3 2.4 1.7 1.4
14 10 4 2.8 2.1 1.7
15 12 4 3.1 2.4 2.1
10 10
0.7
Table 3: Bedding Coefficent (kx):
Installation Condition Inconsistent haunching support (typical direct bury condition) Uniform shaped bottom support
kx
0.1 0.083
For typical installations, use kx = 0.1
Table 4: Soil Support Combining Factor (Sc)
E'n/E'b 1.5 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.04 0.05 0.06 0.07 0.08 0.09 0.10 0.20 0.40 0.60 0.80 1.00 1.50 2.00 3.00 5.00 7.00 10.00 15.00 20.00 0.015 0.030 0.045 0.060 0.075 0.090 0.105 0.120 0.135 0.15 0.30 0.50 0.70 0.85 1.00 1.30 1.50 1.75 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 1.75 0.04 0.05 0.07 0.09 0.11 0.13 0.15 0.17 0.19 0.21 0.36 0.54 0.74 0.87 1.00 1.24 1.42 1.63 1.84 1.95 2.00 2.00 2.00 2 0.10 0.12 0.14 0.16 0.18 0.20 0.22 0.20 0.25 0.30 0.45 0.60 0.80 0.90 1.00 1.15 1.30 1.45 1.60 1.70 1.80 1.92 2.00
B/D Value 2.5 0.15 0.20 0.25 0.30 0.35 0.40 0.45 0.50 0.55 0.60 0.70 0.80 0.90 0.95 1.00 1.10 1.15 1.30 1.40 1.47 1.53 1.58 1.62 3 0.30 0.35 0.40 0.45 0.50 0.55 0.60 0.65 0.75 0.80 0.85 0.90 0.95 0.98 1.00 1.05 1.10 1.20 1.25 1.28 1.30 1.32 1.34 4 0.50 0.56 0.62 0.66 0.70 0.74 0.78 0.82 0.86 0.90 0.92 0.95 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.05 1.08 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 5 0.80 0.84 0.87 0.90 0.93 0.96 0.98 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00
Click here to download the complete AWW M-45 design and analysis software.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- CW Pipe Thickness Calculation - 80% Vacuum - With RCCDocument39 paginiCW Pipe Thickness Calculation - 80% Vacuum - With RCCAshitava Sen0% (1)
- Pipes. Maximum Span Between Pipe Supports For A Given Maximum Bending StressDocument64 paginiPipes. Maximum Span Between Pipe Supports For A Given Maximum Bending StressselisenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Determination of Pipe and Bedding Combinations For Drainage WorksDocument26 paginiDetermination of Pipe and Bedding Combinations For Drainage WorksFitriansyah Adi PutraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculation Sheet Pipe SupportDocument33 paginiCalculation Sheet Pipe SupportKhamal Rachmanda AdamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stiffness Report GRP PIPEDocument19 paginiStiffness Report GRP PIPEanishdev6Încă nu există evaluări
- Thrust Block CalculationDocument12 paginiThrust Block CalculationMegatech Engineering Consultants100% (1)
- BURIED PIPING COMPLIANCEDocument4 paginiBURIED PIPING COMPLIANCEphatmatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Virtual Anchor Length - KBRDocument22 paginiVirtual Anchor Length - KBRSammar Adhikari100% (2)
- HDPE Pipe Thickness CalculationsDocument5 paginiHDPE Pipe Thickness CalculationsBudi SantonyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hdpe Pipe DesignDocument27 paginiHdpe Pipe Designblackk7100% (1)
- Simple Surge AnalysisDocument8 paginiSimple Surge Analysisnaveenaee50% (2)
- Calculation Hdpe 24 InchDocument5 paginiCalculation Hdpe 24 InchBachtiar Ramadhan100% (1)
- Design of Thrust Block for Operating Floor SlabDocument2 paginiDesign of Thrust Block for Operating Floor SlabMUTHUKKUMARAMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Appx-A Formula and CalculationDocument20 paginiAppx-A Formula and CalculationapiscobainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thrust Block Calculations for PipesDocument5 paginiThrust Block Calculations for PipesalbertooooooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cp16 Road Crossing AnalysisDocument3 paginiCp16 Road Crossing Analysisboonico Nicco0% (1)
- Design of Thrust Blocks: A) 150 Dia 90 Degree BendDocument7 paginiDesign of Thrust Blocks: A) 150 Dia 90 Degree BendRajesh Babu100% (1)
- Anchor BlockDocument78 paginiAnchor BlockBishowkumar Shrestha100% (1)
- Design of Anchor BlockDocument4 paginiDesign of Anchor BlockDeepak Das TamrakarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Buried Pipe Design (Flexible) 1Document9 paginiBuried Pipe Design (Flexible) 1Ah Leng Lau100% (2)
- Wheel Load AnalysisDocument8 paginiWheel Load Analysistsoheil100% (2)
- Steel Pipe Design CriteriaDocument3 paginiSteel Pipe Design CriteriaAnonymous 3kDy7eÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pipe Support Design Guidelines SummaryDocument4 paginiPipe Support Design Guidelines SummaryNitya Sheel RohillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thrust Block 1Document1 paginăThrust Block 1Jen EmeraldÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sizing Calculations of Thrust BlocksDocument5 paginiSizing Calculations of Thrust BlocksElvis Gray83% (6)
- Thrust Block Design Horizontal ElbowDocument23 paginiThrust Block Design Horizontal ElbowMd Et100% (1)
- GRP Stress AnalysisDocument13 paginiGRP Stress AnalysisCarlos Luis Esquerdo MarcanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thickness CalculationsDocument6 paginiThickness Calculationsvijayunity100% (1)
- HDPE DGNDocument9 paginiHDPE DGNdsdeshpande100% (1)
- Single Chamber ModifiedDocument46 paginiSingle Chamber ModifiedIsmail Magdy IsmailÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elastic Bending Radius Calculation of PIPELINESDocument1 paginăElastic Bending Radius Calculation of PIPELINESmailmaverick816777% (13)
- HDPE Pipe Calculation MethodsDocument7 paginiHDPE Pipe Calculation Methodssabahiraq100% (2)
- Pipe DesignDocument1 paginăPipe DesignShreevardhan KhoatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Upheaval Buckling PipelineDocument11 paginiUpheaval Buckling PipelineRYZKI EFENDI SIMANULANGÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laying 30Document13 paginiLaying 30Ashok SwamiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stress Analysis of GRP GRE FRP Piping System Using Caesar IIDocument5 paginiStress Analysis of GRP GRE FRP Piping System Using Caesar IIiaftÎncă nu există evaluări
- Underground Pipe THK CalDocument12 paginiUnderground Pipe THK Calmkchy12100% (3)
- Underground Pipe Stress Check CalculationsDocument6 paginiUnderground Pipe Stress Check Calculationsani_datÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anchor Blocks & Pipe SupportsDocument3 paginiAnchor Blocks & Pipe SupportsbonnicoÎncă nu există evaluări
- HORIZONTAL DIRECTIONAL DRILLING CALCULATIONDocument4 paginiHORIZONTAL DIRECTIONAL DRILLING CALCULATIONbulituk100% (1)
- Chain Pulley Block CalculationDocument2 paginiChain Pulley Block CalculationAmit SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pipeline Highway Crossing Design SpreadsheetDocument11 paginiPipeline Highway Crossing Design SpreadsheetBeljun FloresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Buried PipeDocument11 paginiBuried PipePrashant Agrawal100% (4)
- Basic Calculations Piping System Design PDFDocument14 paginiBasic Calculations Piping System Design PDFjeff_shawÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design Calculations for Pipe Support Foundations and PedestalsDocument10 paginiDesign Calculations for Pipe Support Foundations and PedestalsJayanti RahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pipeline Calculations - ASAB Gas Lift LinesDocument11 paginiPipeline Calculations - ASAB Gas Lift LinesSaqib LaeeqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drainage Gutter Downpipe Hipped 06042014Document9 paginiDrainage Gutter Downpipe Hipped 06042014Miguel MarshallÎncă nu există evaluări
- HDD Pipeline Design OptimizationDocument15 paginiHDD Pipeline Design Optimizationoconnorr8133% (3)
- Eqp FoundationDocument41 paginiEqp Foundationirshad313100% (2)
- M45 Design 1000Document7 paginiM45 Design 1000Landon MitchellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trafo Found DesignDocument6 paginiTrafo Found DesignIrshad Khan100% (1)
- R.C. Foundation Design for Oil Storage TankDocument17 paginiR.C. Foundation Design for Oil Storage Tanknerioalfonso100% (2)
- API 650 Design TanksDocument34 paginiAPI 650 Design TanksSyedZainAli100% (13)
- Pipeline Design Calculations PDFDocument21 paginiPipeline Design Calculations PDFjimallen21281% (21)
- Mud HydraulicsDocument5 paginiMud HydraulicsFares NaceredineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Erc - Valve Pit CalculationDocument30 paginiErc - Valve Pit Calculationisaacjoe77Încă nu există evaluări
- Slab On GradeDocument105 paginiSlab On Gradevijaystructural100% (6)
- 184 907Document40 pagini184 907Ankur DubeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indrumator Metal - EGDocument37 paginiIndrumator Metal - EGhooky1100% (1)
- Design of RCC Pier Supporting Deck SlabDocument8 paginiDesign of RCC Pier Supporting Deck SlabiploguÎncă nu există evaluări
- Proper Air-Fuel Ratios for Starting, Idling, Accelerating & MoreDocument9 paginiProper Air-Fuel Ratios for Starting, Idling, Accelerating & MoreVinh Do ThanhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Air-Fuel Ratio, Lambda and Engine Performance: AFR M MDocument12 paginiAir-Fuel Ratio, Lambda and Engine Performance: AFR M MVinh Do ThanhÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Heart of Operations - World Cement - 02-2015Document4 paginiThe Heart of Operations - World Cement - 02-2015fetniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Recycle From ETP Make Up H2O DAP, UreaDocument1 paginăRecycle From ETP Make Up H2O DAP, UreaVinh Do ThanhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modelling and Simulation of A Direct Contact Rotary DryerDocument16 paginiModelling and Simulation of A Direct Contact Rotary DryerVinh Do ThanhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multi-Use Chair DesignDocument7 paginiMulti-Use Chair DesignVinh Do ThanhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effects of Drying Parameters On Heat Transfer During DryingDocument13 paginiEffects of Drying Parameters On Heat Transfer During DryingVinh Do ThanhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Studies On Drying Kinetics of Solids in A Rotary DryerDocument6 paginiStudies On Drying Kinetics of Solids in A Rotary DryerVinh Do ThanhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modeling and Simulation of A Co-Current Rotary Dryer Under Steady ConditionsDocument8 paginiModeling and Simulation of A Co-Current Rotary Dryer Under Steady ConditionsVinh Do ThanhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dryer CalculationsDocument4 paginiDryer CalculationsVinh Do Thanh0% (1)
- NPK-15 8 15Document5 paginiNPK-15 8 15Vinh Do ThanhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ansi B16-104Document1 paginăAnsi B16-104Monica Suarez100% (1)
- PEP Report 267A: Ihs ChemicalDocument8 paginiPEP Report 267A: Ihs ChemicalVinh Do ThanhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aoac - Methods.1.1990. MoistureDocument2 paginiAoac - Methods.1.1990. MoistureVinh Do ThanhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tinh Luong Nuoc Bay HoiDocument22 paginiTinh Luong Nuoc Bay HoiVinh Do ThanhÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4244 12672 1 PB PDFDocument15 pagini4244 12672 1 PB PDFVinh Do ThanhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Natural Evaporation RateDocument16 paginiNatural Evaporation RateVinh Do ThanhÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4244 12672 1 PB PDFDocument15 pagini4244 12672 1 PB PDFVinh Do ThanhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Equivalent Grades of Cast IronsDocument2 paginiEquivalent Grades of Cast IronsVinh Do ThanhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Metal Price IndexDocument1 paginăMetal Price IndexVinh Do ThanhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mau Giay Uy Quyen Bang Tieng AnhDocument3 paginiMau Giay Uy Quyen Bang Tieng AnhVinh Do ThanhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review On Development of Polypropylene Manufacturing ProcessDocument11 paginiReview On Development of Polypropylene Manufacturing ProcessShweta Yadav100% (1)
- How To Calculate Heat Load - 5 StepsDocument1 paginăHow To Calculate Heat Load - 5 StepsVinh Do ThanhÎncă nu există evaluări
- CRACKER A PC Based Simulator For Industr PDFDocument6 paginiCRACKER A PC Based Simulator For Industr PDFVinh Do ThanhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Estimating Evaporation From Water SurfacesDocument27 paginiEstimating Evaporation From Water SurfacesVinh Do ThanhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Investigation of Sensible Heat Storage and Heat Insulation in The Exploitation of Concentrated Solar EnergyDocument5 paginiInvestigation of Sensible Heat Storage and Heat Insulation in The Exploitation of Concentrated Solar EnergyradanpetricaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 0ProjectManagementProceduresDocument8 pagini1 0ProjectManagementProceduresRamiesRahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- DRS 279-2015 Organic Fertilizer - SpecificationDocument17 paginiDRS 279-2015 Organic Fertilizer - SpecificationVinh Do ThanhÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Calculate Heat Load - 5 StepsDocument1 paginăHow To Calculate Heat Load - 5 StepsVinh Do ThanhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optimization of Wall Thickness For Minimum Heat LossesDocument9 paginiOptimization of Wall Thickness For Minimum Heat LossesVinh Do ThanhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fermenting For Health - Pip MagazineDocument2 paginiFermenting For Health - Pip MagazinePip MagazineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment On Types of Retail Marketing: Submitted By: MR - Swapnil S. Ghag. Roll No.10 (A)Document9 paginiAssignment On Types of Retail Marketing: Submitted By: MR - Swapnil S. Ghag. Roll No.10 (A)Swapnil Ghag100% (1)
- Dimensions-Mm (Inch) : Valve Regulated Lead Acid Battery (VRLA)Document2 paginiDimensions-Mm (Inch) : Valve Regulated Lead Acid Battery (VRLA)orunmila123Încă nu există evaluări
- Affidavit of UNDERTAKING AlbayDocument2 paginiAffidavit of UNDERTAKING AlbayEppie SeverinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Port Works Design Manual Part 2 PDFDocument124 paginiPort Works Design Manual Part 2 PDFhessian123Încă nu există evaluări
- CN LSHC The Future of Pharmacy en 031120Document8 paginiCN LSHC The Future of Pharmacy en 031120marina_netÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sodium Chloride MSDSDocument5 paginiSodium Chloride MSDSIbaharmovic LpuÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Refugees - NotesDocument1 paginăThe Refugees - NotesNothing Means to meÎncă nu există evaluări
- Soa Group Health TrackDocument2 paginiSoa Group Health TrackwasabiwafflesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seizure Acute ManagementDocument29 paginiSeizure Acute ManagementFridayana SekaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amnesia With Focus On Post Traumatic AmnesiaDocument27 paginiAmnesia With Focus On Post Traumatic AmnesiaWilliam ClemmonsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Personal Development: Quarter 1 - Module 5: Developmental Tasks and Challenges of AdolescenceDocument16 paginiPersonal Development: Quarter 1 - Module 5: Developmental Tasks and Challenges of AdolescenceMary Joy CejalboÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Island To Oneself - Suvarov, Cook Islands 2Document8 paginiAn Island To Oneself - Suvarov, Cook Islands 2Sándor TóthÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Humanistic Approach To Medical PracticeDocument3 paginiA Humanistic Approach To Medical PracticeFilipos ConstantinÎncă nu există evaluări
- MicrosystemDocument5 paginiMicrosystembabalalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1: Abnormal Behavior in Historical ContextDocument22 paginiChapter 1: Abnormal Behavior in Historical ContextEsraRamos100% (2)
- Computed Tomography (CT) - BodyDocument7 paginiComputed Tomography (CT) - Bodyfery oktoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kluge 2004 MetabolaDocument42 paginiKluge 2004 MetabolaBlah BlahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fall ProtectionDocument5 paginiFall ProtectionAamir AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Essay On Covid 19Document15 paginiEssay On Covid 19Priyanka Dubey67% (3)
- Weld Procedure Specification (WPS) : Joint Design Welding SequenceDocument1 paginăWeld Procedure Specification (WPS) : Joint Design Welding SequenceRicardo SoaresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Binac Ao STR EET: Vicinity Map & Street View, Source Google MapsDocument17 paginiBinac Ao STR EET: Vicinity Map & Street View, Source Google MapsBee AnquilianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interest RatesDocument207 paginiInterest RatesBenjamin RogersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Barangay Ordinance Vaw 2018Document7 paginiBarangay Ordinance Vaw 2018barangay artacho1964 bautista100% (3)
- Nothing But The Truth D2Document89 paginiNothing But The Truth D2Jamie Nicholas100% (1)
- ECG ProjectDocument34 paginiECG Projectsamsai888Încă nu există evaluări
- Respiration PHYSIODocument23 paginiRespiration PHYSIOTauseef AfridiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 6-Q1-M6Document14 paginiScience 6-Q1-M6John Philip LegaspiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maxicare Individual and Family ProgramDocument43 paginiMaxicare Individual and Family Programbzkid82Încă nu există evaluări
- PPC Production PlantDocument106 paginiPPC Production PlantAljay Neeson Imperial100% (1)