Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
School Evaluation Summary: Wendi Straub and Ann-Michelle Levangie, EDTECH 501
Încărcat de
wendistraubTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
School Evaluation Summary: Wendi Straub and Ann-Michelle Levangie, EDTECH 501
Încărcat de
wendistraubDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
EDTECH 501
Boise State University
Wendi Straub and Ann-Michelle Levangie
April 25, 2013
School Evaluation Summary
Wendi Straub and Ann-Michelle Levangie, EDTECH 501
Introduction
This technology use survey was conducted by a faculty member of the surveyed institution, Wendi Straub, and data was summarized by a third party to the institution, Ann-Michelle Levangie. The objective was to synthesize the schools technology environment and determine an overall maturity stage for the institution. The following report includes a description of the institution demographics, rationale for rankings at the category level, and a summary of overall evaluation.
Methodology
Information about the schools technology planning and use were obtained via informal interviews conducted by Wendi Straub. Both the principal and IT support person were each engaged in individual conversations, as well as, one joint conversation within the past two weeks. Teacher use and attitudes were also derived from recent dialogues. Additional input was determined from Mrs. Straubs personal experiences as a manager of two of the schools mobile computer labs, a 2012 Biology curriculum co-developer for the district, and a member of the district Blended Learning PLT.
EDTECH 501
Boise State University
Wendi Straub and Ann-Michelle Levangie
April 25, 2013
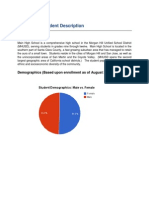
Shermer High School Demographics
2012-2013 school year began with 1367 students in grades 9th-12th. This is the first year that 9th grade was part of the high schools rather than the junior high schools in this school district, consequently more than 600 students were new in the fall. As the school made room for the additional grade, two computer labs (and everything larger than a closet) were converted to classroom space. Three new mobile labs with 30 netbooks each were purchased to mitigate the loss. However, with the additional students, the hardware to student ratio rose from four students per computer to five. Two demographics were also affected by the restructuring of the district to accommodate a freshman class students receiving free and reduced lunch rose from 29% to 40% and students of Hispanic descent grew from 11% to 18%; increasing overall minority groups from 20% to 27%. Black and Asian populations are roughly 1% each; nearly 4% are American Indian and another 4% are other or mixed minority. The remaining nearly 73% are caucasian.
Chart 1
EDTECH 501
Boise State University
Wendi Straub and Ann-Michelle Levangie
April 25, 2013
Maturity Model Benchmarks
ADMINISTRATIVE
Policy Behavioral - ISLANDS The school has a formal policy in place for responsible, educational use of technology.
Personal devices are officially prohibited within classrooms but, in the past two years, have been made allowable on a case-by-case basis. This ranking indicates that technology is either not being used to the letter of the existing policy. Resource/Infrastructure - ISLANDS Though there are shared informal practices, no official policy exists for the implementation of the tools of technology in the daily curriculum.
Planning Behavioral - EMERGENT Technology plans are driven by school budget allotments and teacher-initiated grants for
specific projects. The formal expansion of a school technology plan has been delayed by repealed technology laws. This qualifies the category to be at the Emergent level. Resource/Infrastructure - EMERGENT The school does not have a formal technology plan. Resources are allotted by available budget and influenced by enrollment fluctuations. There is an informal effort made to maintain a 4-5 student per computer ratio.
Budget Behavioral - ISLANDS In line with the Islands description of high priority budget with simple resourcing, this
institution includes technology in the school budget and uses the funds largely for hardware and software. Resource/Infrastructure - ISLANDS The institution has a technology budget from which all resources are funded. No funds are derived from other budget line items. District funds support the network, PowerSchool management, Google Drive support, and one full-time IT employee per school.
Administrative Information Behavioral - INTELLIGENT As the Intelligent benchmark defines, the school utilizes a fully paperless system. Faculty
and administrators communicate with each other, with parents, and with students using electronic systems. Classroom management is electronic. Resource/Infrastructure - INTELLIGENT In support of the paperless communication mentioned prior, the school is equipped with systems for electronic communication using Google applications, email, PowerSchool, and Txtwire. CURRICULAR
Electronic Information Behavioral - INTEGRATED
EDTECH 501
Boise State University
Wendi Straub and Ann-Michelle Levangie
April 25, 2013
The Integrated level indicates dependency on and use of information resources. This school
has curriculum documents provided by the district. While technology resources are included, their use is not required. Technology is integrated into standard curricula by fewer than 30% of teachers on a regular basis. Resource/Infrastructure - INTEGRATED Lesson integration mentioned above is performed largely in computer labs (mobile labs or library stations) by appointment. The school has a network available to students and teachers. It is accessible by personal device and Google Docs is allowed for digital collaboration.
Assessment Behavioral - EMERGENT Use of technology for assessment is limited. Technology is most commonly employed by
teachers and used by students for projects and formal assessments. There is not much depth to the useageword processing is most common. Resource/Infrastructure - ISLANDS The institution supports the use of technology for generating traditional summative assessment. Students take state standardized tests on desktop computers. Systems in place include PLATO, ExamView,Idaho Digital Learning Academy, and BrainHoney.
Curriculum Integration Behavioral - EMERGENT The curricula is only dependent on technology in that it is delivered from district to teacher
via the district network. Because the daily classroom use of technology is limited and driven by individual teachers, this is ranked as Emergent. Resource/Infrastructure - ISLANDS Technology related resources are available through some of the district curricula and their implementation could be supported by the network and hardware.
Teacher Use Behavioral - INTEGRATED Technology is used daily by teachers for administration and curriculum. Useage is heavily
weighed towards the former. All classroom management and most communication is performed using digital systems, but curricular integration is at the discretion of the teacher and dependent on available resources. Hardware is largely outside of individual classrooms, making full integration a challenge. Resource/Infrastructure - INTELLIGENT All teachers have the available hardware and network access for digital classroom management and instructional support as needed.
Student Use Behavioral - ISLANDS As specified by the Islands ranking, students use technology, but in limited ways. Use of
personal devices in the classroom is regulated. Computer stations are only sometimes used outside of classroom instruction. Use of technology is rarely required outside of class. Resource/Infrastructure - INTEGRATED Student technology access within school is consistent and regular. Students have individual accounts, wireless access, and use of hardware as scheduled by the instructor. SUPPORT
EDTECH 501
Boise State University
Wendi Straub and Ann-Michelle Levangie
April 25, 2013
Stakeholder Involvement Behavioral - EMERGENT Although some groups are aware of the planning and implementation process, this is
confined to the school super userstech savvy teachers and those on professional learning teams. None are involved in planning. Resource/Infrastructure - EMERGENT There is not a wide range of involvement in the tech planning process. Participation goes top-to-bottom, starting with district-level decision makers and going down to school administrators and staff.
Administrative Support Behavioral - EMERGENT Administrative involvement in planning is limited to peripheral discussion. Administrators
are interested in the conversation of technology integration, but do not contribute to or implement solutions. Resource/Infrastructure - ISLANDS The infrastructure for planning is slightly ahead of the implementation. Time is scheduled for planning and implementation, but this is limited to district-initiated projects.
Training Behavioral - ISLANDS Many staff members participate in professional development days, the 3-4 days per year of
district-mandated training. A smaller number pursue additional training opportunities through the district or through local college partnerships. Resource/Infrastructure - ISLANDS On-going formal training consists of at least 2 development days per school year. The training is executed by limited personnel, including experts, administrators, and instructional coaches. Some teachers complete additional training on a voluntary basis, and the district encourages them to disseminate their learning to their colleagues.
Technical & Infrastructure Support Behavioral - INTEGRATED Most staff utilize formal IT support as needed. There one IT support employee for the
school, so there are inefficiencies in implementation. Resource/Infrastructure - INTELLIGENT The school has full-time IT support to address all needs. That support consists of a single employee, so response times range from 20 minutes to 4 days, depending on the severity of the issue. CONNECTIVITY
Local Area Networking (LAN) Behavioral - ISLANDS All staff and students use the networks, but with a range of sophistication. Some use the
network to support learning management systems. Fewer still use data, video, or audio services. Resource/Infrastructure - INTEGRATED Though the network can occasionally be overwhelmed by high use or slowed by distance from the hub, the network is consistently functional and available to all via wired or wireless connection. Filters limit access to working environments infrequently.
EDTECH 501
Boise State University
Wendi Straub and Ann-Michelle Levangie
April 25, 2013
District Area Networking (WAN) Behavioral - N/A The institution only utilizes WAN district area networking the sense that it uses the
Internet. Resource/Infrastructure - N/A The institution uses the Internet for district networking.
Internet Access Behavioral - ISLANDS Many staff and students use the internet, though use is primarily by the former. Useage is
only sporadically integrated into the curriculum. Resource/Infrastructure - INTELLIGENT All staff, students, and school guests have access to either wired or wireless internet connections.
Communication Systems Behavioral - INTEGRATED Email is consistently used for communication within the school. Email communication
between teachers and students or teachers and parents is less consistent. Resource/Infrastructure - INTELLIGENT Any inconsistent use described above is behavioral only. Email access is universal through the school. INNOVATION
New Technologies Behavioral - ISLANDS New technologies are accepted by many staff members, but not all. While opportunities for
experimentation are encouraged, they are practiced by only the core group of innovators on staff. Resource/Infrastructure - ISLANDS There is no inherent resistance to new technologiesthey are accepted by many. However, implementation is limited, depending on ease-of-use and motivation.
Comprehensive Technologies Behavioral - INTEGRATED Technology in the institution is fairly comprehensive. Most forms of technology are used
by at least one teacher within the school. Technologies used consistently are the basic hardware and systems provided by the district. Any additional tools come from teacher grants. Resource/Infrastructure - INTEGRATED Technology infrastructure is strong and includes computers and network access in every classroom. In addition to these basics, there are projectors, iPads, clickers, document cameras, and interactive room cameras on a much more limited basis. These tools are used, but frequently not to their full capabilities.
Summary
EDTECH 501
Boise State University
Wendi Straub and Ann-Michelle Levangie
April 25, 2013
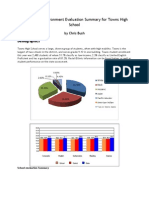
The Maturity Model Benchmarks from the Technology Use Plan Primer by Peter H.R. Sibley and Chip Kimball cover 19 categories across 5 organizational filters. Results of this survey show that there is a consistent trend across the categoriesboth in total (Chart 4) and in looking at Behavioral (Chart 2) and Resource/Infrastructure (Chart 3) types alonethat reveals the Islands stage as the dominant rank in this institution. The only view in which a different stage outranks Island is in the Curricular Filter (Chart 5). The Curricular area is at the Integrated stage, which reveals that the resource availability and the behaviors of the teachers and students are at a higher level that the institution as a whole. Despite this anomaly, the overall stage assigned to this institution is the Islands stage. Characteristic of this stage, the school demonstrates regular use of computers and digital systems, though use is greatly weighed toward administrative and classroom management functionalities and less toward integration with the curriculum. Technology plans are in place and are visible, but they are limited and the process of planning is not transparent and does not involve school staff. The institution sponsors training, but more rigorous professional development is on a voluntary basis.
Chart 2
Chart 3
Chart 4
Chart 5
An interesting factor illuminated by the data is the detail that in 9 of the 19 categories, the Behavioral benchmark stage is behind that of the Resource/Infrastructure stage (Chart 6). This shows that available resources are not being adequately integrated into the curriculum and may inform a recommendation to increase teacher technology training within the institution.
EDTECH 501
Boise State University
Wendi Straub and Ann-Michelle Levangie
April 25, 2013
Chart 6
Additionally, we can see that there are two categories in which both Behavioral and Resource/Infrastructure types are classed at the Emergent stage Planning and Stakeholder Involvement. This suggests a need for a formally defined technology plan with all groups (faculty and administrators) involved with and engaged in the planning. Overall, this school is moving in the right direction for infrastructure and support and will benefit tremendously from additional formalization of processes and increased community involvement. Attitudes and behavior lag behind resource availability, but the Islands of use by core innovators should continue to spread, especially as digital skills are becoming more essential to best practices.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- School Evaluation Summary: Wendi Straub and Ann-Michelle Levangie, EDTECH 501Document9 paginiSchool Evaluation Summary: Wendi Straub and Ann-Michelle Levangie, EDTECH 501amlevangieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summary of The EvaluationDocument6 paginiSummary of The EvaluationcdennylluÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technology Maturity Evaluation: Institution: Border Middle School DemographicsDocument8 paginiTechnology Maturity Evaluation: Institution: Border Middle School Demographicsthe_babushkaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evaluation Johnson Wojnicki, D.Document8 paginiEvaluation Johnson Wojnicki, D.astra_drjw_1260Încă nu există evaluări
- Evaluation Johnson WojnickiD4 24Document9 paginiEvaluation Johnson WojnickiD4 24astra_drjw_1260Încă nu există evaluări
- Evaluation TsadiMDocument6 paginiEvaluation TsadiMmarytsadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technology Evaluation of Roseberry Middle SchoolDocument7 paginiTechnology Evaluation of Roseberry Middle SchoolTara Makani MillerÎncă nu există evaluări
- School and Student Description: Demographics (Based Upon Enrollment As of August 2012)Document8 paginiSchool and Student Description: Demographics (Based Upon Enrollment As of August 2012)tornduff0903Încă nu există evaluări
- School Evaluation Summary-College of The Bay: Edtech 501 Boise State University Pete SurgentDocument8 paginiSchool Evaluation Summary-College of The Bay: Edtech 501 Boise State University Pete Surgentmachu_peterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evaluation of The Establishment As Compared To The Technology Maturity Model Lynn JohnsonDocument8 paginiEvaluation of The Establishment As Compared To The Technology Maturity Model Lynn JohnsonLynnDJJohnsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technology Environment Evaluation Summary For Towns High SchoolDocument11 paginiTechnology Environment Evaluation Summary For Towns High SchoolcjbushÎncă nu există evaluări
- School Evaluation Summary: DemographicsDocument6 paginiSchool Evaluation Summary: DemographicsChristopherHill1Încă nu există evaluări
- School Evaluation Summary: AdministrativeDocument7 paginiSchool Evaluation Summary: AdministrativeellimclaughlinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maturity Benchmarks Survey SheetDocument4 paginiMaturity Benchmarks Survey SheetamlevangieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evaluation - Bennettl, Summer 2012: Tech Times at Ridgemont High - Our DemographicsDocument6 paginiEvaluation - Bennettl, Summer 2012: Tech Times at Ridgemont High - Our DemographicsLinda BennettÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maturity Model Benchmarks Review: - Middle Eastern American SchoolDocument5 paginiMaturity Model Benchmarks Review: - Middle Eastern American SchooldanielkilbackÎncă nu există evaluări
- School Environment Evaluation Technology Maturity Benchmarks Angie Kruzich Edtech 501Document7 paginiSchool Environment Evaluation Technology Maturity Benchmarks Angie Kruzich Edtech 501Angie KruzichÎncă nu există evaluări
- Springfield Secondary Schools Technology Environment Survey EvaluationDocument6 paginiSpringfield Secondary Schools Technology Environment Survey Evaluationhd_franklinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Educ 5324-Research Assignment3Document6 paginiEduc 5324-Research Assignment3api-384631795100% (1)
- School Evaluation Summary: Laul ElementaryDocument5 paginiSchool Evaluation Summary: Laul ElementaryellimclaughlinÎncă nu există evaluări
- School Evaluation Summary: DemographicsDocument9 paginiSchool Evaluation Summary: DemographicsroundyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Schulz Junior High School Evaluation Summary: Institution DemographicsDocument4 paginiSchulz Junior High School Evaluation Summary: Institution DemographicsRachaelle Larsen-GrimsrudÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technology Evaluation of XYZ School: Demographic InformationDocument8 paginiTechnology Evaluation of XYZ School: Demographic InformationRonGardinerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technology Evaluation of T High School: Administrative SummaryDocument8 paginiTechnology Evaluation of T High School: Administrative SummaryCassidy BakerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Demographics For School "P": AdministrativeDocument7 paginiDemographics For School "P": Administrativesbh8812Încă nu există evaluări
- Technology Evaluation of T High SchoolDocument8 paginiTechnology Evaluation of T High SchoolCassidy BakerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technology PlanDocument8 paginiTechnology Planapi-676860965Încă nu există evaluări
- Evaluation Yanowsky VDocument5 paginiEvaluation Yanowsky VVirginia Yenter YanowskyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mybui-Technology PlanDocument11 paginiMybui-Technology Planapi-384697954Încă nu există evaluări
- Evaluation MillsC. 1Document4 paginiEvaluation MillsC. 1cmills26Încă nu există evaluări
- Charter School - Greg CorderoDocument7 paginiCharter School - Greg CorderogregcorderoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Demographics: Cow Pie HighDocument6 paginiDemographics: Cow Pie HighAmyEkoMorganÎncă nu există evaluări
- School Evaluation Summary School Demographics: Behavioral: Integrated StageDocument6 paginiSchool Evaluation Summary School Demographics: Behavioral: Integrated StageMonica MachadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- School Evaluation Summary For Western High School by Noah WeberDocument16 paginiSchool Evaluation Summary For Western High School by Noah WeberNoah WeberÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brian Mitchell - School Evaluation: DemographicsDocument5 paginiBrian Mitchell - School Evaluation: DemographicsBrian MitchellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evaluation LybbertEricCDocument4 paginiEvaluation LybbertEricClybberteÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1433 Fatma Gunonu Technology Plan 65145 393665586Document7 pagini1433 Fatma Gunonu Technology Plan 65145 393665586api-317112547Încă nu există evaluări
- School Evaluation SummaryDocument9 paginiSchool Evaluation SummarychrsitinesimmsÎncă nu există evaluări
- School Evaluation Summary DemographicsDocument4 paginiSchool Evaluation Summary DemographicsKatie SissonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evaluation School - WalkerEDocument8 paginiEvaluation School - WalkerEEldon WalkerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evaluation PagliughiS 1Document9 paginiEvaluation PagliughiS 1Jacquelyn HeflinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technology Evaluation of ABC Elementary SchoolDocument10 paginiTechnology Evaluation of ABC Elementary SchooltonyagrantÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technology Environment Evaluation of Suburb High DemographicsDocument5 paginiTechnology Environment Evaluation of Suburb High DemographicsMatthew TaylorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technology Maturity Evaluation: Institution: DemographicsDocument7 paginiTechnology Maturity Evaluation: Institution: DemographicsDana FredwellÎncă nu există evaluări
- School Environment Evaluation Summary Rocko High School: AdministrativeDocument5 paginiSchool Environment Evaluation Summary Rocko High School: Administrativemarksmith11Încă nu există evaluări
- Maturity Model BenchmarksDocument7 paginiMaturity Model BenchmarksKathryn AverkampÎncă nu există evaluări
- Administrative: Policy (Behavioral: Intelligent, Resource/infrastructure: Intelligent)Document8 paginiAdministrative: Policy (Behavioral: Intelligent, Resource/infrastructure: Intelligent)danielmatthewsÎncă nu există evaluări
- School Evaluation Summary: ABC School District #321 DemographicsDocument8 paginiSchool Evaluation Summary: ABC School District #321 DemographicskjackimijÎncă nu există evaluări
- AWebb Tech Use EvalDocument5 paginiAWebb Tech Use EvalAfton Rose ThompsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- BF High School (BFHS) EvaluationDocument9 paginiBF High School (BFHS) EvaluationkathystricklandÎncă nu există evaluări
- Educ 5324-Technology Plan - 2 ZsDocument9 paginiEduc 5324-Technology Plan - 2 Zsapi-290805552Încă nu există evaluări
- Ballew CBB Needsassessment 8462Document24 paginiBallew CBB Needsassessment 8462api-482950866Încă nu există evaluări
- Technology Maturity Riverton High School 2012-2013 Academic School Year DemographicsDocument7 paginiTechnology Maturity Riverton High School 2012-2013 Academic School Year DemographicsSarah SchneiderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evaluation SalvadorPDocument5 paginiEvaluation SalvadorPPhillip SalvadorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Swot Template ThomasonDocument16 paginiSwot Template Thomasonapi-549212750Încă nu există evaluări
- Educ 5324-Technology PlanDocument14 paginiEduc 5324-Technology PlanQandel N. SaberÎncă nu există evaluări
- Educ 5324-Technology Plan of Murat DemirhanDocument8 paginiEduc 5324-Technology Plan of Murat Demirhanapi-290414741Încă nu există evaluări
- Andersong SwotDocument11 paginiAndersong Swotapi-203218664Încă nu există evaluări
- Demographics:: Students Per Grade For "Mason-Dixon" High School: Total Enrollment: 899 Number of Teachers: 60Document6 paginiDemographics:: Students Per Grade For "Mason-Dixon" High School: Total Enrollment: 899 Number of Teachers: 60Jennie Ellen FinafrockÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Future of Education: Innovations in Learning and TeachingDe la EverandThe Future of Education: Innovations in Learning and TeachingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rationale WStraubDocument29 paginiRationale WStraubwendistraubÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rationale WStraubDocument29 paginiRationale WStraubwendistraubÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rationale WStraubDocument29 paginiRationale WStraubwendistraubÎncă nu există evaluări
- CC PBL TimelineDocument6 paginiCC PBL TimelinewendistraubÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rationale WStraubDocument29 paginiRationale WStraubwendistraubÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mitosis Phases Guided NotesDocument2 paginiMitosis Phases Guided NoteswendistraubÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lacks Essential Features of Effective PBL Needs Further Development Incorporates Best PBL PracticesDocument3 paginiLacks Essential Features of Effective PBL Needs Further Development Incorporates Best PBL PracticeswendistraubÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology BlueprintDocument1 paginăBiology BlueprintwendistraubÎncă nu există evaluări
- Straub 504finalDocument16 paginiStraub 504finalwendistraubÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mitosis Exit TicketDocument1 paginăMitosis Exit TicketwendistraubÎncă nu există evaluări
- Embracing Technology in Constructivist Learning Environments Wendi Straub Boise State UniversityDocument17 paginiEmbracing Technology in Constructivist Learning Environments Wendi Straub Boise State UniversitywendistraubÎncă nu există evaluări
- EDTECH 503: Dr. Yu-Hui ChingDocument32 paginiEDTECH 503: Dr. Yu-Hui ChingwendistraubÎncă nu există evaluări
- Situated Learning Theory and Cognitive ApprenticeshipDocument2 paginiSituated Learning Theory and Cognitive ApprenticeshipwendistraubÎncă nu există evaluări
- Instructor GuideDocument10 paginiInstructor GuidewendistraubÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mitosis StoryboardDocument1 paginăMitosis StoryboardwendistraubÎncă nu există evaluări
- StraubW IDproject NaturalSelectionDocument34 paginiStraubW IDproject NaturalSelectionwendistraubÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology: 10TH Grade Mitosis LessonDocument6 paginiBiology: 10TH Grade Mitosis Lessonwendistraub100% (3)
- B4.2 ModelMitosisWSDocument2 paginiB4.2 ModelMitosisWSwendistraubÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evaluation of IFHS Academic Advisory Program: Prepared For Idaho Falls High School AAD CommitteeDocument19 paginiEvaluation of IFHS Academic Advisory Program: Prepared For Idaho Falls High School AAD CommitteewendistraubÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mitosis in Motion Project: Required ElementsDocument3 paginiMitosis in Motion Project: Required ElementswendistraubÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maturity Benchmark SurveyDocument2 paginiMaturity Benchmark SurveyamlevangieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Essentialism 3.0Document14 paginiEssentialism 3.0MJ MurillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 09 Bloom Gardner Matrix Example 2009Document2 pagini09 Bloom Gardner Matrix Example 2009Ellen Jaye BensonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Department of Education: Lac Session Attendance SheetDocument4 paginiDepartment of Education: Lac Session Attendance SheetKa YeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineeringstandards 150416152325 Conversion Gate01Document42 paginiEngineeringstandards 150416152325 Conversion Gate01Dauødhårø Deivis100% (2)
- CSS Forums - View Single Post - PMS SyllabusDocument9 paginiCSS Forums - View Single Post - PMS SyllabusAdnan AbbasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Enh 1 Compilation 1 4 BEED 4A Set ADocument216 paginiEnh 1 Compilation 1 4 BEED 4A Set AKristel Ariane Aguanta100% (1)
- Sharif 2006Document228 paginiSharif 2006Mansoor Aaqib MalikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 Lesson 1 NCBTS and PPSTDocument32 paginiChapter 2 Lesson 1 NCBTS and PPSTMichael CabangonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Présentation Bootcamp 1 orDocument31 paginiPrésentation Bootcamp 1 orwalid laqrafiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit IV. Communication in Pharmacy Practice PDFDocument54 paginiUnit IV. Communication in Pharmacy Practice PDFGeannea Mae LeañoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nico Krisch (Eds) - Entangled Legalities Beyond The StateDocument522 paginiNico Krisch (Eds) - Entangled Legalities Beyond The StateRoddy89Încă nu există evaluări
- Dr. Manish Kumarcommunity Mental HealthDocument63 paginiDr. Manish Kumarcommunity Mental HealthManish KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Qualification Template V3Document52 paginiQualification Template V3DR-Muhammad ZahidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Glencoe Mcgraw Hill Geometry Homework Practice Workbook Answer KeyDocument8 paginiGlencoe Mcgraw Hill Geometry Homework Practice Workbook Answer Keybodinetuzas2100% (1)
- PCR 271Document205 paginiPCR 271mztayyabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aires DLP English 10Document6 paginiAires DLP English 10Aljean Taylaran AsbiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 8 HMWRK Lesson 8Document2 paginiModule 8 HMWRK Lesson 8ReekhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Co2 LP English 7Document3 paginiCo2 LP English 7Cherrymie Batal Diel100% (1)
- CDC OBE Syllabus NSTP1 Mam QuilloyDocument7 paginiCDC OBE Syllabus NSTP1 Mam QuilloyJose JarlathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compiled Sop, Sos, Sad, Chapter IIDocument8 paginiCompiled Sop, Sos, Sad, Chapter IIJason Mark De GuzmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0408 - s23 - QP - 22 - World LiteratureDocument4 pagini0408 - s23 - QP - 22 - World LiteratureAzrin AzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3Document23 paginiChapter 3Shahmeer AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Portfolio ReflectionDocument2 paginiPortfolio Reflectionapi-527915551Încă nu există evaluări
- Mediating The MessageDocument322 paginiMediating The MessageAnda Vanesky100% (2)
- NIA 1 - National Investigation Agency - Deputaion Nomination - DT 07.09.21Document10 paginiNIA 1 - National Investigation Agency - Deputaion Nomination - DT 07.09.21Adarsh DixitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cognitive Diagnostic AssessmentDocument43 paginiCognitive Diagnostic AssessmentReza MobashsherniaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lista Manuale Macmillan Aprobate Şi Recomandate: Nr. Crt. Manual Level Aprobat MECT Clasa L1 L2 L3Document4 paginiLista Manuale Macmillan Aprobate Şi Recomandate: Nr. Crt. Manual Level Aprobat MECT Clasa L1 L2 L3Cerasela Iuliana PienoiuÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6 Designing A Training SessionDocument34 pagini6 Designing A Training SessionERMIYAS TARIKUÎncă nu există evaluări
- Registered Master Electrician Theories and FormulasDocument21 paginiRegistered Master Electrician Theories and FormulasFrancis Paul92% (13)
- Front Page.20Document24 paginiFront Page.20Nawshad AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări