Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Value Chain
Încărcat de
Devank MaliDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Value Chain
Încărcat de
Devank MaliDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
A summary of IMA guideline I. Need Value chain analysis is a strategic tool to measure the customer's perceive d value.
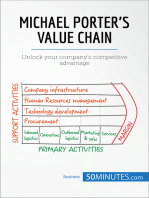
The analysis enables companies to determine the strategic advantages an d disadvantages of their value creating processes and activities. II. Value Chain - Definition Customer value accumulates along the chain of activities that a firm performs a nd delivers an end product or service to customers. Activities and processes are performed by the firm to understand market, design, produce, sell (market), deliver and support its product. A firm's value chain structure and the way the individual activities in the val ue chain are performed are a reflection of the firm's history, its current stra tegy, its approach to implementing its strategy and the underlying economics of the activities. The activities in a value chain are categorised as primary and support activitie s. III. Competing in the Market, Customer Value and Competitive Advantage In order to compete in a market as a supplier of a product or service a firm mus t supply what customers want to buy. It has to create customer value so that cus tomer pays a price for the offering. In any market there are competitors. The fi rm has to be provide some unique benefits to a certain section of persons in the target market to survive the competition. The competitive advantage of a firm derives from the difference between the valu e it offers to customers and its cost of creating that customer value. Thus the competitive advantage is obtained from two sources: 1. Differentiation advantage. Customer perceives more value from the firm's prod ucts. 2. Low cost advantage. The firm is able to provide the service or product at a c ost lower than the market average. IV. The Role of Management Accountant Champion the use of value chain analysis. V. Value Chain Analysis - Procedure Internal cost analysis Internal differentiation analysis Vertical linkage analysis VI. Strategic Frameworks for Value Chain Analysis From the strategy theory the following concepts or frameworks are relevant for v alue chain analysis Industry structure analysis Core competencies Segmentation analysisi VII. Limitations of Value Chain Analysis It is not an exact science. It is not easy. Finding costs, revenues and assets f or each activity sometimes presents serious difficulties. Despite such difficulties, experience indicates that value chain analysis yields firm swith invaluable information on their competitive situation, cost structur e, and linkages with suppliers and customers. VIII. Organizational and Managerial Accounting Challenges Value chain analysis offers an opportunity to integrate strategic planning and m anagement accounting. Management accounting department has to champion this to m aintain its critical role as the information profession.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Michael Porter's Value Chain: Unlock your company's competitive advantageDe la EverandMichael Porter's Value Chain: Unlock your company's competitive advantageEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- What's Value Chain Analysis? How Is It Carried Out? Describe Its Role in Strategic Cost AnalysisDocument15 paginiWhat's Value Chain Analysis? How Is It Carried Out? Describe Its Role in Strategic Cost AnalysisVivek SolankiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marketing Management Concepts and Tools: A Simple IntroductionDe la EverandMarketing Management Concepts and Tools: A Simple IntroductionEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (7)
- Paper 16 Chapters 1 To 5 With Addition MatterDocument372 paginiPaper 16 Chapters 1 To 5 With Addition MatteridealÎncă nu există evaluări
- Value Chain AnalysisDocument6 paginiValue Chain Analysisamolk_87Încă nu există evaluări
- Creating Competitive AdvantageDocument5 paginiCreating Competitive AdvantageAmol Deherkar60% (5)
- Strat Bus AnalysisDocument5 paginiStrat Bus AnalysisAecee CalatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Value Chains, Concepts and Supply Chain: Strategic Management Lesson Number: 8Document15 paginiValue Chains, Concepts and Supply Chain: Strategic Management Lesson Number: 8si touloseÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Concept of A Company Value Chain: BuyersDocument12 paginiThe Concept of A Company Value Chain: BuyersCarolyn ImaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Porters Value ChainDocument3 paginiPorters Value Chainkamal4sitmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Value Chain AnalysisDocument2 paginiValue Chain AnalysismaraelvillamorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Value Chain Analysis Guide for Strategic ManagementDocument16 paginiValue Chain Analysis Guide for Strategic ManagementJazelle Mae DimaanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Value ChainDocument11 paginiThe Value ChainOliviaDuchess100% (1)
- Value-Added Systems: The International Encyclopedia of Business and Management, 2nd Ed., (8 Volume Set)Document11 paginiValue-Added Systems: The International Encyclopedia of Business and Management, 2nd Ed., (8 Volume Set)SaniaMalikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analyze Firm Activities for Competitive Advantage with Value Chain AnalysisDocument6 paginiAnalyze Firm Activities for Competitive Advantage with Value Chain AnalysisNur Hazwani HusnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marketing Management Chapter 2Document13 paginiMarketing Management Chapter 2salman soomroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Company values, strategic groups, industry changes, and competitive advantageDocument1 paginăCompany values, strategic groups, industry changes, and competitive advantagePhạm Thị Bích LoanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic No. 09, 10 & 11Document6 paginiTopic No. 09, 10 & 11vivekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Article Summary of Value Chain Analysis For Assessing Competitive AdvantageDocument3 paginiArticle Summary of Value Chain Analysis For Assessing Competitive AdvantageVanadisa SamuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Operations and Supply Chain Management Week 2Document5 paginiOperations and Supply Chain Management Week 2Rhyn RutherfordÎncă nu există evaluări
- Akuntansi Manajemen Bab 7Document3 paginiAkuntansi Manajemen Bab 7Dik HabibÎncă nu există evaluări
- Value Chain Analysis for Cost Advantage and Differentiation (VCADocument37 paginiValue Chain Analysis for Cost Advantage and Differentiation (VCASrivastav GauravÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optimize your value chain for competitive advantageDocument38 paginiOptimize your value chain for competitive advantageCla Rence OliverosÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 - Evaluating Companys Resources and Competitive PositionDocument53 pagini4 - Evaluating Companys Resources and Competitive PositionNasir HussainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Value-Chain AnalysisDocument30 paginiValue-Chain AnalysisSheikh RubelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter-1 Imperatives For Market Driven StrategyDocument11 paginiChapter-1 Imperatives For Market Driven Strategysajid bhattiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 4 Strategic Position-Strategic CapabilityDocument28 paginiTopic 4 Strategic Position-Strategic CapabilityDumisani NyirendaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strategic Cost Management Activity 1Document2 paginiStrategic Cost Management Activity 1Emerson SalangaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 5 Internal Analysis IDocument19 paginiLecture 5 Internal Analysis IJoey ChinÎncă nu există evaluări
- International Business Strategy & Global ExpansionDocument12 paginiInternational Business Strategy & Global ExpansionduaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Value Chain Analysis: Primary ActivitiesDocument5 paginiValue Chain Analysis: Primary ActivitiesSmiely SafeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Internal Analysis: Distinctive Competencies, Competitive Advantage and ProfitabilityDocument28 paginiInternal Analysis: Distinctive Competencies, Competitive Advantage and ProfitabilityArun Mathews JacobÎncă nu există evaluări
- Decision Making - Rational Model and Bounded RationalityDocument20 paginiDecision Making - Rational Model and Bounded RationalityNidhi SatvekarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 1 - Developing Marketing Strategies and PlansDocument13 paginiModule 1 - Developing Marketing Strategies and PlansAbigail GatmaitanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Value ChainDocument18 paginiValue Chaingoyalprateek92100% (1)
- Ism PyqaDocument2 paginiIsm PyqaAbhijeet PanditÎncă nu există evaluări
- Value Chain Analysis: A Seminar Report OnDocument26 paginiValue Chain Analysis: A Seminar Report OnDinesh ChahalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5: 5 Generic CompeitionDocument12 paginiChapter 5: 5 Generic CompeitionMiscue JoÎncă nu există evaluări
- MDI Strategy Compendium PDFDocument15 paginiMDI Strategy Compendium PDFutkarsh chaudharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- MDI HRD Compendium 2018Document15 paginiMDI HRD Compendium 2018Subhendu PradhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- B2B CommodityDocument3 paginiB2B CommodityAman ChopraÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Value Chains AnalysisDocument6 paginiWhat Is Value Chains Analysispastilles4427Încă nu există evaluări
- Value Chain Models Version 2.1 (Last Updated - July 2010)Document24 paginiValue Chain Models Version 2.1 (Last Updated - July 2010)kashalisahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Value Chain AnalysisDocument33 paginiValue Chain Analysisdiwangkara surya nugrahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Value Chain AnalysisDocument33 paginiValue Chain AnalysisAbhinav GoelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marketing Value Delivery Process & Customer Value CreationDocument11 paginiMarketing Value Delivery Process & Customer Value CreationCarlos Ruiz EstradaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Operations StrategyDocument4 paginiOperations Strategyjth55936zwohocomÎncă nu există evaluări
- bài tập lớnDocument4 paginibài tập lớnBé HoaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reporting ManagmentDocument12 paginiReporting ManagmentTuseef AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- La Cadena de Valor de Michael PorterDocument15 paginiLa Cadena de Valor de Michael PorterAraceli ParedesÎncă nu există evaluări
- L&SCM Unit IDocument22 paginiL&SCM Unit IbhaskaranbalamuraliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Creating Competitive Advantage: Group 3Document10 paginiCreating Competitive Advantage: Group 3Hitesh KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strategic Capabilities and Competitive Advantage: Question of ValueDocument6 paginiStrategic Capabilities and Competitive Advantage: Question of ValueGummadi Banu PrakashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Daniels11 ImDocument13 paginiDaniels11 ImAngels HeartÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5Document44 paginiChapter 5Bridgestone55Încă nu există evaluări
- Value Chain and Supply ChainDocument8 paginiValue Chain and Supply ChainJay SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Essentials of Strategic Management The Quest For Competitive Advantage 5th Edition by Gamble Thompson and Peteraf ISBN Solution ManualDocument15 paginiEssentials of Strategic Management The Quest For Competitive Advantage 5th Edition by Gamble Thompson and Peteraf ISBN Solution Manualalison100% (27)
- Lecture Outline: Chapter 5 The Five Generic Competitive StrategiesDocument36 paginiLecture Outline: Chapter 5 The Five Generic Competitive Strategiespatrick.coutee753100% (11)
- International Strategic Management Mid 2Document17 paginiInternational Strategic Management Mid 2Md HimelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Object Oriented Programming Using C Questions ImportantDocument3 paginiObject Oriented Programming Using C Questions ImportantDevank MaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Be 2Document6 paginiBe 2devank1505Încă nu există evaluări
- Advance Graphics & Animation Questions ImportantDocument3 paginiAdvance Graphics & Animation Questions ImportantDevank MaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Programming Concept Using C Questions ImportantDocument3 paginiProgramming Concept Using C Questions ImportantDevank MaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5yr PlanDocument5 pagini5yr Plandevank1505Încă nu există evaluări
- Industrial PolicyDocument13 paginiIndustrial Policydevank1505Încă nu există evaluări
- Questions ImportantDocument2 paginiQuestions ImportantDevank MaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- RDBMSwithMS-SQLServer Questions ImportantDocument3 paginiRDBMSwithMS-SQLServer Questions ImportantDevank MaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Java Programming Languages Questions ImportantDocument3 paginiJava Programming Languages Questions ImportantDevank MaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fund FlowDocument2 paginiFund FlowDevank MaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- PPMDocument8 paginiPPMdevank1505Încă nu există evaluări
- 1 Business As A Social SystemDocument106 pagini1 Business As A Social Systemdevank1505Încă nu există evaluări
- Role of AccountDocument1 paginăRole of AccountDevank MaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Infleation AccountingDocument1 paginăInfleation AccountingDevank MaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Environmental Scanning & Monitoring TechniquesDocument17 paginiEnvironmental Scanning & Monitoring TechniquesLagrada Angela Marie50% (2)
- E CommerceDocument5 paginiE Commercedevank1505Încă nu există evaluări
- Quick RatioDocument1 paginăQuick RatioDevank MaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Variance Analysis, Flexible Budget and Management ControlDocument1 paginăVariance Analysis, Flexible Budget and Management ControlDevank MaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Target CostDocument1 paginăTarget CostDevank MaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Product Cost PeriodDocument1 paginăProduct Cost PeriodDevank MaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- BBBDocument1 paginăBBBDevank MaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Three Systems FinanDocument4 paginiThree Systems FinanDevank MaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Price LeveDocument1 paginăPrice LeveDevank MaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Master BudgetDocument1 paginăMaster BudgetDevank MaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lang of BusinessDocument1 paginăLang of BusinessDevank MaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kaizen CostingDocument1 paginăKaizen CostingDevank MaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human Resource AccountingDocument4 paginiHuman Resource AccountingDevank MaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Capital Fix AssDocument1 paginăCapital Fix AssDevank MaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dir Indirpri Variable FixDocument1 paginăDir Indirpri Variable FixDevank MaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sap s4 HanaDocument7 paginiSap s4 HanaBhaskarChakrabortyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4255 9913 1 SM - Id.enDocument18 pagini4255 9913 1 SM - Id.enErick HidayatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6 Variable Costing and AnalysisDocument33 paginiChapter 6 Variable Costing and AnalysisVeronica JaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 28 Product Cost ControllingDocument52 paginiChapter 28 Product Cost Controllingzachary kehoeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cost Volume Profit Analysis (CVP Analysis) : Incremental Contribution"Document14 paginiCost Volume Profit Analysis (CVP Analysis) : Incremental Contribution"Corin Ahmed CorinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Le Controle de Gestion de L...Document13 paginiLe Controle de Gestion de L...areffoun0% (1)
- Book 8 Jul 2023Document4 paginiBook 8 Jul 2023Kinza KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- PT Elektro Brilian Sales & Receivables Journal 2014Document3 paginiPT Elektro Brilian Sales & Receivables Journal 2014ViviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quiz 2 - Cost AccountingDocument4 paginiQuiz 2 - Cost AccountingDong WestÎncă nu există evaluări
- ACCA107 MIDTERMS OCT 06 2021 PROBLEMS SOLUTION - Sheet3Document12 paginiACCA107 MIDTERMS OCT 06 2021 PROBLEMS SOLUTION - Sheet3Mary Kate OrobiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Accounting For Joint Products and by ProductsDocument13 paginiAccounting For Joint Products and by ProductsSteffi CabalunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 4 Wileyplus Comm 305Document68 paginiCH 4 Wileyplus Comm 305Aba RIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Production Cost EstimationDocument6 paginiProduction Cost EstimationAbdulla KamalovÎncă nu există evaluări
- True-False and Multiple Choice Questions on Cost Behavior and CVP AnalysisDocument23 paginiTrue-False and Multiple Choice Questions on Cost Behavior and CVP AnalysisGrace100% (1)
- Factory OverheadDocument21 paginiFactory OverheadRey Joyce AbuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Resume - Bharati Desai Senior Accounting PositionsDocument4 paginiResume - Bharati Desai Senior Accounting PositionsJeremy SmithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test CostingDocument186 paginiTest CostingMohammad FiqiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Managerial Accounting: An Overview: Solutions To QuestionsDocument4 paginiManagerial Accounting: An Overview: Solutions To QuestionsMohsin RazaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Process Costing: True / False QuestionsDocument226 paginiProcess Costing: True / False QuestionsElaine Gimarino100% (1)
- Materials From HBS and Text Book - Summary of Management AccountingDocument145 paginiMaterials From HBS and Text Book - Summary of Management AccountingMuhammad Helmi FaisalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Standard Costing and Variance AnalysisDocument56 paginiStandard Costing and Variance AnalysisJoyce Mamoko100% (2)
- Quiz 3 SolutionDocument5 paginiQuiz 3 SolutionMichel BanvoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 7 - INVENTORY MANAGEMENTDocument11 paginiChapter 7 - INVENTORY MANAGEMENTLong Đoàn PhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quiz 16 Activity-Based Costing QuestionsDocument1 paginăQuiz 16 Activity-Based Costing Questionswarning urgentÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subject Code: 101 Subject: Management Concepts and Application Attempt Any TWO Questions From The FollowingDocument12 paginiSubject Code: 101 Subject: Management Concepts and Application Attempt Any TWO Questions From The FollowingVishalKhuranaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Giovannoni Et Al - The Role of Roles in Risk Management Change - The Case of An Italian BankDocument23 paginiGiovannoni Et Al - The Role of Roles in Risk Management Change - The Case of An Italian BankLuis OliveiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 07Document39 paginiCH 07Shahnawaz KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cost ScannerDocument290 paginiCost ScannerRodloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chap 003Document72 paginiChap 003Hà PhươngÎncă nu există evaluări
- Managerial Accounting - Chapter 2Document50 paginiManagerial Accounting - Chapter 2GiorgosDimopoulosÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Goal: A Process of Ongoing Improvement - 30th Aniversary EditionDe la EverandThe Goal: A Process of Ongoing Improvement - 30th Aniversary EditionEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (684)
- The Machine That Changed the World: The Story of Lean Production-- Toyota's Secret Weapon in the Global Car Wars That Is Now Revolutionizing World IndustryDe la EverandThe Machine That Changed the World: The Story of Lean Production-- Toyota's Secret Weapon in the Global Car Wars That Is Now Revolutionizing World IndustryEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (40)
- Financial Modeling and Valuation: A Practical Guide to Investment Banking and Private EquityDe la EverandFinancial Modeling and Valuation: A Practical Guide to Investment Banking and Private EquityEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (4)
- The E-Myth Chief Financial Officer: Why Most Small Businesses Run Out of Money and What to Do About ItDe la EverandThe E-Myth Chief Financial Officer: Why Most Small Businesses Run Out of Money and What to Do About ItEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (13)
- These are the Plunderers: How Private Equity Runs—and Wrecks—AmericaDe la EverandThese are the Plunderers: How Private Equity Runs—and Wrecks—AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (14)
- Self-Discipline: The Ultimate Guide To Beat Procrastination, Achieve Your Goals, and Get What You Want In Your LifeDe la EverandSelf-Discipline: The Ultimate Guide To Beat Procrastination, Achieve Your Goals, and Get What You Want In Your LifeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (661)
- Process!: How Discipline and Consistency Will Set You and Your Business FreeDe la EverandProcess!: How Discipline and Consistency Will Set You and Your Business FreeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (5)
- Value: The Four Cornerstones of Corporate FinanceDe la EverandValue: The Four Cornerstones of Corporate FinanceEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (18)
- Financial Intelligence: A Manager's Guide to Knowing What the Numbers Really MeanDe la EverandFinancial Intelligence: A Manager's Guide to Knowing What the Numbers Really MeanEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (79)
- Mastering Private Equity: Transformation via Venture Capital, Minority Investments and BuyoutsDe la EverandMastering Private Equity: Transformation via Venture Capital, Minority Investments and BuyoutsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Planning and SchedulingDe la EverandProject Planning and SchedulingEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (6)
- Add Then Multiply: How small businesses can think like big businesses and achieve exponential growthDe la EverandAdd Then Multiply: How small businesses can think like big businesses and achieve exponential growthÎncă nu există evaluări
- Burn the Boats: Toss Plan B Overboard and Unleash Your Full PotentialDe la EverandBurn the Boats: Toss Plan B Overboard and Unleash Your Full PotentialÎncă nu există evaluări
- Leading Product Development: The Senior Manager's Guide to Creating and ShapingDe la EverandLeading Product Development: The Senior Manager's Guide to Creating and ShapingEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Summary of The Black Swan: by Nassim Nicholas Taleb | Includes AnalysisDe la EverandSummary of The Black Swan: by Nassim Nicholas Taleb | Includes AnalysisEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (6)
- Venture Deals, 4th Edition: Be Smarter than Your Lawyer and Venture CapitalistDe la EverandVenture Deals, 4th Edition: Be Smarter than Your Lawyer and Venture CapitalistEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (73)
- PMP Exam Prep: How to pass the PMP Exam on your First Attempt – Learn Faster, Retain More and Pass the PMP ExamDe la EverandPMP Exam Prep: How to pass the PMP Exam on your First Attempt – Learn Faster, Retain More and Pass the PMP ExamEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (3)
- Angel: How to Invest in Technology Startups-Timeless Advice from an Angel Investor Who Turned $100,000 into $100,000,000De la EverandAngel: How to Invest in Technology Startups-Timeless Advice from an Angel Investor Who Turned $100,000 into $100,000,000Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (86)
- Startup CEO: A Field Guide to Scaling Up Your Business (Techstars)De la EverandStartup CEO: A Field Guide to Scaling Up Your Business (Techstars)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (4)
- Warren Buffett Book of Investing Wisdom: 350 Quotes from the World's Most Successful InvestorDe la EverandWarren Buffett Book of Investing Wisdom: 350 Quotes from the World's Most Successful InvestorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kanban: A Step-by-Step Guide to Agile Project Management with KanbanDe la EverandKanban: A Step-by-Step Guide to Agile Project Management with KanbanEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (6)
- Burn the Boats: Toss Plan B Overboard and Unleash Your Full PotentialDe la EverandBurn the Boats: Toss Plan B Overboard and Unleash Your Full PotentialEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (32)
- These Are the Plunderers: How Private Equity Runs—and Wrecks—AmericaDe la EverandThese Are the Plunderers: How Private Equity Runs—and Wrecks—AmericaEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (8)
- Finance Basics (HBR 20-Minute Manager Series)De la EverandFinance Basics (HBR 20-Minute Manager Series)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (32)