Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
BENE1123 - Chapter3 Part 3
Încărcat de
马铃淑Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
BENE1123 - Chapter3 Part 3
Încărcat de
马铃淑Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Universiti Teknikal Malaysia, Melaka (UTeM)
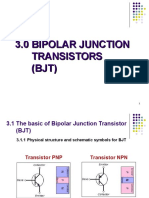
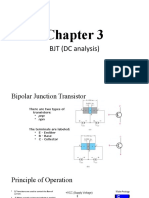
Chapter 3:
Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)
FUNDAMENTALS OF ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING (BENE 1123)
PART 3
Important Basic Relationship of Transistor
B C
I I | =
C B E
I I I ~ + = ) 1 (|
V 7 . 0 =
BE
V
1. In general, I
B
is the 1
st
quantity to be determined.
2. Then, the rest of the equations can be applied to find
the remaining quantities of interest.
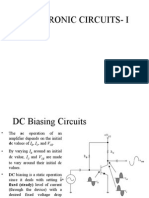
Biasing
Biasing: The DC voltages applied to a
transistor in order to turn it on so that it
can amplify the AC signal.
DC Analysis: What is biasing?
1. Take note that the AC power output is actually a result
of a transfer of energy from the applied DC source.
2. Therefore, biasing means establishing a fixed level of
current and voltage - which establishes an operating
point on the transistors "characteristic curve". The point
at which you bias the transistor depends on how you are
using it; As a switch, for amplification (ac or dc)...etc.
Operating Point
The DC input
establishes an
operating or quiescent
point called the Q-
point.
Biasing circuit can be
designed to set the
device operation on
any points within the
active region.
Q-point A no bias, device completely off
Q-point B if signal is applied to circuit, the device will
vary in current and voltage from the operating point,
allowing the device to react both the positive and negative
excursions of the input signal.
Q-point C allow some positive and negative variation,
but limited by the proximity VCE = 0V and IC = 0mA
Q-point D operating point near the maximum voltage
and power level. Output of positive direction is limited if
the maximum voltage is not to be exceeded.
Q-point B seems to be the best operating point in term of
linear gain and largest voltage and current swing
desired condition for small-signal amplifiers.
Operating Point
Circuit Analysis in Transistor Circuit
Network
1. DC Analysis:
The purpose of this DC analysis is to find the operating
point of the amplifier by supplying DC supply to the
transistor.
It involves with different types of biasing technique.
2. AC Analysis:
The purpose of this AC analysis is to find the frequency
response of the amplifier.
You will learn this in BENE 2153: Analogue Electronics
Biasing Techniques (in Amplifier)
There are six common biasing
circuits used in Bipolar Junction
Transistor (BJT) amplifiers:
1. Fixed bias
2. Collector-to-base bias
3. Emitter-Stabilized bias
4. Voltage divider bias
5. DC Bias with Voltage Feedback
6. Emitter bias
We will learn these biasing techniques
Biasing Technique: Fixed Bias
The common-emitter (CE) circuit with fixed-bias
During DC analysis, the transistor circuit network can be isolated from
the indicated AC input signal by replacing CAPACITOR with OPEN-
CIRCUIT equivalent.
How CAPACITOR = OPEN-CIRCUIT in DC Analysis?.
This is due to HIGH Impedance of capacitor at f = 0 Hz at DC
) (
) 0 ( 2
1
2
1 1
circuit open
C fC C
Z = = = =
t t =
Biasing Technique: Fixed Bias
Then, further DC analysis can be done by separating the transistor
circuit network into TWO DC analysis:
1. Based-Emitter Loop (look at Loop I)
2. Collector-Emitter Loop (look at Loop II)
Biasing Technique: Fixed Bias
Based-Emitter Loop (look at Loop I)
DC Analysis:
B
BE CC
B
BE B B CC
R
V V
I
V R I V
=
+ =
] [
B
BE CC
B C
R
V V
I I
= = | |
Biasing Technique: Fixed Bias
Collector-Emitter Loop (look at Loop II)
DC Analysis:
CE C C CC
V R I V + =
C C CC CE
R I V V =
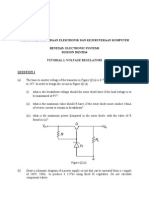
Question1:
Answer:
a) I
B
= 70.6uA, I
C
= 10.59mA
b) V
CE
= 3.88 V
c) V
B
= 0.7 V, V
C
= 3.88 V
d) V
BC
= -3.18 V
Load Line in DC Analysis
As we know, a level ofis a corresponding with
the resulting Q-point (in transistor
characteristic)
Meaning that, without , we still can find current
and voltage in transistor circuit by looking at the
output characteristic of a transistor.
B C
I I | =
Load Line in DC Analysis
The notations are now changed as follow:
Operating point (Q-point)
on the I
C
versus V
CE
characteristics laid on the
load line. It is actually to
determine the value of
currents and voltages
when transistor is
operating in dc condition.
Load Line in DC Analysis
To draw load-line, we analyze KVL from loop II, where
the equation for fixed bias circuit is given as:
CE C C CC
V R I V + =
Load Line in DC Analysis
Based on the I
Cmax
and V
CEmax
, we can draw the load-line
in the output characteristic of transistor.
Load Line in DC Analysis
Movement of the Q-point with increasing level of I
B
.
Load Line in DC Analysis
Effect of an increasing level of R
C
on the load line and
the Q-point.
Load Line in DC Analysis
Effect of lower values of V
CC
on the load line and the
Q-point.
Given the load line below and the defined Q-point,
determine the required values of V
CC
, R
C
and R
B
for a fixed-
bias configuration.
Question 2:
VCE = VCC = 20V at IC = 0 mA
We know, IC = VCC/RC at VCE = 0
RC = VCC/IC = 20V/ 10 mA = 2 kO
We know, IB = ( VCC VBE ) / RB
RB = ( VCC VBE ) / IB
= ( 20V 0.7V ) / 25A = 772 kO
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- EB-300 310 Service ManualDocument32 paginiEB-300 310 Service ManualVictor ArizagaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BJT DC and AC Load LineDocument21 paginiBJT DC and AC Load LineSunny KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Varaah KavachDocument7 paginiVaraah KavachBalagei Nagarajan100% (1)
- Transistor Biasing and Stabilization: Lesson - 1Document57 paginiTransistor Biasing and Stabilization: Lesson - 1Naseer Mohammed100% (1)
- Chapter 3 (Ii) : BJT (DC Analysis)Document17 paginiChapter 3 (Ii) : BJT (DC Analysis)matlela92Încă nu există evaluări
- 4.DC Biasing - BJTsDocument77 pagini4.DC Biasing - BJTsNimra AftabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit Ibiasing of Discrete BJT and MosfetDocument57 paginiUnit Ibiasing of Discrete BJT and MosfetVijayakumar SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bypassed Emitter Resistor CircuitDocument6 paginiBypassed Emitter Resistor CircuitSandesh AdhikaryÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 58 PDFDocument18 paginiCH 58 PDFJawad Ul Hassan Shah100% (1)
- Biasing: Unit - Ii Transistor Biasing Circuits Ans Small Signal Analysis of BJT Amplifiers 9 HrsDocument19 paginiBiasing: Unit - Ii Transistor Biasing Circuits Ans Small Signal Analysis of BJT Amplifiers 9 HrsCamilla IrunguÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biasing: Unit - Ii Transistor Biasing Circuits Ans Small Signal Analysis of BJT Amplifiers 9 HrsDocument19 paginiBiasing: Unit - Ii Transistor Biasing Circuits Ans Small Signal Analysis of BJT Amplifiers 9 HrsGoran WnisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Investigatory ProjectsDocument36 paginiPhysics Investigatory ProjectsTushar Kush100% (4)
- Lab 2Document4 paginiLab 2Muhammad TehreemÎncă nu există evaluări
- DEE20023 Chapter 3 (B) BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR SESI II 20222023Document23 paginiDEE20023 Chapter 3 (B) BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR SESI II 20222023Muhd ZarifÎncă nu există evaluări
- PSpice Simulation Model MOSFETDocument6 paginiPSpice Simulation Model MOSFETTowsifTaherÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chap 4 DC Biasing BJTDocument44 paginiChap 4 DC Biasing BJTUgeswran ThamalinggamÎncă nu există evaluări
- DC Biasing BJTsDocument30 paginiDC Biasing BJTsrobat20140% (1)
- Topic 3 (B)Document25 paginiTopic 3 (B)F1038 IFFAH SYAZANA BINTI MD HASNIN HADIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 - AmplifiersDocument65 paginiChapter 1 - Amplifierssai ineshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter3 2Document32 paginiChapter3 2Elvis NgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)Document45 paginiBipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)RizalÎncă nu există evaluări
- EC-302 Lecture NotesDocument4 paginiEC-302 Lecture NotesPraveen KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- L07 DC and AC Load LineDocument21 paginiL07 DC and AC Load LineDebashish Pal100% (1)
- Ec I (16 M) - Unit IDocument19 paginiEc I (16 M) - Unit IGtecEceÎncă nu există evaluări
- AnalogElectronics - TH 1 BJTDocument20 paginiAnalogElectronics - TH 1 BJTAlbert GenceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exp 5Document16 paginiExp 5neelu marturuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Term 2, Lecture 4: Transistor Bias Circuits The DC Operating PointDocument7 paginiTerm 2, Lecture 4: Transistor Bias Circuits The DC Operating Pointrafal mahmodÎncă nu există evaluări
- BJT NotesDocument110 paginiBJT NotesHardesh Chauhan100% (1)
- Module 3Document10 paginiModule 3Joseph JohnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture - BJT DC Analysis PDFDocument60 paginiLecture - BJT DC Analysis PDFAdam MoutasemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 TransistorsDocument17 paginiChapter 3 TransistorsFikri RahimÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECE 027 - DC Analysis For Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT)Document65 paginiECE 027 - DC Analysis For Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT)Miyuki NakiriÎncă nu există evaluări
- BJT 2Document25 paginiBJT 2fsms2020gÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 05 Subject: Electronics: Submitted To Ma'am Salma Submitted byDocument8 paginiAssignment 05 Subject: Electronics: Submitted To Ma'am Salma Submitted byAresha GhazalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab10 2011Document5 paginiLab10 2011Venkat RamananÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 BJT DC AnalysisDocument39 pagini3 BJT DC AnalysisA TalkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 PDFDocument39 paginiChapter 4 PDFAdel AtawiÎncă nu există evaluări
- DC BiasingDocument9 paginiDC BiasingnagarajÎncă nu există evaluări
- DC and AC Load LineDocument21 paginiDC and AC Load LineBenazir BegamÎncă nu există evaluări
- L07 DC and AC Load LineDocument21 paginiL07 DC and AC Load LineNipuna Thushara WijesekaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bjts DC BiasingDocument89 paginiBjts DC BiasingVenugopal ReddyvariÎncă nu există evaluări
- BJT DC BiasingDocument58 paginiBJT DC BiasingMohammad Gulam AhamadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 4 Dcbiasingofbjts 150222163832 Conversion Gate01 PDFDocument49 paginiLecture 4 Dcbiasingofbjts 150222163832 Conversion Gate01 PDFJim Agcaoili LindaÎncă nu există evaluări
- L07 DC and AC Load LineDocument21 paginiL07 DC and AC Load LineNancy NalluÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab6 Bipolar Junction Transistor Characteristics1588857204Document4 paginiLab6 Bipolar Junction Transistor Characteristics1588857204badalabhinav10Încă nu există evaluări
- Bipolar Junction Transistors (DC Biasing of BJTS)Document29 paginiBipolar Junction Transistors (DC Biasing of BJTS)RAUNAK GARGÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit IDocument156 paginiUnit IrevathianuÎncă nu există evaluări
- BJT Load LineDocument5 paginiBJT Load LineSunilAjmeeraÎncă nu există evaluări
- RC Coupled Transistor AmplifierDocument7 paginiRC Coupled Transistor AmplifierIshratÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ee 352 Ec Ii LabDocument61 paginiEe 352 Ec Ii LabSatya SandeepÎncă nu există evaluări
- ADEC - Lab 3Document14 paginiADEC - Lab 3syed furqan javedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Electronics Lab Exp 4-6-pdf Ayush Anshuman Supakar (118MN0579)Document10 paginiBasic Electronics Lab Exp 4-6-pdf Ayush Anshuman Supakar (118MN0579)Ayush Anshuman SupakarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ex.2 - Ecad 1Document6 paginiEx.2 - Ecad 1Saturn MoonÎncă nu există evaluări
- INC221 Lecture6 Transistor Biasing Circuit - ToDocument14 paginiINC221 Lecture6 Transistor Biasing Circuit - ToidatscribdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analog Lab ManualDocument57 paginiAnalog Lab ManualMukesh Sahu100% (1)
- Design A RC Coupled CE Transistor AmplifierDocument7 paginiDesign A RC Coupled CE Transistor AmplifierSudeep Nayak100% (1)
- TransistorDocument93 paginiTransistorIbnu Zaqi Firdaus100% (2)
- Analog CircuitsDocument76 paginiAnalog CircuitsIshtiaque Ahmed TanimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1De la EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Evaluare: 2.5 din 5 stele2.5/5 (3)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2De la EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Încă nu există evaluări
- Modern Control of DC-Based Power Systems: A Problem-Based ApproachDe la EverandModern Control of DC-Based Power Systems: A Problem-Based ApproachÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial 1 PDFDocument9 paginiTutorial 1 PDF马铃淑Încă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 6 BJT1Document13 paginiLecture 6 BJT1马铃淑Încă nu există evaluări
- BENE1123 - Chapter3 Part 2Document17 paginiBENE1123 - Chapter3 Part 2马铃淑Încă nu există evaluări
- BENE1123 - Chapter3 Part 1Document17 paginiBENE1123 - Chapter3 Part 1马铃淑Încă nu există evaluări
- Pi 0614 Hiblack f890b en WebDocument2 paginiPi 0614 Hiblack f890b en Web王偉仲Încă nu există evaluări
- Augocom Micro 768 Battery Tester User ManualDocument29 paginiAugocom Micro 768 Battery Tester User ManualJorge PontonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculate Cable Size and Voltage Drop Electrical Notes Articles PDFDocument10 paginiCalculate Cable Size and Voltage Drop Electrical Notes Articles PDFRavi SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thesis 1-15Document15 paginiThesis 1-15hewelirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scientific American Psychology 2nd Edition Licht Test BankDocument44 paginiScientific American Psychology 2nd Edition Licht Test Bankpurelychittra3ae3100% (24)
- Important Notice 38-2021 Dated 24-03-2021 Available Seats Foreign National Spon INI CET PG Courses July 2021Document3 paginiImportant Notice 38-2021 Dated 24-03-2021 Available Seats Foreign National Spon INI CET PG Courses July 2021Priyobrata KonjengbamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Glacial Lakes of Himachal PradeshDocument4 paginiGlacial Lakes of Himachal PradeshMonidipa DeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scientific Exploration and Expeditions PDFDocument406 paginiScientific Exploration and Expeditions PDFana_petrescu100% (2)
- Ays 082914 3331 PDFDocument18 paginiAys 082914 3331 PDFFabian R. GoldmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phineas Gage: From The Passage of An Iron Rod Through The Head"Document1 paginăPhineas Gage: From The Passage of An Iron Rod Through The Head"GlupiaSprawaÎncă nu există evaluări
- VAM Must Sumitomo 1209 PDFDocument4 paginiVAM Must Sumitomo 1209 PDFnwohapeterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fatigue Consideration in DesignDocument3 paginiFatigue Consideration in DesigngouthamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Offsetting Macro-Shrinkage in Ductile IronDocument13 paginiOffsetting Macro-Shrinkage in Ductile IronmetkarthikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Afectiuni Si SimptomeDocument22 paginiAfectiuni Si SimptomeIOANA_ROX_DRÎncă nu există evaluări
- NURS1108 Lecture 10 - Nervous System ENHANCEDDocument40 paginiNURS1108 Lecture 10 - Nervous System ENHANCEDJacia’s SpaceshipÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Explanation of The Fundamentals of Islamic BeliefDocument95 paginiThe Explanation of The Fundamentals of Islamic BeliefbooksofthesalafÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mobile Communication Networks: Exercices 4Document2 paginiMobile Communication Networks: Exercices 4Shirley RodriguesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Welding Research Council: BulletinDocument28 paginiWelding Research Council: BulletinRogerio Tropia GranjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theology of Work and Practical ImplicationsDocument28 paginiTheology of Work and Practical ImplicationsVinicius CardosoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Master Key Utbk Saintek 2022 (Paket 3) Bahasa InggrisDocument5 paginiMaster Key Utbk Saintek 2022 (Paket 3) Bahasa InggrisRina SetiawatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modern Views Catalogue/Sotheby's BenefitDocument36 paginiModern Views Catalogue/Sotheby's BenefitStudio AdjayeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manual de Taller sk350 PDFDocument31 paginiManual de Taller sk350 PDFLeo Perez100% (1)
- MX 400Document231 paginiMX 400Percy JimenezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Timer Relay ERV-09Document1 paginăTimer Relay ERV-09wal idÎncă nu există evaluări
- BLANCHARD-The Debate Over Laissez Faire, 1880-1914Document304 paginiBLANCHARD-The Debate Over Laissez Faire, 1880-1914fantasmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Collage Lab PDFDocument145 paginiCollage Lab PDFmaa siddhi92% (12)
- FPAL Product Code GuideDocument53 paginiFPAL Product Code GuideSRARÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Anaesthesia MCQsDocument5 paginiGeneral Anaesthesia MCQsWasi Khan100% (3)