Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Coronary Atherosclerosis: Cardiovascular System: Coronary Vascular Disease Topics Discussed Here Are
Încărcat de
Kamx Mohammed0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
33 vizualizări6 paginiasd
Titlu original
Ncm103 6th Cv II
Drepturi de autor
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentasd
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
33 vizualizări6 paginiCoronary Atherosclerosis: Cardiovascular System: Coronary Vascular Disease Topics Discussed Here Are
Încărcat de
Kamx Mohammedasd
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 6
jcmendiola_Achievers2013
Care of Clients with Problems In Oxygenation,
Fluids and Electrolytes, Metabolism and Endocrine
(NCM103)
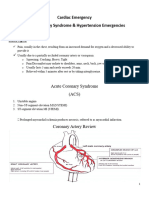
Cardiovascular System: Coronary Vascular Disease
Coronary Atherosclerosis
Definition:
Abnormal accumulation of fatty substances
Creates BLOCKAGE
Repetitious inflammatory response
o Obstruction + Inflammation = Blood Flow MI or AP
Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis
1. Definition Lumen Lumen
2. Cause Deposition of fatty substances Elasticity of blood vessels
3. Age Toddlers Aging process
4. Layer Tunica intima Tunica media
Risk Factors:
Blood lipid level
Smoking lumen; vasoconstriction
Hypertension Narrowing down of blood vessels
Diabetes / Hyperlipidemia
Obesity
Metabolic Syndrome
o Hyperglycemia FBS, Glucose Tolerance Test
o Hypertension
o Level of lipids in blood
o Presence of elevation CRP
Clinical Manifestations:
- Depends on
1. Location and degree of
narrowing
2. Thrombus formation and
obstruction of blood
CHEST PAIN~ Asymptomatic~
Prevention:
Control of cholesterol level
Get lipid profile once ever 5 years (20
y/o and above)
a. Diet
b. Physical Activity
c. Medications Anti-lipid Drugs
d. Promoting cessation of tobacco
Nicotine!!
Viscosity
of blood
Vasoconstric
tion of Blood
Vessels
e. Managing Hypertension
Religious intake of
DRUGS
Regular exercise
Diet
Alcohol intake
Topics Discussed Here Are:
1. Coronary Atherosclerosis
2. Angina Pectoris
3. Myocardial Infarction
LOOKY
HERE
jcmendiola_Achievers2013
NUTRIENT CONTENT OF THE THERAPEUTIC LIFESTYLE CHANGES (TLC) DIET
Nutrient Recommended Intake
Total calories Balance intake and expenditure to maintain desirable weight
Total fat
Saturated fat
Polyunsaturated fat
Monounsaturated fat
25% - 35% of total calories
Less than 7% of total calories
Up to 10% of total calories
Up to 20% of total calories
Carbohydrate 50% - 60% of total calories
Dietary fiber 20 30 g/day
Protein Approximately 15% of total calories
Cholesterol Less than 200 mg/day
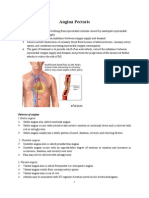
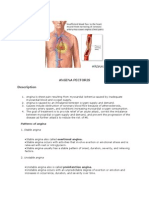
Angina Pectoris
Factors: Blood Flow due to Lumen
Non-modifiable Factors
1. Age
2. Sex
3. Race
4. Family History
Modifiable Factors
5. Diet ( Na, Fat, Nicotine)
6. Alcohol
7. Obesity
8. Sedentary activity
9. Stress
Coronary
Insufficiency
Coronary occlusion
(Continuation of coronary insufficiency)
Lumen
CHEST
PAIN On and Off
Bearable
Short Duration
Angina Pectoris
CONSTANT
SEVERE
LONGER
Myocardial
Infarction
Ischemia
What is Angina Pectoris?
Associated With:
+ Outside factors
+ Mental / Emotional problems
Relieved With:
+ Rest
+ Coronary vasodilators
Levines Sign
Types of Angina Pectoris
1. Stable Angina
` Predictable and consistent pain
` Relieved by rest and / nitroglycerin
2. Unstable Angina / Preinfarction Angina / Crescendo Angina
` Symptoms increase in frequency
` May not be relieved by rest and nitroglycerin
3. Variant Angina (Prinzmetals Angina)
` Pain at rest
` Reversible ST-segment elevation
4. Silent Ischemia
` Objective evidence of ischemia
` But NO PAIN :o
Management:
1. Medical Management
a. Rest Minimum of 2 hours
jcmendiola_Achievers2013
b. Drugs
1. Coronary Vasodilators
O Dilates lumen of blood vessels in the myocardium
O Drugs:
o Nitroglycerin
+ 1 Tab, SL q5 min PRN for chest pain
+ Maximum of 3 Tablets; if not resolved considered
MI
+ Take the medications before
any stressful event
+ Loses potency when
exposed in the sun; store in
dark colored bottles
+ If head gets big, warm, and
flushing of face it is
NORMAL, not SIDE EFFECT or ADVERSE
EFFECT
2. Anti-platelet Drugs
O Aspirin (Produces GIT disturbance; Coated Aspirin New)
O Heparin
o Side Effect = Bleeding (Petechiae, Ecchymosis, Hematoma)
o WOF: Tea colored urine for HEMATURIA
o WOF: BLACK STOOLS
O NO PARENTERAL ADMINISTRATION OF DRUGS; if needed,
apply pressure after!!
O Dont use dental floss
3. Beta Blockers To reduce O
2
demand of myocardium
4. Ca
+
Channel Blocking Agent Relaxes the Blood Vessel to BP
c. Take 30 60 cc of BRANDY/WHISKY
To reduce chest pain by vasodilation
Amount = Vasoconstriction
Amount = Vasodilation
2. Prevention of Succeeding Attacks to Angina Pectoris
a. Diet
Fat Diet (THE FOLLOWING FOODS ARE NOT ALLOWED OR MODERATE)
- 4 Legged animals
- Foods with wings (Moderate)
- White meat
- Chicken (NO SKIN)
- Intake of food in WATER; but grows in SOIL
Na Diet (2 gm Na) AVOID THE FF FOODS
1. Na Nitrate Food colorings, cold cuts, preserved food
2. Na Nitrite Tocino, Tapa
3. Na HCO
3
Baking Soda, bread, biscuit, pastries
8:00 1
st
Tablet
8:05 2
nd
Tablet
8:10 3
rd
Tablet
8:00 1
st
Tablet
8:05 2
nd
Tablet
3:30 1
st
Tablet
jcmendiola_Achievers2013
4. NaCl Fish sauce, soy sauce, dried fish
5. Na Saccharin
b. Must be with the patient all the time!!
Coronary Vasodilators
- DONT EXPOSE IN THE SUN!!
- DONT LEAVE IN THE CAR!!
Myocardial Infarction
Brought about by lack of blood supply going to the myocardium
A.k.a. Coronary occlusion or Heart Attack
Pain:
- CRUSHING
- TIGHTNESS
- Sudden onset
- Substernal
- Severe
- Unrelieved by Nitroglycerin
- May radiate to: Back, neck, jaw, shoulders, arm
- Dyspnea
- Syncope ( BP)
- Nausea / Vomiting
- Extreme weakness
- Diaphoresis
- Denial is common
- HR
Treatment:
- O2 IV Medications
- Dietary restrictions
- Na, Cholesterol, Caffeine
- Surgery? Pacemaker?
Causes:
1. Atheroma Associated with body metabolism
2. O
2
/ Blood demand Patients with hyperthyroidism
3. O
2
Supply (Anemia, BP)
4. Vasospasm Sudden constriction / narrowing of coronary arteries
How to Diagnose Clients With MI
1. Presenting Manifestations
` Chief complaint
` Previous illnesses
` ECG: Done in 10 minutes PRIOR to admission
P
Q
R
S
T
ANG HIRAP MAG DROWING NG ECG PQRST SA PC XD
Components
1. P Wave Atrial Contraction / Depolarization (0.08 seconds)
2. PR Interval Time for impulses to travel from Artery to Ventricle (0.16 seconds)
3. QRS Complex Ventricular Contraction / Depolarization (0.08 seconds)
4. ST Segment Length of time for the ventricle to relax (0.12 seconds)
5. T Wave Ventricular relaxation / Repolarization (0.16 seconds)
0.08
seconds
2
seconds
jcmendiola_Achievers2013
Diagnosing Myocardial Infarction
Inverted T Wave
+ Injury becomes ischemic, myocardial Repolarization is altered and delayed
+ Which causes the T Wave to invert
Elevated ST-segment
+ Injured myocardial cells depolarize normally, but repolarize more rapidly than normal
cells
+ Causing the ST-segment to rise at least 1 mm above the isoelectric line
Laboratory Results
+ Creatinine Kinase (CK-MB)
+ Lactic Dehydrogenase
+ Myoglobin
+ Troponin T and I
Management
1. Minimize Myocardial damage
a. Cardiac overload
Place patient on absolute bed rest
- NO VISITORS ALLOWED (NEAREST RELATIVE ONLY)
- Health team should be calm
b. Get baseline Vital Signs
TPR
- Temperature = Due to cell death
- Pulse =
- Respiration =
- Blood Pressure =
Baseline ECG
Basic serum electrolytes
c. Administration of Drugs
Thrombolytic Drugs (Alteplase)
- 1
st
Drug
- To dissolve the blood clot
- The faster it is given, it is better
Analgesics
- To relieve chest pain
- Morphine - Pain and Anxiety related to MI
ACE Inhibitors
- To prevent BP
2. Cardiac Rehabilitation
Main objective: To extend the life of the patient and improve the quality of life of
patients
Consists of different activities
3 Phases of Cardiac Rehabilitation
1. Phase I
Time of diagnosis of atherosclerosis
Found out by lipid profile
Management:
- Preventive measures
1. Level of activities (Walking)
2. Initial education of patient and family (For self care)
3. Quit Smoking!
4. DIET > NO FATTY FOODS
If patient is not compliant, there
would be repeated attacks of
angina pectoris and myocardial
infarction .
jcmendiola_Achievers2013
2. Phase II
_ Time the patient has been discharged from the hospital
_ All activities are supervised; support from an outside person
_ Based on the stress test of the client
_ Dietitian would make a list of foods to be eaten and not eaten
3. Phase III
e Maintain cardiovascular stability
e Patient can still be on diet and exercise, but no longer supervised
Reperfusion Therapy
- Procedures wherein to further improve the blood flow to the myocardium such as:
o Angioplasty: Repair of blood vessel
PTA (Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty)
PTCA (Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty)
It is the inflation of a balloon pushing atheromas to the side, done not to attain
100%
o Coronary Stent
Inserted through the femur
Placement of a spring
Can cause thrombus formation
But eventually becomes part of the endothelial tissue
o Atherectomy
Removal of atheromas
Hollow cylinder
Diamond chip-blade
Rotation: Scrape atheromas
Not full scraping of atheromas
o Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG)
They cannot perform not until there are still very minimal amount of blood to
the myocardium
Harvest a Graft
Artery
Vein
o Common blood vessel used
Internal mammary artery
Saphenous vein
Nursing Care
Patient should be VERY compliant
+ Drugs be taken religiously
Thrombolytics
Beta blockers
Digitalis
+ Compliance to diet
FAT
Na
+ Ambulation
Gradually increasing
+ Sexual Intercourse
Patient should be able to make 5 7 steps in the stairs without fatigability
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Cardio PPT Module 5Document45 paginiCardio PPT Module 5ʕ•ᴥ•ʔÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Coronary Syndrome Acs 2Document6 paginiAcute Coronary Syndrome Acs 2grazelantonette.calubÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coronary Artery Disease Nclex, Peripheral Vascular DiseaseDocument88 paginiCoronary Artery Disease Nclex, Peripheral Vascular DiseaseKrishna SapkotaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cad, MiDocument23 paginiCad, MiSandeep ChaudharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coronary Heart DiseaseDocument13 paginiCoronary Heart DiseaseLea Recto VinuyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardio Ms Hand OutDocument10 paginiCardio Ms Hand OutVictor ShonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coronary Heart DiseaseDocument12 paginiCoronary Heart DiseaseandeishaferminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coronary Artery Disease (Cad) Definition:: Atherosclerosis - AccumulationDocument8 paginiCoronary Artery Disease (Cad) Definition:: Atherosclerosis - AccumulationReiche GomezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nclex Study Content - UseDocument65 paginiNclex Study Content - Usesbrooks6914100% (22)
- 2myocardial InfarctionDocument29 pagini2myocardial Infarctionblessed23Încă nu există evaluări
- Cardiovascular I: CAD: Coronary Artery Disease (Most Common in US) Risk FactorsDocument4 paginiCardiovascular I: CAD: Coronary Artery Disease (Most Common in US) Risk FactorsJessica100% (1)
- Cardiovascular Lecture Notes: AnginaDocument23 paginiCardiovascular Lecture Notes: AnginaAnonymous iG0DCOfÎncă nu există evaluări
- Care of Patient With CADDocument22 paginiCare of Patient With CADBader ZawahrehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Family Med EOR Study Guide 1Document86 paginiFamily Med EOR Study Guide 1Ranjani ammuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unstable Angina PectorisDocument24 paginiUnstable Angina PectorisAkbar IskandarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Angina & Heart Attack Causes, Symptoms, TreatmentDocument37 paginiAngina & Heart Attack Causes, Symptoms, TreatmentLennie LennieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing 4 Final ReviewDocument41 paginiNursing 4 Final Reviewemeraldwxyz100% (1)
- Care of Clients With Cardiovascular DisordersDocument67 paginiCare of Clients With Cardiovascular DisordersMatt Lao DionelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCM 112 MidtermDocument25 paginiNCM 112 MidtermJan Charlie Sophia100% (1)
- Care and Management of The Client With Cardiac Alterations: Presented By: Jessaly Joyce SiosonDocument38 paginiCare and Management of The Client With Cardiac Alterations: Presented By: Jessaly Joyce SiosonJoyce SiosonÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Ischemic Heart Disease - PPTX Year 3 2Document40 pagini3 Ischemic Heart Disease - PPTX Year 3 2Danny DesuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Step Up To MedicineDocument68 paginiStep Up To MedicineAmadou N'Dow100% (1)
- Presentor: John Hommer E. Dy M.D. Moderator: Joy Marchadesch M.DDocument57 paginiPresentor: John Hommer E. Dy M.D. Moderator: Joy Marchadesch M.DJohn Hommer DyÎncă nu există evaluări
- CardioDocument9 paginiCardioVirgilio Reyes ManuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guide to Cardiovascular DisordersDocument5 paginiGuide to Cardiovascular DisordersmagnacumlaudeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiac EmergencyDocument34 paginiCardiac EmergencyRima HannaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Angina PectorisDocument11 paginiAngina Pectorisjialin80% (5)
- StemiDocument35 paginiStemiIndra ChristiantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Nursing Care of Client With IMA: Alfrina HanyDocument42 paginiThe Nursing Care of Client With IMA: Alfrina HanyVio Alveolita PrimayaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Myocardial InfarctionDocument3 paginiMyocardial Infarctionaja_delÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coronary Artery Diseases Dr. TarekDocument80 paginiCoronary Artery Diseases Dr. TarekHero StoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiovascular System Diseases Part 1Document22 paginiCardiovascular System Diseases Part 1Prince Rener Velasco PeraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiac Lecture NotesDocument10 paginiCardiac Lecture NotesKateÎncă nu există evaluări
- Angina PectorisDocument17 paginiAngina PectorisRacel HernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug-Induced Arrhythmia TreatmentDocument27 paginiDrug-Induced Arrhythmia TreatmentLoiseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiac Disease NotesDocument4 paginiCardiac Disease NotesKyla Mae JumaritoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic: Advance Nursing Management of Cardiovascular: DiseasesDocument16 paginiTopic: Advance Nursing Management of Cardiovascular: DiseasesFareedullah PathanÎncă nu există evaluări
- PrelimsDocument11 paginiPrelimsJess Fabra100% (1)
- Cardiovascular Agents: Florianne E. Adlawan, R.NDocument31 paginiCardiovascular Agents: Florianne E. Adlawan, R.NadlawanflorianneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hypertension and Cardiovascular Disease Risk FactorsDocument9 paginiHypertension and Cardiovascular Disease Risk FactorslizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardio DiseasesDocument77 paginiCardio Diseasesrea bentayaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiovacular DisordersDocument7 paginiCardiovacular DisordersAbo AmgadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Myocardial Infarction: Alternative NamesDocument5 paginiMyocardial Infarction: Alternative NamesKhalid Mahmud ArifinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nclex Study 1Document11 paginiNclex Study 1Katie Shortt100% (4)
- Myocardial Infarction Guide: Causes, Types, Symptoms & TreatmentDocument27 paginiMyocardial Infarction Guide: Causes, Types, Symptoms & TreatmentKyrajane EsguerraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Welcome: What We All Should KnowDocument44 paginiWelcome: What We All Should KnowSuman ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes For Responses To Altered Tissue PerfusionDocument12 paginiNotes For Responses To Altered Tissue Perfusiondivine armentonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardio GuideDocument29 paginiCardio GuideGlenn JavellanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coronay Artery Disease: Dr. Bibek Poudel Department of Medicine City Medical College HospitalDocument22 paginiCoronay Artery Disease: Dr. Bibek Poudel Department of Medicine City Medical College HospitalitsmailbbkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Myocardial Infarction: Ns. Dendy Kharisna, M.KepDocument26 paginiMyocardial Infarction: Ns. Dendy Kharisna, M.KepChristinaSitompulÎncă nu există evaluări
- CardioDocument7 paginiCardioGerald AndrinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathogenesis of Cardiac DisordersDocument28 paginiPathogenesis of Cardiac DisordersUdochukwu EnebeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiac FailureDocument63 paginiCardiac FailureNina OaipÎncă nu există evaluări
- Myocardial InfarctionDocument4 paginiMyocardial InfarctionLetecia MooreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study 01 Myocardial InfarctionDocument11 paginiCase Study 01 Myocardial InfarctionAldrin BardeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tell Me What to Eat If I Suffer from Heart Disease: Nutrition You Can Live WithDe la EverandTell Me What to Eat If I Suffer from Heart Disease: Nutrition You Can Live WithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atrial Fibrillation A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesDe la EverandAtrial Fibrillation A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- Unveiling the Unseen: A Journey Into the Hearts Labyrinth SeanDe la EverandUnveiling the Unseen: A Journey Into the Hearts Labyrinth SeanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Mnemonics: The Ultimate Tips and Notes For NursesDe la EverandNursing Mnemonics: The Ultimate Tips and Notes For NursesEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Ncm103 30th Gi IVDocument6 paginiNcm103 30th Gi IVKamx MohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ncm103 29th Gi IIIDocument11 paginiNcm103 29th Gi IIIKamx MohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCM103 23rd F&E IIIDocument6 paginiNCM103 23rd F&E IIIKamx MohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCM103 20th Respi VIDocument6 paginiNCM103 20th Respi VIKamx MohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ncm103 27th Gi IDocument10 paginiNcm103 27th Gi IKamx MohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCM103 19th Respi VDocument5 paginiNCM103 19th Respi VKamx MohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCM103 25th F&E VDocument6 paginiNCM103 25th F&E VKamx MohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ncm103 28th Gi IIDocument12 paginiNcm103 28th Gi IIKamx MohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCM103 26th Acce IDocument31 paginiNCM103 26th Acce IKamx MohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCM103 24th F&E IVDocument5 paginiNCM103 24th F&E IVKamx MohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCM103 21st F&E IDocument7 paginiNCM103 21st F&E IKamx MohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Concepts on Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument5 paginiBasic Concepts on Fluids and ElectrolytesKamx MohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ncm103 17th Respi IIIDocument3 paginiNcm103 17th Respi IIIKamx MohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCM103 18th Respi IVDocument6 paginiNCM103 18th Respi IVKamx MohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCM103 14th Endoc IVDocument9 paginiNCM103 14th Endoc IVKamx MohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Care of Clients with Respiratory AlterationsDocument10 paginiCare of Clients with Respiratory AlterationsKamx MohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ncm103 13th Endoc IIIDocument5 paginiNcm103 13th Endoc IIIKamx MohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCM103 16th Respi IIDocument5 paginiNCM103 16th Respi IIKamx MohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCM103 12th Endoc IIDocument9 paginiNCM103 12th Endoc IIKamx MohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCM103 11th Endoc IDocument8 paginiNCM103 11th Endoc IKamx MohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Right Sided Heart FailureDocument5 paginiRight Sided Heart FailureKamx MohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ncm103 10th Hema IIDocument8 paginiNcm103 10th Hema IIKamx MohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCM103 3rd & 4th Periop II and IIIDocument5 paginiNCM103 3rd & 4th Periop II and IIIKamx MohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Care of Clients with Hematologic Alterations: ErythrocytesDocument10 paginiCare of Clients with Hematologic Alterations: ErythrocytesKamx MohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCM103 5th CV IDocument7 paginiNCM103 5th CV IKamx MohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCM103 2nd Periop IDocument3 paginiNCM103 2nd Periop IKamx MohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ncm103 8th CV IVDocument5 paginiNcm103 8th CV IVKamx Mohammed0% (1)
- NCM103 2nd Periop IDocument3 paginiNCM103 2nd Periop IKamx MohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCM103 1st PainDocument5 paginiNCM103 1st PainKamx MohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Photosynthesis Question Booklet: Name . .Document16 paginiPhotosynthesis Question Booklet: Name . .ajithaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Developing Child - The First Seven Years - EbookDocument141 paginiThe Developing Child - The First Seven Years - Ebookall-natural-nutÎncă nu există evaluări
- Altitude PhysiologyDocument41 paginiAltitude Physiologyshepherd jeremiahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vacuole FunctionDocument8 paginiVacuole Functionkbansal981Încă nu există evaluări
- Nervous System - All NotesDocument6 paginiNervous System - All NotesJÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blue Bio V DoH and HFMADocument21 paginiBlue Bio V DoH and HFMAShane StarlingÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Difference Between Toxic and Nontoxic GoiterDocument2 paginiThe Difference Between Toxic and Nontoxic GoiterJawad Rehman100% (1)
- Top Knife - Cutted - Top PDFDocument238 paginiTop Knife - Cutted - Top PDFIvanKazaiev100% (1)
- Animal Morphology (GeoZoo Topics)Document5 paginiAnimal Morphology (GeoZoo Topics)niravhirparaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Anterior Cranial FossaDocument4 paginiThe Anterior Cranial FossaArshad hussainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pengaruh Faktor-Faktor Psikososial Dan Insomnia Terhadap Depresi Pada Lansia Di Kota YogyakartaDocument5 paginiPengaruh Faktor-Faktor Psikososial Dan Insomnia Terhadap Depresi Pada Lansia Di Kota YogyakartaKristina Puji LestariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1, InvertebratesDocument4 paginiUnit 1, InvertebratesnatalescorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biochemistry QuizDocument28 paginiBiochemistry Quizsanjviews100% (3)
- Supranuclear Control Opf Eye MovementsDocument162 paginiSupranuclear Control Opf Eye Movementsknowledgeguruos179Încă nu există evaluări
- Biology PDFDocument1.447 paginiBiology PDFPrincess Ethel Atillo100% (2)
- Parasites Immunity and PathologyDocument389 paginiParasites Immunity and Pathologyrild278111Încă nu există evaluări
- Focusing Instruction ManualDocument15 paginiFocusing Instruction Manualplan2222100% (1)
- Introduction to MedicineDocument156 paginiIntroduction to MedicineEshetu BizunehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Excretory System QuizDocument17 paginiExcretory System QuizShadab HanafiÎncă nu există evaluări
- CorneaDocument41 paginiCorneaNikhil KorripatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Liver Injury and FailureDocument14 paginiAcute Liver Injury and FailureWeslei ChaconÎncă nu există evaluări
- MRCP 2 Nephrology NOTESDocument74 paginiMRCP 2 Nephrology NOTESMuhammad HaneefÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abdominal SurgeryDocument166 paginiAbdominal SurgeryIndera VyasÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECG Interpretation For ACLSDocument27 paginiECG Interpretation For ACLSZH. omg sarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pass MRCP Part 2 (Sample)Document26 paginiPass MRCP Part 2 (Sample)Ahmad Shokry100% (1)
- Francisco Aboitiz (Auth.) - A Brain For Speech - A View From Evolutionary Neuroanatomy-Palgrave Macmillan UK (2017)Document515 paginiFrancisco Aboitiz (Auth.) - A Brain For Speech - A View From Evolutionary Neuroanatomy-Palgrave Macmillan UK (2017)TecuitlatlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fruit and Vegetable Diseases PDFDocument563 paginiFruit and Vegetable Diseases PDFgrigorasalexandru100% (1)
- NCM 103 RLE NOTESDocument8 paginiNCM 103 RLE NOTESgallardo.bettinarose.iÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pe Lecture NotesDocument7 paginiPe Lecture NotesAnonymous LJrX4dzÎncă nu există evaluări