Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Maharishi Secondary School Curriculum - Science Y11 Course Overview
Încărcat de
Martin KearnsDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Maharishi Secondary School Curriculum - Science Y11 Course Overview
Încărcat de
Martin KearnsDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
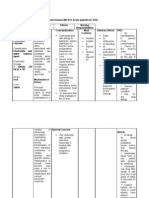
Year 11 Twenty first century Additional Science Course overview (Main Science subjects are alternated) Biology: B4 B5 B6 B4 The
Processes of life How do chemical reactions take place in living things? How do plants make food? How do living organisms obtain energy Chemistry: C4 C5 C6 Lesson 1: Features of all living things Lesson 2: Enzymes and pH Lesson 3: Enzymes and temperature Lesson 4: Enzymes at work: photosynthesis Lesson 5: Gas exchange- diffusion Lesson 6: Investigating Osmosis Lesson 7: Active transport- nitrate uptake in plants Lesson 8: Photosynthesis rate limiting factors Lesson 9: Fieldwork investigation Lesson 10: Aerobic respiration Lesson 11: Comparing aerobic and anaerobic respiration Lesson 12: Using anaerobic respiration Physics: P4 P5 P6 - investigate the effects of an enzyme on biological processes - investigate the factors affecting photosynthesis - use microscopes to look carefully at the structure of leaves - investigate rates of diffusion in different media - investigate the effect of solute concentration on potato cell water balance -use soil tests to compare soils and composts - use field work to investigate factors affecting the species of plants in different environmental conditions - investigate the energy content of different foods - use data logging to track temperature changes during respiration in peas - investigate anaerobic respiration in yeast. animations to explain enzyme action and the effect of temperature on enzyme activity -animations of diffusion, osmosis and active transport. - reactions of the alkali metals - reactions of the halogens - experiments to test the properties of ionic compounds. - using an interactive Periodic Table to explore similarities and differences between elements - using a spreadsheet to display patterns in chemical data - video clips to test predictions about the reactions of elements such as caesium and fluorine - using the internet to research the uses of alkali metals or halogens and their compounds. - use data logging to investigate motion - investigate the behaviour of colliding and exploding objects - investigate the effect of different combinations of surfaces on the frictional forces - investigate the motion of objects in free fall and the effects of air
C4 Chemical Patterns What are the patterns in the properties of elements? How do chemists explain the patterns in the properties of elements? How do chemists explain the properties of compounds of Group 1 and Group 7 elements? P4 Explaining motion How can we describe motion? What are forces? What is the connection between forces and motion? How can we describe
Lesson 1: The elements in order Lesson 2: The periodic table Lesson 3: The alkali metals Lesson 4: Chemical equations Lesson 5: The halogens Lesson 6: Displacement reactions of halogens Lesson 7: Flame colour and spectra Lesson 8: Atomic structure Lesson 9: Atomic structure and the periodic table Lesson 10: Properties of salt Lesson 11: Ionic theory and the atomic structure Lesson 12: Atoms into ions Lesson 1: Forces and interactions Lesson 2: Getting moving Lesson 3: Friction Lesson 4: Vertical forces Lesson 5: Describing motion Lesson 6: Using graphs to summarise motion Lesson 7: Momentum Lesson 8: Force and change of
motion in terms of energy changes?
momentum Lesson 9: Changing momentum safely Lesson 10: Steady motion requires no resultant force Lesson 11: Work and change of energy Lesson 12: From potential to kinetic energy
B5 Growth and development How do organisms develop? How does an organism produce new cells? How do genes control growth and development within the cell?
Lesson 1: Cells, tissues and organs Lesson 2: Growing and changing Lesson 3: Diffrences in animal and plant growth Lesson 4: Cloning plants Lesson 5: Phototropism Lesson 6: The nucleus and mitosis Lesson 7: Looking at gametes Lesson 8: Looking at DNA Lesson 9: The mystery of DNA Lesson 10: DNA to proteins Lesson 11: Switching genes Lesson 12: Stem cells and gene switching
C5 Chemicals of the natural environment What types of chemicals make up the atmosphere? What reactions happen in the hydrosphere? What types of chemicals make up the Earths lithosphere? How can we extract useful metals from minerals?
P5 Electric circuits Electric current a flow of what? What determines the size of the current in an electric circuit and the energy it transfers? How do parallel and series circuits work? How is mains electricity produced? How are voltages and currents
Lesson 1: The Earths spheres Lesson 2: Bonding within molecules Lesson 3: Water and salts in the hydrosphere Lesson 4: Predicting precipitation Lesson 5: Detecting ions in salts Lesson 6: Chemicals in the lithosphere Lesson 7: Extracting metals from ores Lesson 8: How much metal? Lesson 9: Electrolysis Lesson 10: Extracting aluminium from electrolysis Lesson 11: The life cycle of metals Lesson 12: Properties, structure and bonding Lesson 1: Static electricity Lesson 2: Current in series circuits Lesson 3: Current in parallel circuits Lesson 4: Controlling the current Lesson 5: Ohms law Lesson 6: Combining resistors Lesson 7: Potential differences Lesson 8: Variable resistors and sensors Lesson 9: Electrical power Lesson 10: Magnets and motors Lesson 11: Electromagnetic induction and generators Lesson 12: Mains electricity
resistance. - video clips to provide contexts for learning about forces and motion - animations to illustrate interactive force pairs in various situations - animations to show the meaning of distance-time and other graphs - sensors and data loggers to collect measurements of movement for analysis - modelling software to analyse motion. - use microscopes to look at a variety of plant and animal cells -dissect and draw a broad bean -take plant cuttings and investigate the effects of using hormone rooting powder - investigate the effects of phototropism - view germinating pollen - extract DNA from plants. - animations to illustrate DNA structure, replication, and protein synthesis - animations to illustrate cell division -video clips to show stages in human development. - crystallisation experiments - using precipitation reactions to identify ions in salts - extracting metals with carbon - extracting metals by electrolysis. - animations to show the movement of molecules in a gas over a range of temperatures - modelling software to show the shapes of molecules and illustrate giant structures - video clips to show metals being extracted on a large scale - animations to illustrate the ionic theory of electrolysis.
- investigating the behaviour of electric circuits - making both model generators and motors and investigating factors affecting their behaviour - investigating the behaviour of transformers. - modelling software to explore electric circuit theory - animations to illustrate models of electric current as flowing charges.
induced? How do electric motors work? B6 Brain and mind How do animals respond to changes in their environment? How is information passed through the nervous system? Can reflex responses be learned? How do humans develop more complex behaviour?
Lesson 1: Behaviour Lesson 2: Receptors and effectors Lesson 3: Linking receptors and effectors Lesson 4: Fast reactions Lesson 5: Drugs affect the nervous system Lesson 6: Finding out about brain structure Lesson 7: Learning through conditioning Lesson 8: Learning and behaviour Lesson 9: Learning new skills Lesson 10: Memory Lesson 11: Learning your work Lesson 12: Mind mapping
C6 Chemical synthesis Chemicals and why we need them. Planning, carrying out and controlling a chemical synthesis.
P6 Radioactive materials Why are some materials radioactive? How can radioactive materials be used and handled safely, including wastes?
Lesson 1: Bulk and fine chemicals Lesson 2: Acids and alkalis Lesson 3: Neutralisation Lesson 4: Explaining neutralisation Lesson 5: Testing purity Lesson 6: Exothermic and endothermic reactions Lesson 7: Surface area and rates Lesson 8: Concentration and rates Lesson 9: Temperature changes and catalysts Lesson 10: Rates and collision theory Lesson 11: Synthesis of a health salt Lesson 12: Yields Lesson 1: Why are some materials radioactive? Lesson 2: A model of the atom Lesson 3: Changes in the nucleus Lesson 4: More about alpha, beta and gamma Lesson 5: Background radiation Lesson 6: Radioactivity and health Lesson 7: The pattern of radioactive decay
- investigate reflex behaviour of woodlice -look at microscope slides of neurons - research reflex behaviour in newborn babies and in other animals - investigate receptor cells on the tongue -measure the speed at which a nerve impulse travels - investigate factors that affect reaction times - measure the touch sensitivity of different areas of the body - make a presentation about Pavlov and his work on conditioned reflexes - investigate how practice of a skill improves performance - investigate pupils own learning -investigate whether woodlice have a memory. video clips to illustrate patterns in the behaviour of living things - animations to explain synapse function and the effects of drugs on synapses - interactive animations on brain function - using the internet to research behaviour and memory. - reactions of acids - reactions of alkalis - exothermic and endothermic reactions - titration experiments - rate of reaction experiments - synthesis of a salt. - video clips to illustrate the manufacture of chemicals on a large-scale in industry - using sensors and data loggers to monitor neutralisation reactions and the rates of chemical changes. - investigations of the properties of ionising radiations - half-life of radioactive materials - modelling half-life, using ICT or dice throwing. - data logging to show decay of protactinium - animations to illustrate atomic structure and decay - video clips to illustrate key ideas
Lesson 8: More about half-life Lesson 9: Health care imaging and treatment Lesson 10: Fission and nuclear reactors Lesson 11: Dealing with radioactive waste Lesson 12: Nuclear fission
of risk in the context of radioactive materials - animations to illustrate key processes in power stations.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Maharishi School Value For Money StatementDocument3 paginiMaharishi School Value For Money StatementMartin KearnsÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2014 KS2 and KS4 ResultsDocument2 pagini2014 KS2 and KS4 ResultsMartin KearnsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maharishi School Trust Report and Financial Statements Year Ending 31 August 2013Document53 paginiMaharishi School Trust Report and Financial Statements Year Ending 31 August 2013Martin KearnsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maharishi School Race Equality, Equal Opportunities and InclusionDocument5 paginiMaharishi School Race Equality, Equal Opportunities and InclusionMartin KearnsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maharishi School Safeguarding Policy AbridgedDocument16 paginiMaharishi School Safeguarding Policy AbridgedMartin KearnsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maharishi School 2014-2015 TermDocument1 paginăMaharishi School 2014-2015 TermMartin KearnsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maharishi School Admissions 2015-16Document3 paginiMaharishi School Admissions 2015-16Martin KearnsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maharishi School 2015 2016 Term & Holiday ScheduleDocument1 paginăMaharishi School 2015 2016 Term & Holiday ScheduleMartin KearnsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maharishi Free School Local OfferDocument5 paginiMaharishi Free School Local OfferMartin KearnsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maharishi School Trust LTD 2011 - 2012 AccountsDocument38 paginiMaharishi School Trust LTD 2011 - 2012 AccountsMartin KearnsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maharishi Free School Lancashire 2013 Key Stage 2 SATs ResultsDocument2 paginiMaharishi Free School Lancashire 2013 Key Stage 2 SATs ResultsMartin KearnsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maharishi School Value For Money StatementDocument5 paginiMaharishi School Value For Money StatementMartin KearnsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maharishi Secondary School Curriculum Mathematics Scheme of Work Y10 and Y11Document2 paginiMaharishi Secondary School Curriculum Mathematics Scheme of Work Y10 and Y11Martin KearnsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maharishi School Equal Opportunities PolicyDocument5 paginiMaharishi School Equal Opportunities PolicyMartin KearnsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maharishi Secondary School Curriculum Mathematics Scheme of Work Overview Y7Document1 paginăMaharishi Secondary School Curriculum Mathematics Scheme of Work Overview Y7Martin KearnsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maharishi Secondary School Curriculum Mathematics Scheme of Work Overview Y8Document1 paginăMaharishi Secondary School Curriculum Mathematics Scheme of Work Overview Y8Martin KearnsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maharishi Secondary School Curriculum Course Overview Chart Art 2013Document3 paginiMaharishi Secondary School Curriculum Course Overview Chart Art 2013Martin KearnsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maharishi Secondary School Curriculum Mathematics Scheme of Work Overview Y9Document1 paginăMaharishi Secondary School Curriculum Mathematics Scheme of Work Overview Y9Martin KearnsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maharishi Secondary School Curriculum - Art Years 7-11Document22 paginiMaharishi Secondary School Curriculum - Art Years 7-11Martin KearnsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maharishi Secondary School Curriculum Geography Scheme of Work Overview Chart For The Year 2012 2013Document1 paginăMaharishi Secondary School Curriculum Geography Scheme of Work Overview Chart For The Year 2012 2013Martin KearnsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maharishi Secondary School Curriculum French Scheme of Work Y9Document3 paginiMaharishi Secondary School Curriculum French Scheme of Work Y9Martin KearnsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maharishi Secondary School Curriculum Geography Policy DocumentDocument2 paginiMaharishi Secondary School Curriculum Geography Policy DocumentMartin KearnsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maharishi Secondary School Curriculum French - Course Overview For Year 10Document3 paginiMaharishi Secondary School Curriculum French - Course Overview For Year 10Martin KearnsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maharishi Secondary School Curriculum French Scheme of Work Y11Document1 paginăMaharishi Secondary School Curriculum French Scheme of Work Y11Martin KearnsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maharishi Secondary School Curriculum French Scheme of Work Y8Document1 paginăMaharishi Secondary School Curriculum French Scheme of Work Y8Martin KearnsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maharishi Secondary School Curriculum ICT Year 11 OverviewDocument1 paginăMaharishi Secondary School Curriculum ICT Year 11 OverviewMartin KearnsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maharishi Secondary School Curriculum French Scheme of Work Y10Document1 paginăMaharishi Secondary School Curriculum French Scheme of Work Y10Martin KearnsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maharishi Secondary School Curriculum French Scheme of Work Y7Document1 paginăMaharishi Secondary School Curriculum French Scheme of Work Y7Martin KearnsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maharishi Secondary School Curriculum French - Course Overview For Year 9Document3 paginiMaharishi Secondary School Curriculum French - Course Overview For Year 9Martin KearnsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maharishi Secondary School Curriculum ICT Year 9 OverviewDocument2 paginiMaharishi Secondary School Curriculum ICT Year 9 OverviewMartin KearnsÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- C5 - Metabolism and Enzyme Part 1Document20 paginiC5 - Metabolism and Enzyme Part 1Daniel LohÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rate and RhythmDocument10 paginiRate and RhythmSamanta Luiza de AraujoÎncă nu există evaluări
- NIOSH Investigation - CR 337 Fire LODDDocument32 paginiNIOSH Investigation - CR 337 Fire LODDRamblingChiefÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Mcqs Part IDocument17 paginiBiology Mcqs Part IUsama NiaziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutritional Management of High Output Enterocutaneous FistulaDocument2 paginiNutritional Management of High Output Enterocutaneous FistulaAfra AmiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles of Endocrinology and Hormone PDFDocument794 paginiPrinciples of Endocrinology and Hormone PDFleogmail100% (4)
- HerniaDocument36 paginiHerniashankarrao3Încă nu există evaluări
- LAB EXERCISE 1 Organization of The Human BodyDocument8 paginiLAB EXERCISE 1 Organization of The Human Bodyley leynÎncă nu există evaluări
- GIT Physio D&R AgamDocument67 paginiGIT Physio D&R Agamvisweswar030406Încă nu există evaluări
- Anesthesiology Resident Survival Guide 2014-2015Document32 paginiAnesthesiology Resident Survival Guide 2014-2015Karla Matos100% (1)
- Lecture 8 - 30.12.2022Document17 paginiLecture 8 - 30.12.2022Adnan Mohammad Adnan HailatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Supranuclear Control Opf Eye MovementsDocument162 paginiSupranuclear Control Opf Eye Movementsknowledgeguruos179Încă nu există evaluări
- Uji Aktivitas Antioksidan Ekstrak Etanol 70% Bunga Telang (Clitoria TernateaL) Dari Daerah Sleman Dengan Metode DPPHDocument7 paginiUji Aktivitas Antioksidan Ekstrak Etanol 70% Bunga Telang (Clitoria TernateaL) Dari Daerah Sleman Dengan Metode DPPHAnastasia FebruestiÎncă nu există evaluări
- T2DMDocument24 paginiT2DMXyra BadangayonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Six Elements and Chinese MedicineDocument182 paginiSix Elements and Chinese MedicinePedro Maia67% (3)
- Battle of BrainDocument7 paginiBattle of BrainKhalida Zia SiregarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Glycolysis and cellular respiration overviewDocument3 paginiGlycolysis and cellular respiration overviewPaul PanizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ANAESTHESIOLOGYDocument38 paginiANAESTHESIOLOGYcollinsmagÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP of CavDocument3 paginiNCP of CavHenry Roque TagalagÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCM 100 H.A Procedure DPPER 3Document51 paginiNCM 100 H.A Procedure DPPER 3Richelle Joy Durano RegatunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modul Strategik Bab 1 Ting 5Document6 paginiModul Strategik Bab 1 Ting 5SK Pos TenauÎncă nu există evaluări
- Top Knife - Cutted - Top PDFDocument238 paginiTop Knife - Cutted - Top PDFIvanKazaiev100% (1)
- Traumatic Hyphema PDFDocument10 paginiTraumatic Hyphema PDFPratiwi SimanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Center For Prehospital Care: Benjamin E. EsparzaDocument10 paginiCenter For Prehospital Care: Benjamin E. EsparzasenjahipgabiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Body Systems NotesDocument2 paginiBody Systems NotesAndrea González MercadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 6 - Musculoskeletal and Nervous SystemsDocument20 paginiLesson 6 - Musculoskeletal and Nervous Systemsapi-307592530Încă nu există evaluări
- Seed Germination, Dormancy & Breaking of DormancyDocument35 paginiSeed Germination, Dormancy & Breaking of DormancySaravananÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument11 paginiDrug StudyKimberly Ann MendozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ICSE Class 10 Biology Previous Year Question Paper 2011 PDFDocument9 paginiICSE Class 10 Biology Previous Year Question Paper 2011 PDFmohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Head to Toe Physical Assessment GuideDocument16 paginiHead to Toe Physical Assessment Guideabagatsing100% (5)