Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Problem Set 5
Încărcat de
bus242Descriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Problem Set 5
Încărcat de
bus242Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Middle East Technical University-Northern Cyprus Campus Problem Set 5 Eco 102 Instructor: Hasan Cmert Multiple Choice
Questions
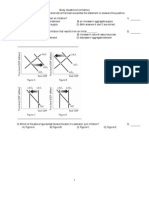
Figure 1:
1. Refer to Figure 1 An aggregate demand shift from AD2 to AD0 can be caused by A) a decrease in the price level. C) a decrease in taxes. B) an increase in the price level. D) a decrease in money supply.
2. Refer to Figure1. An aggregate demand shift from AD1 to AD0 can be caused by A) a decrease in government spending. B) an increase in money supply. C) a decrease in the price level. D) an increase in the price level.
3. Refer to Figure 1 Suppose the economy is at Point A, an increase in the price level can cause a movement to Point A) E. B) B. C) C. D) D.
4. A rightward shift in the aggregate demand curve can be caused by A) a decrease in government spending. B) an increase in taxes. C) a decrease in money supply. D) the Fed buying government bonds.
5. The aggregate supply curve A) is the sum of the individual supply curves in the economy. B) is a market supply curve. C) embodies the same logic that lies behind an individual firms supply curve. D) relates output with the price level.
6. It is very important to distinguish between the short run and the long run when we are discussing A) the aggregate demand. B) the aggregate expenditures. C) the aggregate supply. D) changes in the price level. 7. What determines the slope of the aggregate supply curve is A) how fast the price of factors of production respond to changes in the price level. B) how much more the economy can produce without any change in the price level. C) how fast the output level changes after a technological advance. D) none of the above 8. When the aggregate supply curve is vertical, which of the following is NOT true? A) The economy is at capacity. B) The economy is producing the maximum sustainable level of output. C) Any increase in the price level will not cause an increase in aggregate output. D) The economy is expanding quickly. 9. If the economy is operating on the relatively vertical segment of the aggregate supply curve, an increase in aggregate demand causes a ________ change in the price level and a ________ change in output. A) small; small B) big; big C) big; small D) small; big 10. If the economy is operating way below capacity, an increase in aggregate demand causes a ________ change in the price level and ________ change in output. A) big; big B) big; small C) small; big D) small; small
11. An increase in aggregate demand when the economy is operating at high levels of output is likely to result in A) a large increase in both output and the overall price level. B) an increase in the overall price level but little or no increase in output. C) an increase in output but little or no increase in the overall price level. D) little or no increase in either output or the overall price level.
12. An increase in the price level is likely to increase the aggregate amount of output supplied in the short run because A) interest rate is high in the short-run. B) wages and interest rates are relatively fixed in the short-run. C) wages change in the short-run. D) the aggregate supply curve is vertical in the short-run.
13. If input prices changed at exactly the same rate as output prices, the aggregate supply curve would be A) vertical. B) upward sloping. C) horizontal. D) downward sloping.
14. If there is a decrease in the percentage of employees whose wages adjust automatically with changes in the price level, the aggregate supply curve will become A) steeper. B) flatter. C) horizontal. D) vertical.
15. Coal is used as a source of energy in many manufacturing processes. Assume a long strike by coal miners reduced the supply of coal and increased the price of coal. This would cause A) the short-run aggregate supply curve to shift to the right. B) the short-run aggregate supply curve to become flatter. C) the short-run aggregate supply curve to shift to the left. D) the short-run aggregate supply curve to become nearly vertical at all levels of output.
16. All of the following shift the short-run aggregate supply curve EXCEPT A) a change in the price level. B) a change in the price of oil. C) a change in the price of raw material. D) a change in wages as a result of a labor strike. 17. If a decrease in net taxes in the United States resulted in a very large increase in aggregate output and a very small increase in the price level, then the U.S. economy must have been A) on the very steep part of the short-run aggregate supply curve. B) on the very flat part of the short-run aggregate supply curve. C) on the very steep part of the short-run aggregate demand curve. D) on the very flat part of the short-run aggregate demand curve.
18. Economic policies are ineffective concerning quantities of output directly when
A) the aggregate supply curve is flat. B) the aggregate demand is flat. C) the aggregate supply is vertical. D) the economy is not producing at capacity. 19. If the long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical, the multiplier effect of a change in net taxes on aggregate output in the long run A) depends on the price level. B) is one. C) is zero. D) is infinitely large.
20. Refer to Figure 2,. Suppose the economy is currently at Point A producing potential outputY0. If the government increases spending, the economy moves to Point ________ in the short-run and to Point ________ in the long-run. A) D; E B) B; C C) C; B D) B; D 21. Refer to Figure 2, If the economy is currently at Point D producing output level Y2, which of the following is NOT true? A) The economy is operating below full employment. B) Input prices are likely to fall. C) Aggregate supply shifts to the right and the economy ends up at Point E. D) The economy is operating above full employment.
22. Refer to Figure 2, If the economy is at point A currently producing Y0 and the Fed decreases the money supply, the economy will move to Point ________ in the short run and to Point ________ in the long run. A) B; C B) D; E C) E; D D) C; B 23. Refer to Figure 2 This economy cannot continue to produce Y1 (or at point B) because A) the price of raw material and wages will increase shifting the aggregate supply curve to AS1. B) the price of inputs will decrease, shifting the aggregate supply curve to AS2. C) the price of raw material will increase, shifting the aggregate demand curve to AD2. D) all of the above 24. Refer to Figure 2. For this economy to produce Y1 and sustain it without inflation A) the price of oil must increase. B) the government must implement an expansionary fiscal policy. C) the government must implement an expansionary monetary policy. D) potential output must increase. Figure 3
25. Refer to Figure 3. Cost-push inflation occurs if A) the economy moves from Point A to Point B on aggregate supply curve AS1. B) the economy moves from Point A to Point C on the aggregate supply curve AS1. C) the aggregate supply curve shifts from AS1 to AS0. D) the aggregate supply curve shifts from AS1 to AS2.
26. A rightward shift in the aggregate demand curve generates a ________ inflation and ________ output. A) demand-pull; lower B) cost-push; higher C) demand-pull; higher D) cost-push; lower
27. Refer to Figure 4. If the economy is currently at the intersection of AS and AD, the Fed should A) increase money supply to reduce the unemployment rate. B) increase money supply to move closer to capacity. C) decrease money supply to reduce inflationary pressures. D) decrease money supply to increase output. Figure 4:
28. The measured unemployment rate can be pushed below the natural rate, but A) only in the long run and only if the price level is constant. B) only in the long run and not without inflation. C) only in the short run and only if the price level is constant. D) only in the short run and not without inflation. 29. If the economy is at potential output, actual inflation A) is greater than expected inflation. B) equals expected inflation. C) is less than expected inflation. D) equals the natural rate of unemployment. 30. When there is stagflation, the policy choices facing a central bank are A) increasing monetary growth to increase GDP but that will make inflation worse. B) increasing monetary growth to increase GDP and reduce inflation. C) reducing monetary growth to reduce inflation, but that will make shortfall in GDP worse. D) A and C
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Essentials of Development Economics, Third EditionDe la EverandEssentials of Development Economics, Third EditionEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Mankiw-Test Chapter 20Document4 paginiMankiw-Test Chapter 20Thùy NguyễnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jerome Bruner by David R. OlsonDocument225 paginiJerome Bruner by David R. OlsonAnthony100% (4)
- Untitled13 PDFDocument22 paginiUntitled13 PDFErsin TukenmezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Macro Review IIIDocument22 paginiMacro Review IIIAnonymous K8b1TFPyZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ec305 1Document120 paginiEc305 1sahmed7060% (1)
- Ad As Without AnsDocument5 paginiAd As Without AnsnomanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chap 011Document26 paginiChap 011Himanshu DhamijaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 - Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument36 paginiChapter 4 - Multiple Choice Questionstoaa ahmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 11 Aggregate Demand and SupplyDocument5 paginiChapter 11 Aggregate Demand and SupplyPinaki MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 26 Ad & AsDocument25 paginiCH 26 Ad & AsAli HussinÎncă nu există evaluări
- The CorrectionDocument8 paginiThe CorrectionDiamante GomezÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECO1102, Practice 2nd MT (With Answers), CH 11-13Document8 paginiECO1102, Practice 2nd MT (With Answers), CH 11-13Faris BarkawiÎncă nu există evaluări
- TBCH05Document13 paginiTBCH05Shayne LimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Exam Sample QuestionsDocument11 paginiFinal Exam Sample Questionsecobalas7100% (1)
- 1311 - As-Ad HW (Ans)Document6 pagini1311 - As-Ad HW (Ans)Haifa Al-humayydÎncă nu există evaluări
- Macro Quiz 5 PDFDocument4 paginiMacro Quiz 5 PDFcvofoxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 5 ECON 343Document7 paginiAssignment 5 ECON 343Jack BÎncă nu există evaluări
- Macroeconomics 10th Edition Parkin Test BankDocument23 paginiMacroeconomics 10th Edition Parkin Test Banklouisbeatrixzk9u100% (32)
- Macroeconomics 10th Edition Parkin Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument44 paginiMacroeconomics 10th Edition Parkin Test Bank Full Chapter PDFcarlarodriquezajbns100% (11)
- Study Questions 9 (Inflation and Phillips Curve)Document8 paginiStudy Questions 9 (Inflation and Phillips Curve)Kiran KachhawahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Macroeconomics Practice Exam: FIGURE 24-1Document13 paginiMacroeconomics Practice Exam: FIGURE 24-1adam jamesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intermediate Microeconomics 2 Year Dr. Eman Gamal El-Din M. Chapter 4 Part 1Document31 paginiIntermediate Microeconomics 2 Year Dr. Eman Gamal El-Din M. Chapter 4 Part 1Ceren Gökçe KeskinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Macro II ch4 Q1 PDFDocument32 paginiMacro II ch4 Q1 PDFSimren DhillonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Economics Model GR12Document15 paginiEconomics Model GR12Mamush kasimoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Macroeconomics Canadian 8th Edition Sayre Test Bank 1Document36 paginiMacroeconomics Canadian 8th Edition Sayre Test Bank 1marychaveznpfesgkmwx100% (28)
- Macroeconomics Canadian 8Th Edition Sayre Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument36 paginiMacroeconomics Canadian 8Th Edition Sayre Test Bank Full Chapter PDFkevin.reider416100% (11)
- w10 112 v1Document22 paginiw10 112 v1Rusty ButlerÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECON 102 Midterm1 SampleDocument5 paginiECON 102 Midterm1 SampleexamkillerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Self Study Quiz and Exercises Final 17 March 20113Document161 paginiSelf Study Quiz and Exercises Final 17 March 20113markÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practice Questions On International Linkages - With Answer KeyDocument6 paginiPractice Questions On International Linkages - With Answer KeyronÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inflation (Multiple Choice Questions)Document16 paginiInflation (Multiple Choice Questions)NickÎncă nu există evaluări
- MacroDocument7 paginiMacroraveen007Încă nu există evaluări
- FIN201 - Quiz - 2 - FA - 2022 - Nguyễn Đức Minh-HS173138Document12 paginiFIN201 - Quiz - 2 - FA - 2022 - Nguyễn Đức Minh-HS17313828- Nguyễn Đức Minh - Chíp PơÎncă nu există evaluări
- Baims-1644406705 13 MLF Altmaryn PDFDocument5 paginiBaims-1644406705 13 MLF Altmaryn PDFShahadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Econ2123 18fall Practicefinal SolutionDocument17 paginiEcon2123 18fall Practicefinal SolutionwucorlinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pe Final Mocktest - Fow9Document12 paginiPe Final Mocktest - Fow9wwwpa2005Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 17 Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply (1) - 15-21Document7 paginiChapter 17 Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply (1) - 15-21Kayla YuÎncă nu există evaluări
- MacroDocument107 paginiMacroThảo NgânÎncă nu există evaluări
- 203 Sample Midterm2Document16 pagini203 Sample Midterm2Annas GhafoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Macro Qch1Document13 paginiMacro Qch1Kiều AnhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Econ exam+1+VADocument13 paginiEcon exam+1+VABlackBunny103Încă nu există evaluări
- Self Study Quiz and Exercises With AnswersDocument127 paginiSelf Study Quiz and Exercises With AnswersRobinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercises Chapter 1Document19 paginiExercises Chapter 1D LVÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles of Macroeconomics Version 2 0 2nd Edition Rittenberg Test BankDocument44 paginiPrinciples of Macroeconomics Version 2 0 2nd Edition Rittenberg Test Bankbirdmanzopiloter7te2100% (25)
- Self Study Quiz and Exercises With AnswersDocument70 paginiSelf Study Quiz and Exercises With Answers李昂80% (5)
- Practice Problem Set 1 With AnswersDocument7 paginiPractice Problem Set 1 With AnswersJoy colabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exam #2 Economics 2113 Principles of Microeconomics Dr. Philip Rothman 10/19/2001Document9 paginiExam #2 Economics 2113 Principles of Microeconomics Dr. Philip Rothman 10/19/2001Ahmed GamalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fall Macro 2016-3.tst PDFDocument7 paginiFall Macro 2016-3.tst PDFctyre34Încă nu există evaluări
- Tugas Bab 27 (15 Maret 2021)Document7 paginiTugas Bab 27 (15 Maret 2021)MutiaraMorentÎncă nu există evaluări
- PR 13Document5 paginiPR 13jmoline228Încă nu există evaluări
- Econ 202 Pre-Test 1 Chapters (4, 22-24)Document8 paginiEcon 202 Pre-Test 1 Chapters (4, 22-24)Amogh SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practice Problem Set 1Document5 paginiPractice Problem Set 1AkshayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 6 ECON 343Document7 paginiAssignment 6 ECON 343Jack BÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 17 Questionnaire - AdjustedDocument11 paginiChapter 17 Questionnaire - AdjustedNatalia Cabrera LazaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chap 05 - 10ce - Macro-26-30Document5 paginiChap 05 - 10ce - Macro-26-30shienalycabiles98Încă nu există evaluări
- ECO202-Practice Test - 23 (CH 23)Document5 paginiECO202-Practice Test - 23 (CH 23)Aly HoudrojÎncă nu există evaluări
- Midterm1718 (With Answers)Document5 paginiMidterm1718 (With Answers)yns6jgzd8tÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problems and Possibilities of the Us EconomyDe la EverandProblems and Possibilities of the Us EconomyÎncă nu există evaluări
- COVID-19 and Energy Sector Development in Asia and the Pacific: Guidance NoteDe la EverandCOVID-19 and Energy Sector Development in Asia and the Pacific: Guidance NoteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practice Midterm 2Document10 paginiPractice Midterm 2bus242Încă nu există evaluări
- CH 28Document35 paginiCH 28bus242Încă nu există evaluări
- CH 29Document36 paginiCH 29bus242Încă nu există evaluări
- Hilton 9th Edition Chap 001Document15 paginiHilton 9th Edition Chap 001octositinjak100% (1)
- MLB From 3G SideDocument16 paginiMLB From 3G Sidemalikst3Încă nu există evaluări
- Presentation Management Trainee Batch VII - Mohammad Arian RahmatullahDocument8 paginiPresentation Management Trainee Batch VII - Mohammad Arian RahmatullahMohammad Arian RahmatullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Debate QuestionsDocument7 paginiDebate Questionsapi-522661051Încă nu există evaluări
- Personal Entrepreneurial Competencies (Pecs) Self-Rating QuestionnaireDocument3 paginiPersonal Entrepreneurial Competencies (Pecs) Self-Rating QuestionnaireMESIE JEAN PARAL100% (3)
- Quarter 4 Week 4 Parallel Lines Cut by A TransversalDocument26 paginiQuarter 4 Week 4 Parallel Lines Cut by A TransversalZaldy Roman MendozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CONTARE Notes and ReviewerDocument4 paginiCONTARE Notes and ReviewerApong VillegasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research MethodologyDocument5 paginiResearch Methodologysonal gargÎncă nu există evaluări
- Torts and Damages Midterm ReviewerDocument25 paginiTorts and Damages Midterm ReviewerErika-Anne ThereseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Courtesy Begins at HomeDocument2 paginiCourtesy Begins at Homell Snowitchy llÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial-Midterm - CHEM 1020 General Chemistry - IB - AnsDocument71 paginiTutorial-Midterm - CHEM 1020 General Chemistry - IB - AnsWing Chi Rainbow TamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cytomegalovirus in Primary ImmunodeficiencyDocument9 paginiCytomegalovirus in Primary ImmunodeficiencyAle Pushoa UlloaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Beginner's Guide To Reading Jung - Jungian Center For The Spiritual SciencesDocument6 paginiA Beginner's Guide To Reading Jung - Jungian Center For The Spiritual SciencesRosa ChacónÎncă nu există evaluări
- C.S. - Lewis A Journey To ChristDocument5 paginiC.S. - Lewis A Journey To ChristMichelle CrawfordÎncă nu există evaluări
- Graph Theory and ApplicationsDocument45 paginiGraph Theory and Applicationssubramanyam62Încă nu există evaluări
- Estoryang BinisayaDocument27 paginiEstoryang BinisayaAngel GellaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HAPPY CHRISTMAS b2 ActivitiesDocument2 paginiHAPPY CHRISTMAS b2 ActivitiesnereaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Semiconductor DevicesDocument11 paginiPower Semiconductor DevicesBhavesh Kaushal100% (1)
- Introduction and Assessment of The Renal - Urological SystemDocument182 paginiIntroduction and Assessment of The Renal - Urological SystemValerie Suge-Michieka100% (1)
- Changing Views of Tattoos in JapanDocument14 paginiChanging Views of Tattoos in JapanpanpapogÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hemzo M. Marketing Luxury Services. Concepts, Strategy and Practice 2023Document219 paginiHemzo M. Marketing Luxury Services. Concepts, Strategy and Practice 2023ichigosonix66Încă nu există evaluări
- Aarvee Denim & Export LTD.: CertificateDocument46 paginiAarvee Denim & Export LTD.: CertificateVinita AgrawalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Orthogonal Curvilinear CoordinatesDocument16 paginiOrthogonal Curvilinear CoordinatesstriaukasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Corpuz V Cuaderno, G.R. No. L-17860, March 30, 1962Document3 paginiCorpuz V Cuaderno, G.R. No. L-17860, March 30, 1962Lyle BucolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oxalic Acid E11a BDocument52 paginiOxalic Acid E11a BFaradilah Binti Ajma'inÎncă nu există evaluări
- WaveDocument5 paginiWaveArijitSherlockMudiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Navneet Publications India Limited HardDocument34 paginiNavneet Publications India Limited Harddyumna100% (1)
- தசம பின்னம் ஆண்டு 4Document22 paginiதசம பின்னம் ஆண்டு 4Jessica BarnesÎncă nu există evaluări
- 04 HPGD1103 T1Document24 pagini04 HPGD1103 T1aton hudaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oils and Lard by Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy. Relationships Between Composition and Frequency of Concrete Bands in The Fingerprint Region.Document6 paginiOils and Lard by Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy. Relationships Between Composition and Frequency of Concrete Bands in The Fingerprint Region.Nong NakaÎncă nu există evaluări