Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
H1 Physics J2 CT1 2013 Paper 2 Solutions
Încărcat de
Michael LeungDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
H1 Physics J2 CT1 2013 Paper 2 Solutions
Încărcat de
Michael LeungDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
JURONG JUNIOR COLLEGE PHYSICS DEPARTMENT JC2 Common Test 1 H1 Physics Paper 2 solutions Qn Suggested solution 1(a) Random
error is one that occurs without a fixed pattern resulting in a scatter of readings about a mean value. (b)(i) R = V/I => R/R = V/V + I/I = (0.01/1.30) + (0.01/0.76) = 0.0209 (to 3 s.f.) OR Largest possible value of R = 1.31/0.75 = 1.7467 Smallest possible value of R = 1.29/0.77 = 1.6753 Absolute error of R = (1.7467 1.6753)/2 = 0.0357 Mean value of R = 1.30/0.76 = 1.7105 Fractional uncertainty in R = 0.0357/1.7105 = 0.0209 (ii) Mean value of R = 1.30/0.76 = 1.711 Absolute error in R = (R/R) x R = 0.0209 x 1.7105 = 0.04 Hence, R = (1.71 0.04) (c)(i) A scalar quantity has magnitude only while a vector quantity has both magnitude and direction. (ii)1.
Remarks [1] [2] correct working [1] final answer (3 s.f.)
[1] answer for mean value [1] final expression [1]
[1] for vi, vf [1] for v
2.
Magnitude of change in velocity = (6.02 + 8.02) = 10 m s-1 = tan-1 (8.0/6.0) = 53 Change in velocity is 10 m s-1 in a direction 53 south of east. [1] answer for magnitude of change in velocity [1] working for finding [1] answer for direction of change in velocity (accept either correct description or just the answer for , if is correctly marked on diagram)
(d)(i)1.
Displacement is the linear distance in a given direction from a reference point.
[1] [1]
2. Velocity is the rate of change of displacement.
Page 1 of 4
Qn (ii)1.
JURONG JUNIOR COLLEGE PHYSICS DEPARTMENT JC2 Common Test 1 H1 Physics Paper 2 solutions Suggested solution s = ut + at2 100 = (0)(t) + (4)t2 t = 7.1 s
Remarks [1] subst [1] answer
2.
[1] subst The cyclist would also have taken the same amount of time t = 7.1 s to reach Point [1] answer A. Since she is travelling at constant speed, a = 0. s = ut + at2 100 = u(7.1) + 0 u = 14 m s-1 [1] correct shape for cyclist graph [1] correct shape for ranger graph
3.
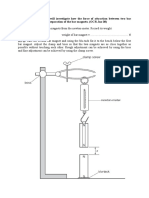
2(a) The e.m.f. is defined as the non-electrical energy converted to electrical energy per unit charge driven through the source. (b) The resistance of a sample is directly proportional to its length and inversely proportional to its cross-sectional area. The proportionality constant is called the resistivity. It is a property of the material and is dependent on temperature. (c)(i) Some of the energy generated by the source will be dissipated within the source itself. This can be represented by a series resistor within the source. / This opposition to the flow of current within the source is called internal resistance. (ii) 1.6 V (iii)
[2 or 0]
[1]
[1] [1] [1] [1] answer [1] working
= Ir + IR
1.6 = 0.5r + 1.2 r = 0.8
Page 2 of 4
Qn (iv) 1. V = Ir = (0.3)(0.8) = 0.24 V
JURONG JUNIOR COLLEGE PHYSICS DEPARTMENT JC2 Common Test 1 H1 Physics Paper 2 solutions Suggested solution
Remarks [1] answer [1] answer [2] any reasonable justification or working [1] answer [1] subst [1] answer [1] working [1] answer [1] answer
2. = Ir + IR 1.6 = 0.24 + IR IR = 1.36 V (v)
X = X =
(1.6)(0.5) (0.5)2 (0.8) = 0.75 = 75% (1.6)(0.5) (1.6)(0.3) (0.3)2 (0.8) = 0.85 = 85% (1.6)(0.3)
Using bulb Y is more efficient. (vi)
resistance =
(d)(ii) (12 // 30 + 4.5) // 18 = 7.572 = 7.57 (iii)
1.5 = 2.31 0.65
(16)2 =2W 18
6 6 = 0.459 A 7.572 18
1. From the definition of speed, Speed = Distance Time 2. A wave travels a distance of one wavelength, , in a time interval of one period, 1 T
(iv)
[1] working [1] answer [2] for all the three points, deduct 1 mark for any missing points [1] [1] subst [1] answer [1] correct sinusoidal shape including axes values
3(a)
3. The frequency, f , of a wave is equal to Therefore, speed, v = 1 = = f T T
(b)(i)
= 4 = 2 2
(ii)
(c)(i)
1. Transverse waves are waves in which the direction of oscillation of the wave [1] elements is perpendicular to the direction of wave motion/ Longitudinal waves are waves in which the direction of oscillation of the wave elements is parallel to the direction of wave motion. 2. Transverse wave can be polarised/ Longitudinal wave cannot be polarized. [1]
Page 3 of 4
Qn (ii)
JURONG JUNIOR COLLEGE PHYSICS DEPARTMENT JC2 Common Test 1 H1 Physics Paper 2 solutions Suggested solution
Remarks
It is a phenomenon in a transverse wave where the oscillation of the elements of [1] the wave is restricted to a plane. The elements in the wave oscillate parallel to the wave direction and cannot be [1] restricted to vibrate in any plane.
(iii)
(d)(i)
Intensity =
(ii)
P P 80 103 = = = 7.0735 104 7.07 10 4 Wm -2 A 4 r 2 4 32
[1]subst [1] answer [2] correct workings [1] answer [2] workings (e.g.correct relationship, correct subst) [1] answer
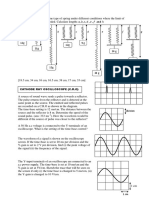
New intensity = 0.67.073510-4 = 4.244110-4 P P 8010-3 -4 Using intensity = = 4.244110 = A 4r 2 4r 2 Solving, r = 3.873 3.87m
(iii)
r 1 A 20 10 Using A , 1 = ( 2 ) = ( ) A2 = 6.0 m r A2 r1 A2 3
(iv) [1]correct sinusoidal shape including axes values; [1] constant amplitude)
Page 4 of 4
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Aiats Practise Test-1Document46 paginiAiats Practise Test-1Arunanshu Pal75% (4)
- AS PHYSICS: FORCES, ENERGY AND ELECTRICITYDocument5 paginiAS PHYSICS: FORCES, ENERGY AND ELECTRICITYPraphul MalolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Refraction & Superposition AnswerDocument6 paginiRefraction & Superposition Answergrace_ng_45Încă nu există evaluări
- Answers: T Est - 10Document8 paginiAnswers: T Est - 10rinostatsÎncă nu există evaluări
- H2 Physics J2 CT1 2013 Paper 2 SolutionsDocument10 paginiH2 Physics J2 CT1 2013 Paper 2 SolutionsMichael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aakash Medical Test Series Code A Answers & HintsDocument18 paginiAakash Medical Test Series Code A Answers & HintsMiss JasmineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circular MotionpdfDocument24 paginiCircular MotionpdfChandra SekharÎncă nu există evaluări
- GCE Physics 2012 Mark SchemeDocument8 paginiGCE Physics 2012 Mark SchemeCka DohaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NTSEDocument22 paginiNTSESurya Prakash100% (6)
- CLS Aipmt-19-20 XIII Phy Study-Package-1 Level-1 Chapter-2 PDFDocument16 paginiCLS Aipmt-19-20 XIII Phy Study-Package-1 Level-1 Chapter-2 PDFOptics Career Institute -OCIÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2007 Physics Intermediate 2 Finalised Marking InstructionsDocument14 pagini2007 Physics Intermediate 2 Finalised Marking InstructionsWilliam BrownÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9792 PHYSICS: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2010 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersDocument14 pagini9792 PHYSICS: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2010 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersbobÎncă nu există evaluări
- AIEEE 2010 Paper+SolutionsDocument31 paginiAIEEE 2010 Paper+SolutionsAasif ShaikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answers: T Est - 6Document11 paginiAnswers: T Est - 6Arunanshu PalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toaz.info Cape Physics Unit 1 p2 Mark Schemes 2022 2007 Pr a23546bc9de6a1164ebabb4d1f5ce055Document171 paginiToaz.info Cape Physics Unit 1 p2 Mark Schemes 2022 2007 Pr a23546bc9de6a1164ebabb4d1f5ce055Nirvan RampersadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aakash InstituteDocument40 paginiAakash InstituteAbhinav AgarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- G484 Module 1 Newtons Laws and Momentum Questions MSDocument3 paginiG484 Module 1 Newtons Laws and Momentum Questions MSTrishnee MunusamiÎncă nu există evaluări
- CLS Aipmt-17-18 XI Phy Study-Package-1 SET-2 Chapter-2 PDFDocument28 paginiCLS Aipmt-17-18 XI Phy Study-Package-1 SET-2 Chapter-2 PDFMonishaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aiats Jee Main2014 Paper 1 Test2Document8 paginiAiats Jee Main2014 Paper 1 Test2Sudeep SahaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Statics & Resolving Forces 2 MSDocument8 paginiStatics & Resolving Forces 2 MSelsieÎncă nu există evaluări
- GCE Physics Mark Scheme January 2011Document9 paginiGCE Physics Mark Scheme January 2011shangardeziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elasticity AssignmentDocument12 paginiElasticity AssignmentManav PtelÎncă nu există evaluări
- R1 2016 2017 1 (Q+S) PDFDocument10 paginiR1 2016 2017 1 (Q+S) PDFmarwanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aakash Medical Test Series 2013 Test 7 AnswersDocument10 paginiAakash Medical Test Series 2013 Test 7 AnswersArunanshu PalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topper Sample Paper 2 Physics - Xi Q. No Value Points MarksDocument10 paginiTopper Sample Paper 2 Physics - Xi Q. No Value Points MarksvinodwarriorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aiats Medical Two Yr Test-2Document20 paginiAiats Medical Two Yr Test-2SantanuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aakash Medical Test Series 2013 Test 1 Answers and HintsDocument7 paginiAakash Medical Test Series 2013 Test 1 Answers and HintsArunanshu Pal100% (1)
- Mark Scheme: Assessment Unit AS 2Document8 paginiMark Scheme: Assessment Unit AS 2Mark McKinsnkeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHYSICS-23-07 - 11th (J-Batch)Document9 paginiPHYSICS-23-07 - 11th (J-Batch)Raju SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test - 2: Physics Chemistry MathematicsDocument8 paginiTest - 2: Physics Chemistry MathematicsShalu GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- JEE Main 2015 Code A Solution AakashDocument23 paginiJEE Main 2015 Code A Solution AakashYasmin TajÎncă nu există evaluări
- CLS Aipmt-18-19 XIII Phy Study-Package-1 SET-1 Chapter-2 PDFDocument28 paginiCLS Aipmt-18-19 XIII Phy Study-Package-1 SET-1 Chapter-2 PDFTJÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answers: TEST - 1 (Paper-I)Document10 paginiAnswers: TEST - 1 (Paper-I)Vishal DaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answers: T Est - 6Document7 paginiAnswers: T Est - 6Chirag SheokandÎncă nu există evaluări
- AGS AS Physics MC and SA Answers Term 2 2012: Answers / Explanatory Notes Marks AvailableDocument6 paginiAGS AS Physics MC and SA Answers Term 2 2012: Answers / Explanatory Notes Marks AvailableGeneralBrainsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Units and MeasurementsDocument28 paginiUnits and MeasurementsHs BamrahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Common P.G. Entrance Test 2020 Physics QuestionsDocument19 paginiCommon P.G. Entrance Test 2020 Physics Questionsamar nayakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edexcel A Level Bk2 Physics Answers FINAL PDFDocument39 paginiEdexcel A Level Bk2 Physics Answers FINAL PDFNasrin SultanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- G-Cakna Kelantan 2015 - Physics Term 2 - Module 2 - MSDocument8 paginiG-Cakna Kelantan 2015 - Physics Term 2 - Module 2 - MSannahiazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linear Regression Analysis and Confidence IntervalsDocument58 paginiLinear Regression Analysis and Confidence IntervalsdmksÎncă nu există evaluări
- AIPMT 2012 Physics, Biology & Chemistry ExamDocument36 paginiAIPMT 2012 Physics, Biology & Chemistry ExamOnkar JhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Z TransformDocument12 pagini3 Z TransformNitinÎncă nu există evaluări
- JEE Main 24th Jan Shift 2Document28 paginiJEE Main 24th Jan Shift 2Alisha AgarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solutions AIATS Medical-2017 Test-01 (Code-A & B)Document18 paginiSolutions AIATS Medical-2017 Test-01 (Code-A & B)Saptarsi PalÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCE IGCSE Physics TWB C04 - Full SolutionsDocument6 paginiMCE IGCSE Physics TWB C04 - Full SolutionsXIN ZHANGÎncă nu există evaluări
- CLS Aipmt 18 19 XII Che Study Package 5 SET 2 Chapter 4Document42 paginiCLS Aipmt 18 19 XII Che Study Package 5 SET 2 Chapter 4BklÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solved 540 541 AIEEE Past 5 Years’ PapersDocument35 paginiSolved 540 541 AIEEE Past 5 Years’ PapersAmal Krishna TÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 3 Kinematics in One Dimension - StudentDocument51 paginiLecture 3 Kinematics in One Dimension - StudentSmurf TanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11 12 H2 J1 CT P2solnDocument8 pagini11 12 H2 J1 CT P2solnMichael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- IOQA-2022-23 - (Answers & Solutions)Document16 paginiIOQA-2022-23 - (Answers & Solutions)Akshay TiwariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Autopilot and Mission Planning - Lecture04Document18 paginiAutopilot and Mission Planning - Lecture04mohammed.yassen987Încă nu există evaluări
- Co4 Problem Sheet For CIADocument2 paginiCo4 Problem Sheet For CIAsurya13905Încă nu există evaluări
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)De la EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)Încă nu există evaluări
- Applications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankDe la EverandApplications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankÎncă nu există evaluări
- Constructed Layered Systems: Measurements and AnalysisDe la EverandConstructed Layered Systems: Measurements and AnalysisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankDe la EverandInverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsDe la EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Dyn g12 ws22Document5 paginiDyn g12 ws22Michael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mini PhysDocument10 paginiMini PhysMichael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zoom 8 August 2021Document1 paginăZoom 8 August 2021Michael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- A CarbonDocument3 paginiA CarbonMichael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Analog ModulationDocument7 paginiTypes of Analog ModulationMichael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- OUM Social Work exams ethics and law guideDocument4 paginiOUM Social Work exams ethics and law guideMichael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Certificate in Social ProtectionDocument1 paginăCertificate in Social ProtectionMichael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- A+bi, Whether A, B R, (A) Z+W, (B) Z W, (C) ZW, (D) Z Z W ZDocument3 paginiA+bi, Whether A, B R, (A) Z+W, (B) Z W, (C) ZW, (D) Z Z W ZMichael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- M A Grams, Where A Is The Mass Nucleonnumber of The ElementDocument1 paginăM A Grams, Where A Is The Mass Nucleonnumber of The ElementMichael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Here are the stem and leaf plots for the given data:1) (a) 7|45|26|7 8 96|87|17|68|18|67|36|86|47|57|15|76|75|75|97|27|96|47|07|47|77|96|56|87|68|36|16|3(bDocument2 paginiHere are the stem and leaf plots for the given data:1) (a) 7|45|26|7 8 96|87|17|68|18|67|36|86|47|57|15|76|75|75|97|27|96|47|07|47|77|96|56|87|68|36|16|3(bMichael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cro Exr F5Document1 paginăCro Exr F5Michael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test Form Iv 1. (A) Write Down The Readings BelowDocument26 paginiTest Form Iv 1. (A) Write Down The Readings BelowMichael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elec IgcseDocument7 paginiElec IgcseMichael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- State, With A Reason, Whether A Binomial Distribution Would Be A Good Model in The Following SituationsDocument2 paginiState, With A Reason, Whether A Binomial Distribution Would Be A Good Model in The Following SituationsMichael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical Power Output Electrical Power Supplied: Paper 5 Revision QuestionsDocument5 paginiMechanical Power Output Electrical Power Supplied: Paper 5 Revision QuestionsMichael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Defn&FormsDocument10 paginiDefn&FormsMichael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- MRI Student WorksheetDocument1 paginăMRI Student WorksheetMichael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculate fundamental frequency of original tubeDocument7 paginiCalculate fundamental frequency of original tubeMichael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- PH 2008 OcDocument2 paginiPH 2008 OcMichael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics ATP NotesDocument8 paginiPhysics ATP NotesImran MirzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic Learning OutcomesDocument3 paginiTopic Learning OutcomesMichael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circles: Higher Maths Exam QuestionsDocument8 paginiCircles: Higher Maths Exam QuestionsMichael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics 9702 Paper 5 Skill Breakdown of MarksDocument12 paginiPhysics 9702 Paper 5 Skill Breakdown of MarksMichael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Band TheoryDocument4 paginiBand TheoryMichael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Opt D1Document2 paginiOpt D1Michael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- WS CroDocument1 paginăWS CroMichael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ans-Hall EffectDocument2 paginiAns-Hall EffectMichael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fund ParticlesDocument2 paginiFund ParticlesMichael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9702 P5 Q1Document4 pagini9702 P5 Q1Michael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Current Electricity Electric Current (I) : ElectronDocument12 paginiCurrent Electricity Electric Current (I) : ElectronMichael LeungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample Wps Multi ProcessDocument1 paginăSample Wps Multi ProcessMohammed Elmodathir Ali100% (1)
- Practice Test - 7, Atomic Structure and Gaseous StateDocument12 paginiPractice Test - 7, Atomic Structure and Gaseous StateBadNik 007Încă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial 2 (ME332) : Problems On Strain Rate, Stokes Laws, Surface Forces and Basic Equations & Boundary ConditionsDocument2 paginiTutorial 2 (ME332) : Problems On Strain Rate, Stokes Laws, Surface Forces and Basic Equations & Boundary ConditionsPrateeksha ShakyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- English SuperFlowDocument1 paginăEnglish SuperFlowJujemar GujeldeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 424a 2016Document5 pagini424a 2016IrsyadnurJ.MargiantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sealeze APH Brush Seals BrochureDocument2 paginiSealeze APH Brush Seals BrochureMurilo Camisão SchwindenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earth's Internal Geologic Processes ExplainedDocument2 paginiEarth's Internal Geologic Processes ExplainedAj AsaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vicker HardnessDocument3 paginiVicker HardnessEhsanulhaq786100% (1)
- JEE Adv. - Growth - Sample Paper-2 - StudentDocument15 paginiJEE Adv. - Growth - Sample Paper-2 - Studentanurag jaiswalÎncă nu există evaluări
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: Geotechnical Engineering - IiDocument1 paginăWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: Geotechnical Engineering - IimaheshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spring and Spring BalanceDocument7 paginiSpring and Spring BalanceullasagwÎncă nu există evaluări
- Distribution of Shear Stresses in Circular ShaftsDocument5 paginiDistribution of Shear Stresses in Circular ShaftsSnehasish IsharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aerospace Engineering, PG. Scholar (Aero), PG. Scholar (Aero), MLR Institute of Technology, Hyderabad, IndiaDocument8 paginiAerospace Engineering, PG. Scholar (Aero), PG. Scholar (Aero), MLR Institute of Technology, Hyderabad, IndiaMasoud doskiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 185hr DatasheetDocument3 pagini185hr DatasheetAsh VigilÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0-1-DEBRIEFING-Ca'c 1, Cal'c 2 and Fluid-StudentsDocument2 pagini0-1-DEBRIEFING-Ca'c 1, Cal'c 2 and Fluid-StudentsPaul Philip LabitoriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- How fiber addition affects properties of low cement castablesDocument4 paginiHow fiber addition affects properties of low cement castablesAndrian Hadiana100% (1)
- Fine Blanking - Literature SurveyDocument8 paginiFine Blanking - Literature Surveysickman100% (1)
- Exercise 2 - FastenersDocument2 paginiExercise 2 - FastenersAhmed EidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heat Input Effects in WeldingDocument34 paginiHeat Input Effects in WeldingMohammed SulemanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cambridge Chemistry For The IB Diploma 2nd Edition - P336-337Document2 paginiCambridge Chemistry For The IB Diploma 2nd Edition - P336-337NithaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Choi 2012Document5 paginiChoi 2012tuanhoa123Încă nu există evaluări
- Ejercicio 7.45: Ing. Juan Diego Regalado MartiínezDocument10 paginiEjercicio 7.45: Ing. Juan Diego Regalado MartiínezTzuliber RomeroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brochure Ftir Cary 630 5990-8570en Us AgilentDocument12 paginiBrochure Ftir Cary 630 5990-8570en Us AgilentMarcela RobayoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problems On DiffractionDocument2 paginiProblems On DiffractionBrajesh Kumar67% (3)
- Electrolysis Cell Student ActivityDocument3 paginiElectrolysis Cell Student ActivityPersonnumberunoo0% (2)
- Overview of Solid State PhysicsDocument1 paginăOverview of Solid State PhysicsHenkVriesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluids 05 00240Document16 paginiFluids 05 00240Liviu BadeaÎncă nu există evaluări
- STAINLESS STEEL - Chemical & Mechanical PropertiesDocument3 paginiSTAINLESS STEEL - Chemical & Mechanical PropertiesGregorio KilatonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ashrae 90.1-2013 Hvac-ExplainedDocument146 paginiAshrae 90.1-2013 Hvac-Explainedjames100% (1)