Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Nina Bacteria Chart Medical School Step 1
Încărcat de
M PatelDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Nina Bacteria Chart Medical School Step 1
Încărcat de
M PatelDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
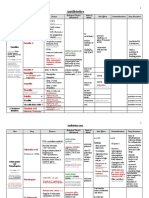
Bacteria Disease Cell Structure Differential Staining Oxygen Requirements Endospore Formation Motility Misc.
Reservoir Virulence Factor/Toxin
Corynebacterium Diphtheriae Diphtheria Rod Gram + Aerobic Catalase Positive No No Tellurite agar Human carriers on skin or nasopharynx
-tox phage; regulated by DtxR FeDtxR bd to tox gene FeRNAP bd to tox gene AB subunit exotoxin B: bd glycoptn R, heparin-bding EGF, on ep surface (NAD+EF2ADP-ribosyl-EF2) A: ADP-ribosylase (irreversibly block ptn syn)
Clostridium Tetani Tetanus Rod Gram + Strict Anaerobe (very sensitive to O2) Yes Yes Water, normal human flora (GI), spores in soil
Tetanospasmin AB subunit exotoxin B: bd gangliosides on CNS n.n. A: Zn-dependent metalloprotease Toxinendocytosisactivation by acidification of endosome cleaves synaptobrevins (ess for nt rel)block rel of inhibitory nt Spastic paralysis
Clostridium Botulinum Botulism Very long rod Gram + Strict anaerobe (extremely sensitive to O2) Yes
Vibrio Cholerae Cholera Rod Gram Facultative Anaerobe
Prefer slightly alkaline conditions
Botox AB subunit exotoxin B: protective against acid A: Zn-protease Potent neurotoxin (similar to tetanus toxin) Blocks rel of Ach at NMJinhibits muscle contraction Flaccid paralysis
Yes (highly) O-Ag: O1/O139 cause cholera Contaminated water
Flagella, mucinase, Zot (get bet cells) Adhesins Cholera toxin/AB subunit exotoxin B: bind GM1 ganglioside A: ADP-ribosylatesinactivates GptnACcAMP hypersecretion of H2O/Cl-, blocked absorption of Na+ explosive hypermotility, copious watery diarrhea
Transmission Pathogenesis
Aerosol route, sometimes fomites
Infl Reponseinflux of PMN, killed by toxinneucrosis *anorexia, lethargy, enlarged cervical lymph nodes Pseudomembrane in throat (dead ep cells, bld, leukocytes, fribin) block respiration Systemic Toxemia myocarditis
Injection of spores into deep traumatic wound, low ID50
Toxin spreads thru nerve fibers or blood to CNS Spastic Paralysis: locked jaw (masseter), back and neck, abdominal, extremity m.m.
Food Not person-to-person
Flaccid Paralysis Foodbourne Botulism: double/blurred vision, drooping eyelids, slurred speech, difficulty swallowing, dry mouth, m. weakness, paraylysis, no fever Also wound and inhalation botulism possible
Must survive acidic pH of stomach, ID50~109 ; oral-fecal route
No inflammation Rica water stools of Cholera: mucus flecked, watery, no blood or fecal leukocytes
Diagnosis Treatment
Throat culture, difficult Antitoxin, antibiotics, vaccine
Clinical presentation Antitoxin (human tetanus immune globulin), sometimes antibiotics
Cant culture Antitoxin, most recover after supportive care
Symptoms, selective medium Replacement of fluids/electrolytes *improved sanitation
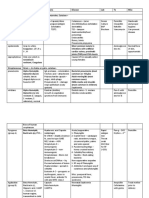
Bacteria Disease
Staphylococcus Aureus Invasive: abscesses, wound infections, pneumonia Toxigenic: scalded skin syndrome, toxic shock syndrome, food poisoning
Direct Invasion Pharyngitis (Strep throat) Skin & Wound Infections
Cell Structure Differential Staining Oxygen Requirements Motility Misc. Reservoir Virulence Factor Toxin
Cocci in clusters Gram + Facultative anaerobes Catalase positive No -hemolytic, high salt media, form golden colonies Human anterior nasopharynx, skin, normal microbiota, thrive in high salt environment
Surface Ags: capsule (prevent phago/chemotaxis by PMN), slime layer (bioflims), ptn A (prevent opsonization), peptidoglycan (act. alt C), Teichoic acid (bd fibronectin, act. C), MSCRAMM Toxins: -hemolysin: pore-forming -toxin: sphinogomyelinase C, hydrolyze mem P.lipids -toxin: dermonecrotic toxin, acts as surfactant P-V leukocidin & -toxin: pore-forming, damage PMN/m Super Ag Toxins: Toxic shock syndrome toxin (TSST-1, system toxicity), Enterotoxins: heat-resist, resist gastric enzymes, food pois Spreading factors & enzymes: coagulase, catalase, staphylokinase/ fibrinolysin, hyaluronidase, penicillinase, DNase, proteases, lipases,etc *AgrD controls expression of RNAIII which act/represses translation and transcription
Streptococcus Pyogenes Toxin mediated Delayed immunologic reaction Toxic-Shock like Rheumatic Fever, Syndrome, Scarlet Glomerulonephritis fever, Necrotizing fasciitis Cocci in chains Gram +
Strictly fermenatative (no respiration) Catalase negative Bacitricin-sensitive, -hemolytic (complete lysis of RBC), Lancefield groupings (cell wall carbohydrate Ag: not capsule) Human nasopharynx, (normal flora)
Surface Ags: hyaluronic acid capsule (mucoid-antiphag), lipoteichoic acid (bd fibronectin, attachment to pharayngeal cells), M ptn (adh, anti-phag, degrade C C3b, bd IgM), M-like ptns (bd IgM, IgG, 2-microglobulin), Ptn F, G (bd fibronectin) Toxins: Streptolysin O- O2 labile: pore-forming , lyse WBC, RBC, immunogenic Streptolysin S-serum soluble: O2 stable, non-immunogenic Pyogenic exotoxins, SPE: superAg Extracellular enzymes: streptokinase A & B (lyse blood clots), hyaluronidase (degrades capsule), C5a peptidase (degrade C), DNAses (degrade free DNA, viscosity in pus)
Transmission Pathogenesis
Direct contact or aerosol
Attachment: FNBP, CBP, EBP; Toxins: tissue damage; spread: further damage Pyogenic Diseases (Pus forming disease): locally destructive boils, carbuncles, folliculitis, impetigo
Direct contact or aerosol
Avoid phag/opsonizationmultiplication/invasion into tissuesspread Localized epithelial After spread 1-3 weeks after scarlet damage before spread erythrogenic toxin fever
*Toxic Shock Syndrome: no bacteremia; toxin released fever, rash, hypotension, desquamation, diarrhea, vonmiting, sore throat, m. pain, purura fulminans *Scalded Skin Syndrome: large blisters, fluid-filled, complete desquamation of epithelium, no scarring Food poisoning: no ingestion of organisms necessary; rapid onset of vomiting, diarrhea, nausea Others: osteomyelitis, septic arthritis, endocarditis, pneumonia, empyema (pneumonia complication)
*impetigo (pyoderma), puerperal childbed fever, erysipelas, cellulitis, necrotizing fasciitis
lead to scarlet fever (12 days after pharyngitis) Toxic shock-like syndrome: pyogenic exotoxin, SpeA (bacteria are systemic)
Rheumatic Fever: infl of heart, joints, bld vessels, chronic progressive damage Glomerulonephritis Accumulation of immune complexes in kidneys, acute infl, blood, ptn in urine, edema, hypertension
Diagnosis Treatment
Easily cultured, yellow on MSA, no lasting immunity Penicillin resistant, Vancomycin (only useful one)
Easily cultured Penicillin is drug of choice! Add aminoglycoside if serious, vancomycin if penicillin allergy (no affect on glomerulonephritis)
Bacteria Disease
Cell Structure Differential Staining Oxygen Requirements Endospore Formation Motility Misc. Reservoir Virulence Factor Toxin
Streptococcus Pneumoniae Pneumonia (also Sinusitis, Otitis Media, Meningitis, Bacteremia) Cocci Gram + Facultative anaerobe Catalase negative
Legionella Pneumophila Legionnaires Disease Pontiac Fever Rod Gram Obligate Aerobe Catalase positive Facultative intracellular parasite Motile (flagella) Metabolize amino acids for energy, heatresistant, Cl- resistant Fresh water streams & lakes
Pili (type IV class, adh to m), outer membrane ptn (MOMP, bd C3b), m invasion protentiator (MIP), LPS, DOT (defect organelle trafficking ptnsinh maturation of phagosome/m), Icm (intracellular multiplication ptn, Type IV sec Dot), Degradative enzymes: phospholipase, extracel protease, Type II *can survive in m
Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Tuberculosis (also Leprosy, M. avium complex) Rod Acid fast (Gram + like) Strict Aerobe No Facultative intracellular pathogen Cell Wall: Very high lipid, mycolic acids, arabinogalactan, lipoarabinomannan (LAM) Humans
Cord factor: trehalose dimycolate (toxic, inh PMN migration), Wax D: immunostimulatory Lipoarabinomannan: (T cell prolif, prevent m act), Tuberculin: delayed hypersensitivity -produce NO extotoxins/endotoxins Ability to survive in m: bd C3b on muptakeinh ox burstsulfatidesinh phag-lysosome fusionfuse w/other vesicles
No Lancefield Ag, optochin sensitive -hemolytic Upper respiratory tract (normal flora)
Pneumolysin: not secreted, shed by autolysis, pore-forming, slow ciliary beating, act. C, inh resp burst. Polysac capsule: anti-phag, immunogenic, required for virulence Neuramindase, sIgA protease, H2O2, surface ptns (MSCRAMM), peptidoglycan, teichoic acid, phosphorylcholine
Transmission Pathogenesis
Aerosol Productive cough w/ bloody sputum, chest pain
Aerosols, no person-to-person, no asymptomatic carriage Coiling phagocytosisuptake into mmultiplylyse/spread to others Legionnaires Disease: severe, progressive, toxic pneumonia: necrotizing, myalgia, headache, fever, dry coughshock, respiratory failure Pontiac Fever: non-progressive, selflimiting, fever, chills, headache, myalgia
Aerosol ID very low (< CFU) Hypersensitivitytissue destruction and necrosis (heightened immune response: cell mediated immunitymIL-12, IL-1, TNF; TH1recruit m; CD8) resistant to humoral immunity *chronic fever, weight loss, night sweats, productive cough w/ blood sputum, extensive tissue damage to lung Ghon Complex: influx of m (cheesy-like)
Diagnosis
Gram stain of sputum, quelling test
Treatment
Resistance against penicillin Erythromycin, vancomycin, vaccine
1 Macrolides, fluroquinolones 2 doxycylcine Penicillin resistant
PPD skin text: measure DTH reaction to Tuberculin Culture sputum, acid-fast rods 1st line: isoniazids, ethambutol, rifampin 2nd line: ethionamid, streptomycin, etc
Bacteria Disease Cell Structure Differential Staining Oxygen Requirements Endospore Formation Motility Reservoir Misc. Virulence Factor Toxin Transmission Pathogenesis
Treponema Pallidum Syphilis Helical/Spirochetes Gram -
Borrelia Burgdorferi Lyme Disease Helical/Spirochetes Gram -
Corkscrew motility Periplasmic flagella Human mucosal surfaces, strict pathogen Cant be cultured No known toxins (some hly-like genes), adhesins, hyaluronidase (anti-phag) Sexually
Primary Syphilitic chancre 10-90 days after infection, painless ulceration, elevated, neucrotic lymphadenopathy Secondary Metastatic stage 6 weeks after 1 Bacteria systemic Diffuse skin eruptions, widespread rash; CMI Asymptomatic for yearslatency Tertiary Bacteria hard to find, not infectious, granulomatous lesions (skin,bones,joints) Irreversible
Corkscrew motility Periplasmic flagella Deer, ticks, and rodents No person-to-person, linear genome, Fe abstinence, no LPS, TCAC, ETC None listed Ticks
Initial (Skin) Phase Erythema migrans (bulls eye), local infl, fatigue, chills, fever, headache, m./joint ache, swollen lymph nodes Second (Systemic) Phase Bacteria systemic, between endothelial cells, in joints, disseminated rash *skin, nervous system, heart, joints Chronic Phase Immunopathologic reactions, Autoimmunity, inh C, neurological manifestations, difficult to cure
Diagnosis Treatment
Difficult, not culturable, darkfield microscopy Penicillin, tetracycline, erythromycin,
Can be cultured Antibiotic prophylaxis, doxycycline, amoxicillin, cerfuroxime
Bacteria Disease Cell Structure Differential Staining Oxygen Requirements Endospore Formation Motility Reservoir Misc. Virulence Factor Toxin
Chlamydia Trachomatis Chlamydia
Neisseria Gonorrhoeae Gonorrhea (localized infection) Cocci Gram Oxidase positive Catalase positive Facultative intracellular pathogen
Neisseria Meningitis Meningitis Cocci Gram Oxidase positive Catalase positive Facultative intracellular pathogen
Gram type No peptidylglycan Can respire, has ETC Obligate Intracellular pathogen
Strictly human Do not synthesize amino acids, do syn ATP
Two Cell Types: Elementary body (EB): hardy, EC form, nonreplicative, infectious form, stores ATP Reticulate body (RB): fragile, metabolically active, replicative, dont survive EC, line up around periphery of inclusion, take nutrients from host 1. Dormant phase 2. Entry: Adherance: heparin sulfate, estrogen rec, Invasion: actin arrangements, pedestal formation w/o use of trigger or zipper mech 3. EBRB: (endocyticexocytic) 4. RB multiplication 5. RBEB (Type III) IncA (necessary for inclusions): phos by host cellvacuole fusionexit (destroy vacuole or fuse with cell membrane)
Require CO2 for growth Strictly human mucosal ep surfaces Human upper respiratory tract
Pili (type IV class, adhesin, twitch motility, Ag variation), Outer membrane ptns: P I (Porin, adh, invasion, resist C, inh phag-lysosomal fusion), P II (Opa, phase/Ag variation, adh, invasion), P III (Rmp, block Ab), Fe-bding ptns, LOS: endotoxin, IgA1 proteases: cleave IgA/lysosomal ptns, Peptidoglycan: cytotoxic Fe-bding ptns, LOS: may be sialylated, IgA1 protease: cleave IgA and lysosomal ptns in cells Type IV Pili: adh, phase/Ag variation Outer membrane ptns: porins (adh/invasion), PII: adherence, phase/Ag variation, LOS: 1 toxin, damage ep/endo cells, infl response Not in GC: Capsule: polysac, -phag
Transmission Pathogenesis
Sex Men: epididymitis, prostatitis Women: vaginitis/cervicitis Lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV): chronic disease caused by L1, L2, L2a, L3 *Infl of draining lymph nodes, painful buboes Trachoma: can lead to blindness
Direct contact of mucosal surfaces Men: epididymitis, prostatitis Women: vaginitis/cervicitis Disseminated Gonococcal Infection: Tbp: acquire Fe in blood, LOS (can survive in PMNs), OMPs, piliGonococcal arthritis
Respiratory aerosols Meningitis: cross BBB, replicate in the meningesmassive infl resp in SAS Meningococcal septicemia: Nasopharynxsubmucosabloodstream meningococcemia frequently fatal bacteremia
Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome: Diagnosis Treatment Obtain infected ep cells, grow in cell, ELISA, PCR No vaccine, antibiotics: tetracycline, azithromycin, trichaisis (surgery) Gram stain purulent of exudates, antibiogram No vaccine, antibiotic resistance (esp to penicillin/tetracycline/cipro, tx with ceftriaxone, doxycycline, azithromycin
Vaccine-capsular polysaccharide subunit vaccine, multivalent ptn conjugate vaccine Antibiotics-penicillin, chloramphenicol
Bacteria Disease Cell Structure Differential Staining Oxygen Requirements Endospore Formation Motility Reservoir Misc. Virulence Factor Toxin
Shigella Dysenteriae Dysentery (Bloody Diarrhea) Rod Gram Facultative anaerobe Oxidase negative No Resistant to bile salts No, no flagella Human intestinal tract, contaminated water/food, strict pathogen Glucose fermenter, not lactose fermenter, does not produce H2S, Ag based on O-Ag
Ipa ptns: invasion plasmid organisms (A-D, adh, invasion, escape endocytic vesicle, Type III sec), IcsA, IcsB: intracellular spread on polymerized actin tails Shigatoxin: AB subunitdegrade 23S RNAblock ptn synthesisNa abs, excess fluid, cell death, necrosis of colonic ep, hemorrhagic colitis, neurocytotoxin
Enterobacteriaceae Salmonella Typhi Typhoid Fever Rod Gram Facultative anaerobe Oxidase negative No Resistant to bile salts Yes Human carriers, not part of the normal flora Glucose fermenter, Non-lactose fermenter, produces H2S, Ag based on O-Ag & H-Ag
LPS Invasins Inv-H: Type III sec, PAI I/SPI-1 Ability to survive in m: Type III sec, PAI II/SPI-2 Vi Ag: polysac capsule surrounds O Ag Complex regulatory cascade
Escherichia coli Watery, Cholera-like diarrhea Rod Gram Facultative anaerobe Oxidase negative No Resistant to bile salts EHEC: large intestine Glucose AND Lactose fermenter
Enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC) Heat-labile toxin (LT): LT-I, AB-subunit like Cholera toxin, LTII (animal disease); Heat-stable toxin (ST): STa (bd GCcGMPhyper-secretion of H2O), STb (animal dis, HCO3-, Colonizing factors (CF) Enteroinvasive E. coli (EIEC) Like Shigella but no shiga toxin, Ipas (invasion ptns) Enteropathogenic E. coli (EPEC) Bundle-forming pili (BFP): Type IV, local adh, on EPEC adh factor, microcolony formation (interbac interactions, twitch motility LEE Locus: Intimin (bd Tir), Tir (translocated intimin rec, on surf of host cell), Esp (EPEC sec ptns, Type III sec, trigger signals/actin rearrangement) Enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC) Acid-resistant, LEE Locus (Intimin, Tir, Esp), Shiga-like Toxin: bd 28S rRNA, stimulate infl cytokine production Uropathogenic E. coli Adhesins: Type I pili (bd mannose-containing glycoptn rec, fim gene cluster); Pyelonephritis-associated pili Toxins: Hemolysin (HlyA, poreslyses), Cytotoxic necrotizing factor (CNF-1, change cytoskeleton)
SEC Capusle: polysac K Ag, poorly immunogenic, anti-phag, serum resistance, block C, Ab deposition Adhesins: Type I pili, S-fimbriae (bd fibronectin) Invasins: Ibe (invasion of brain endothelium), OmpA (pore forming)
Transmission
Oral-fecal (food handlers) ID50 very low, highly infectious
Evade Host Immune Response: 1. trigger uptake to non-prof APC 2. escape phagosome 3. spread to other epithelial cells via actin tails LPSsevere inflammatory response *Fever, abdominal pain, diarrhea (w/bright red blood and pus)
Oral-fecal ID50 very low (S. enteritidis: ID50)
Infect M cells in mucosa of lg intestine 1. trigger endocytosis in M cells 2. membrane ruffling (via inv & T3SS) 3. pass thru M cellsubmucosa 4. ingested by m (T3SS) 5. multiply in spleen/liver 6. LPS in blood streaminfl response (high fever, flushing, anorexia) Samonellosis (Gastroenteritis); S. enteritidis: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, muscle ache and cramping, bacteremia Typhoid Fever: enter GI, travel via mfever, headache, fatigue, myalgia Enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC) Relatively high ID50 Watery, cholera-like diarrhea Enteroinvasive E. coli (EIEC) Require higher ID Water, sometimes bloody diarrhea Enteropathogenic E. coli (EPEC) Fever, Nausea, Vomiting, Diarrhea (mainly infant diarrhea) Enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC) Low ID50 Hemorrhagic colitis: watery diarrheabloody diarrheahemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) Uropathogenic E. coli Urinary Tract Infectionspyelonephritis SEC Sepsis Meningitis
Pathogenesis
Diagnosis Treatment
Samenellosis (Gastroenteritis): spontaneously resolves in a couple of days Typhoid Fever: antibiotics, vaccine
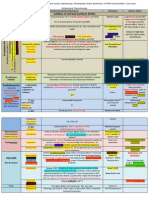
Bugs in a Nut Shell: Hey, Im a bug and Im in a nutshell *We only need to know 17 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE: CAN YOU FILL IN THE REST OF THIS CHART? Bacteria Staining (only 6 G+ and 1 acid fast, the rest are G-) G+ G+ G+ GG+ G+ G+ GAF GGGGGGGGShape O2 Requirements Toxin Disease
1. Corynebacterium Diphtheriae 2. Clostridium Tetani 3. Clostridium botulinum 4. Vibrio Cholera 5. Staphylococcus aureus 6. Streptococcus pyogenes 7. Streptococcus pnemoniae 8. Legionella pnemoniae 9. Mycobacterium Tuberculosis 10. Treponema pallidum 11. Borrelia burgdorferi 12. Chlamydia trachomatis 13. Neisseria gonorrhoeae 14. Neisseria meningitis 15. Shigella dysenteriae 16. Salmonella typhi 17. Escherichia coli
Rod Rod Rod Rod Cocci Cocci Cocci Rod Rod Helical Helical Cocci Cocci Rod Rod Rod
Aerobe Anaerobe Anaerobe Facultative anaerobe Facultative anaerobe Anaerobe Facultative anaerobe Aerobe Aerobe
Facultative anaerobe Facultative anaerobe Facultative anaerobe
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Micro Final Buzz Word CheatsheetDocument10 paginiMicro Final Buzz Word CheatsheetThesmith FamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Micro I ReviewDocument15 paginiMicro I ReviewEmilee Tu100% (1)
- Bacteria Notes SketchyDocument3 paginiBacteria Notes SketchyJayÎncă nu există evaluări
- MicrobesDocument12 paginiMicrobesDiMa MarshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microbiology - Bacteria Summary (Updated)Document26 paginiMicrobiology - Bacteria Summary (Updated)moZZeltovÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antibiotics ChartDocument10 paginiAntibiotics Chartadom09Încă nu există evaluări
- Harrison TablesDocument163 paginiHarrison Tablesfrancieudo1Încă nu există evaluări
- Flashcards FinalDocument272 paginiFlashcards FinalMarie SantoroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microbiology Quick TableDocument2 paginiMicrobiology Quick TableCoy Nuñez100% (2)
- Pharma Super TableDocument56 paginiPharma Super TableMarco Paulo Reyes NaoeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharma Super TableDocument87 paginiPharma Super TableMarton Emile DesalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antimicrobial AgentsDocument3 paginiAntimicrobial AgentsErnie G. Bautista II, RN, MD100% (2)
- Endocrine Pathology p17-32Document16 paginiEndocrine Pathology p17-32zeroun24Încă nu există evaluări
- Virology - Study GuideDocument5 paginiVirology - Study GuideMatt McGlothlinÎncă nu există evaluări
- SketchyMicro ChartDocument14 paginiSketchyMicro ChartSonia100% (8)
- Microbiology Key WordsDocument5 paginiMicrobiology Key Wordsmoilo86020% (1)
- Antimicrobial Drugs TableDocument19 paginiAntimicrobial Drugs TableLaylee ClareÎncă nu există evaluări
- Patho ReviewDocument40 paginiPatho ReviewCoy Nuñez100% (2)
- Microbiology Step 1 Antimicrobials ChartDocument6 paginiMicrobiology Step 1 Antimicrobials ChartM Patel100% (1)
- Micro Buzz Words - KEY WordsDocument8 paginiMicro Buzz Words - KEY WordsKris GulleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- AB ClassesDocument4 paginiAB Classesrayooona88100% (2)
- Antibiotic SummaryDocument4 paginiAntibiotic Summaryshazia100% (1)
- Pulmonary PathologyDocument6 paginiPulmonary PathologyjamesjaanÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Pathology Bimonthly Exam Compilation Updated 2Document197 paginiGeneral Pathology Bimonthly Exam Compilation Updated 2Cherry Rahima100% (1)
- Gi Pathology - Block 3 ReviewDocument34 paginiGi Pathology - Block 3 ReviewMatt McGlothlin100% (1)
- WBC Neoplasms Review - PathologyDocument6 paginiWBC Neoplasms Review - Pathologylas100% (6)
- Robbins Ch. 20 The Kidney Review QuestionsDocument10 paginiRobbins Ch. 20 The Kidney Review QuestionsPA2014100% (4)
- Hi Yield Notes in SurgeryDocument16 paginiHi Yield Notes in SurgeryNiñoTan100% (2)
- Free AssociationDocument10 paginiFree AssociationimorkzoneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Penicillins Pen&G Pen&V: T.%pallidum% (Syphilis)Document1 paginăPenicillins Pen&G Pen&V: T.%pallidum% (Syphilis)gregoryvo100% (5)
- Mnemonic SDocument42 paginiMnemonic SWen Jie LauÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 8 Infectious Diseases Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of DiseaseDocument12 paginiChapter 8 Infectious Diseases Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of DiseaseArun Nayak86% (7)
- Pharm I - Abx ChartDocument4 paginiPharm I - Abx ChartNicole BerryÎncă nu există evaluări
- A.1. Community-Acquired: Use Antibiotics JudiciouslyDocument33 paginiA.1. Community-Acquired: Use Antibiotics JudiciouslymaxgroovesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacology Complete Drug TableDocument6 paginiPharmacology Complete Drug Tableninja-2001100% (4)
- Pathology MnemonicsDocument148 paginiPathology MnemonicsOmar Gomez100% (1)
- BacteriologyDocument20 paginiBacteriologyOj Alimbuyuguen100% (2)
- USMLE Most CommonDocument3 paginiUSMLE Most Commonibrahim 12100% (1)
- All MicrobesDocument81 paginiAll Microbesallybish100% (1)
- Microbiology FlashcardsDocument36 paginiMicrobiology FlashcardsKrisha Bernadette TillamanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Board Recall Must ReadDocument8 paginiBoard Recall Must ReadSarahSalvanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antibiotic Study Cheat Sheet October 2018Document1 paginăAntibiotic Study Cheat Sheet October 2018Nourhan100% (3)
- Microbiology MnemonicsDocument3 paginiMicrobiology MnemonicsRAllan75% (16)
- Robbins Pathology Chapter 14 - RBCsDocument7 paginiRobbins Pathology Chapter 14 - RBCsscorpiosphinx79100% (10)
- Malassezia Furfur An-An Ap-Ap Naturally Found On The SkinDocument48 paginiMalassezia Furfur An-An Ap-Ap Naturally Found On The SkinNikki ValerioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bacteria TableDocument4 paginiBacteria TableBrittany Lynn MyersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Step 1 Micro ChartsDocument38 paginiStep 1 Micro ChartsRitika AgarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- 14 Patho Head and Neck PathologyDocument10 pagini14 Patho Head and Neck PathologyMartin TanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review Parasitology ChartsDocument8 paginiReview Parasitology Chartseezah100% (2)
- Inhibitor of Cell Wall Synthesis (ICWS) : Proteus ComboDocument12 paginiInhibitor of Cell Wall Synthesis (ICWS) : Proteus Comboflomax23100% (1)
- Harrisons Reviewer 2Document59 paginiHarrisons Reviewer 2pluiedecielÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sketchy WordDocument9 paginiSketchy WordPäw Yusoph100% (1)
- Microbiology MnemonicsDocument8 paginiMicrobiology MnemonicsArshad AzizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Disease Deficient Enzyme Cardinal Clinical Features Glycogen Structure Von Gierke'sDocument84 paginiDisease Deficient Enzyme Cardinal Clinical Features Glycogen Structure Von Gierke'sclubstar100% (4)
- ChartDocument5 paginiChartWesley CooperÎncă nu există evaluări
- ClostridiumDocument44 paginiClostridiummajoragarwal1195Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 15 StreptococciDocument8 paginiChapter 15 Streptococcinonie jacobÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory Tract MicrobiologyDocument68 paginiRespiratory Tract Microbiologysultan khabeebÎncă nu există evaluări
- Staphylococcus & StreptococcusDocument100 paginiStaphylococcus & StreptococcusFahim NadvyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharm AntibioticsDocument8 paginiPharm AntibioticsM PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- E Coli Types-PrintedDocument2 paginiE Coli Types-PrintedM PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tumor Genes Growth FactorsDocument4 paginiTumor Genes Growth FactorsM PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Surgery Oral ExamDocument46 paginiSurgery Oral ExamM Patel100% (9)
- Microbiology Step 1 Antimicrobials ChartDocument6 paginiMicrobiology Step 1 Antimicrobials ChartM Patel100% (1)
- Biochemistry Word AssociationDocument12 paginiBiochemistry Word AssociationM PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Embroyology Word AssociationDocument5 paginiEmbroyology Word AssociationM PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Micriobiology Medical School Flowchart PrintedDocument1 paginăMicriobiology Medical School Flowchart PrintedM PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiology Arteritis ChartDocument3 paginiCardiology Arteritis ChartM PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iv. Concentric Hypertrophy: A. Increase Vent Mass Relative To VolumeDocument8 paginiIv. Concentric Hypertrophy: A. Increase Vent Mass Relative To VolumeM PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kidney Acidosis-Alkalosis PRoblemsDocument3 paginiKidney Acidosis-Alkalosis PRoblemsM PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microbiolology Medical School Cultivation Media For BacteriaDocument11 paginiMicrobiolology Medical School Cultivation Media For BacteriaM PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nephrology Chronic Renal FailureDocument9 paginiNephrology Chronic Renal FailureM PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nephrology FormulasDocument3 paginiNephrology FormulasM Patel0% (1)
- Psych Drugs List - To Be Filled inDocument3 paginiPsych Drugs List - To Be Filled inM Patel100% (1)
- Name Types Disease Mechanism AE Other C. Cycle Resistance (CP Pg. 326) Alkylating AgentsDocument12 paginiName Types Disease Mechanism AE Other C. Cycle Resistance (CP Pg. 326) Alkylating AgentsM PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Charts For Kidney and Lower Urinary Tract Pathology. NephrologyDocument34 paginiCharts For Kidney and Lower Urinary Tract Pathology. NephrologyM PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digestive Domain Diarrhea, IBSDocument3 paginiDigestive Domain Diarrhea, IBSM PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heme-Onc-Anemia Blank TableDocument2 paginiHeme-Onc-Anemia Blank TableM PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biostatistics Epidemiology Definitions ChartDocument10 paginiBiostatistics Epidemiology Definitions ChartM PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Newborn ChartDocument1 paginăNewborn ChartM PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anemias ChartDocument14 paginiAnemias ChartM Patel100% (2)
- COPD ChartDocument6 paginiCOPD ChartM PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mnemonics CondensedDocument4 paginiMnemonics CondensedM PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychiatry MnemonicsDocument7 paginiPsychiatry MnemonicsFahad Almalki93% (15)
- Newborn ChartDocument1 paginăNewborn ChartM PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mnemonics CondensedDocument4 paginiMnemonics CondensedM PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- GI Tract Epithelium - GastroenterologyDocument3 paginiGI Tract Epithelium - GastroenterologyM PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Obstetrics Gynecology TableDocument22 paginiObstetrics Gynecology TableM PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Small Pox Is DeadDocument46 paginiSmall Pox Is Deadtummalapalli venkateswara raoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Y 0870 e 51Document12 paginiY 0870 e 51Yohanes BaptistaÎncă nu există evaluări
- FINAL Na DLP ZOOLOGYDocument18 paginiFINAL Na DLP ZOOLOGYDarlyn Joy TolentinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Obra de Teatro en InglèsDocument11 paginiObra de Teatro en InglèsLEIDY TATIANA RAMÍREZ PIMIENTOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class 3 EVS Question Bank 1Document8 paginiClass 3 EVS Question Bank 1ᴅᴇᴇᴘ ᴘʀᴀᴋᴀsʜ ᴍᴏᴅɪ xɪ-ᴅÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adrienne EnglishDocument13 paginiAdrienne EnglishMiguel Sulis100% (1)
- Dodram Handon - 2016 (Dodram Food)Document13 paginiDodram Handon - 2016 (Dodram Food)wong winkinÎncă nu există evaluări
- NEW ETHICS NNNNNNNNN)Document12 paginiNEW ETHICS NNNNNNNNN)Mulugeta100% (1)
- The Lord of The Flies QuestionsDocument2 paginiThe Lord of The Flies QuestionsMichael NutleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sale Catalog - World Classic SaleDocument52 paginiSale Catalog - World Classic SaleHolstein PlazaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DND 5e Races and SubracesDocument3 paginiDND 5e Races and SubracesCursedLich89% (9)
- AmulDocument36 paginiAmulvahid100% (1)
- A 2nd Helping of Chicken Soup For The SoulDocument6 paginiA 2nd Helping of Chicken Soup For The SoulApril N50% (4)
- Chaparrí: Ubicación: Región Lambayeque. Provincia de Chiclayo, Distrito de Chongoyape, Caserío TierrasDocument3 paginiChaparrí: Ubicación: Región Lambayeque. Provincia de Chiclayo, Distrito de Chongoyape, Caserío TierrasAlexs TomapascaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seidel's Guide To Physical Examination, Chapter 16, 350-369 PDFDocument20 paginiSeidel's Guide To Physical Examination, Chapter 16, 350-369 PDFAlexandra PalagaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exam (1) On Unit (1) :: Connect Plus 4 - 1st TermDocument12 paginiExam (1) On Unit (1) :: Connect Plus 4 - 1st TermHassan k1455 rashidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cambridge Latin Courses 1 To 4 All Books Complete Cambridge Press Full ChapterDocument67 paginiCambridge Latin Courses 1 To 4 All Books Complete Cambridge Press Full Chapterrobert.short872100% (4)
- Chhiarpui Neih Tan A Ni: Hunawl Hman That Zofate Hmasawnna Ngaihtuah Kriastian Nun Dan Tha NgaihsanDocument4 paginiChhiarpui Neih Tan A Ni: Hunawl Hman That Zofate Hmasawnna Ngaihtuah Kriastian Nun Dan Tha NgaihsanchanmariansÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interpretation Chest X RayDocument127 paginiInterpretation Chest X RayVimal NishadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class 1 CBSE English Worksheets Term 2-DBXDocument10 paginiClass 1 CBSE English Worksheets Term 2-DBXBS100% (1)
- Genesis RevisitedDocument4 paginiGenesis RevisitedAgus alfin hidayatÎncă nu există evaluări
- F. Y. B. Sc. (Zoology) Question BankDocument51 paginiF. Y. B. Sc. (Zoology) Question BankHassan Ahmed100% (2)
- 4ES0 02 Que 20110617Document8 pagini4ES0 02 Que 20110617Syed AhadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diagnostic Traditional MedicineDocument225 paginiDiagnostic Traditional MedicineJRA100% (17)
- 18XX OutlawDocument4 pagini18XX OutlawConnor BrassfieldÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amsa 43Document70 paginiAmsa 43smithworkÎncă nu există evaluări
- HAYDUKE, George - ''Make'Em Pay - Ultimate Revenge Techniques From The Master Trickster''Document125 paginiHAYDUKE, George - ''Make'Em Pay - Ultimate Revenge Techniques From The Master Trickster''Mitko Krumov100% (3)
- The Northern Sierra Madre Natural ParkDocument2 paginiThe Northern Sierra Madre Natural ParkZamora Enguerra EmmalyneÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.movers Pratice Test - RW Part 1 - 2Document20 pagini2.movers Pratice Test - RW Part 1 - 2Ngoc Huyen HoangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EyesDocument20 paginiAnatomy and Physiology of The EyesLaidy Aizahlyn Indoc Angod100% (2)
- Summary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDe la EverandSummary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (9)
- The Bodies of Others: The New Authoritarians, COVID-19 and The War Against the HumanDe la EverandThe Bodies of Others: The New Authoritarians, COVID-19 and The War Against the HumanEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (12)
- Uncontrolled Spread: Why COVID-19 Crushed Us and How We Can Defeat the Next PandemicDe la EverandUncontrolled Spread: Why COVID-19 Crushed Us and How We Can Defeat the Next PandemicÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Wisdom of Plagues: Lessons from 25 Years of Covering PandemicsDe la EverandThe Wisdom of Plagues: Lessons from 25 Years of Covering PandemicsEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (6)
- The Gut-Immune Connection: How Understanding the Connection Between Food and Immunity Can Help Us Regain Our HealthDe la EverandThe Gut-Immune Connection: How Understanding the Connection Between Food and Immunity Can Help Us Regain Our HealthÎncă nu există evaluări
- Do You Believe in Magic?: The Sense and Nonsense of Alternative MedicineDe la EverandDo You Believe in Magic?: The Sense and Nonsense of Alternative MedicineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Epic Measures: One Doctor. Seven Billion Patients.De la EverandEpic Measures: One Doctor. Seven Billion Patients.Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (13)
- The Wuhan Cover-Up: And the Terrifying Bioweapons Arms RaceDe la EverandThe Wuhan Cover-Up: And the Terrifying Bioweapons Arms RaceÎncă nu există evaluări
- There Are No Accidents: The Deadly Rise of Injury and Disaster—Who Profits and Who Pays the PriceDe la EverandThere Are No Accidents: The Deadly Rise of Injury and Disaster—Who Profits and Who Pays the PriceEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (11)
- Deaths of Despair and the Future of CapitalismDe la EverandDeaths of Despair and the Future of CapitalismEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (30)
- Mama Might Be Better Off Dead: The Failure of Health Care in Urban AmericaDe la EverandMama Might Be Better Off Dead: The Failure of Health Care in Urban AmericaÎncă nu există evaluări
- There Are No Accidents: The Deadly Rise of Injury and Disaster—Who Profits and Who Pays the PriceDe la EverandThere Are No Accidents: The Deadly Rise of Injury and Disaster—Who Profits and Who Pays the PriceEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (15)
- Fatal Conveniences: The Toxic Products and Harmful Habits That Are Making You Sick—and the Simple Changes That Will Save Your HealthDe la EverandFatal Conveniences: The Toxic Products and Harmful Habits That Are Making You Sick—and the Simple Changes That Will Save Your HealthEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (7)
- Coronary: A True Story of Medicine Gone AwryDe la EverandCoronary: A True Story of Medicine Gone AwryEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (4)
- Clean: Overcoming Addiction and Ending America’s Greatest TragedyDe la EverandClean: Overcoming Addiction and Ending America’s Greatest TragedyEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (18)
- Summary: The Real Anthony Fauci: Bill Gates, Big Pharma, and the Global War on Democracy and Public Health by Robert F. Kennedy Jr: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedDe la EverandSummary: The Real Anthony Fauci: Bill Gates, Big Pharma, and the Global War on Democracy and Public Health by Robert F. Kennedy Jr: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inflamed: Deep Medicine and the Anatomy of InjusticeDe la EverandInflamed: Deep Medicine and the Anatomy of InjusticeEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (12)
- Heat Wave: A Social Autopsy of Disaster in ChicagoDe la EverandHeat Wave: A Social Autopsy of Disaster in ChicagoEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (40)
- The Hair Color Mix Book: More Than 150 Recipes for Salon-Perfect Color at HomeDe la EverandThe Hair Color Mix Book: More Than 150 Recipes for Salon-Perfect Color at HomeEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (7)
- Breaking out of the Health Care Abyss: Transformational Tips for Agents of ChangeDe la EverandBreaking out of the Health Care Abyss: Transformational Tips for Agents of ChangeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Beyond the Next Village: A Year of Magic and Medicine in NepalDe la EverandBeyond the Next Village: A Year of Magic and Medicine in NepalÎncă nu există evaluări
- COVID-19: The Victims, The Heroes, The Comlicit, and Our New NormalDe la EverandCOVID-19: The Victims, The Heroes, The Comlicit, and Our New NormalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Healthy Buildings: How Indoor Spaces Drive Performance and ProductivityDe la EverandHealthy Buildings: How Indoor Spaces Drive Performance and ProductivityEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (2)
- Get Well Soon: History's Worst Plagues and the Heroes Who Fought ThemDe la EverandGet Well Soon: History's Worst Plagues and the Heroes Who Fought ThemEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (234)
- The Promise of Lithium: How an Over-the-Counter Supplement May Prevent and Slow Alzheimer's and Parkinson's DiseaseDe la EverandThe Promise of Lithium: How an Over-the-Counter Supplement May Prevent and Slow Alzheimer's and Parkinson's DiseaseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Community-Acquired Pneumonia: Strategies for ManagementDe la EverandCommunity-Acquired Pneumonia: Strategies for ManagementAntoni TorresEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (2)