Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
SSM
Încărcat de
Gosai JaydeepTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
SSM
Încărcat de
Gosai JaydeepDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
For ManagementParadise.com By ex-TYBMS students.
DIFFERENCE IN GOODS AND SERVICES The most basic and universally cited, difference between goods and services is intangibility. Because services are performances or actions rather than objects, they cannot be seen, felt, tasted or touched in the same manner that we can sense intangible goods. E.g., health care services are actions (surgery, diagnosis, examination and treatment) performers by providers and directed towards the patients and their families. The services cannot be actually seen or touched by the patients, although the patient may be able to see or touch the tangible components of the service (e.g. equipment, hospital room) Intangibility presents several marketing challenges: Services cannot be inventoried, and therefore fluctuations in demand are often difficult to manage. E.g. there is tremendous demand for resort accommodations in phoenix in February, but little demand in July. Yet the resort owners have the same number of rooms to sell year-round. Services cannot be patented legally, and new service concepts can therefore easily be copied by the competitors. Services cannot be readily displayed or easily communicated to the customers, so quality may be difficult for the consumers to assess. Decisions about what to include in advertising and other promotional materials challenging, as is pricing. The actual cost of a unit of service is hard to determine and the price-quality relationship is complex. Heterogeneity: Because services are performances, frequently produced by humans, no 2 services will be precisely alike. Heterogeneity also results because no two customers are precisely alike; each will have unique demands or experience the service in a unique way. Thus, the heterogeneity connected with services is largely the result of human interaction (between and among employees and customers) and all of the vagaries that accompany it. E.g. a tax accountant may provide a different service experience to two different customers on the same day depending upon their personal needs and personalities. Because services are heterogeneous across time, organizations and people, ensuring consistent service quality is important. Quality actually
More Notes and Projects and Resources for BMS and MBA students available at http://www.ManagementParadise.com : The TRUE Voice of Management Students
For ManagementParadise.com By ex-TYBMS students.
depends on many factors that cannot be fully controlled by the service supplier, such as ability of consumer to articulate his needs, willingness & ability of the personnel to satisfy those needs, presence of other consumers and level of demand for the service. Simultaneous production and consumption Whereas most goods are produced first, then sold and consumed, most services are sold first and then produced and consumed simultaneously. For example, an automobile can be manufactured in Detroit, shipped to San Francisco, sold 2 months later and consumed over a period of years. But restaurant services cannot be provided until they have been sold, and the dining experience is essentially produced and consumed at the same time. This means that the customer is present while the service is being produced and thus his views are taken in the production process. Because services are often produced and consumed at the same time, mass production is difficult. The quality of service and customer satisfaction depends on the real time including actions of employees and interaction between employees and customers. It is not possible to gain economies of scale through centralization. If the services are decentralized they can be delivered to the consumer in convenient locations. As the customer is part of the production process, they affect the outcome of the service. A problem employee can cause problems for themselves and for others in the service setting leading to lower level satisfaction. E.g. in a restaurant setting, an over demanding and intoxicated customer will command extra attention of service provider and negatively impact the experiences of other customers. Perishability: Refers to the fact that services cannot be saved, stored, resold or returned. A seat on an airplane or restaurant not used cannot be reclaimed or used or resold at a later time. Due to this nature a service cannot be inventoried. Demand forecasting and creative planning for capacity utilization are therefore important. Since services cannot typically be returned or resold it implies strong recovery strategies when things go wrong. E.g. a bad haircut cannot be returned,
More Notes and Projects and Resources for BMS and MBA students available at http://www.ManagementParadise.com : The TRUE Voice of Management Students
For ManagementParadise.com By ex-TYBMS students.
the customer should have strategies to recover the customers good will if and when such problems occur
More Notes and Projects and Resources for BMS and MBA students available at http://www.ManagementParadise.com : The TRUE Voice of Management Students
For ManagementParadise.com By ex-TYBMS students.
Classification of services: There are a number of ways in which services can be classified. Some of them are mentioned here. 1. On the basis of the END USER the services can be classified into following categories: Consumer : leisure, hairdressing, personal finance and package holidays Business to Business: advertising agencies, printing, accountancy, Consultancy Industrial: Plant Maintenance and repair and hygiene, installation and project management. 2. The DEGREE OF TANGIBILITY can be used to classify a service. Highly tangible: car rental, vending machines, telecommunications Service linked to tangible goods: domestic appliance repair, car service. Highly tangible: psychotherapy, Consultancy, legal services. 3. Services can be broken down into LABOR INTENSIVE (PEOPLE based) and EQUIPMENT based services. This can also be represented by degree of contact. People based services: high contact : education, dental care, restaurants and medical services Equipment based: low contact: automatic car wash, launderette, vending machine, cinema. 4. The EXPERTISE and SKILLS of the service provider can be broken down into the following categories: Professional: medical services, legal services, accountancy, tutoring. Non Professional: baby sitting, care taking, and casual labor. 5. The overall BUSINESS ORIENTATION ( PROFIT) is a recognized means of classifications:
More Notes and Projects and Resources for BMS and MBA students available at http://www.ManagementParadise.com : The TRUE Voice of Management Students
For ManagementParadise.com By ex-TYBMS students.
Not for profit: The Scouts Association, charities, and public sector leisure facilities. Commercial: banks, airlines, tour operators, hotel and catering services Christopher Lovelock gives another classification of services based on the customer involvement in production process: People processing: tangible actions to peoples bodies, such as airline transportation, haircutting and surgery. Customers need to be physically present throughout service delivery in order to receive the desired benefits of such services. It is important to figure the process and output to identify the benefits created. Also some non- financial costs are to be identified such as time, mental and physical effort and even tear and pain that customers incur in obtaining these benefits. Possession Processing: Tangible actions to goods and other physical possessions, such as air freight, lawn mowing, and janitorial services. In these instances, the object requiring processing must be present, but the customer need not be. Mental Stimulus Processing: intangible actions directed at peoples mind, such as broadcasting and education. In this instance the customers must be present mentally but can be located either in specific service facility or in a remote location connected by broadcast signals or telecommunication linkages. Services that interact with peoples mind have the power to shape attitudes and influence behavior. So when the customer is in a position of dependency or there is a potential for manipulation, strong ethical standards and careful oversight is required. This type of service can easily be converted to digital bits or analog signals, recorded for prosperity, and transformed into a manufactured product, such as a compact disc, videotape, or audio cassette, which may then be packaged and marketed much like any other physical good Information Processing: Intangible actions directed at intangible assets, such as insurance, investment banking, and Consulting. For these
More Notes and Projects and Resources for BMS and MBA students available at http://www.ManagementParadise.com : The TRUE Voice of Management Students
For ManagementParadise.com By ex-TYBMS students.
services, no direct involvement with the customer may be needed, once the request for the service is initiated. Services highly dependent on effective collection and processing of information include financial services, accounting, and law, marketing research, management consulting, medical diagnosis and a variety of other professional services. Tradition and a personal desire to meet the supplier than often determine the extent of customer involvement in such services more by the needs of operation process.
More Notes and Projects and Resources for BMS and MBA students available at http://www.ManagementParadise.com : The TRUE Voice of Management Students
For ManagementParadise.com By ex-TYBMS students.
Reasons for growth in the service sector: Households as well as firms are demanding more services as well as services of increasing quality and sophistication. There are number of reasons for this growth in the service sector as mentioned below: Greater affluence: With the increasing affluence of people resulting from the growth of economies there has been a greater desire for Quality life. Consumers are willing to spend more on leisure resulting in greater demand for recreation and entertainment facilities, tourist resorts and other hospitality services. Also, there has been a tendency on externalization of services production from households to the formal economy. Demand for services like interior decoration, laundry, care of household products etc. has increased which consumers used to perform themselves earlier. Also, with increased incomes, there has been a greater demand for financial services. Working women: As more and more women have started working, the time has become most scarce commodity in family life. This has led to more demand for crches, baby sitting, household domestic help etc. Further, working women and the resulting two income households have created greater demand for, certain services like retailing, real estate and personal finance services Greater life expectancy: The economic growth and increasing standard of living have also resulted in the greater life expectancy and there by an expanding old age population. Thus there is an increased need for services like old age homes, nursing homes, healthcare centers, etc. Greater complexity of products: With rapid development in technology, the consumer today uses a lot of complex products in his day to day life. Thus there is a greater demand for specialists who provide maintenance and upkeep of such products like cars, home computers, household appliances etc.
More Notes and Projects and Resources for BMS and MBA students available at http://www.ManagementParadise.com : The TRUE Voice of Management Students
For ManagementParadise.com By ex-TYBMS students.
Increased complexity of life: The greater complexity of life has created demand for a wide range of services, especially legal and financial advice. The number of specialists in income tax, labor laws, legal affairs, marriage counseling, employment services etc. has been increasing. Globalization Globalization of economies has led to an increased demand of communication, travel and information services. Also there has been an increased and new demand on legal and other professional services. While the role of agriculture gas been reducing in the economies of industrial societies, that of service sector ahs been increasing at a fast pace. Thus, as the economies shift from developing to developed economies the, they show more and more shift towards services.
More Notes and Projects and Resources for BMS and MBA students available at http://www.ManagementParadise.com : The TRUE Voice of Management Students
For ManagementParadise.com By ex-TYBMS students.
For a market offer, which is primarily intangible, managing quality is a major issue. In the manufacturing sector, quality is a major issue. In the manufacturing sector, the quality of a physical product can be checked before it is taken to the market. However, in case of service organizations, the quality is more of perception of the intangible market offer. Service quality is a subjective assessment that the customers arrive at by comparing the service level they believe an organization ought to deliver to the service level they perceive is being delivered. Therefore, to compete successfully, service firms must develop quality to their service. This service quality is measured on two levels: Technical Quality: The overall efficiency with which a bank handles its customer accounts in terms of prompt statements, rate of interest offered and so on. Functional Quality: the way the service is actually delivered; this includes personal courtesy, the service environment in terms of comfort and dcor, the customers own role (are there long queues, are pens and forms provided to make the entire transaction simpler?) However, functional quality is the more important aspect of perceived service than technical quality. Therefore, essence of effectiveness in managing services lies in improving the functional quality of a firms service by managing the buyer-seller interaction (interactive marketing) as compared to traditional marketing activities. Managing the perceived quality of a service means that one has to match the expected service and the perceived service to each other so that consumer satisfaction is achieved. To keep the gap between expected & perceived service minimal, two things are critical. First the promises about how the service will perform must not be unrealistic when compared to the service the customer will eventually perceive. Secondly it is necessary to understand how the technical & functional quality of a service is influenced and how the consumers perceive these quality dimensions. Consumers quality perceptions are influenced by a series of five distinct gaps occurring in organizations:
More Notes and Projects and Resources for BMS and MBA students available at http://www.ManagementParadise.com : The TRUE Voice of Management Students
For ManagementParadise.com By ex-TYBMS students.
Gap1: difference between consumer expectations and management expectation of consumer expectations. Gap2: difference between management perception of consumer expectations and service quality specifications. Gap3: difference between service quality specifications and service actually delivered. Gap4: difference between service delivery and what is communicated about the service to consumers. Gap5: difference between the perceived service and expected service. This gap depends on the size and direction of the first four gaps associated with the delivery of service quality. The service quality can be measured on the following five dimensions which also help you close the above 5 quality gaps: Reliability: the ability to perform the promised service dependably and accurately. Tangibles: the appearance of physical facilities equipment, personnel and communication materials. Responsiveness: the willingness to help the customers and provide prompt service Assurance: the knowledge and courtesy of the employees and their ability to convey trust and confidence. Empathy: the caring, individualized attention provided to the customer.
More Notes and Projects and Resources for BMS and MBA students available at http://www.ManagementParadise.com : The TRUE Voice of Management Students
For ManagementParadise.com By ex-TYBMS students.
Productivity is defined as the ratio of the output of a production process to an aggregate value of inputs. This concept of productivity involves around two basic assumptions. First, the factors of output are perfectly defined so that they can be measured and second, the utility of output is not questioned. Cowell has suggested ways for improving productivity which include improving staff performance through training, introduction of technology into the system, reducing service levels, substituting products for services, using customers in service production and reducing the mismatch between supply and demand. Improving Staff Performance through training: The staff in contact with the customers provides a visible element of the service. They should be trained to provide better service not only through hard work but also with skills this would result better productivity and also higher customer satisfaction. Introducing Systems and Technology: For industrialization of services, technology can be applied in three ways. First, is the hard technology, which implies substituting machinery for people (e.g. airport surveillance of baggage with X-ray equipment)? The second called the soft technology, which implies substituting preprogrammed systems for individual service operations. (E.g., fast food operations). The third, hybrid technology that implies combining the above two, i.e., equipment with planned systems to gain greater order, speed and efficiency. Parsuraman created a three-stage model of external, internal and interactive marketing where introduction of technology as a service delivery option adds a whole new dimension. By putting existing technologies, labor force and capital stock into work, the productivity growth rate can be increased considerably. Reducing Service Levels: Productivity can be reduced by reducing the quality of the service (E.g., a doctor can give less time to a patient and the preliminary investigations or history can be documented by a junior doctor). A proper balance should be maintained between quality and quality of service delivered.
More Notes and Projects and Resources for BMS and MBA students available at http://www.ManagementParadise.com : The TRUE Voice of Management Students
For ManagementParadise.com By ex-TYBMS students.
Substituting Products for Services or Adding New Services One can increase productivity by increasing the number of services. For example, Department of post introduced courier service and followed by introducing the non- document courier service thus adding to their services. A hotel can add parties and marriages to their banquet services to introduce productivity. Customer Interaction: Involving the customer in the service delivery process in the place of your own employees can enhance the productivity. E.g., a self-service restaurant. However consumers can constraint and can become a barrier to productivity. Therefore productivity related changes must be identified and implemented from the consumers viewpoint. The customer insensitivity can be avoided by: First, by developing customer trust in the productivity related changes through a systematic and planned communication program. Second, understanding customer habits and determinants of consumer behavior. Third, pre-testing new procedures and technology before commercially introducing the same. Fourth, educating customers about how to use innovations. Productivity improvement is not a static process but a dynamic, which occurs over time. Therefore it is necessary to monitor and evaluate performance periodically. Reduce Mismatch between Supply and Demand The concept of Sycro-marketing is used to manage demand and supply. Sasser suggested some basic to alter demand so as to fit it within the available capacity. In such situations where capacity is restricted, the four strategic options are as follows: 1. 2. 3. 4. Developing off peak pricing schemes Non peak promotion and demand creation Developing complementary services Creation of reservation system
More Notes and Projects and Resources for BMS and MBA students available at http://www.ManagementParadise.com : The TRUE Voice of Management Students
For ManagementParadise.com By ex-TYBMS students.
Developing off peak pricing schemes will help in shifting the demand from peak periods to non-peak periods. Resorts and hotels offer off-season packages to shift demand from peak to non- peak seasons. Developing complementary or facilitating services not only attracts customers away from bottle neck operations at peak times but might also provide an alternative service while they are in queue for capacity related operations. For e.g. at a casino, a lounge with wide screen television or a bar will shift some tourists from restricted capacity service operations. Such a strategy wouldnt only give additional value but also an opportunity to differentiate the service offer from the competitors. The reservation strategy would also help in managing demand and thus, customer satisfaction e.g. reservation of cinema tickets in advance. Managing capacity and controlling the supply side can be done in the following manner: Using part time employees: Employing part time employees is one of the solutions to increase capacity. At a resort hotel, local students are engaged at peak seasons to cater to the customers. Increasing efficiency of existing personnel involving customers: Training can increase the efficiency of an employee. By training the staff in multiple functions, most employees can be engaged in essential tasks of delivering the service during peak hours and the support tasks are deferred to slack periods The third method is that consumers participate in delivery of service and, thereby, lower labor requirements of the producer. E.g. .Self service restaurant The fourth method is that of sharing capacity with others rather than creating capacity in-house. E.g. Restaurants are selling branded ice creams rather than investing in ice cream making facilities in- house. Lastly the capacity can be increased by investing in expansions so as to cater to the increase in demand.
More Notes and Projects and Resources for BMS and MBA students available at http://www.ManagementParadise.com : The TRUE Voice of Management Students
For ManagementParadise.com By ex-TYBMS students.
Although productivity will result in better profitability, quality should not be affected. A proper balance has to be maintained between productivity, standardized quality and customers
More Notes and Projects and Resources for BMS and MBA students available at http://www.ManagementParadise.com : The TRUE Voice of Management Students
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Consumerdecisionmakingandbeyond 110214023948 Phpapp01Document18 paginiConsumerdecisionmakingandbeyond 110214023948 Phpapp01Gosai JaydeepÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trainingdevelopment 130117130211 Phpapp01Document12 paginiTrainingdevelopment 130117130211 Phpapp01Gosai JaydeepÎncă nu există evaluări
- Customer Value Scale Development: Merchandise and Differentiation ValueDocument7 paginiCustomer Value Scale Development: Merchandise and Differentiation ValueGosai JaydeepÎncă nu există evaluări
- Economic Planning in IndiaDocument23 paginiEconomic Planning in IndiaGosai JaydeepÎncă nu există evaluări
- Market ResearchDocument25 paginiMarket ResearchPriyanka ChaudharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summer Project KPTLDocument89 paginiSummer Project KPTLGosai JaydeepÎncă nu există evaluări
- Monopolies & Restrictive Trade Practices Act, 1969Document32 paginiMonopolies & Restrictive Trade Practices Act, 1969Gosai JaydeepÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1101 Customer Satisfaction GuideDocument40 pagini1101 Customer Satisfaction GuideGosai JaydeepÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 15Document25 paginiUnit 15Gosai JaydeepÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1101 Customer Satisfaction GuideDocument40 pagini1101 Customer Satisfaction GuideGosai JaydeepÎncă nu există evaluări
- Retailing, Direct Marketing & Integrated Marketing CommunicationsDocument20 paginiRetailing, Direct Marketing & Integrated Marketing CommunicationsGosai JaydeepÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chocolate Bloom - A Thing of The Past - tcm39-6253Document2 paginiChocolate Bloom - A Thing of The Past - tcm39-6253Gosai JaydeepÎncă nu există evaluări
- Taj Hotel ProjectDocument51 paginiTaj Hotel ProjectGosai Jaydeep67% (3)
- 8 Impact of Training and Development On Organizational PerformanceDocument7 pagini8 Impact of Training and Development On Organizational PerformanceHelen GabrielÎncă nu există evaluări
- If Undelivered, Please Return ToDocument4 paginiIf Undelivered, Please Return ToGosai JaydeepÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hero Honda Project by Robin & Group.Document24 paginiHero Honda Project by Robin & Group.Gosai JaydeepÎncă nu există evaluări
- Percived Quality, Purchase Intension..Document10 paginiPercived Quality, Purchase Intension..Gosai JaydeepÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHP 3B-Recruitment & SelectionDocument25 paginiCHP 3B-Recruitment & SelectionRajnita ChakrabortyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nature of Training and DevelopmentDocument47 paginiNature of Training and DevelopmentGosai JaydeepÎncă nu există evaluări
- Identification of Training NeedsDocument92 paginiIdentification of Training Needsmakaranddharkar0% (1)
- Final Report On IPO-654Document35 paginiFinal Report On IPO-654Gosai JaydeepÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tata Still HR ProjectDocument39 paginiTata Still HR ProjectGosai JaydeepÎncă nu există evaluări
- KSA Reliance ReportDocument30 paginiKSA Reliance ReportCrispy BetelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ibm ManagementDocument8 paginiIbm ManagementGosai JaydeepÎncă nu există evaluări
- IPCL Project ReportDocument98 paginiIPCL Project ReportGosai Jaydeep100% (1)
- Confilict ManagementDocument15 paginiConfilict Managementprincy8925Încă nu există evaluări
- Pizza HutDocument34 paginiPizza HutGosai JaydeepÎncă nu există evaluări
- IPCL Project ReportDocument98 paginiIPCL Project ReportGosai Jaydeep100% (1)
- All About DHL Logistics - Live ProjectDocument39 paginiAll About DHL Logistics - Live ProjectMihir Thakkar85% (26)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5782)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (72)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Types of Sentence: 1. Simple SentencesDocument2 paginiTypes of Sentence: 1. Simple SentencesRahmat HaryadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- OBE Syllabus Template - Intro To Educational Research - 1st Sem 2018-2019 - NewDocument12 paginiOBE Syllabus Template - Intro To Educational Research - 1st Sem 2018-2019 - NewDorinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PPSC Assistant Architect Question Paper 2016Document15 paginiPPSC Assistant Architect Question Paper 2016Akash Jaglan100% (1)
- Artificial Intelligence and Law OverviewDocument2 paginiArtificial Intelligence and Law Overviewdevika mcaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CGC1D Final Exam Review QuestionsDocument3 paginiCGC1D Final Exam Review QuestionsYehia El Manawaty100% (2)
- Ken Dyne - BairnDocument272 paginiKen Dyne - Bairnsebastien dimirdjian100% (5)
- Mandatory Minimum SentencingDocument10 paginiMandatory Minimum Sentencingapi-302985199Încă nu există evaluări
- SaponificationDocument10 paginiSaponificationAnshika SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yd37746 Perkins Spare PartDocument185 paginiYd37746 Perkins Spare PartLeyla Yılmaz100% (2)
- Night College Program: Financial ManagementDocument75 paginiNight College Program: Financial ManagementMike Cabrales100% (1)
- Jim Rohn's QuotesDocument68 paginiJim Rohn's QuotesĐương NguyễnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sriman NarayaneeyamDocument280 paginiSriman NarayaneeyamSharma Joshi100% (1)
- Zingerman's News Issue #223, November-December 2010Document15 paginiZingerman's News Issue #223, November-December 2010Zingerman's Community of BusinessesÎncă nu există evaluări
- AspenONE Engineering Cloud V12 Using Windows Virtual DesktopDocument22 paginiAspenONE Engineering Cloud V12 Using Windows Virtual DesktopKARLA VALERIA MENDOZA JIMENEZÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1ice 120SDocument2 pagini1ice 120Sendimarc.cuicasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Output in Intermediate Accounting Problems on Shareholders' EquityDocument15 paginiFinal Output in Intermediate Accounting Problems on Shareholders' Equityennaira 06Încă nu există evaluări
- Sholawat Diba, Simtud DhurorDocument12 paginiSholawat Diba, Simtud DhurorMaulana MudrikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scope of Work gasGDUDocument24 paginiScope of Work gasGDUvienergresourcesÎncă nu există evaluări
- XXX Marketing StrategyDocument9 paginiXXX Marketing StrategyJoel MitchellÎncă nu există evaluări
- DCBAC Testmony of Ellen JonesDocument4 paginiDCBAC Testmony of Ellen JonesD.C. Bicycle Advisory CouncilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kabbalah For Complete Life ManagementDocument177 paginiKabbalah For Complete Life ManagementRudy Tombeng Lopez100% (2)
- Central Hindu School Class 6th Exam: Model Paper SetDocument13 paginiCentral Hindu School Class 6th Exam: Model Paper SetVikas ChaudharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ebismen - NenengDocument14 paginiEbismen - NenengANDRA ABDURAHMANÎncă nu există evaluări
- MV SSI BRILLIANT Daily Report 04 - 12.11.2023Document16 paginiMV SSI BRILLIANT Daily Report 04 - 12.11.2023DanielÎncă nu există evaluări
- Powerpoint PBL 2Document13 paginiPowerpoint PBL 2tariqÎncă nu există evaluări
- CBT TestDocument18 paginiCBT TestJulieBarrieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mortification of The Mind and The WillDocument3 paginiMortification of The Mind and The WillvinformationÎncă nu există evaluări
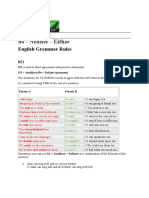
- English Grammar Rules: SO, NEITHER, EITHERDocument2 paginiEnglish Grammar Rules: SO, NEITHER, EITHERAlex BrunoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tl642 Cat Services Manual TelehandlerDocument197 paginiTl642 Cat Services Manual TelehandlerRoxana Elizabeth Valencia NavarrteÎncă nu există evaluări
- INTRO TO PNEUMATICDocument10 paginiINTRO TO PNEUMATICMuhamad HaziqÎncă nu există evaluări