Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Angles in Trigonometry - Angle PDF
Încărcat de
Erick AbarientosTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Angles in Trigonometry - Angle PDF
Încărcat de
Erick AbarientosDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
http://www.analyzemath.com/Trigonometry.html http://www.analyzemath.com/trigonometry_worksheets.
html
Angles In Trigonometry
This large window applet helps you understand the definition and properties of an angle in standard position. It can also be used to understand the concept of coterminal angles. Interactive Tutorial Two ways to investigate angle interactively. 1) An html5 applet on Angles in Standard Position. 2) and a java applet below
click on the button above "click here to start" and MAXIMIZE the window obtained. Type in any angle (in degrees, negative or positive) then click on start. coterminal angles : Type in the following angles: 390 degrees, 30 degrees, -330 degrees. Each time note the position of the terminal side. Do these angles have the same terminal side? Why?
More references on angles.
Angles in trigonometry. Find the coterminal angle Trigonometry calculator. Find The Reference Angle Trigonometry calculator.
http://www.analyzemath.com/Trigonometry.html http://www.analyzemath.com/trigonometry_worksheets.html
Find the Quadrant of an Angle Trigonometry calculator.
http://www.analyzemath.com/Trigonometry.html http://www.analyzemath.com/trigonometry_worksheets.html
http://www.analyzemath.com/Trigonometry.html http://www.analyzemath.com/trigonometry_worksheets.html
Find Coterminal Angles
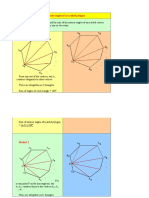
Find coterminal angles Ac to a given angle A. What are coterminal angles? If you graph angles x = 30o and y = - 330o in standard position, these angles will have the same terminal side. See figure below.
Coterminal angles Ac to angle A may be obtained by adding or subtracting k*360 degrees or k* (2 Pi). Hence Ac = A + k*360o if A is given in degrees. or Ac = A + k*(2 PI) if A is given in radians. where k is any negative or positive integer. Example 1: Find a positive and a negative coterminal angles to angle A = -200o Solution to example 1: There is an infinite number of possible ansers to the above question since k in the formula for coterminal angles is any positive or negative integer. A positive coterminal angle to angle A may
http://www.analyzemath.com/Trigonometry.html http://www.analyzemath.com/trigonometry_worksheets.html
be obtained by adding 360o, 2(360)o = 720o (or any other positive angle multiple of 360o). A positive coterminal angle Ac may be given by Ac = -200o + 360o = 160o A negative coterminal angle to angle A may be obtained by adding -360o, -2(360)o = 720o (or any other negative angle multiple of 360o). A negative coterminal angle Ac may be given by Ac = -200o - 360o = -560o Example 2: Find a coterminal angle Ac to angle A = - 17 Pi / 3 such that Ac is greater than or equal to 0 and smaller than 2 Pi Solution to example 2: A positive coterminal angle to angle A may be obtained by adding 2 Pi, 2(2 Pi) = 4 Pi (or any other positive angle multiple of 2 Pi). A positive coterminal angle Ac may be given by Ac = - 17 Pi / 3 + 2 Pi = -11 Pi / 3 As you can see adding 2*Pi is not enough to obtain a positive coterminal angle and we need to add a larger angle but what is the size of the angle to add?. We need to write our negative angle in the form - n (2 Pi) - x, where n is positive integer and x is a positive angle such that x < 2 pi. - 17 Pi /3 = - 12 Pi / 3 - 5 Pi / 3 = - 2 (2 Pi) 5 Pi / 3 From the above we can deduce that to make our angle positive, we need to add 3(2*Pi) = 6 Pi Ac = - 17 Pi /3 + 6 Pi = Pi / 3
http://www.analyzemath.com/Trigonometry.html http://www.analyzemath.com/trigonometry_worksheets.html
Example 3: Find a coterminal angle Ac to angle A = 35 Pi / 4 such that Ac is greater than or equal to 0 and smaller than 2 Pi Solution to example 3: We will use a similar method to that used in example 2 above: First rewrite angle A in the form n(2Pi) + x so that we can "see" what angle to add. A = 35 Pi / 4 = 32 Pi / 4 + 3 Pi / 4 = 4(2 Pi) + 3 Pi /4 From the above we can deduce that to make our angle smaller than 2 Pi we need to add - 4(2Pi) = - 8 Pi to angle A Ac = 35 Pi / 4 - 8 pi = 3 Pi /4 Exercises: (see solutions below) 1. Find a positive coterminal angle smaller than 360o to angles a) A = -700o , b) B = 940o 2. Find a positive coterminal angle smaller than 2 Pi to angles a) A = - 29 Pi / 6 , b) B = 47 Pi / 4 Solutions to Above Exercises: 1. a) Ac = 20o , b) Bc = 220o 2. Find a positive coterminal angle smaller than 2 Pi to angles a) Ac = 7 Pi / 6 , b) Bc = 7 Pi / 4
http://www.analyzemath.com/Trigonometry.html http://www.analyzemath.com/trigonometry_worksheets.html
More references on angles.
Angles in trigonometry. Find the coterminal angle Trigonometry calculator. Find The Reference Angle Trigonometry calculator. Find the Quadrant of an Angle Trigonometry calculator.
http://www.analyzemath.com/Trigonometry.html http://www.analyzemath.com/trigonometry_worksheets.html
Find Reference Angle
Find reference angle Ar to a given angle A. What is the reference angle to an angle in standard position? If A is an angle in standard positon, its reference angle Ar is the acute angle formed by the x axis and the terminal side of angle A. See figure below.
Two or more coterminal angles have the same reference angle. Assume angle A is postive and less than 360 o (2Pi), we have 4 possible cases: 1. If angle A is in quadrant I then the reference angle A r = A. 2. If angle A is in quadrant II then the reference angle A r = 180 o - A if A is given degrees and A r = Pi - A if A is given in radians. 3. If angle A is in quadrant III then the reference
http://www.analyzemath.com/Trigonometry.html http://www.analyzemath.com/trigonometry_worksheets.html
angle A r = A - 180 o if A is given degrees and A r = A - Pi if A is given in radians. 4. If angle A is in quadrant IV then the reference angle A r = 360 o - A if A is given degrees and A r = 2Pi - A if A is given in radians. Example 1: Find the reference angle to angle A = 120 o. Solution to example 1: Angle A is in quadrant II and the reference angle is given by A r = 180o - 120o = 60o Example 2: Find the reference to angle A = - 15 Pi / 4. Solution to example 2: The given angle is not positive and less than 2Pi. We can use the positive and less than 2Pi coterminal Ac to angle A. Ac = - 15 Pi / 4 + 2 (2 Pi) = Pi / 4 Angle A and Ac are coterminal and have the same reference angle. Ac is in quadrant I, therefore A r = A c = Pi / 4 Example 3: Find the reference angle to angle A = - 30 o Solution to example 3: Angle A is negative, in quadrant IV and its absolute value is less than 90 o. Hence
http://www.analyzemath.com/Trigonometry.html http://www.analyzemath.com/trigonometry_worksheets.html
A r = | -30 o | = 30 o Exercises:Find the reference angle to angles 1. A = 1620o 2. A = - 29 Pi / 6 3. A = - Pi / 7 Solutions to Above Exercises: 1. A r = 25o 2. A r = Pi / 6 3. A r = Pi / 7
More references on angles.
Angles in trigonometry. Find The Reference Angle - Trigonometry calculator. Find the coterminal angle - Trigonometry calculator. Find the Quadrant of an Angle Trigonometry calculator.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Pure Math 30 - Trigonometry Lesson 1Document8 paginiPure Math 30 - Trigonometry Lesson 1josephmwÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 - Angle in Standard Position and The Six Trigonometric FunctionsDocument55 paginiChapter 1 - Angle in Standard Position and The Six Trigonometric Functionsjesscorpuzblando050101Încă nu există evaluări
- CH 4 NotesDocument15 paginiCH 4 NotesMarina XuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trigonometry PresentationDocument55 paginiTrigonometry PresentationNazir PriceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coordinate Geometry Fundamentals 2012Document60 paginiCoordinate Geometry Fundamentals 2012Taqi ZaidiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math 2: Lazaro, Mark Vincent J. BS CriminologyDocument13 paginiMath 2: Lazaro, Mark Vincent J. BS CriminologyArrojo Rhiane Hilary MaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 1 - Angle in Standard Position and The Six Trigonometric Functions-CombinedDocument185 paginiLesson 1 - Angle in Standard Position and The Six Trigonometric Functions-CombinedSharmaine TuliaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 1 - Angle in Standard Position and The Six Trigonometric FunctionsDocument51 paginiLesson 1 - Angle in Standard Position and The Six Trigonometric FunctionsSharmaine TuliaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Further TrigonometryDocument71 paginiFurther TrigonometryCarl Agape DavisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 9 Study GuideDocument21 paginiUnit 9 Study Guideapi-241102240Încă nu există evaluări
- 3 - Trigonometric FunctionsDocument26 pagini3 - Trigonometric FunctionsZamanoden D. UndaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 2 - Acute Angle & Right TriangleDocument60 paginiLesson 2 - Acute Angle & Right TriangleSharmaine TuliaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math30-1 Workbook TwoDocument230 paginiMath30-1 Workbook Twodeepteck000Încă nu există evaluări
- Angles and Trig WorksheetDocument13 paginiAngles and Trig WorksheetJanet Garrett0% (1)
- Module in Mathematics 03: TrigonometryDocument21 paginiModule in Mathematics 03: TrigonometryRene Jay-ar Morante SegundoÎncă nu există evaluări
- TRIGONOMETRYDocument8 paginiTRIGONOMETRYurfriend_jjn05100% (1)
- The Sine and Cosine RuleDocument69 paginiThe Sine and Cosine RuleCarl Agape Davis100% (1)
- Gcse Geometry Angles Property ExerciseDocument9 paginiGcse Geometry Angles Property ExerciseGodfred WelbeckÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sum of Interior Angles of An NDocument13 paginiSum of Interior Angles of An Nமாதவன் மகேஸ்வரிÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit Circle PowerpointDocument44 paginiUnit Circle Powerpointboostoberoi100% (1)
- Circle TheoremsDocument15 paginiCircle TheoremsAyesha NoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 16Document51 paginiCH 16iwouldwishforyouÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class 8 - Maths - Understanding Quadrilaterals PDFDocument32 paginiClass 8 - Maths - Understanding Quadrilaterals PDFAnand MekalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Write Up of All Angle RulesDocument6 paginiWrite Up of All Angle Rulesapi-233663523100% (1)
- 7.4 Trigonometric Functions of General Angles-Fall 2020Document10 pagini7.4 Trigonometric Functions of General Angles-Fall 2020ali alqahtaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review in Plane TrigonometryDocument51 paginiReview in Plane TrigonometryDoone Heart Santander CabuguasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trigonometric Function of Any Angle 1205193741318798 2Document11 paginiTrigonometric Function of Any Angle 1205193741318798 2jayanthnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Las Math9 Q4 W5Document12 paginiLas Math9 Q4 W5Maxene Angelie RabanalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pimsat CollegesDocument24 paginiPimsat CollegesAnne PadillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application of Geometry and TrigonometryDocument70 paginiApplication of Geometry and Trigonometrybealu0312100% (3)
- 6) C2 Radian Measure and Its ApplicationsDocument21 pagini6) C2 Radian Measure and Its ApplicationsIbrahim ElbeharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- And AnglesDocument19 paginiAnd AnglesJeevithra RobertÎncă nu există evaluări
- Triginometry by Abhishek Jain For SSC ExamsDocument35 paginiTriginometry by Abhishek Jain For SSC ExamsStudy IQ100% (3)
- Mr. Yates: 270° Coordinates: (,) 105° Coordinates: (,) A Graph: B GraphDocument3 paginiMr. Yates: 270° Coordinates: (,) 105° Coordinates: (,) A Graph: B GraphNicholas YatesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trigonometric FunctionsDocument25 paginiTrigonometric FunctionsMichelle EmmertÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trigonometry: Measurement of AnglesDocument57 paginiTrigonometry: Measurement of AnglesLeo V. Baker100% (2)
- Lect1 IntroToAnglesDocument18 paginiLect1 IntroToAnglesWapaya JacobÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pre Calculus TrigonometryDocument77 paginiPre Calculus TrigonometryTeacher JasonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geometry Formula Book 02Document22 paginiGeometry Formula Book 02Aditya ModaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amc8 V5Document181 paginiAmc8 V5Shuai ChenÎncă nu există evaluări
- GeometryDocument62 paginiGeometryRamana ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Angles - Exam Revision and QuestionsDocument11 paginiAngles - Exam Revision and QuestionsShah Hasan FarazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Appendix B: Geometry Facts and TheoremsDocument0 paginiAppendix B: Geometry Facts and TheoremsVķ MãħëšħÎncă nu există evaluări
- Captura de Pantalla 2022-09-25 A La(s) 11.10.37 P.M.Document1 paginăCaptura de Pantalla 2022-09-25 A La(s) 11.10.37 P.M.perlaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 4 Applications Trigonometry To TrianglesDocument12 pagini4 4 Applications Trigonometry To Trianglessonicdan1234Încă nu există evaluări
- Pure ch10Document0 paginiPure ch10Singh SudipÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4.7 Solutions of Triangles PDFDocument5 paginiChapter 4.7 Solutions of Triangles PDFjiiÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHYSICS M1 - With AnswerDocument9 paginiPHYSICS M1 - With AnswerayalarolenzÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5.4 Trig Ratios Between 0 and 360Document5 pagini5.4 Trig Ratios Between 0 and 360Brady CousinsÎncă nu există evaluări
- MAJ 3 - Handout 2Document12 paginiMAJ 3 - Handout 2Annalie LobianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- BSED MATH 3 Plane Trigo Module 2 1Document15 paginiBSED MATH 3 Plane Trigo Module 2 1Jhanes Kent FatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Precal ModuleeeeeeeDocument18 paginiPrecal ModuleeeeeeeCaila AlfonsoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math 17 4.7Document25 paginiMath 17 4.7jiiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 5 TrigonometryDocument0 paginiModule 5 TrigonometryManish MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- TrigonometryDocument20 paginiTrigonometryTan Wei Quan67% (3)
- Mathematical Analysis 1: theory and solved exercisesDe la EverandMathematical Analysis 1: theory and solved exercisesEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Phobio 2Document21 paginiPhobio 2Erick AbarientosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Specification Requirements and Environmental Performance of Portland-Limestone CementsDocument18 paginiSpecification Requirements and Environmental Performance of Portland-Limestone CementsErick AbarientosÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIR Form 2316Document1 paginăBIR Form 2316edz_ramirez87% (15)
- Program of TopicsDocument2 paginiProgram of TopicsErick AbarientosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Materials Engineer ReviewDocument1 paginăMaterials Engineer ReviewRamilArtatesÎncă nu există evaluări
- 13 Melander-AASHTO M240 - ASTM C595 PDFDocument0 pagini13 Melander-AASHTO M240 - ASTM C595 PDFErick AbarientosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mentor'S Profile: I. Personal DataDocument4 paginiMentor'S Profile: I. Personal DataErick AbarientosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asphalt Cutback Mc30, 70, 250, 500, 800, 3000 - Gibson Energy LimitedDocument11 paginiAsphalt Cutback Mc30, 70, 250, 500, 800, 3000 - Gibson Energy LimitedErick AbarientosÎncă nu există evaluări
- RA 1378 - Master Plumber LawDocument5 paginiRA 1378 - Master Plumber LawFzoe YambaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Board of Interior Design-SB PDFDocument5 paginiBoard of Interior Design-SB PDFErick AbarientosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Board of Interior Design-SB PDFDocument5 paginiBoard of Interior Design-SB PDFErick AbarientosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Resolution No.16, Series of 1995, Syllabi For ME and CPM Licensure ExaminationDocument8 paginiResolution No.16, Series of 1995, Syllabi For ME and CPM Licensure ExaminationzampacaanasÎncă nu există evaluări
- R.A. 7920Document21 paginiR.A. 7920Jezreel P. ImportanteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Board of Architecture-SBDocument8 paginiBoard of Architecture-SBarki_clintÎncă nu există evaluări
- Board of Chemical Engineering-SB PDFDocument5 paginiBoard of Chemical Engineering-SB PDFErick AbarientosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Roll of Successful Examinees in TheDocument1 paginăRoll of Successful Examinees in TheErick AbarientosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Board of Chemical Engineering-CE PDFDocument5 paginiBoard of Chemical Engineering-CE PDFErick AbarientosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Board of Electrical Engineering-SB PDFDocument2 paginiBoard of Electrical Engineering-SB PDFErick AbarientosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Board of Electrical Engineering-Code of EthicDocument2 paginiBoard of Electrical Engineering-Code of Ethicraul_bsuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Board of Chemical Engineering-CE PDFDocument5 paginiBoard of Chemical Engineering-CE PDFErick AbarientosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sanitary Engineer List of Passers 2013Document4 paginiSanitary Engineer List of Passers 2013Erick AbarientosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sanitary Engineer Board Exam Topnotchers (Top 10 Passers) Sanitary Engineer Top Performing Schools and Performance of SchoolsDocument2 paginiSanitary Engineer Board Exam Topnotchers (Top 10 Passers) Sanitary Engineer Top Performing Schools and Performance of SchoolsErick AbarientosÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Professional Regulation CommissionDocument1 paginăThe Professional Regulation CommissionErick AbarientosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Board La1Document1 paginăBoard La1Erick AbarientosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reinforced ConcreteDocument1 paginăReinforced ConcreteErick AbarientosÎncă nu există evaluări
- PRC Announced That There AreDocument1 paginăPRC Announced That There AreErick AbarientosÎncă nu există evaluări
- ConstructionDocument1 paginăConstructionErick AbarientosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iii. Conduct of The ExaminationsDocument1 paginăIii. Conduct of The ExaminationsErick AbarientosÎncă nu există evaluări
- SteelDocument1 paginăSteelErick AbarientosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Timber 3Document1 paginăTimber 3Erick AbarientosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Graphics (EG)Document8 paginiEngineering Graphics (EG)Sudalai MadanÎncă nu există evaluări
- It Is Vital To Good Project Management To Be Meticulously Honest in Estimat Ing The Time Required To Complete Each of The Various Tasks Included in The Project. Note ThatDocument16 paginiIt Is Vital To Good Project Management To Be Meticulously Honest in Estimat Ing The Time Required To Complete Each of The Various Tasks Included in The Project. Note ThatSuraj SinghalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modelling and Simulation of An AFBC Steam Heating Plant Using ASPEN - SPDocument10 paginiModelling and Simulation of An AFBC Steam Heating Plant Using ASPEN - SPapi-3799861Încă nu există evaluări
- Impact of Gadget Use On The Learning Process of The Grade 11 Humss LearnersDocument45 paginiImpact of Gadget Use On The Learning Process of The Grade 11 Humss LearnersJade75% (12)
- Computer Networks - The International Journal of Computer and Telecommunications Networking HomeDocument6 paginiComputer Networks - The International Journal of Computer and Telecommunications Networking HomeMike MikkelsenÎncă nu există evaluări
- UntitledDocument7 paginiUntitledIndra Rian JayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- EWM Transaction CodesDocument22 paginiEWM Transaction CodesChuks Osagwu100% (1)
- Dynamics 365 Enterprise Edition Licensing GuideDocument52 paginiDynamics 365 Enterprise Edition Licensing Guidefran.obando1332Încă nu există evaluări
- SAPDocument19 paginiSAPdzulfatuhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Azure DevOps - User CreationDocument68 paginiAzure DevOps - User CreationInge SmitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sachin S. Pawar: Career ObjectivesDocument3 paginiSachin S. Pawar: Career ObjectivesSachin PawarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subject: Technical and Cost Proposal of Online Manpower Management System IntegratedDocument12 paginiSubject: Technical and Cost Proposal of Online Manpower Management System IntegratedMainuddin BhuiyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Connectivity Pack Info System en USDocument226 paginiConnectivity Pack Info System en USCatCesarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 12Document34 paginiChapter 12Thanh Van DaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Growth Marketing Final PresentationDocument17 paginiGrowth Marketing Final PresentationAmna AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Robot Operating SystemDocument11 paginiRobot Operating SystemAbdullah Abbas100% (1)
- Process Owner Manager Difference PDFDocument2 paginiProcess Owner Manager Difference PDFNikolay DilanovÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oracle® Service Fulfillment Manager: Implementation Guide Release 12.2Document148 paginiOracle® Service Fulfillment Manager: Implementation Guide Release 12.2yadavdevenderÎncă nu există evaluări
- DELEM Install GBDocument81 paginiDELEM Install GBSylwester C.Încă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 4 CSE 205Document8 paginiAssignment 4 CSE 205Dewank SainiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strapack I-10 Instruction-Parts Manual MBDocument26 paginiStrapack I-10 Instruction-Parts Manual MBJesus PempengcoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Deep LearningDocument34 paginiDeep Learningtheepi murugesanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1602.07360v1 - SqueezeNet: AlexNet-level Accuracy With 50x Fewer Parameters and 1MB Model Size - 2016Document5 pagini1602.07360v1 - SqueezeNet: AlexNet-level Accuracy With 50x Fewer Parameters and 1MB Model Size - 2016ajgallegoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optimization of Shovel-Truck System For Surface MiningDocument8 paginiOptimization of Shovel-Truck System For Surface MiningWilkhen ChuraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2006 - Pew Future of The Internet 2Document9 pagini2006 - Pew Future of The Internet 2_sdpÎncă nu există evaluări
- L5Document75 paginiL5anon_584584906Încă nu există evaluări
- Lathe - LVDocument23 paginiLathe - LVakshaygiitmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clmd4a Ictg6Document25 paginiClmd4a Ictg6Rose RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Learning Disabilities 2Document29 paginiLearning Disabilities 2Sarah Emmanuel HaryonoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industrial Safety CurriculumDocument67 paginiIndustrial Safety Curriculumrashid_siddiqi144100% (1)