Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Solid Works
Încărcat de
Georgiana DumitruTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Solid Works
Încărcat de
Georgiana DumitruDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
8
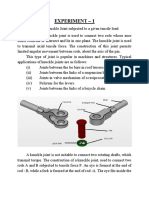
Working with Patterns
In this chapter, you learn how to create a linear pattern and a circular pattern. A linear pattern is a one- or two-dimensional array of features. A circular pattern is a circular array of features. The steps include:
q Creating a revolved base feature q Using mirroring to create a feature q Creating a linear pattern q Deleting and restoring an instance of the linear pattern q Creating a circular pattern q Using an equation to drive the circular pattern
SolidWorks 99 Tutorial
8-1
Chapter 8 Working with Patterns
Creating the Revolved Base Feature
In this example you create a housing for a microphone. Because the housing is cylindrical, you can create the housing as a revolved feature.
1 Open a new part, and open a sketch on the default plane, Plane1. 2 Click Grid and make sure that Length Unit is set to Millimeters, set Decimal places to 0, and click to clear Snap to points. Click OK. 3 Sketch and dimension the profile as shown. 4 Click the Fillet
tool on the Sketch Tools
toolbar.
a)
Set Radius to 30mm. b) Leave Keep constrained corners selected so that the corner dimensions and relations are retained to a virtual intersection point. c) Select the endpoint of the 50mm vertical line that is coincident with the endpoint of the diagonal line. d) Click Close.
The corner is filleted away.
8-2
5 Sketch a vertical Centerline
through the
origin. The centerline is the axis around which the profile revolves.
6 Click Revolved Boss/Base on the Features toolbar, or click Insert, Base, Revolve. 7 Leave the default values of Type as One-Direction, Angle at 360, and Revolve as at Solid Feature. Click OK to create the
revolved base.
8 Click Hidden Lines Removed
9 Click Save , and save the part as Mhousing.sldprt.
SolidWorks 99 Tutorial
8-3
Chapter 8 Working with Patterns
Extruding a Thin Feature
Now, create a thin-walled extrusion for the microphone capsule.
1 Select the top face and open a sketch. 2 Click Top a)
to change the view orientation. .
3 Click Offset Entities
Set Offset to 2mm. b) Click Reverse to offset the edge to the inside. c) Click Apply, then click Close to exit the Offset Entities dialog box.
4 Click Extruded Boss/Base Extrude. a)
or Insert, Boss,
Leave Type as Blind. b) Specify a Depth of 5mm. c) Set Extrude as to Thin Feature. d) Click the Thin Feature tab. Leave Type as One-Direction. Set Wall Thickness to 3mm. Click Reverse to extrude the wall to the inside. e) Click OK to create the thin-walled extrusion.
5 Click Isometric
for a better view of the thin-walled
extrusion.
6 Save the part.
8-4
Shelling the Part
Hollow out the part by removing the top and bottom faces.
1 Click Hidden In Gray 2 Click Shell
or Insert, Features, Shell.
The Shell Feature dialog box appears.
3 Set Thickness to 3mm. 4 Click the Faces to remove box, then click the top and
Select these faces
bottom faces as shown.
TIP:
To select an edge or face that is behind the near surface (a hidden edge or face), right-click and choose Select Other from the shortcut menu. The Yes/No pointer appears. When you point and right-click (N), you cycle through the edges or faces under the pointer, highlighting each of them in turn. When the edge or face that you want is highlighted, click (Y).
5 Click OK. 6 To see the shelled part better, click Shaded
and rotate the
part.
SolidWorks 99 Tutorial
8-5
Chapter 8 Working with Patterns
Creating an Oblong Cut
Next you create a profile of an oblong on a reference plane. Use mirroring to take advantage of symmetry and to decrease the number of relations needed to fully define the sketch.
1 Click Hidden Lines Removed
. .
2 Open a sketch on Plane1, and click Normal to 3 Click Centerline 4 Click Line
, and sketch a vertical centerline through the origin.
, and sketch two horizontal lines of equal length, beginning at the centerline. Watch for the on-curve pointer that indicates when you are exactly on the centerline.
5 Click 3 Pt Arc or right-click and select 3 Point Arc. Create a 3-point arc as shown.
Adjust the angle of the arc to 180. Then press Esc to deselect the 3-point arc tool.
8-6
6 Mirror the sketch entities.
Hold down Ctrl, and select the centerline, both horizontal lines, and the 3-point arc. b) Click Mirror on the Sketch Tools toolbar, or click Tools, Sketch Tools, Mirror.
a)
The sketch is mirrored on the other side of the centerline.
7 Dimension the oblong as shown.
Now that the sketch is fully defined, create the cut.
8 Click Isometric 9 Click Extruded Cut
. or Insert, Cut, Extrude.
Select Type as Through All. Click Reverse Direction. Leave Extrude as at Solid Feature.
10 Click OK to create the cut.
SolidWorks 99 Tutorial
8-7
Chapter 8 Working with Patterns
Creating the Linear Pattern
Next create a linear pattern of the oblong cut. You use a vertical dimension to specify the direction in which to create the linear pattern.
1 Double-click Cut-Extrude1 in the FeatureManager design tree.
The dimensions of the Cut-Extrude1 feature appear in the graphics area.
2 Click Linear Pattern Linear Pattern.
on the Features toolbar, or click Insert, Pattern/Mirror,
Leave at First Direction. Click the Direction selected box, then click the 60mm dimension in the graphics area. An arrow appears in the preview indicating the direction of the pattern. If the arrow is not pointing up, click Reverse direction. Set Spacing to 10mm. This value is the distance from a point on one instance of the patterned feature to the corresponding point on the next instance. Set Total instances to 4. This value includes the original cut-extrude feature. Make sure that Cut-Extrude1 is listed in the Items to copy box.
3 Click OK to create the linear pattern. 4 Save the part.
8-8
Deleting and Restoring an Instance of a Pattern
You can delete an instance of a pattern if necessary.
1 Click Zoom To Area 2 Click Select
, then drag the pointer to create a rectangle around the linear pattern. , and select a face on the top
pattern instance.
3 Press the Delete key.
The Pattern Deletion dialog box appears.
4 Make sure that Delete Pattern Instances is
selected and that the location of the pattern instance to be deleted in the Instances Deleted box is (4, 1).
5 Click OK to close the dialog box.
The selected instance of the pattern is deleted.
6 Click Zoom To Fit
to view the entire part.
Now restore the deleted instance of the pattern.
1 Right-click LPattern1 in the FeatureManager design tree, then select Edit Definition.
The Linear Pattern dialog box appears.
2 In the Instances deleted box, click the deleted instance (4, 1), then press the Delete key.
The pattern instance is removed from the Instances deleted box, and restored in the preview.
3 Click OK.
SolidWorks 99 Tutorial
8-9
Chapter 8 Working with Patterns
Creating a Circular Pattern of a Linear Pattern
Now create a circular pattern of the linear pattern, using a temporary axis as the axis of revolution.
1 Click View, Temporary Axes. 2 Click Circular Pattern on the Features toolbar, or click Insert, Pattern/Mirror, Circular Pattern.
Click the Direction selected box, then click the temporary axis that passes through the center of the revolved feature. An arrow appears in the preview indicating the direction of the pattern. If the arrow is not pointing up, click Reverse direction. Set Spacing to 120. Set Total instances to 3. Make sure that LPattern1 is listed in the Items to copy box.
3 Click OK to create the circular pattern.
A circular pattern of the linear pattern is created around the parts axis of revolution.
4 Click View, Temporary Axes to turn off the display of axes, then click Shaded .
NOTE: If you need to use a circular pattern in a part that does not have a temporary
axis in the desired place, you can create an axis, or you can use a linear edge as an axis. For more information about creating an axis, see Chapter 3, Reference Geometry, in the SolidWorks 99 Users Guide and online help.
8-10
Using an Equation in the Pattern
You can use an equation to drive the circular pattern. In this example, the equation calculates the spacing angle by dividing 360 by the number of instances desired. This creates a full circle of equally spaced patterns.
1 In the FeatureManager design tree, double-click CirPattern1.
Two values appear on the part: 3 (total instances) and 120 (spacing angle).
2 Click Equations
on the Tools toolbar, or click Tools, Equations.
3 Click Add in the Equations dialog box. 4 Click the spacing angle value (120) on the part. (You may have to move the dialog
boxes to uncover the dimension.) The name of the value, D2@CirPattern1 (the second dimension in the circular pattern), is entered the New Equation dialog box.
5 Using the calculator buttons in the New Equation box, enter = 360 / (or type =360/). 6 Click the total instances value (3). D1@CirPattern1 is added to the equation.
The equation should look as follows:
D2@CirPattern1 = 360 / D1@CirPattern1 7 Click OK to complete the equation, and click OK again to close the Equations dialog
box. An Equations folder is added to the FeatureManager design tree. To add, delete, or edit an equation, right-click the folder, and select the desired operation. Now test the equation.
1 Increase the total instances of the circular pattern from three to four.
Double-click the total instances value (3). b) Set the value in the Modify dialog box to 4.
a) 2 Click
in the Modify dialog box to rebuild the model, then click to save the current value and to close the Modify dialog box. Press Enter, then click Rebuild or click Edit, Rebuild. on the Standard toolbar,
or
3 Save the part.
SolidWorks 99 Tutorial
8-11
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Tutorial Shipcon PDFDocument330 paginiTutorial Shipcon PDFMaiDinh DinhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Routing - Pipes and TubesDocument27 paginiRouting - Pipes and TubesricoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Jigs Fixtures and Press Tools PDFDocument4 paginiDesign of Jigs Fixtures and Press Tools PDFniharika kadiriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Csol 580 Week 7Document8 paginiCsol 580 Week 7api-487513274Încă nu există evaluări
- TLE ICT 10 - Install An Application Software - Activity SheetDocument5 paginiTLE ICT 10 - Install An Application Software - Activity SheetGioSanBuenaventuraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple Teapot Catia Iss 01Document51 paginiSimple Teapot Catia Iss 01Murali AnirudhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Design TechniquesDocument23 paginiAdvanced Design Techniquesapi-3748063Încă nu există evaluări
- Part Design PDFDocument244 paginiPart Design PDFOstromafÎncă nu există evaluări
- CATIADocument5 paginiCATIAkiran2381100% (1)
- Selection of Material For FrameDocument7 paginiSelection of Material For FramePrashant BachhavÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2015 SolidWorks - WeldmentsDocument19 pagini2015 SolidWorks - WeldmentsKiran Kumar KondapalliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Welcome To Sheetmetal DesignDocument153 paginiWelcome To Sheetmetal Designjd4uÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 6 - Face Milling On CNC MachineDocument5 paginiLab 6 - Face Milling On CNC MachineHaris NaveedÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Cosmos Companion: Analyzing Sheet Metal Parts & Assys in CosmosworksDocument31 paginiThe Cosmos Companion: Analyzing Sheet Metal Parts & Assys in CosmosworksraddyrajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Drawing PrinciplesDocument21 paginiEngineering Drawing PrinciplesMarco Septian100% (2)
- Computer Aided Machine Drawing Laboratory: Lab ManualDocument31 paginiComputer Aided Machine Drawing Laboratory: Lab ManualGiridharadhayalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Creo Tool Design: PrerequisitesDocument23 paginiCreo Tool Design: PrerequisitesLucianÎncă nu există evaluări
- NTTF Press Tool Standards Ebook GeneralDocument231 paginiNTTF Press Tool Standards Ebook GeneralKvs PhaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- ProE Surfacing - Module 1Document52 paginiProE Surfacing - Module 1inthemoney8100% (1)
- Chapter 9 Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing (GD&T) : FPOLR-52332Document12 paginiChapter 9 Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing (GD&T) : FPOLR-52332Jackie HwangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 16 Sheet Metal Design Solidworks 2003Document80 paginiChapter 16 Sheet Metal Design Solidworks 2003Oscar LeonardoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluent - Tutorial - Dynamic Mesh - 2D Adiabatic CompressionDocument29 paginiFluent - Tutorial - Dynamic Mesh - 2D Adiabatic Compressionmm0hammadi100% (2)
- Gear and Gear TrainDocument21 paginiGear and Gear Trainm_er100Încă nu există evaluări
- Assign I MD IDocument3 paginiAssign I MD IAtharva KÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sheet Metal Design in SolidworksDocument27 paginiSheet Metal Design in SolidworkstnchsgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sheet Forming Process of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastics For Lightweight Parts PDFDocument4 paginiSheet Forming Process of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastics For Lightweight Parts PDFlolycanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dathan Tool and Gauge HandbookDocument32 paginiDathan Tool and Gauge HandbooksamirkaminskyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Equation Driven Spur GearDocument4 paginiEquation Driven Spur GearGoutam AcharjeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Is 7054 1973Document16 paginiIs 7054 1973m_verma21Încă nu există evaluări
- 2013 Turbine Manufacture Pelton TurbineDocument60 pagini2013 Turbine Manufacture Pelton TurbineAnonymous K48TgviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Screw Jack Designing Project Report PDFDocument26 paginiScrew Jack Designing Project Report PDFfasil100% (1)
- Ch3 - Metal CuttingDocument30 paginiCh3 - Metal Cutting03 ABHISHEKÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cumulative Effect of TolereanceDocument7 paginiCumulative Effect of Tolereancecoolcrab89Încă nu există evaluări
- Screw Threads and Assembly Drawing Class NotesNotesDocument17 paginiScrew Threads and Assembly Drawing Class NotesNotesRay NjorogeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Catia Lab ManualDocument93 paginiCatia Lab ManualRameez Farouk100% (3)
- Creo2 SheetmetalDocument77 paginiCreo2 SheetmetalBahadır UysalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water Control Gates TrainingDocument132 paginiWater Control Gates TrainingsaishankarlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Create 1 - 2 Hex Bolt - SolidWorks TutorialsDocument9 paginiCreate 1 - 2 Hex Bolt - SolidWorks Tutorialsandres_palacios_1433Încă nu există evaluări
- Inventorcam 2014 Application Tutorial: Multiblade Machining: ©1995-2013 Solidcam All Rights ReservedDocument45 paginiInventorcam 2014 Application Tutorial: Multiblade Machining: ©1995-2013 Solidcam All Rights ReservedKhai Huynh100% (1)
- SolidWorks Motion Study TutorialDocument37 paginiSolidWorks Motion Study TutorialVega R JoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- TE B Gearbox Design Oral QuestionsDocument5 paginiTE B Gearbox Design Oral QuestionsapteashutoshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Creo Lesson - Drawing Layout and ViewsDocument83 paginiCreo Lesson - Drawing Layout and ViewsAleksandar100% (1)
- Sheet MetalDocument186 paginiSheet Metalwalid_mohammady1616100% (1)
- How To Interpret Injection Moulding Simulation ResultsDocument27 paginiHow To Interpret Injection Moulding Simulation ResultsAhmad Zhafri SamsudinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manual Unigraphics NX - 09 The Master ModelDocument13 paginiManual Unigraphics NX - 09 The Master ModelthiagomcasimiroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manually Operated Hydraulic Pipe Bending MachineDocument16 paginiManually Operated Hydraulic Pipe Bending MachineRohitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Machine Design NotesDocument349 paginiMachine Design NotesAkshay More100% (1)
- Knuckle JointDocument10 paginiKnuckle JointRajat MathurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heat TreatmentDocument16 paginiHeat TreatmentPrabir Kumar Pati100% (1)
- PLP Solar PanelDocument8 paginiPLP Solar PanelCarlos SolerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solidworks 2018 Reference Guide: A Comprehensive Reference Guide With Over 250 Standalone TutorialsDocument70 paginiSolidworks 2018 Reference Guide: A Comprehensive Reference Guide With Over 250 Standalone TutorialsInnabilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solid WorksDocument10 paginiSolid WorksGeorgiana Dumitru100% (1)
- Solid WorksDocument65 paginiSolid WorkssumanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 30 Minute LessonDocument27 pagini30 Minute Lessonapi-3748063100% (3)
- 7 Shades of ArtDocument40 pagini7 Shades of ArtsamiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Creo ParametricDocument8 paginiCreo ParametricAmar DeepuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Angrenaj CilindricDocument1 paginăAngrenaj CilindricGeorgiana DumitruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solid WorksDocument9 paginiSolid WorksGeorgiana DumitruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solid WorksDocument6 paginiSolid WorksGeorgiana DumitruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solid WorksDocument10 paginiSolid WorksGeorgiana Dumitru100% (1)
- Three-Dimensional Viscoelastic Simulation of Woven CompositeDocument13 paginiThree-Dimensional Viscoelastic Simulation of Woven CompositeGeorgiana DumitruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prisma Certified Cloud Security Engineer (PCCSE) BlueprintDocument4 paginiPrisma Certified Cloud Security Engineer (PCCSE) BlueprintJohn LinÎncă nu există evaluări
- No Me AcuerdoDocument194 paginiNo Me AcuerdoCamila Salvador BejaranoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Have Info MapDocument361 paginiHave Info MapjohnÎncă nu există evaluări
- BSC6900 GSM Initial Integration Procedure (V900R013C00 - 04)Document172 paginiBSC6900 GSM Initial Integration Procedure (V900R013C00 - 04)touaiti2009100% (1)
- Mischief User GuideDocument26 paginiMischief User Guidedarth_sphincterÎncă nu există evaluări
- World Tourism Day by SlidesgoDocument56 paginiWorld Tourism Day by SlidesgoLe Anh Quan B2105684Încă nu există evaluări
- Modular I/O System Profibus Dpv1 750-333 / 750-833: Technical Description, Installation and ConfigurationDocument154 paginiModular I/O System Profibus Dpv1 750-333 / 750-833: Technical Description, Installation and Configurationandreas bahdaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Product Introduce-RRU InstallationDocument10 paginiProduct Introduce-RRU InstallationMuhammad AhsanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Localizacao Brasil Servicos PDFDocument68 paginiLocalizacao Brasil Servicos PDFMarcelo MestiÎncă nu există evaluări
- TWS Troubleshooting GuideDocument203 paginiTWS Troubleshooting GuideJosé E. FélixÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course Registration System: Ex. No.:7Document44 paginiCourse Registration System: Ex. No.:7abcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sentiment Analysis On Grab User Reviews Using Support Vector Machine and Maximum Entropy MethodsDocument6 paginiSentiment Analysis On Grab User Reviews Using Support Vector Machine and Maximum Entropy Methodsإمحمد السنوسي القزيريÎncă nu există evaluări
- BUMC MEDLINE Plus/OVID Fact Sheet: Alumni Medical Library Boston University Medical CenterDocument2 paginiBUMC MEDLINE Plus/OVID Fact Sheet: Alumni Medical Library Boston University Medical CenterRay PermanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Himax: Digital Output Module ManualDocument52 paginiHimax: Digital Output Module ManualRoberto FinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BVMS - Quick Selection GuideDocument3 paginiBVMS - Quick Selection Guideabdullah rehmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cypecad Vs Etabs - En2Document33 paginiCypecad Vs Etabs - En2dskumar49100% (2)
- Network Security v1.0 - Module 3 ESDocument51 paginiNetwork Security v1.0 - Module 3 ESbcdavila0% (1)
- Enhanced Table Maintenance With Automatic Change Recording - My Experiments With ABAPDocument6 paginiEnhanced Table Maintenance With Automatic Change Recording - My Experiments With ABAPpraneeth abapÎncă nu există evaluări
- File - SK.312 MENLHK SETJEN PSKL.1 4 2019 PDFDocument3 paginiFile - SK.312 MENLHK SETJEN PSKL.1 4 2019 PDFCDK MeraukeÎncă nu există evaluări
- A 6 R 4Document2 paginiA 6 R 4Ghanshyam SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prashant (1) .Shrivastava Resume (System Admin)Document2 paginiPrashant (1) .Shrivastava Resume (System Admin)Sapna MathurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Block Customer Master DataDocument11 paginiBlock Customer Master DataArun DalalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sistem Tarantula I-NILAMDocument1 paginăSistem Tarantula I-NILAMJazfrul FahmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hit 7300 TSMNDocument159 paginiHit 7300 TSMNMohammed Kumayl100% (1)
- Curriculum Vitae of Md. Mahabubur RahmanDocument2 paginiCurriculum Vitae of Md. Mahabubur Rahmanzakaria masud sonyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Princeton Survey Research Associates InternationalDocument19 paginiPrinceton Survey Research Associates InternationalTan Chun HeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pubg CCDocument9 paginiPubg CCRukmini AdithyaÎncă nu există evaluări