Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
CH 1 - Info System Strategy Triangle
Încărcat de
Justin L De ArmondDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
CH 1 - Info System Strategy Triangle
Încărcat de
Justin L De ArmondDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
MBUS 0626 CH 1 Systems Strategy Triangle 1. Info Systems Strategy Triangle a.
. EX: BP failure highlighted need for proper alignment of biz strategy, info systems (IS), and org mechanisms & practices when designing the safety mechanisms of an oilrig i. Issues with org culture, process, and leadership b. GMs MUST take/play a role in decisions about IS; seek to understand consequences of using technologies relevant to the biz envoi c. GMs MUST ask questions when things are not clear d. GMs that leave IS decisions to IS professionals put Orgs and selves at a disadvantage/risk e. IS Strategy Triangle relates biz strategy with IS strategy and Org strategy f. Successful firms have an overriding biz strategy that drives both org strategy and IS strategy i. Decisions w/respect to structure, hiring, vendor policies, & other components of org strategy, decisions regarding applications, hardware, & other IS components = driven by bizs objectives, strategies, & tactics ii. MUST Balance three strategies to be successful iii. One strategy changes, the others must be adjusted as well, CONSTANTLY iv. Each decision has consequences, thus managers need to ensure that all strategies are considered when making an adjustment to just one v. Alignment can be fixed if issues arise; Alignment situation in which a companys current & emerging biz strategy is enabled, supported, and unconstrained by technology 1. Higher states = synchronization & convergence Orgs should strive a. Sync enables current biz strategy, anticipates future strategy b. Converg biz strategy & tech strategy are intertwined & managers operate interchangeably 2. Alignment means any of these states! g. Focus of Book = Ask the right questions, baseline framework to develop questions, and a basic understanding on how to answer those questions 2. Brief Overview of Business Strategy Frameworks a. Strategy = coordinated set of actions to fulfill objectives, purposes, & goals. i. Essence set limits on what to accomplish b. Mission starting point of strategy, = clear and compelling statement that unifies an orgs effort & describes what the firm is all about (Purpose) i. Set measurable objectives & performance targets c. Biz Strategy = plan articulating where a biz seeks to go & how it expects to get there; means by which it communicates its goals i. MGMT plan to respond to market forces, customer demands, and org capabilities 1. Market Forces create competitive context for biz 2. Customer demand wants/needs of IDV & companies who purchase products & services
MBUS 0626 3. Org capabilities skills & experience that give Org a currency that can add value in a marketplace 4. EX: Dell direct-to-customer model, no inventories, kept costs down d. The Generic Strategies Framework (Porter) basis of above-avg performance = sustainable competitive advantage; three strategies i. Cost leadership (IND Wide) org aims to be the lowest-cost producer in marketplace; minimize costs leads to above-avg performance; good quality to others; generally only one cost leader w/in industry; can lead to price war (WALMART) 1. Use of mass distro, economies of scale, & IS to generate efficiencies ii. Differentiation (IND Wide) uniqueness perceived by customer; qual dimensions important to customer and add value to one or more dimensions 1. Price charge by differentiator (Org) must seem fair to competitors price (PROGRESSIVE) iii. Focus (Segment Only) tailor offerings to a narrow group of customers 1. Cost focus cost adv w/in segment 2. Differentiation focus distinguish products w/in segment 3. Marriot / Ritz-Carlton a. M Kiosk & CRM b. RC Class system of CRM PAX use to improve current/future visits 4. JetBlue Low-cost coupled with unique customer experience iv. Application to IS 1. Understand which strategy is chosen by a firm is critical to choosing IS to complement the strategy e. Dynamic Environment Strategies orgs need to adapt instantly or they could fail i. Generic Strategy good for = Diagnostics, how biz seeks to profit, prescriptions, OR building new opportunities for adv 1. Balancing of countervailing competitive forces, substitute products & services = good tool for THINKING about strategy 2. Developed when rate of change was slow & manageable ii. Hyper-competition speed & aggressiveness of the moves & countermoves in any given market create an enviro in which adv are rapidly created & eroded 1. Value agility = competitive adv! 2. Build in components of Biz Intelligence; still focus on customer satisfaction, profit maximization, & other biz goal & beliefs a. Predict new opportunities, org designs that can sense & restructure & respond quickly; strategic signaling & actions that surprise & confuse competitors 3. Most striking in sectors that spend most on IT iii. Destroy your Biz (DYB) = Creative Destruction Jack Welch @ GE 1. Must recognize weakness, Act as competition to ID issues 2. Use Grow Your Biz (GYB) strategy to find fresh ways to reach new customers and serve current customers
MBUS 0626 a. Apple iPod leads to iPhone, mac leads to iPad b. Gillette Mach3 leads to Fusion iv. Application to IS 1. IS are critical to achieving the speed needed for moves and countermoves; IS are in a constant state of flux or development f. Why are Strategic Models Essential to Planning for Information Systems? Must be able to answer the following questions: i. What is the biz goal or obj? ii. What is the plan for achieving it? What is the role of IS in this plan? iii. Who are the crucial competitors & partners, and what is required of a successful player in this marketplace? iv. What are the industry forces in this marketplace? 3. Brief Overview of Organizational Strategies a. Org Strategy orgs design as well as the choices it makes to define, set up, coordinate, and control its work processes b. Answers Q: How will firm organize to achieve its goals and implement its biz strategy? i. Biz Diamond (Harold Leavitt) crucial components of an orgs plan; all interrelated; change one thing, need to realize how it affects other aspects of biz
1. Usefulness in IS using IS in Org will affect each of these components; use this framework to ID where these impacts are likely to occur ii. Managerial levers Model success of Orgs strategy is best combo of org, control, & cultural variables
iii. 1. Usefulness in IS more detailed than biz diamond, gives specific areas where IS can be used to manage Org & to change the Org iv. Understanding Org strategy means answering the following: 1. What are the important structures & reporting relationships w/in the Org? 2. Who holds the decision rights to critical decisions?
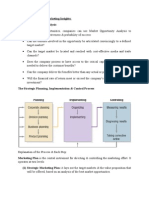
MBUS 0626 3. What are the important people-based networks (social & informational) & how can we use them to get work done better? 4. What are the characteristics, experiences, & skill levels of the people w/in the Org? 5. What are the key biz processes? 6. What control systems (MGMT & measurement systems) are in place? 7. What are the culture, values, & beliefs of the Org? 4. Social Business Lens: Building a Social Business Strategy a. SBS = plan of how the firm will use Social IT, aligned with orgs strategy and IS strategy. i. Vision of how the biz would operate if it seamlessly and thoroughly incorporate social & collaborative capabilities throughout the biz model b. Collaboration using social IT to extend reach of stakeholders; find/connect with each other to share ideas, info, and expertise c. Engagement involve stakeholders in traditional biz of enterprise; communities & blogs allow IDVs to join in conversations, crate new conversations, offer support for each other, create a deeper feeling of connection to Org, brand, enterprise d. Innovation ID, describe, prioritize, & create new ideas for the Org; offer super idea box, vote for favorite idea 5. Brief Overview of Info Systems Strategy a. IS Strategy plan an Org uses to provide information services i. Allows Org to implement its biz strategy ii. JB: define what biz needs, then go find technology to support that iii. Function of: 1. Competition What does the customer want & what does the competition do? 2. Positioning in what ways does the firm want to compete? 3. Capabilities - what can the firm do? iv. IS helps determine the Orgs capabilities
b. c. Above graph gives managers High-level view of relation between for IS infrastructure components & other resource considerations that are keys to IS strategy
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Corporate, Business & Marketing StrategiesDocument43 paginiCorporate, Business & Marketing StrategiesAhsan ShahidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mis Information System StrategyDocument13 paginiMis Information System StrategyKaren RotichÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial 1Document4 paginiTutorial 1PEIYEEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marketing Management ProcessDocument4 paginiMarketing Management ProcessAayush GiriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rekap QManHRDocument29 paginiRekap QManHRViscany ResidenceÎncă nu există evaluări
- SM MSE NotesDocument17 paginiSM MSE NotesishaaneduvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 1 - Marketing ManagementDocument9 paginiAssignment 1 - Marketing Managementwidi tigustiÎncă nu există evaluări
- A e - Q2-M2Document21 paginiA e - Q2-M2Vince Nylser BorbonÎncă nu există evaluări
- StrategyDocument21 paginiStrategyAmar ItagiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Information System For Strategic Management: Ihr LogoDocument56 paginiInformation System For Strategic Management: Ihr LogoRicha GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strategic ManagementDocument4 paginiStrategic ManagementDK BalochÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parts of The Business Plan NewDocument2 paginiParts of The Business Plan NewRomel Giannor AgcaoiliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 - Capturing Marketing InsightsDocument14 paginiChapter 2 - Capturing Marketing InsightsHusain Sulemani100% (1)
- 01 - 01 - The Different StrategiesDocument6 pagini01 - 01 - The Different Strategiesndeiamimi13613Încă nu există evaluări
- Strategy Implementation and ExecutionDocument57 paginiStrategy Implementation and ExecutionAjil RafaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Determining The Business Information Systems StrategyDocument56 paginiDetermining The Business Information Systems StrategyIrpanÎncă nu există evaluări
- BBA202Document6 paginiBBA202mreenal kalitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 2Document35 paginiLecture 2MBA SAWLACAMPUS2014Încă nu există evaluări
- Assignment - 2 Strategic Management Submitted By-Ansh Chhiba (2593) Submitted To - Dr. TanviDocument4 paginiAssignment - 2 Strategic Management Submitted By-Ansh Chhiba (2593) Submitted To - Dr. TanviTejas VigÎncă nu există evaluări
- MISY 427 Fall 2007 Chapter 1Document33 paginiMISY 427 Fall 2007 Chapter 1Nirmit OzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 1Document8 paginiAssignment 1Neha Sinha100% (1)
- Bba 207 Guide BookDocument37 paginiBba 207 Guide BooklalsinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Puneet Thakur 2608Document4 paginiPuneet Thakur 2608Tejas VigÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 7 AssignmentDocument11 paginiUnit 7 AssignmentDeepak ChiripalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Core Strategy: I. Objective & PrioitiesDocument7 paginiCore Strategy: I. Objective & PrioitiesDietmar LengauerÎncă nu există evaluări
- A. Strategy ImplementationDocument8 paginiA. Strategy ImplementationJerusha AlmonteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Information System For ManagersDocument9 paginiInformation System For ManagersKush BafnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parts of The Business PlanDocument8 paginiParts of The Business PlanSherylle Joyce Tomas100% (1)
- ESBM Notes Unit-4Document37 paginiESBM Notes Unit-4satyamtiwari44003Încă nu există evaluări
- Discussion QuestionsDocument12 paginiDiscussion QuestionsSalman SajidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lê Nhật Xuân-bài Tập Cá Nhân 1Document2 paginiLê Nhật Xuân-bài Tập Cá Nhân 1Ánh TuyếtÎncă nu există evaluări
- CI - Final Exam - Radwa Mohamed Fayez - Fall21 CI 04Document5 paginiCI - Final Exam - Radwa Mohamed Fayez - Fall21 CI 04wafaa mustafaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Business Enterprise Simulation ExamDocument3 paginiBusiness Enterprise Simulation ExamCherilyn Mabutol100% (5)
- HW XXM JWy ANTD1705578188342Document3 paginiHW XXM JWy ANTD1705578188342Farahan RazaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strategic Planning: HDCS 4393/4394 Internship Dr. Shirley EzellDocument18 paginiStrategic Planning: HDCS 4393/4394 Internship Dr. Shirley Ezellravi pratapÎncă nu există evaluări
- Business Intelligence Strategy at Canadian TireDocument3 paginiBusiness Intelligence Strategy at Canadian Tiretirthmehta@gmail.com50% (4)
- Strategic Management SMDocument9 paginiStrategic Management SMVINAY BETHAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bus MKTG PlanningDocument62 paginiBus MKTG PlanningMaulick JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- SM Unit-1Document16 paginiSM Unit-1Sagar PanditÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strategic Marketing 10th Edition Cravens Solutions Manual 1Document36 paginiStrategic Marketing 10th Edition Cravens Solutions Manual 1guymontgomerygpbocfyamt100% (28)
- Strategic Marketing 10th Edition Cravens Solutions Manual 1Document74 paginiStrategic Marketing 10th Edition Cravens Solutions Manual 1michael100% (35)
- Lesson 3 Strategic Marketing PlanningDocument11 paginiLesson 3 Strategic Marketing PlanningAMOS WASIKEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tổng Hợp Lý Thuyết EssayDocument26 paginiTổng Hợp Lý Thuyết EssayHong Phuc PhamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strategic Management in Action 6th Edition Coulter Solutions ManualDocument26 paginiStrategic Management in Action 6th Edition Coulter Solutions Manualkeishadylanrhimlb100% (29)
- Strategic Management in Action 6Th Edition Coulter Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument47 paginiStrategic Management in Action 6Th Edition Coulter Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFdisfleshsipidwcqzs100% (7)
- 1) Covering The Market Globally and Locally: 2) Grow SmartlyDocument3 pagini1) Covering The Market Globally and Locally: 2) Grow SmartlySukalp MittalÎncă nu există evaluări
- SASDocument4 paginiSASAnamitra BhattacharyyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parts of Business ModelDocument2 paginiParts of Business ModelJarel MarabutÎncă nu există evaluări
- Safari - 10 Sep 2019 at 7:00 AMDocument1 paginăSafari - 10 Sep 2019 at 7:00 AMYAChIÎncă nu există evaluări
- ADMS4900 3 0 - Midterm NotesDocument46 paginiADMS4900 3 0 - Midterm NotesAliAamirMalikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marketing Plan 18 19Document10 paginiMarketing Plan 18 19SailyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strategy Formulation and SelectionDocument3 paginiStrategy Formulation and SelectionDungÎncă nu există evaluări
- C 11 I S O: Hapter Nternational Trategy and Rganization L ODocument9 paginiC 11 I S O: Hapter Nternational Trategy and Rganization L OAbdirizak AbdirizakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Competitive AdvantageDocument60 paginiCompetitive AdvantageFibin Haneefa100% (1)
- SM 1Document93 paginiSM 1alibhai1Încă nu există evaluări
- 9th August 2006Document6 pagini9th August 2006nishantÎncă nu există evaluări
- Task 1 Stratbusana Holy Angel UniversityDocument3 paginiTask 1 Stratbusana Holy Angel UniversityJane DizonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Value Creation Paper44Document7 paginiValue Creation Paper44Justin L De ArmondÎncă nu există evaluări
- Entry Into Dog Food MarketDocument2 paginiEntry Into Dog Food MarketJustin L De ArmondÎncă nu există evaluări
- Value Creation Paper-4Document7 paginiValue Creation Paper-4Justin L De ArmondÎncă nu există evaluări
- MediSys Individual CaseDocument16 paginiMediSys Individual CaseJustin L De Armond60% (5)
- Corp Financial ReportingDocument7 paginiCorp Financial ReportingJustin L De ArmondÎncă nu există evaluări
- Corp Financial ReportingDocument7 paginiCorp Financial ReportingJustin L De ArmondÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pe#4158 Group#5 - SSPDocument2 paginiPe#4158 Group#5 - SSPJustin L De ArmondÎncă nu există evaluări
- Each Life Raft Must Contain A Few ItemsDocument2 paginiEach Life Raft Must Contain A Few ItemsMar SundayÎncă nu există evaluări
- DC Motor: F Bli NewtonDocument35 paginiDC Motor: F Bli NewtonMuhammad TausiqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- SKF CMSS2200 PDFDocument2 paginiSKF CMSS2200 PDFSANTIAGOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sap EwmDocument2 paginiSap EwmsirivirishiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Column Buckling TestDocument8 paginiColumn Buckling TestWiy GuomÎncă nu există evaluări
- Handbook+for+Participants+ +GCC+TeenDocument59 paginiHandbook+for+Participants+ +GCC+Teenchloe.2021164Încă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To SCRDocument19 paginiIntroduction To SCRAlbin RobinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lalkitab Varshphal Chart PDFDocument6 paginiLalkitab Varshphal Chart PDFcalvinklein_22ukÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tensile Strength of Ferro Cement With Respect To Specific SurfaceDocument3 paginiTensile Strength of Ferro Cement With Respect To Specific SurfaceheminÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Genius of Marie Curie Shohini GhoseDocument4 paginiThe Genius of Marie Curie Shohini GhoseMarta HrynyovskaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Integration Plan Grade 9 Mapeh SeptemberDocument3 paginiIntegration Plan Grade 9 Mapeh Septemberbernie evaristo bacsaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Logic of Repetition: A Guide To Trading, Thinking, and The Cycles of LifeDocument10 paginiThe Logic of Repetition: A Guide To Trading, Thinking, and The Cycles of LifeRaghvendra kÎncă nu există evaluări
- Routine (27th April)Document1 paginăRoutine (27th April)SoumitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gr. 10 Persuasive EssayDocument22 paginiGr. 10 Persuasive EssayZephania JandayanÎncă nu există evaluări
- APPSC GROUP 4 RESULTS 2012 - Khammam District Group 4 Merit ListDocument824 paginiAPPSC GROUP 4 RESULTS 2012 - Khammam District Group 4 Merit ListReviewKeys.comÎncă nu există evaluări
- Distillation Column DesignDocument42 paginiDistillation Column DesignAakanksha Raul100% (1)
- Technical Test 03Document13 paginiTechnical Test 03KartikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Apps Android StudioDocument12 paginiApps Android StudioDaniel AlcocerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mis Report On Ola CabsDocument18 paginiMis Report On Ola CabsDaksh MaruÎncă nu există evaluări
- TMS320C67x Reference GuideDocument465 paginiTMS320C67x Reference Guideclenx0% (1)
- Report Painter GR55Document17 paginiReport Painter GR55Islam EldeebÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Theory of Production and Cost: Chapter FourDocument32 paginiThe Theory of Production and Cost: Chapter FourOromay Elias100% (1)
- Disney - QMDocument14 paginiDisney - QMSyarifuddin Zulkifli0% (1)
- Warning: Shaded Answers Without Corresponding Solution Will Incur Deductive PointsDocument1 paginăWarning: Shaded Answers Without Corresponding Solution Will Incur Deductive PointsKhiara Claudine EspinosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aerated Concrete Production Using Various Raw MaterialsDocument5 paginiAerated Concrete Production Using Various Raw Materialskinley dorjee100% (1)
- EE 8602 - Protection and Switchgear Unit I - MCQ BankDocument11 paginiEE 8602 - Protection and Switchgear Unit I - MCQ Bankpoonam yadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Using Impact IX49 and 61 With Nektar DAW Integration 1.1Document21 paginiUsing Impact IX49 and 61 With Nektar DAW Integration 1.1Eko SeynÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power - Factor - Correction - LegrandDocument24 paginiPower - Factor - Correction - LegrandrehanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2022 Summer Question Paper (Msbte Study Resources)Document4 pagini2022 Summer Question Paper (Msbte Study Resources)Ganesh GopalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Slip Ring Motor CheckDocument3 paginiSlip Ring Motor CheckRolando LoayzaÎncă nu există evaluări