Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Basics: What Is A Digital System?
Încărcat de
Harshit BoradTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Basics: What Is A Digital System?
Încărcat de
Harshit BoradDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
1
Tutorial 1
Basics
What is a Digital system?
In most general terms, this systems behavior is sufficiently explained by using only two of its states can be Voltage(more than x volts or less?),distance covered(more than 2.5 km or less?],true-false or weight of an elephant(will my weighing machine withstand it?) ) Note that although in every case, the all the intermediate states ARE POSSIBLE AND DO EXIST, our point of interest are such that we dont require their explicit description. In electronic systems we mostly deal with Voltage levels as digital entities.
Assigning States
There is no specific fixed definition of logic levels in electronics. Most commonly used level designation is the one used in CMOS and TTL (transistor transistor logic) families: Logic high > designated as 1 Logic low > designated as 0 GOOGLY: Why assign 0and 1 and not a and b, x and y ,cat and dog? ANS: Computational ease! Where high and low are actually higher and lower with respect to a reference voltage level (ideally taken as 2.5V)
Number Systems in digital electronics
1. Binary: Only 0 and 1. 2. Hexadecimal: 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,A,B,C,D,E,F
Types of Digital Circuits
Combinatorial Circuits: In these circuits, the past states are immaterial output depends only upon the present state. Example logic gates . Sequential circuits: In these circuits, the next state is completely determined by the past states. Hence these follow a predictable structure essentially require a timing device. Ex. counters, flip flops.
and the and
Robotics Club,IIT-Kanpur
Clock: Building block of a sequential circuit
Tutorial 1
A clock is simply alternate high and low states of voltage with time i.e. essentially a square wave. Important terms related to clock are its duty cycle and its frequency: Duty cycle: It is the ratio of Th and Th+Tl
= +
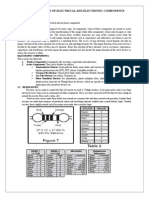
Logic Gates: Building block of a combinatorial circuitry
These are essentially combinatorial circuits used to implement logical Boolean operations like AND, NAND, OR, XOR and NOT. NOT and NAND are called universal gates as any other gate can be formed using either of them!
Figure 1
Figure 2: Table of Logic Gates
Robotics Club,IIT-Kanpur
Practical Circuiting Elements
Resistor:
Tutorial 1
A color scheme is followed to give the specifications of a resistor. The table for color code is shown below:
The 1st two bands specify the 2 digits of the resistor value whereas the 3rd band specifies the multiplier in terms of the power to which 10 is raised and multiplied to the 2 digits. The tolerance tells the possible % variation of the resistor value about the value indicated by bands.
Figure 3: Table of Resistance
Capacitor:
The 2 types of capacitors we frequently use in circuits are ceramic and electrolytic capacitors. While ceramic capacitors do not have a fixed polarity; electrolytic capacitors should be connected in their specified polarities only else they might blow off! This polarity is usually provided on the side of the capacitors corresponding leg.
Figure 5: Electrolytic cap with ve polarity leg seen
Figure 4: Ceramic cap with value 15x104 pF
Robotics Club,IIT-Kanpur
Breadboard:
Tutorial 1
This is the base used for setting up the circuit. This has embedded metal strips in it that form a grid of connections inside its body. This allows us to take multiple connections from a single point without any need of soldering/disordering as in PCBs. It is always a good habit to test the circuit on breadboard before making it on a PCB.
Figure 6: Top view showing the connecting holes. Bottom view shows the contact metal strips
Integrated Circuits (IC)
ICs or Integrated Circuits are packaged circuits designed for some purpose. An IC has its fixed IC name/number that can be used to of its functions and pin configuration. ICs come in various sizes and depending upon the purpose. NOTE: Numbering scheme of IC pins will be explained in the lab Different ICs may have different number of pins. fixed get catalog packages session.
Figure 7: IC
Robotics Club,IIT-Kanpur
LED
Tutorial 1
LED (Light Emitting Diode) is frequently used to display the outputs at various stages of the circuit. It is essentially a Diode with the energy released in the form of photons due to electron transitions falling in the visible region. Hence normal diode properties apply to it. It glows only in fwd bias mode i.e. with p junction connected to +ve voltage and n junction to negative. Diodes are essentially low power devices. The current through the LED should be less than 20mA.Hence always put a 220 ohm resistor in series with the LED. Never forget that LEDs consume a significant amount of power of the outputs of the ICs (CMOS based).Hence it is advisable to only use them for checking the voltage level (high or low) and then remove them.
Figure 8: LEDs
Robotics Club,IIT-Kanpur
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- TDSG5150, TDSG5160, TDSO5150, TDSO5160, TDSY5150, TDSY5160: Vishay SemiconductorsDocument12 paginiTDSG5150, TDSG5160, TDSO5150, TDSO5160, TDSY5150, TDSY5160: Vishay SemiconductorsFirman SetiawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3G Yagi Antenna PDFDocument1 pagină3G Yagi Antenna PDFHarshit BoradÎncă nu există evaluări
- Led - Blink in Lpc2148Document1 paginăLed - Blink in Lpc2148Harshit BoradÎncă nu există evaluări
- Embedded System ProjectDocument9 paginiEmbedded System ProjectIvan TehÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Electronic Technology: Lesson 1Document393 paginiElectronic Technology: Lesson 1Ali MohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- LM117, LM317-N Wide Temperature Three-Pin Adjustable RegulatorDocument50 paginiLM117, LM317-N Wide Temperature Three-Pin Adjustable RegulatorAnonymous IQkGuypÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Project Report On: "Wireless Data Acquisition System of Single Phase Induction Motor Using MATLAB"Document73 paginiA Project Report On: "Wireless Data Acquisition System of Single Phase Induction Motor Using MATLAB"AparnaghoshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nichicon Series Chart PDFDocument4 paginiNichicon Series Chart PDFIvan LukićÎncă nu există evaluări
- National - LM2575Document28 paginiNational - LM2575Irin ChoÎncă nu există evaluări
- NIC Components NTP SeriesDocument7 paginiNIC Components NTP SeriesNICCompÎncă nu există evaluări
- CS - 530-hướng - dẫn - sử - dụng - tiếng - anh 11Document155 paginiCS - 530-hướng - dẫn - sử - dụng - tiếng - anh 11Nguyễn Hảo100% (2)
- hfc19 Isol 8 72dpiDocument1 paginăhfc19 Isol 8 72dpivbraoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Capacitors (Capitulo de Testing Electronic Components Collin Mitchell)Document17 paginiCapacitors (Capitulo de Testing Electronic Components Collin Mitchell)arnoldo3551Încă nu există evaluări
- Databook 2021 Rev.6Document178 paginiDatabook 2021 Rev.6Brunophb2012Încă nu există evaluări
- Capacitors. Description and FunctionDocument12 paginiCapacitors. Description and FunctionscufigÎncă nu există evaluări
- 38 Richtek RT9183Document17 pagini38 Richtek RT9183Makhtar SeyeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technical Bulletin: Other ModelsDocument88 paginiTechnical Bulletin: Other ModelsSid Ahmed GANAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kit 17. LM386 Low Voltage Audio Amplifier: Circuit DescriptionDocument2 paginiKit 17. LM386 Low Voltage Audio Amplifier: Circuit Descriptionszolid79Încă nu există evaluări
- DC-DC Step-Down FelixDocument31 paginiDC-DC Step-Down FelixGFGHJHKÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zldo1117 PDFDocument12 paginiZldo1117 PDFJose Barroso GuerraÎncă nu există evaluări
- NIC Components NRWS SeriesDocument6 paginiNIC Components NRWS SeriesNICCompÎncă nu există evaluări
- MP4559 01Document19 paginiMP4559 01MaruthiÎncă nu există evaluări
- EkeDocument7 paginiEkeLorisBruzziÎncă nu există evaluări
- LM117 PDFDocument28 paginiLM117 PDFPedro OspinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- KP-38027 Maintenance Instructions A EnglishDocument34 paginiKP-38027 Maintenance Instructions A EnglishRonaldo GeradoresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electronic Playground: and Learning CenterDocument160 paginiElectronic Playground: and Learning CenterPaco AlemanyÎncă nu există evaluări
- IC-ON-LINE - CN dm0365r 44840Document20 paginiIC-ON-LINE - CN dm0365r 44840MoscandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- EmperorDocument12 paginiEmperorRafik HergéÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heathkit IT-28 Restoration - Thomas Bonomo K6ADDocument25 paginiHeathkit IT-28 Restoration - Thomas Bonomo K6ADMichel CormierÎncă nu există evaluări
- 110V LdoDocument20 pagini110V LdoJohn MelchizedekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rubycon CapacitorDocument4 paginiRubycon CapacitorAlan HoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electric and Electronic ComponentsDocument7 paginiElectric and Electronic ComponentsSyamala JothyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sony - DCR - hc44 DCR hc46 l3 v1.3Document56 paginiSony - DCR - hc44 DCR hc46 l3 v1.3h_trifonovÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rubycon Al Eectrolytics DatasheetDocument2 paginiRubycon Al Eectrolytics DatasheetEdgar DauzonÎncă nu există evaluări