Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Chapter 7 Nervous System Vocab
Încărcat de
famouspotatoDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Chapter 7 Nervous System Vocab
Încărcat de
famouspotatoDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Chapter 7 Nervous System Vocab
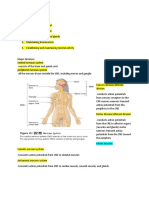
7-1 NERVOUS SYSTEM- master controlling and communicating system of body SENSORY INPUT- gathered information/changes occurring MOTOR OUTPUT- response by active muscles or glands CNS- brain & spinal cord, act as integrating and command centers of nervous system, interpret incoming sensory info and issue instructions PNS- peripheral nervous system, nerves that extend from brain & spinal cord, link all parts of body by carrying impulses from sensory receptors to CNS and from CNS to the appropriate glands or muscles SENSORY DIVISION- afferent, nerve fibers that convey impulses to the CNS from sensory receptors MOTOR DIVISION- efferent, carries impulses from CNS to effector organs (muscles & glands SOMATIC DIVISION- conscious control of skeletal muscles ANS- autonomic nervous system, regulates automatic/involuntary activity of smooth & cardiac muscles and glands, sympathetic and parasympathetic NEUROGLIA- supporting cells in CNS, nerve glue, includes astrocyte, microglia, ependymal, oligodendrocytes ASTROCYTE- star-shaped, of neural tissue, living barrier between capillaries and neurons, help protect neurons from harmful things in blood MICROGLIA- spiderlike phagocyte, dispose of debris like dead brain cells, bacteria EPENDYMAL- lines cavities of brain and spinal cord, circulate cerebrospinal fluid, cushion CNS OLIGODENDROCYTE - wrap extensions around nerve fibers, fatty insulating covers (myelin sheaths) SCHWANN CELL- form myelin sheaths around nerve fibers in PNS SATELLITE CELL- protective cushioning cells of PNS 7-2 NEURON- nerve cell CELL BODY- metabolic center of the neuron DENDRITE- incoming towards cell body AXON- conduct impulses away from cell body SYNAPTIC CLEFT- tiny gap in axon terminals separating each neuron SYNAPSE- a junction of 2 neurons MYELIN- whitish, fatty material, waxy appearance MYELIN SHEATH-tight coil of wrapped membranes, enclose axon NODE OF RANVIER- gaps in myelin in myelin sheath along the axon GANGLIA- small collections of cell bodies found in few sites outside the CNS in the PNS WHITE MATTER- myelinated fibers (tracts CNS) GRAY MATTER- unmyelinated fibers & cell bodies SENSORY/AFFERENT- nerves that carry impulses from sensory receptors to CNS, cell bodies found in ganglion outside CNS
MOTOR/EFFERENT- impulses from CNS to muscles and glands, cell bodies found in CNS INTERNEURON- association neurons, found in neural pathways in CNS, connect sensory and motor neurons, cell bodies found in CNS 7-3 POLARIZED- when plasma membrane is at rest (inactive) DEPOLARIZED- polarity is changed, results from inward rush of Na+, inside is more +/outside less + ACTION POTENTIAL- nerve impulse, all or none response IMPULSE- transmitted signal along a nerve REPOLARIZED- outflow of + ions from the cell restores electrical conditions at the membrane to a polarized (resting) state REFLEX ARC- neural pathway where reflexes occur sensory neuron, to interneuron, to effector REFLEX- rapid, predictable, involuntary responses to stimuli AUTONOMIC REFLEX- regulate activity of smooth muscles (digestion, elimination, blood pressure, sweating) SOMATIC REFLEX- stimulate skeletal muscles, e.g. pull hand away quickly from hot object 7-4 VENTRICLE- chambers resulting from enlarged central canal of the neural tube, 4 regions CEREBRAL HEMISPHERES- most superior part of brain, enclose and obscure most of brain stem GYRI- elevated ridges of tissue, covers surface of cerebral hem. SULCI- shallow grooves that separate gyri FISSURES- deeper grooves, separate large regions of brain LOBES- regions of cerebral hem divided by fissures OCCIPITAL LOBE- visual area located here in posterior part TEMPORAL LOBE- auditory & olfactory areas PARIETAL LOBE- somatic sensory area FRONTAL LOBE- primary motor area that allows us to consciously move skeletal muscles located here BROCAS AREA- speaking, base of precentral gyrus CORPUS CALLOSUM- large fiber tract that connects the cerebral hemispheres INTERBRAIN- diencephalon, sits atop brain stem & enclosed by cerebral hemispheres, includes thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus THALAMUS- encloses 3rd ventricle, relay station for sensory impulses, whether pleasant/unpleasant HYPOTHALAMUS- makes up floor of diencephalon, regulating body temperature, water balance, metabolism, center for drives & emotions, part of limbic system, regulates pituitary gland PITUITARY GLAND- hangs from anterior floor of hypothalamus, produces hormones PINEAL GLAND- part of endocrine system, part of the epithalamus BRAIN STEM- structures are midbrain, pons & medulla oblongata, has many small gray matter areas, control breathing & blood pressure
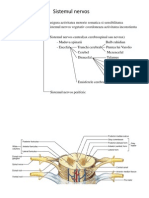
MIDBRAIN- small part of brain stem, extends from mammillary bodies to pons inferiorly, structures are cerebral aqueduct, cerebral peduncles, corpora quadrigemina PONS- rounded structures protruding just below midbrain, bridge, mostly fiber tracts, control of breathing CEREBELLUM- 2 hem, convoluted surface, outer cortex made up of gray matter and inner region of white matter, controls balance & equilibrium MEDULLA- most inferior part of brain stem, fiber tract area, control heart rate, blood pressure, breathing, swallowing, etc. RAS- reticular activating system, role in consciousness and awake/sleep cycles 7-5 MENINGES- 3 connective tissue membranes covering and protecting CNS structures DURA MATER- outermost layer, leathery, double-layered membrane surrounding brain ARACHNOID MATER - middle meningeal layer, weblike, threadlike extensions span subarachnoid space to attach to pia mater PIA MATER- innermost membrane, delicate, clings tightly to the surface of brain and spinal cord, following every fold CSF- cerebrospinal fluid, watery broth similar to blood in its makeup, but contains less protein and more vitamin C, forms a watery cushion that protects brain and cord CONCUSSION- slight brain injury, victim is dizzy or lose consciousness briefly but no perm dmg to brain CEREBRAL EDEMA- swelling of brain due to inflammatory response to injury, victim may die CVA- cerebrovascular accident, strokes, when blood circulation to brain is blocked and part of brain tissue dies DORSAL HORNS- posterior projection of the gray matter of spinal cord, contain interneurons VENTRAL HORNS-anterior projection of the gray matter of spinal cord , contain motor neuron cell bodies CENTRAL CANAL- in spinal cord, surrounded by gray matter, contains CSF QUADRIPLEGIC- when spinal cord injury occurs high in the cord so that all 4 limbs are affected PARAPLEGIC- caused by injury to spinal cord, only legs are paralyzed DORSAL ROOT- sensory neuron fibers enter the cord from these VENTRAL ROOT- motor neuron axons exit the cord from these 7-6 ENDONEURIUM PERINEURIUM EPINEURIUM CRANIAL NERVES SPINAL NERVES RAMI PLEXUS INVOLUNTARY NERVOUS SYSTEM SYMPATHETIC DIVISION
PARASYMPATHETIC DIVISION PREGANGLIONIC AXON POSTGANGLIONIC AXON TERMINAL GANGLION
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Nervous System: The Dog Stole the Professor's NotesDe la EverandNervous System: The Dog Stole the Professor's NotesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nervous Tissue List of TermsDocument7 paginiNervous Tissue List of TermsMARKUS GERARD REYESÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nervous System Part 1Document6 paginiNervous System Part 1rb YangzonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nervous System Reviewer!Document5 paginiNervous System Reviewer!Madelle Capending DebutonÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Nervous System: Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument85 paginiThe Nervous System: Anatomy & PhysiologyJamie Bagundol100% (3)
- 7-Nervous SystemDocument69 pagini7-Nervous SystemCarl Vincent VingnoÎncă nu există evaluări
- NeurophysiologyDocument21 paginiNeurophysiologyKeya PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 12 - An Introduction To The Nervous System: Peripheral Nerves)Document7 paginiChapter 12 - An Introduction To The Nervous System: Peripheral Nerves)tomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nervous System Transes 1Document6 paginiNervous System Transes 1Rhodie BatislaonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nervous (Doc Notes)Document8 paginiNervous (Doc Notes)besinioaleahjaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nervous TermsDocument1 paginăNervous TermsTorio Kristine Anne P.Încă nu există evaluări
- Nerves ReflexesDocument35 paginiNerves ReflexesFelisa Pauline VallarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nervous System: Chapter # 7Document69 paginiNervous System: Chapter # 7saddam ud dinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report in Physiological Psy. (Nervous System)Document27 paginiReport in Physiological Psy. (Nervous System)Francia VenancioÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Central Nervous SystemDocument59 paginiThe Central Nervous SystemJuliville Hora Salinas100% (1)
- Recap: Nervous System Biological Basis of Behavior Peripheral Nervous SystemDocument27 paginiRecap: Nervous System Biological Basis of Behavior Peripheral Nervous Systemfatima shahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio Terms DefDocument3 paginiBio Terms Defapi-31355470Încă nu există evaluări
- Overview of The Nervous SystemDocument32 paginiOverview of The Nervous Systemanita adamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nervous System - Lecture ReviewDocument23 paginiNervous System - Lecture ReviewLeinah RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 7 The Nervous System NotesDocument21 paginiCH 7 The Nervous System Notesbiswa217Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 8: Nervous SystemDocument15 paginiChapter 8: Nervous SystemAndrea BoocÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 2 Biological Foundations of Behaviour - Student OutlineDocument43 paginiModule 2 Biological Foundations of Behaviour - Student OutlineDweep BajajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Central Nervous SystemDocument7 paginiCentral Nervous SystemCaroleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Point Nervous Part 3cDocument11 paginiPower Point Nervous Part 3cnhicksxz000Încă nu există evaluări
- Module 1Document8 paginiModule 1laaraybmehmood1503Încă nu există evaluări
- NeurologyDocument118 paginiNeurologykep1313Încă nu există evaluări
- NeurologyDocument42 paginiNeurologybuzz Q100% (2)
- UntitledDocument2 paginiUntitledI am JÎncă nu există evaluări
- ISAP Lecture 1 Module 1 - Studocu NotesDocument6 paginiISAP Lecture 1 Module 1 - Studocu NotesLyndonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To NeuroanatomyDocument14 paginiIntroduction To NeuroanatomyRosalie CalisinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anaphy 3RD EXAM NOTESDocument2 paginiAnaphy 3RD EXAM NOTESJoel CastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science ReviewerDocument2 paginiScience ReviewerMarbel SsgÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Nervous System - Prepared by Group 3 1Document71 paginiThe Nervous System - Prepared by Group 3 1Shawn Henry CepedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nervous System - All NotesDocument6 paginiNervous System - All NotesJÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neuro Anatomy Neuro AssessmentDocument96 paginiNeuro Anatomy Neuro AssessmentJulia Rae Delos SantosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neuro Anatomy Neuro AssessmentDocument96 paginiNeuro Anatomy Neuro AssessmentJulia Rae Delos SantosÎncă nu există evaluări
- What To Study Nervous Endocrine ReproDocument2 paginiWhat To Study Nervous Endocrine ReproSean CampbellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit A - The Nervous and Endocrine SystemsDocument54 paginiUnit A - The Nervous and Endocrine Systemsdutritinh0806Încă nu există evaluări
- ??????? ?????? H. Idris N. Macmod A. Mangondato M. OmarDocument70 pagini??????? ?????? H. Idris N. Macmod A. Mangondato M. OmarHestia GreyertÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nervous SystemDocument9 paginiNervous SystemMuhamad Hafiz Bin Mohd BakriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brain and Cranial NervesaDocument38 paginiBrain and Cranial NervesaBenner BagsterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report in Physiological Psy. Nervous SystemDocument23 paginiReport in Physiological Psy. Nervous SystemFrancia VenancioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physiology ReviewDocument65 paginiPhysiology ReviewNandita KÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reviewer 3Document2 paginiReviewer 3blessiejamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nervous SystemDocument25 paginiNervous SystemRocky MrRockyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nervous SystemDocument53 paginiNervous SystemKing OmbionÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Nervous SystemDocument12 paginiThe Nervous SystemJoyce ElizaldeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neuroanatomy NotesDocument51 paginiNeuroanatomy NotesAditi MangalÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Paper Regarding The System of AnatomyDocument2 paginiA Paper Regarding The System of AnatomyPeidian PooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nervous SystemDocument27 paginiNervous SystemNARESH JANDIALÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nervous System - GeneralDocument81 paginiNervous System - Generalyash rajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oral Exam ReviewerDocument39 paginiOral Exam ReviewerFayena JoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nervous SystemDocument15 paginiNervous Systemchoudhryhamza124Încă nu există evaluări
- Nervous Systems, Cardiovascular, BloodDocument43 paginiNervous Systems, Cardiovascular, BloodArianne Jen GenotivaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 3Document4 paginiLesson 3JessieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nervous System: Two Major DivisionsDocument33 paginiNervous System: Two Major DivisionsRudi ArfiansyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anaphy MIDTERMS ReviewerDocument45 paginiAnaphy MIDTERMS Reviewerangelita aquinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nervous System 2Document7 paginiNervous System 2Darlin Karyle EncisoÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Central Nervous SystemDocument7 paginiThe Central Nervous Systemjoeywap29Încă nu există evaluări
- Wawa - Sistem Saraf PusatDocument38 paginiWawa - Sistem Saraf PusatnuhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Space Occupying Lesion: Case ReportDocument31 paginiSpace Occupying Lesion: Case ReportMaria Margareta HutajuluÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control and Coordination: Stick Progression Sheet and Pre-Assessment Sheet in Two Different PagesDocument45 paginiControl and Coordination: Stick Progression Sheet and Pre-Assessment Sheet in Two Different PagesPriyanshu ManwaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nervous SYSTESTDocument19 paginiNervous SYSTESTedwalk1250% (2)
- D'Mello, A. M., & Gabrieli, J. D. E. (2018) - Cognitive Neuroscience of Dyslexia.Document12 paginiD'Mello, A. M., & Gabrieli, J. D. E. (2018) - Cognitive Neuroscience of Dyslexia.Juli BailoneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blumenfeld Neuroanatomy Ch. 5 SummaryDocument5 paginiBlumenfeld Neuroanatomy Ch. 5 SummaryMeeraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Q Bank Physiology: Every Chapter Every Important Question Marks DistributionDocument27 paginiQ Bank Physiology: Every Chapter Every Important Question Marks DistributionHK Nova ChiuÎncă nu există evaluări
- PPYA - Advanced General Psychology Q - A 50 WordsDocument9 paginiPPYA - Advanced General Psychology Q - A 50 WordspradeepajoshiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neuroanatomy Notes UAWDocument252 paginiNeuroanatomy Notes UAWNabeel ShahzadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maduva Spinarii. Trunchiul Cerebral. CerebelDocument35 paginiMaduva Spinarii. Trunchiul Cerebral. CerebelI.m. DanielÎncă nu există evaluări
- CT I MRI Tumora MozgaDocument126 paginiCT I MRI Tumora MozgaElvir MalicevicÎncă nu există evaluări
- RADIOLOGY 1.7 Neuroradiology (CT)Document7 paginiRADIOLOGY 1.7 Neuroradiology (CT)ZazaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BiologyyDocument15 paginiBiologyyBrittany Tuyet SotoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report TextDocument5 paginiReport TextJuniorzSunshinersÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6.1 One Pager Nervous System - MEMODocument1 pagină6.1 One Pager Nervous System - MEMORudzi UdziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lim Tze Ying 184661 Fce3204Document19 paginiLim Tze Ying 184661 Fce3204Tze YingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan - CotDocument8 paginiLesson Plan - CotRutchie Quillo TuandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Korteks DoneDocument16 paginiKorteks DoneNur WahyudiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neuro DynamicsDocument26 paginiNeuro DynamicsRahul ChhatlaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neuroanatomy Notes PDFDocument66 paginiNeuroanatomy Notes PDFfatimaabeer083% (6)
- Hydrocephalus: Alka Sara Saju Ii Year MSC NursingDocument73 paginiHydrocephalus: Alka Sara Saju Ii Year MSC NursingNinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- KKD Cranial NDocument23 paginiKKD Cranial NAdie Kristanto100% (1)
- Gambaran Makroskopik Dan Mikroskopik Neoplasma Sistem Saraf PusatDocument7 paginiGambaran Makroskopik Dan Mikroskopik Neoplasma Sistem Saraf PusatIngrid NataschaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCQ For Students PractiseDocument37 paginiMCQ For Students PractiseSULOCHANA ARORAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Extra Class This Sat: Time: 9am-12pm Venue: CG04 PurposeDocument35 paginiExtra Class This Sat: Time: 9am-12pm Venue: CG04 Purposelengers poworÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Nervous System: Elaine N. MariebDocument91 paginiThe Nervous System: Elaine N. MariebLol lolÎncă nu există evaluări
- HAP1 Review: Dr. Garry NiedermayerDocument37 paginiHAP1 Review: Dr. Garry Niedermayersweta paudelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diencephalon and Brainstem - AMBOSS PDFDocument1 paginăDiencephalon and Brainstem - AMBOSS PDFOpio IsaacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dura Mater & Cranial SinusDocument30 paginiDura Mater & Cranial SinusSadiq Wadood Siddiqui100% (1)
- ELS Q2 M6 Organ Systems of Representative Animals 1 RDocument22 paginiELS Q2 M6 Organ Systems of Representative Animals 1 RtjeremyalleneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blood Supply of The BrainDocument11 paginiBlood Supply of The Brainneleh grayÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossDe la EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (6)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityDe la EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (28)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsDe la EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeDe la EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeEvaluare: 2 din 5 stele2/5 (1)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDDe la EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionDe la EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (404)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsDe la EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDe la EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (42)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedDe la EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (81)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsDe la EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (3)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDe la EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityDe la EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (3)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaDe la EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- Sleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningDe la EverandSleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (3)
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)De la EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Încă nu există evaluări
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDe la EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerDe la EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (392)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryDe la EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (44)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.De la EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (110)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlDe la EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (58)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessDe la EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (328)
- Dark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingDe la EverandDark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1138)
- Troubled: A Memoir of Foster Care, Family, and Social ClassDe la EverandTroubled: A Memoir of Foster Care, Family, and Social ClassEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (26)