Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Warehouse Science
Încărcat de
Anonymous 1gbsuaafddDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Warehouse Science
Încărcat de
Anonymous 1gbsuaafddDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Why We Have A Warehouse ? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
To better match the supply and demand To consolidate the product To reduce the transportation cost To improve customer service To provide value added processing / deferred product differentiation
Supply Chain is the sequence of processes through which product moves from it origin to customer Stock Keeping Unit (SKU) is the smallest physical unit of a product tracked by the organization and unique identifier for each product / service Honeycombing can be defined as waste of space resulting from partial depletion and inability to use remaining space in the pallet. Tie is the term used to describe the pattern of boxes / cartons in a layer. Load Stabilizers Stretch Wrap, Shrink Wrap, Adhesive tapes etc., DC Operating Cost Receiving Put away Order Picking Check, Pack & Ship Returns % 15% 10% 55% (Travel 50%,Search 15%,Extract 15%,Paper/Misc 20%) 15% 5%
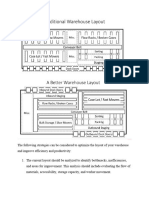
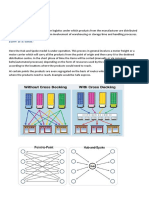
SKU / Pick Density If a warehouse area has high SKU density then it is likely to achieve high no. of picks Assigning Pick Face Locations for various SKUs 1. Calculate average cases / pcs picked per order 2. Calculate no of visits to the location (Pallet Qty/Average cases per order) 3. Arrange data in descending order - no. of visit to location 4. Higher the number, pick face should be closure to the shipping area Warehouse Layouts 1. U Shaped or Cross-docking a. Receiving and shipping located in the same side of the warehouse b. Appropriate when product movements has strong ABC skew c. Provides flexibility between Receiving and shipping d. More efficient usage of Fork Lift e. Limited set back area f. Expansion possible in other three sides of the warehouse
2. Flow Through a. Receiving and shipping is done in opposite sides of the warehouse b. Appropriate for high volume warehouse c. Preferable when building is narrow at receiving & shipping side of the warehouse
Assigning Fast Pick / Forward Pick Locations 1. Arrange sku wise data of (a) no. of LTP (Less than pallet) picks per pallet (b) Qty Picked (c) Pallet Ti x Hi or UPP 2. Calculate b / c x a and arrange data in descending order. 3. Lower the number, it is a candidate for direct pick from rack location. 4. Higher the number, most convenient locations to be allocated 5. If no of fast pick locations available are less, locations to be allocated from top of the list and sku in the bottom should be picked through direct pick from rack location. Slotting Slotting means assigning items or SKUs to the correct storage location. The goal is to make fast moving products easily accessible without large amounts of walking required to pick them. Determine where to store each SKU, what storage method to use and how much to store by capturing the following slotting measures: 1. Popularity: The no. of requests for a SKU during a certain period. 2. Cube-per-order: Average volume of the SKU per order 3. Volume: Total volume of a SKU shipped during the period. 4. Pick density: The number of requests per CBM of a SKU Points to be considers while slotting: - Increase picking accuracy by separating similar products to avoid proximity picking errors. - Reduce possibility of injuries by placing SKU in ergonomically best location - Reduce product damage by organizing heavier product first in the pick path, ahead of crushable product - Group products with similar case height for easy palletization & reduction of damages - Reserve/bulk stocks to be stored in the same aisle as fast pick location Re-slotting to done on regular frequency once in 3 months or whenever new product range is introduced since SKUs profile keep changing.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- KANBAN: Streamlining Workflow for Effortless Efficiency (2023 Guide for Beginners)De la EverandKANBAN: Streamlining Workflow for Effortless Efficiency (2023 Guide for Beginners)Încă nu există evaluări
- Receiving PutawayDocument16 paginiReceiving Putawaypurplestains88Încă nu există evaluări
- Warehouse DesignDocument24 paginiWarehouse DesignAmrit100% (1)
- The Official Supply Chain Dictionary: 8000 Researched Definitions for Industry Best-Practice GloballyDe la EverandThe Official Supply Chain Dictionary: 8000 Researched Definitions for Industry Best-Practice GloballyEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (4)
- Ankit Singhvi Mahipatraj - GroupAssignment - Group2Document6 paginiAnkit Singhvi Mahipatraj - GroupAssignment - Group2Ankit SinghviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Order Picking and Order AccumulationDocument4 paginiOrder Picking and Order Accumulationschool chelcie100% (1)
- Surviving the Spare Parts Crisis: Maintenance Storeroom and Inventory ControlDe la EverandSurviving the Spare Parts Crisis: Maintenance Storeroom and Inventory ControlÎncă nu există evaluări
- WarehousingDocument54 paginiWarehousingTimothy FieldsÎncă nu există evaluări
- System Directed PutawayDocument3 paginiSystem Directed PutawayJovan ĆetkovićÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expert Insight: Optimizing Warehouse Facility DesignDocument4 paginiExpert Insight: Optimizing Warehouse Facility DesignMd Abdullah Al ArmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Storage & Warehousing: BY: Prof. Maria Nieves D. ElarcoDocument19 paginiStorage & Warehousing: BY: Prof. Maria Nieves D. ElarcoLevi BrianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Racking SystemDocument76 paginiRacking SystemmlogvijayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Warehouse LogisticsDocument12 paginiWarehouse LogisticsarzusafranÎncă nu există evaluări
- C H A P T E R 9 Storage and Warehouse SystemsDocument114 paginiC H A P T E R 9 Storage and Warehouse SystemsKhaled SamaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ipm01 - (Guardian&barrios) Industrial Planning and Material HandlingDocument124 paginiIpm01 - (Guardian&barrios) Industrial Planning and Material HandlingEllen Jane Cantuba GuardianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inventory Management: Presenter NameDocument33 paginiInventory Management: Presenter NameMuhammad Sajid SaeedÎncă nu există evaluări
- WarehousingDocument33 paginiWarehousingOnkar SawantÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lean Management: Warehousing Decisions & LayoutsDocument55 paginiLean Management: Warehousing Decisions & Layoutsmegaspice100% (5)
- Cross Docking PPT AVENGERSDocument13 paginiCross Docking PPT AVENGERSRei RacazaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation Stores and Inventory Management 2Document20 paginiPresentation Stores and Inventory Management 2PMU Chimhanda District HospitalÎncă nu există evaluări
- IE-484 Ch7Document11 paginiIE-484 Ch7ecelara02Încă nu există evaluări
- Warehouse EquipmentDocument21 paginiWarehouse EquipmentSarin Paraparakath100% (1)
- DM PreviousDocument4 paginiDM PreviousRanan AlaghaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) - WarehousingDocument5 paginiKey Performance Indicators (KPIs) - WarehousingPerumal DM100% (1)
- Dpl30033 - Fundamentals of Warehouse Operations: Lecturer'S Name: Puan Hasnieza Binti Mokhtar Class: Dls3ADocument16 paginiDpl30033 - Fundamentals of Warehouse Operations: Lecturer'S Name: Puan Hasnieza Binti Mokhtar Class: Dls3AAinIdris 1007Încă nu există evaluări
- Conventional Storage ModelsDocument16 paginiConventional Storage ModelsmershaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Warehouse ProcessesDocument27 paginiWarehouse ProcessesPrasad Ganti100% (1)
- Meaning of Logistics & Market Logistics DecisionDocument41 paginiMeaning of Logistics & Market Logistics Decisionyuktichauhan07100% (2)
- NITIE Game Changers JNJ QuestDocument10 paginiNITIE Game Changers JNJ QuestVarun Mitra100% (1)
- Manual de Logística y Almacenes IDocument12 paginiManual de Logística y Almacenes IK-PurpleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reduction of Walking Time in The Distribution Center of de BijenkorfDocument20 paginiReduction of Walking Time in The Distribution Center of de BijenkorfBipin DevÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 9. Warehouse ManagementDocument7 paginiTopic 9. Warehouse ManagementAbigail SalasÎncă nu există evaluări
- شبكة لوجستيةDocument4 paginiشبكة لوجستيةAbdulrhman AlshameriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Distribution SystemDocument29 paginiPhysical Distribution Systemshweta_466640% (1)
- An Efficient Model For Allocating Products and Designing A WarehouseDocument10 paginiAn Efficient Model For Allocating Products and Designing A WarehouseSelvi AnandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Raymond Case StudyDocument4 paginiRaymond Case StudyANANTA VISHAIN-IB 21IB307Încă nu există evaluări
- Ch12 - WarehousingDocument20 paginiCh12 - WarehousingSwarnadevi GanesanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity ProfilingDocument9 paginiActivity ProfilingSafijo AlphonsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inventory BasicsDocument63 paginiInventory BasicsMaulikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Warehouse OperationsDocument9 paginiWarehouse Operationssanzit100% (1)
- Notes: Supply Chain Management - Maria Carmela Rojo CaupayanDocument4 paginiNotes: Supply Chain Management - Maria Carmela Rojo CaupayanMaria CarmelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inventory Accuracy Through Warehouse Control - ProQuest Central - ProQuest PDFDocument4 paginiInventory Accuracy Through Warehouse Control - ProQuest Central - ProQuest PDFphamanh1803Încă nu există evaluări
- Answer Key: False FalseDocument11 paginiAnswer Key: False FalseHannah Felisa MalizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 Storage SystemDocument42 paginiChapter 4 Storage SystemDiscord YtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kuliah - 10 Dan 11 Logistics-Warehousing1Document67 paginiKuliah - 10 Dan 11 Logistics-Warehousing1Syukri SyahabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review MHS So N PDFDocument11 paginiReview MHS So N PDFNhan DOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Warehousing 101Document69 paginiWarehousing 101silfi100% (1)
- 2 - Supply - Chain - 009 - Supply - Chain - Execution - Basics - GlossaryDocument43 pagini2 - Supply - Chain - 009 - Supply - Chain - Execution - Basics - GlossaryJuhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Cross Docking?Document2 paginiWhat Is Cross Docking?Shubham DixitÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Application of Discrete Event Simulation On OrderDocument7 paginiAn Application of Discrete Event Simulation On OrderAhmad BuchoriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Business Process: Goods Receipt and Rejecting Goods ProcessDocument3 paginiBusiness Process: Goods Receipt and Rejecting Goods ProcessAbhijit GhodakeÎncă nu există evaluări
- White Paper: Goods To Person Order FulfillmentDocument9 paginiWhite Paper: Goods To Person Order FulfillmentAlzany OsmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Routing Orderpickers in A Warehouse: A Comparison Between Optimal and Heuristic SolutionsDocument12 paginiRouting Orderpickers in A Warehouse: A Comparison Between Optimal and Heuristic SolutionsDityan KaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basics of Warehouse ManagementDocument32 paginiBasics of Warehouse Managementvijaysangam89% (18)
- An Introduction To Warehousing and The Underlying Facility Design IssuesDocument47 paginiAn Introduction To Warehousing and The Underlying Facility Design IssuesTrinath OjhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Warehouse Layout and PlanningDocument12 paginiWarehouse Layout and PlanningJasmine KariukiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASRSDocument38 paginiASRSAnonymous eQlZsMmi940% (1)
- An Introduction To Warehousing and The Underlying Facility Design IssuesDocument54 paginiAn Introduction To Warehousing and The Underlying Facility Design IssuesGabriele LorussoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Overview of Standard WeightsDocument16 paginiOverview of Standard WeightsAnonymous 1gbsuaafddÎncă nu există evaluări
- Designing Layout For Manual Order Picking in WarehousesDocument34 paginiDesigning Layout For Manual Order Picking in WarehousesAnonymous 1gbsuaafddÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ganapathipura Building Cost: Date Particulars Sub Amount Total Amount Cumulative AmountDocument1 paginăGanapathipura Building Cost: Date Particulars Sub Amount Total Amount Cumulative AmountAnonymous 1gbsuaafddÎncă nu există evaluări
- Articles On Order Picking and Warehouse ManagementDocument52 paginiArticles On Order Picking and Warehouse ManagementAnonymous 1gbsuaafddÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industry I Table of Key Performance IndicatorsDocument26 paginiIndustry I Table of Key Performance IndicatorsAnonymous 1gbsuaafddÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thing To DoDocument1 paginăThing To DoAnonymous 1gbsuaafddÎncă nu există evaluări
- AbcanalysisDocument298 paginiAbcanalysisAnonymous 1gbsuaafddÎncă nu există evaluări
- Supply Chain Management in International Logistics - RFID ApplicationsDocument25 paginiSupply Chain Management in International Logistics - RFID ApplicationsAnonymous 1gbsuaafddÎncă nu există evaluări
- Motorola RFID Transportation Logistics White PaperDocument8 paginiMotorola RFID Transportation Logistics White PaperAnonymous 1gbsuaafddÎncă nu există evaluări
- Refrigeration Heat Load EstimatingDocument17 paginiRefrigeration Heat Load EstimatingAnonymous 1gbsuaafddÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pallet Racking GuideDocument33 paginiPallet Racking GuideAnonymous 1gbsuaafddÎncă nu există evaluări
- Warehousing DesignDocument34 paginiWarehousing DesignRamneek Singh KhalsaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Logistics Technology Final 02.16.10Document32 paginiLogistics Technology Final 02.16.10Anonymous 1gbsuaafddÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flow Chart SymbolsDocument3 paginiFlow Chart SymbolsAnonymous 1gbsuaafddÎncă nu există evaluări
- Warehouse Staff Performance AppraisalDocument3 paginiWarehouse Staff Performance AppraisalAnonymous 1gbsuaafdd50% (2)
- Thirteen Aesthetic Tie KnotsDocument51 paginiThirteen Aesthetic Tie KnotsAnonymous 1gbsuaafddÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of Jewelleries With Tamil Selvi: Purchase Date Item Grams ValueDocument2 paginiList of Jewelleries With Tamil Selvi: Purchase Date Item Grams ValueAnonymous 1gbsuaafddÎncă nu există evaluări
- EstimateDocument5 paginiEstimateAnonymous 1gbsuaafddÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cheat Code Excel 2010Document2 paginiCheat Code Excel 2010Hasan ShahariarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nestle Refusal Analysis by Customer: PERIOD: JanuaryDocument7 paginiNestle Refusal Analysis by Customer: PERIOD: JanuaryAnonymous 1gbsuaafddÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clearing Negative SpiritsDocument6 paginiClearing Negative SpiritsmehorseblessedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample Midterm ExamDocument6 paginiSample Midterm ExamRenel AluciljaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fundamental Rights-Right To Equality, Prohibition of Discrimination, Right To Equality of OpportunityDocument76 paginiFundamental Rights-Right To Equality, Prohibition of Discrimination, Right To Equality of OpportunityutkarshÎncă nu există evaluări
- ESU Mauritius Newsletter Dec 2014Document8 paginiESU Mauritius Newsletter Dec 2014Ashesh RamjeeawonÎncă nu există evaluări
- VtDA - The Ashen Cults (Vampire Dark Ages) PDFDocument94 paginiVtDA - The Ashen Cults (Vampire Dark Ages) PDFRafãoAraujo100% (1)
- AASW Code of Ethics-2004Document36 paginiAASW Code of Ethics-2004Steven TanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Infusion Site Selection and Infusion Set ChangeDocument8 paginiInfusion Site Selection and Infusion Set ChangegaridanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Essay EnglishDocument4 paginiEssay Englishkiera.kassellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Islamic Meditation (Full) PDFDocument10 paginiIslamic Meditation (Full) PDFIslamicfaith Introspection0% (1)
- Mathematics Paper 1 TZ2 HLDocument16 paginiMathematics Paper 1 TZ2 HLPavlos StavropoulosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Top 100 Questions On Modern India History PDFDocument16 paginiTop 100 Questions On Modern India History PDFmohammed arsalan khan pathan100% (1)
- Reported Speech StatementsDocument1 paginăReported Speech StatementsEmilijus Bartasevic100% (1)
- WFRP - White Dwarf 99 - The Ritual (The Enemy Within)Document10 paginiWFRP - White Dwarf 99 - The Ritual (The Enemy Within)Luife Lopez100% (2)
- Customizable Feature Based Design Pattern Recognition Integrating Multiple TechniquesDocument191 paginiCustomizable Feature Based Design Pattern Recognition Integrating Multiple TechniquesCalina Sechel100% (1)
- The Role of Mahatma Gandhi in The Freedom Movement of IndiaDocument11 paginiThe Role of Mahatma Gandhi in The Freedom Movement of IndiaSwathi Prasad100% (6)
- Diode ExercisesDocument5 paginiDiode ExercisesbruhÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9m.2-L.5@i Have A Dream & Literary DevicesDocument2 pagini9m.2-L.5@i Have A Dream & Literary DevicesMaria BuizonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem ManagementDocument33 paginiProblem Managementdhirajsatyam98982285Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 - Risk Assessment ProceduresDocument40 paginiChapter 4 - Risk Assessment ProceduresTeltel BillenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trudy Scott Amino-AcidsDocument35 paginiTrudy Scott Amino-AcidsPreeti100% (5)
- Windows SCADA Disturbance Capture: User's GuideDocument23 paginiWindows SCADA Disturbance Capture: User's GuideANDREA LILIANA BAUTISTA ACEVEDOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Influencing Factors Behind The Criminal Attitude: A Study of Central Jail PeshawarDocument13 paginiInfluencing Factors Behind The Criminal Attitude: A Study of Central Jail PeshawarAmir Hamza KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hombres Mujeres Cmo Salir Del Camino Equivocado Spanish Edition by Badinter Lisabeth 950557584xDocument5 paginiHombres Mujeres Cmo Salir Del Camino Equivocado Spanish Edition by Badinter Lisabeth 950557584xFernanda Avilés CartagenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Druze ScriptureDocument15 paginiDruze ScriptureChristopher DeMott100% (2)
- Indg 264.3 w02Document15 paginiIndg 264.3 w02FrauÎncă nu există evaluări
- Business Finance and The SMEsDocument6 paginiBusiness Finance and The SMEstcandelarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Book of Dynamic Assessment in Practice PDFDocument421 paginiBook of Dynamic Assessment in Practice PDFkamalazizi100% (1)
- A Quality Improvement Initiative To Engage Older Adults in The DiDocument128 paginiA Quality Improvement Initiative To Engage Older Adults in The Disara mohamedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 INTRODUCTION TO PRESTRESSED CONCRETEDocument15 paginiChapter 4 INTRODUCTION TO PRESTRESSED CONCRETEyosef gemessaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Beginning AutoCAD® 2022 Exercise Workbook: For Windows®De la EverandBeginning AutoCAD® 2022 Exercise Workbook: For Windows®Încă nu există evaluări
- From Vision to Version - Step by step guide for crafting and aligning your product vision, strategy and roadmap: Strategy Framework for Digital Product Management RockstarsDe la EverandFrom Vision to Version - Step by step guide for crafting and aligning your product vision, strategy and roadmap: Strategy Framework for Digital Product Management RockstarsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Certified Solidworks Professional Advanced Surface Modeling Exam PreparationDe la EverandCertified Solidworks Professional Advanced Surface Modeling Exam PreparationEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Autodesk Fusion 360: A Power Guide for Beginners and Intermediate Users (3rd Edition)De la EverandAutodesk Fusion 360: A Power Guide for Beginners and Intermediate Users (3rd Edition)Evaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (2)
- AutoCAD 2010 Tutorial Series: Drawing Dimensions, Elevations and SectionsDe la EverandAutoCAD 2010 Tutorial Series: Drawing Dimensions, Elevations and SectionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Comprehensive Guide to Video Game Design SchoolsDe la EverandA Comprehensive Guide to Video Game Design SchoolsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Autodesk Fusion 360 Black Book (V 2.0.12670) - Part 1De la EverandAutodesk Fusion 360 Black Book (V 2.0.12670) - Part 1Încă nu există evaluări
- Autodesk Fusion 360 Black Book (V 2.0.10027) - Part 2De la EverandAutodesk Fusion 360 Black Book (V 2.0.10027) - Part 2Încă nu există evaluări