Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Learn To Read Latin: Ch. 14 Outline
Încărcat de
Jessica ChaseTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Learn To Read Latin: Ch. 14 Outline
Încărcat de
Jessica ChaseDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
LEARN TO READ LATIN CH.
14
Learn to Read Latin: Ch. 14
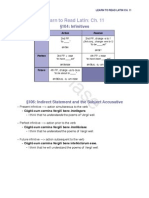
131: Result Clauses
Subordinate clause reporting the result of an action. A result may be: an event likely to follow upon the action of a main verb an event actually occurring or actually having occurred Result clauses are introduced by ut and take verbs in the subjunctive based on the rules of sequence. Result clauses are usually signaled by adverbs or adjectives of degree, including: ade, ita, sc, tam, tlis, tle, tantus, -a, -um, tot
A result clause combined with the Relative Clause of Characteristic. Uses qu / qun.
Certain verbs and verb phrases appear with noun clauses called Substantive Ut clauses. These clauses function as either subjects or direct objects. Common expressions that introduce these clauses: accidit or t it happens er potest it is able to happen / it is possible efcere or facere to bring it about / to see to it Negated by ut nn, ut nm, etc. N may be used in a command or exhortation.
To make an Indirect Statement containing a future passive verb, Latin uses fore the future active innitive of sum, esse, fu, futrus substantive ut clause with a subjunctive verb in sequence
j.
132: Relative Clauses of Result 133: Substantive Ut Clauses 134: Fore ut Construction
ch
e as
LEARN TO READ LATIN CH. 14
135: Impersonal Constructions
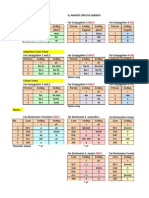
Common regular impersonal verbs: licet, licre, licuit / licitum est it is allowed, it is permitted necesse est it is necessary oportet, oportre, oportuit it is proper, it is right Impersonal constructions can take: subject innitive + subject accusative Necesse est homins sse cibum. It is necessary for men to eat food. subject innitive + dative of Reference Licet Domina Gaga canat. Lady Gaga singing is permitted. subjunctive (without ut) Oportet omns d morte timeant. All fearing death is proper.
Genitive of Possession, extended to describe characteristics. Vocabulary
lna, lnae f. moon aets, aettis f. age; lifetime; time agmen, agminis n. line (of march), column; army; multitude, throng auctrits, auctrittis f. authority; inuence nmen, nminis n. name s, ris n. [in sing. or pl.] mouth; face sl, slis m. sun aliquis, aliquid or quis, quid or quisquam, quicquam [indef. pron.] someone, something; anyone, anything aliqu, aliqua, aliquod or qu, qua, quod [indef. adj.] some, any quisque, quidque / quicque [indef. pron.] each/every man/woman, each/every thing quque, quaeque, quodque [indef. adj.] each, every spect, spectre, spectv, specttus to look (at), observe accid, accidere, accid, to happen efci, efcere, effc, effectus to make; bring about
j.
136: Genitive of Characteristic
ch e as
LEARN TO READ LATIN CH. 14
metu, metuere, metu, to fear, dread occid, occidere, occid, occsrus to fall, set; die prem, premere, press, pressus to press (hard); overpower; check opprim, opprimere, oppress, oppressus to press on; close, overwhelm, oppress orior, orr, ortus sum to rise, arise absum, abesse, fu, futrus to be absent, be distant adsum, adesse, adfu, adfutrus to be present, be near cnfer, cnferre, contul, colltus to bring together, collect; compare; direct; confer licet, licre, licuit / licitum est it is permitted oportet, oportre, oportuit it is proper, it is right cnctus, -a, -um all reliquus, -a, -um remaining, rest (of) absns, absentis absent vetus, veteris old necesse [indecl. adj.] necessary ade [adv.] to such/so great an extent, (so) very haud [adv.] not at all, by no means quods [conj.] but if vel [conj.] or; [adv.] even vel vel either or vix [adv.] scarcely, hardly
j.
ch
e as
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Learn To Read Latin: Ch. 15 OutlineDocument4 paginiLearn To Read Latin: Ch. 15 OutlineJessica ChaseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Learn To Read Latin: Ch. 13 OutlineDocument4 paginiLearn To Read Latin: Ch. 13 OutlineJessica ChaseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Learn To Read Latin: Ch. 11 OutlineDocument4 paginiLearn To Read Latin: Ch. 11 OutlineJessica ChaseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Learn To Read Latin: Ch. 12 OutlineDocument3 paginiLearn To Read Latin: Ch. 12 OutlineJessica ChaseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Learn To Read Latin: Ch. 10 OutlineDocument3 paginiLearn To Read Latin: Ch. 10 OutlineJessica Chase100% (1)
- Latin 123Document3 paginiLatin 123Christina Danielle GoldsbyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Latin Verb ConjugationsDocument1 paginăLatin Verb ConjugationsStephanieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Singular Plural 1 Person 2 Person 3 Person: MackeyDocument12 paginiSingular Plural 1 Person 2 Person 3 Person: MackeyshaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Latin Phrase Book C. MeissnerDocument118 paginiLatin Phrase Book C. MeissnerjpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Latin Participles ExplainedDocument5 paginiLatin Participles Explainednik_nitchÎncă nu există evaluări
- As Latin - Vocabulary ListDocument12 paginiAs Latin - Vocabulary ListjrewingheroÎncă nu există evaluări
- SimplicissimusDocument184 paginiSimplicissimusbelinaro8000Încă nu există evaluări
- Dictionaries: Language ToolsDocument2 paginiDictionaries: Language ToolscatalinccÎncă nu există evaluări
- Latin 3rd Declension & Verb ConjugationsDocument14 paginiLatin 3rd Declension & Verb ConjugationsAmandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Latin I Notes Pronunciation Verb ConjugationDocument1 paginăLatin I Notes Pronunciation Verb ConjugationScott RobertsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rules for Latin Indirect StatementDocument6 paginiRules for Latin Indirect StatementEsteban ArangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Latin Dictionary Entry DoubleDocument2 paginiLatin Dictionary Entry DoubleMagister Cummings100% (2)
- Latin GrammarDocument353 paginiLatin GrammarAngelo MiradoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Latin OnlineDocument5 paginiLatin OnlinehascribdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Latin Study Guide Book 2Document66 paginiLatin Study Guide Book 2GÎncă nu există evaluări
- Latin XLSMDocument18 paginiLatin XLSMPrince Otchere67% (3)
- 17 (Latin)Document9 pagini17 (Latin)nookmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Latin ParticlesDocument2 paginiLatin ParticlesJohn KasioÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Chants of ChristmasDocument4 paginiThe Chants of ChristmasTomDokÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pronunciation of LatinDocument38 paginiPronunciation of Latinpaulo201088Încă nu există evaluări
- Latin Grammar Tables From Second Steps To LatinDocument16 paginiLatin Grammar Tables From Second Steps To LatinHaroun MahmudÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chronology of TLM Event in The PhilippinesDocument3 paginiChronology of TLM Event in The PhilippinesTheus LineusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principal Parts: The 4th P.P. Means - Ed (And Nothing Else)Document22 paginiPrincipal Parts: The 4th P.P. Means - Ed (And Nothing Else)daviduck100% (1)
- Ecclesiastical LatinDocument3 paginiEcclesiastical LatinbogarguzÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of Latin Phrases (Full) - WikipediaDocument339 paginiList of Latin Phrases (Full) - WikipediaEdgar ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- AblativeAbsolute PDFDocument1 paginăAblativeAbsolute PDFjayursusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Latin-English VocabularyDocument42 paginiLatin-English Vocabularycnselhdjs100% (1)
- PdfPro Archia Allcroft and PlaistoweDocument116 paginiPdfPro Archia Allcroft and Plaistowemjrmjr6401Încă nu există evaluări
- Latin Cases Study GuideDocument3 paginiLatin Cases Study GuideIvan WaddellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Latin II NotesDocument10 paginiLatin II NotesbillyjenningsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ordo Visitandum Ad CoemeteriumDocument4 paginiOrdo Visitandum Ad CoemeteriumJericho AguiatanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Primer VocabularyDocument74 paginiPrimer VocabularyHassile EntatanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Latin Vocabulary ChartDocument2 paginiLatin Vocabulary ChartAbel Delgado100% (1)
- Latin 4 Grammar PacketDocument33 paginiLatin 4 Grammar PacketmagistramccawleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conversational LatinDocument2 paginiConversational LatinmagistramccawleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wheelock's Latin Noun Review1Document27 paginiWheelock's Latin Noun Review1Paul Whalen100% (1)
- Donaldson, James - Elementary Latin Grammar (1872)Document148 paginiDonaldson, James - Elementary Latin Grammar (1872)Verónica Díaz Pereyro100% (1)
- Latin@StemcivicsDocument41 paginiLatin@StemcivicsLucÎncă nu există evaluări
- Latin Grammar TablesDocument16 paginiLatin Grammar TablesDylan NickelsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Greek Verbs: An Introduction For The LearnerDocument10 paginiGreek Verbs: An Introduction For The LearnerMira Spasova100% (1)
- Latin Is Not Different (Patrick 2011)Document15 paginiLatin Is Not Different (Patrick 2011)Renato Felipe0% (1)
- Proarchiaeditedb 00 CiceuoftDocument118 paginiProarchiaeditedb 00 CiceuofttangosiniestroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Classroom Expressions 1Document7 paginiClassroom Expressions 1Reuel MartinezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summary of The First 17 Lessons of Homeric GreekDocument54 paginiSummary of The First 17 Lessons of Homeric Greekutuk3333Încă nu există evaluări
- Divine Office HymnsDocument6 paginiDivine Office Hymnsafrothunder7260% (1)
- Latin - Emerging Nomen - Tweet HoraDocument1 paginăLatin - Emerging Nomen - Tweet HoraMagister Cummings100% (1)
- Glossary of Latin WordsDocument682 paginiGlossary of Latin WordsJorge HegelÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Order of MarriageDocument6 paginiThe Order of MarriageVince DeVendra100% (1)
- Irregular Latin VerbsDocument6 paginiIrregular Latin VerbsiapostolatuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hebrew Grammar DavidsonDocument248 paginiHebrew Grammar DavidsonDav ChhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Latin Unit 1 (Primer Ecclesiastical Latin Textbook)Document2 paginiLatin Unit 1 (Primer Ecclesiastical Latin Textbook)Clarence AG YueÎncă nu există evaluări
- 16 Latin EnglishDocument4 pagini16 Latin EnglishGABRIELEÎncă nu există evaluări
- English GrammerDocument72 paginiEnglish GrammerBhupendra Kumar100% (1)
- Present Perfect For PresentationDocument11 paginiPresent Perfect For PresentationMohammadZulhusniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mock Test 5Document15 paginiMock Test 5MadhuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Absolute Beginner S1 #1 First Encounters in Filipino: Lesson TranscriptDocument4 paginiAbsolute Beginner S1 #1 First Encounters in Filipino: Lesson TranscriptPeter shaanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Open Communicative BeginnersDocument38 paginiOpen Communicative BeginnersJamie León-BassettÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nwea Vocabulary Appendix ADocument38 paginiNwea Vocabulary Appendix Aapi-242331349100% (1)
- Linguistic Characteristics of SinhaleseDocument14 paginiLinguistic Characteristics of SinhaleseRanjini VarnasuriyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- My Financial CareerDocument8 paginiMy Financial CareerRahul Dodiya100% (3)
- 2024 GKS-G Available Departments (SeoulNational Univ.)Document4 pagini2024 GKS-G Available Departments (SeoulNational Univ.)zafarmughal215Încă nu există evaluări
- Least-Learned Skills: 2021-2022 Grade Ii DaisyDocument4 paginiLeast-Learned Skills: 2021-2022 Grade Ii DaisyMaica Magnolia SullanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Writing Warm-Up CampingDocument35 paginiWriting Warm-Up Campingapi-459118418Încă nu există evaluări
- Lesson PlanDocument4 paginiLesson PlanKen CamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Twister 4 WDocument89 paginiTwister 4 Wliam1972100% (3)
- Hul IslamDocument2 paginiHul IslamAnonymous P98yy1Încă nu există evaluări
- Thomas Dubay - Authenticity PDFDocument139 paginiThomas Dubay - Authenticity PDFTesinaES0% (1)
- English II tag questions and activitiesDocument11 paginiEnglish II tag questions and activitiesWilliam Giovanny SASTOQUE OVALLEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group A - SUMMER CAMP 2008 - Lesson PlansDocument4 paginiGroup A - SUMMER CAMP 2008 - Lesson Plansapi-19635461Încă nu există evaluări
- Wonderware InTouch 10.1 Readme PDFDocument10 paginiWonderware InTouch 10.1 Readme PDFvishadkapadiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Countable and Uncountable NounsDocument20 paginiCountable and Uncountable NounsmscarletbÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engl 101 Final Test 2018Document4 paginiEngl 101 Final Test 2018api-417692500Încă nu există evaluări
- 3250 L532M DatasheetDocument2 pagini3250 L532M DatasheetJavaid HosanyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Origin of Meitei PungDocument53 paginiOrigin of Meitei Pungdiana100% (4)
- Herminder Ohri Taposhi GhoshalDocument24 paginiHerminder Ohri Taposhi GhoshalPratham Books100% (6)
- Hari Rao-History of Srirangam TempleDocument209 paginiHari Rao-History of Srirangam TempleSuganya86% (7)
- GERVER 1976 - Empirical Studies of Simultaneous Interpretation - A Review and A ModelDocument43 paginiGERVER 1976 - Empirical Studies of Simultaneous Interpretation - A Review and A ModelKarina Borges Lima100% (1)
- Serial Port CommunicationDocument4 paginiSerial Port CommunicationAshPan123100% (1)
- 4 NoDocument3 pagini4 NoFor StudentsÎncă nu există evaluări
- German Verbs With Prepositions: Denken An Arbeiten AnDocument4 paginiGerman Verbs With Prepositions: Denken An Arbeiten Anabhinay lakkireddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8969 AgDocument25 pagini8969 Agtabisa dunjanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- English 9: Quarter 1 - Module 1ADocument22 paginiEnglish 9: Quarter 1 - Module 1ACarlo GilberoÎncă nu există evaluări
- TEACHERDocument143 paginiTEACHERTamara TrajkoskiÎncă nu există evaluări
- EU Tobul-1Document4 paginiEU Tobul-1Sam Tc LalduhthlanaÎncă nu există evaluări