Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Assignment 05 - Virgin Group
Încărcat de
FazlanMarikkarDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Assignment 05 - Virgin Group
Încărcat de
FazlanMarikkarDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Strategic Management
Individual Assignment
Ba (honors) in business & management
Offered by Cardiff metropolitan university
Strategic management
Assignment 05 the virgin group
Word count - 1060
Submitted to: Mr. Shane De Silva
M.F.M.M Fazlan ICBT/ BABM/07/12
BABM/07/12 Page 1
Strategic Management
Individual Assignment
Table of Contents
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Introduction ............................................................................................................................. 3 The Corporate Rationale of Virgin as a Group of Companies ................................................ 4 The Relationships of a Strategic Nature Between Businesses Within the Virgin Portfolio .... 4 The Ways of Virgin Group add Value as a Corporate Parent ................................................. 5 The Main Issues of Virgin Group and How Can Should they Tackled ................................... 6 Conclusion ............................................................................................................................... 7 Recommendations ................................................................................................................... 7 Reference ................................................................................................................................. 8
BABM/07/12
Page 2
Strategic Management
Individual Assignment
1. Introduction
Virgin is a leading international investment group and one of the world's most recognized and respected brands. Conceived in 1970 by Sir Richard Branson, the Virgin Group has gone on to grow successful businesses in sectors ranging from mobile telephony, travel, financial services, leisure, music, holidays and health & wellness. Across its companies, Virgin employs approximately 50,000 people, in 34 countries and global branded revenues in 2011 were around 13bn (Virgin Group. 2001)
BABM/07/12
Page 3
Strategic Management
Individual Assignment
2. The Corporate Rationale of Virgin as a Group of Companies
Companies use different strategies to compete in the market. The main strategy which is followed by Virgin is diversification in the Ansoff Matrix. Corporate-level executives perform a corporate parent role with regard to the individual business units that make the Virgin Group portfolio. They properly understand how corporate-level activities should be undertaken and how decisions should be taken to add value to the business. They recognize how to achieve a good mix of businesses within the corporate portfolio and which businesses corporate parents should cultivate and which they should divest. They diversify into as many markets as feasible. They extend the Virgin brand name further at a low cost, where their stature could be relied upon to reduce barriers to entry into static markets. Their excellent management practices have also been named as a major strength. Their corporate rationale is heavily depended upon detailed analysis and research of any new venture that the group considers. Another important effective strategy is to put their selves in the customers shoes to see what could make the market better.
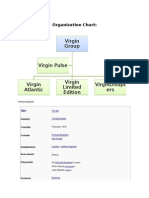
3. The Relationships of a Strategic Nature Between Businesses Within the Virgin Portfolio
There arent any relationships of a strategic nature between businesses within the Virgin portfolio. The Virgin Group is formed by various strategic business units (SBU). There are currently 56 strategic business units in the Virgin Group. Therefore the companies within the Virgin Group are part of a family rather than a hierarchy. Every SBU in the Virgin Group is ring-fenced, separated and independent. Each of them operate independently and follow their own competitive strategies in their own segmented markets. By 2002, the group included over 200 businesses spanning three continents. As the Virgin Group follows unrelated diversification, the resources of one business are not useful for other business and also the structure of Virgin Group is so opaque that the true financial position of Virgin Group is unclear. Due to its status as a private company, the complex group structure, and unavailability of consolidated accounts, it is difficult to arrive at accurate turnover and profit and companies within the group did not even share a common accounting year end. Therefore there are no relationships of a strategic nature between businesses within the Virgin portfolio.
BABM/07/12 Page 4
Strategic Management
Individual Assignment
4. The Ways Virgin Group adds Value as a Corporate Parent
Virgin Group as a corporate parent has added value to its businesses. The brand is the single most important asset for them. The ultimate objective of Virgin is to establish itself as a major global name. That means they need to have a number of core businesses with global potential while they try to deliver on the promises they make while entering into new market. They add value to its core business Virgin Atlantic in the following ways: Virgin brand name to overcome barriers to entry
The Virgin brand name is a consumers champion and as mentioned previously is a much respected brand with the British public. Limiting risk in joint ventures
Any company, corporation or organization in a joint venture with the Virgin Group has the benefit of limiting its risk in the market place because of their stability as an established brand. Management is not restricted
A flat management structure helps encourage innovation; provides flexibility and promotes the values of shared ownership and responsibility. Innovation
Virgins senior staff consists of individuals with successful careers. The Group acquires likeminded partners in ventures who match their ability to innovate and differentiate. These collective innovative thoughts and ideas are applied directly into business; which most often bares fruit.
BABM/07/12
Page 5
Strategic Management
Individual Assignment
5. The Main Issues Faced by Virgin Group and How they Should be Tackled
They develop new business units (SBU) by leveraging their brand name. They focus more on unrelated diversification. From one perspective their greatest threat may be their brand. The reason for this is that, when a customer who had a bad experience will blame the Virgin company or product. Therefore that particular customer will not use any other Virgin products or services. One solution to this issue is to develop partnerships and licensing. This could be instrumental both for globalizing the brand and for managing the different business by local experts. One way to extend the brand would be for Virgin to license its name to existing businesses with proven records of quality. The group could then be extended to new markets much more rapidly. Joint ventures have proven to be a successful strategy for Virgin and should be further developed.
BABM/07/12
Page 6
Strategic Management
Individual Assignment
6. Conclusion
The Virgin brand is the groups greatest asset. Virgins role is to be the consumer champion, and Virgin does this by delivering to Virgins brand values. Virgin has penetrated a large number of very diverse industries, from the music industry, airline industry to the telecom industry and on-line car sales. Although the industries are unrelated, Virgin has penetrated each of them with great or reasonable success.
7. Recommendations
Virgin should become less diverse. Excessive diversity will lead to dilution of brand, create management problems and reduce competitive advantages. Therefore diversification should occur within existing stable companies. There are some current businesses in the Virgin Group with low financial return, namely the airline industry. Therefore when selecting new diversification, thorough financial analysis should be made. The Virgin brand should foster further globalization of brand by opening subsidiaries or branches of its existing companies in more locations worldwide. Its name has become diluted and its brand a purely endorsement brand. Virgin as a corporate parent can add workable value to its businesses by investing and developing real expertise. The Virgin Group should change its policy to accommodate both independent and joint ventures to rely upon short-term profits on a few of its businesses for the sake of raising capital and release the ring-fenced policy so that important revenue making Virgin Atlantic businesses can be bailed out during the low times.
BABM/07/12
Page 7
Strategic Management
Individual Assignment
8. Reference
Abdul, Rob , Virgin corporate strategy, 2003. Strategic Relationships [Online]. 1, Available at: http://www.robabdul.com/the-virgin-group-case-study.asp [Accessed 21 June 2013] Bosmia, Mitesh , 2010. CIP on Virgin case. Virgin Strategic Relationships , [Online]. 1, 1. Available at:http://www.scribd.com/doc/21694481/Virgin [Accessed 21 June 2013]. G. Johnson K. Scholes and R. Whittington, 2008. EXPLORING CORPORATE STRATEGY. 5th ed. England: Pearson Publication. Virgin Group. 2001. About Virgin . [ONLINE] Available at: http://www.virgin.com/about-us. [Accessed 21 June 13]
BABM/07/12
Page 8
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Virgin Group's Diverse Corporate StrategyDocument6 paginiVirgin Group's Diverse Corporate StrategyAvinash Rai0% (1)
- Global Strategy of Virgin GroupDocument0 paginiGlobal Strategy of Virgin GroupSanjay Maharjan Nepali100% (1)
- Virgin Corporate Strategy Case Study FinalDocument9 paginiVirgin Corporate Strategy Case Study FinalAnkit Bhosale100% (1)
- Virgin Case StudyDocument26 paginiVirgin Case StudySabzaMtimande100% (1)
- Virgin Group: On Business Management Implementation and PracticesDocument10 paginiVirgin Group: On Business Management Implementation and Practicesriyaz_badarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anggi Pramita Ester Gani Ricky W Robino I Emmanuel PrianditoDocument48 paginiAnggi Pramita Ester Gani Ricky W Robino I Emmanuel Prianditoanggi08100% (1)
- The Virgin Group: An Innovative Corporate StructureDocument25 paginiThe Virgin Group: An Innovative Corporate Structurerohanag25% (4)
- The Virgin Group: Executive Summary The VirginDocument13 paginiThe Virgin Group: Executive Summary The Virginkimchee8886% (7)
- Virgin Group Organization Chart and OverviewDocument3 paginiVirgin Group Organization Chart and Overviewerarun22Încă nu există evaluări
- VirginDocument11 paginiVirginNeil Heywood100% (2)
- Virgin Group Ltd. A British Conglomerate Founded by Richard BransonDocument21 paginiVirgin Group Ltd. A British Conglomerate Founded by Richard BransonAnmol AidasaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Virgin Case StudyDocument28 paginiVirgin Case StudyAlain Blaise50% (2)
- Virgin Strategy1Document34 paginiVirgin Strategy1Ikay Hargley88% (8)
- Strategy Management-Lu MingkuanDocument33 paginiStrategy Management-Lu MingkuanWeimin Joseph CheongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Birds Eye Case AnalysisDocument5 paginiBirds Eye Case AnalysisakwadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strategic Managment Report On Virgin TrainsDocument20 paginiStrategic Managment Report On Virgin TrainsAnant Johri100% (3)
- Porter's Five Forces: A Model For Industry AnalysisDocument6 paginiPorter's Five Forces: A Model For Industry AnalysiskimsrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brand and Strategic Management of P&GDocument21 paginiBrand and Strategic Management of P&Gxuni34Încă nu există evaluări
- Case Study 2Document6 paginiCase Study 2Saima Binte IkramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strategy Implementation at UnileverDocument12 paginiStrategy Implementation at UnileverSYED MANSOOR ALI SHAHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gap Inc Strategic Analysis: Competitors, Emerging Markets, Online StrategyDocument2 paginiGap Inc Strategic Analysis: Competitors, Emerging Markets, Online StrategyAh BengÎncă nu există evaluări
- Primark Case Study: How CSR Improves LivesDocument3 paginiPrimark Case Study: How CSR Improves LivesMd. Khairul IslamÎncă nu există evaluări
- MFS case study on compensation strategyDocument2 paginiMFS case study on compensation strategyTushar ChaudhariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Richard Branson and Virgin Group Case STDocument28 paginiRichard Branson and Virgin Group Case STPrakhar50% (2)
- Ws Virgin Atlantic Marketing Case StudyDocument43 paginiWs Virgin Atlantic Marketing Case StudyPrang Kannarun100% (1)
- Richard Branson and Virgin Group Case STDocument30 paginiRichard Branson and Virgin Group Case STPrakhar0% (1)
- Marketting AssignementDocument4 paginiMarketting Assignementmulabbi brianÎncă nu există evaluări
- VirginDocument10 paginiVirginMahqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strategic Management DecisionsDocument14 paginiStrategic Management DecisionsSuren TheannilawuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Walt Disney - BRAMDocument3 paginiWalt Disney - BRAMBramanto Adi NegoroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Corporate StrategyDocument52 paginiCorporate Strategytomstor9Încă nu există evaluări
- Audi & Harley-Davidson Case Study AnalysisDocument22 paginiAudi & Harley-Davidson Case Study AnalysisKiran YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Secret of Multi-Branding: The Brand As The Ultimate Business DriverDocument13 paginiThe Secret of Multi-Branding: The Brand As The Ultimate Business DriverJamaica LayuganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Competitive Stratergy Case StudiesDocument7 paginiCompetitive Stratergy Case StudiesDeepti Verma83% (6)
- Case Study D Jetblue AirwaysDocument29 paginiCase Study D Jetblue AirwaysSamehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation 1Document20 paginiPresentation 1api-308703671Încă nu există evaluări
- A Critical Analysis of Zomato's Brand ActivismDocument5 paginiA Critical Analysis of Zomato's Brand ActivismNeerej DevÎncă nu există evaluări
- Porter's Diamond Model Explains South Korea's Automotive SuccessDocument11 paginiPorter's Diamond Model Explains South Korea's Automotive SuccessamitkpatÎncă nu există evaluări
- CageDocument7 paginiCageabhishek gupta100% (1)
- Walmart Final DraftDocument10 paginiWalmart Final Draftapi-254527850100% (1)
- Virgin GroupDocument2 paginiVirgin GroupAlexander OlsenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dương Thị Tường Vy - 2199137 - Group 3: Why is the niche market occupied by Nespresso attractive to generic rivals?Document1 paginăDương Thị Tường Vy - 2199137 - Group 3: Why is the niche market occupied by Nespresso attractive to generic rivals?Dương Thị Tường VyÎncă nu există evaluări
- NissanDocument4 paginiNissanfara_munawarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment II - Wulan YSDocument3 paginiAssignment II - Wulan YSWulan Yulia SariÎncă nu există evaluări
- 45c48case Analysis On Wal-Mart Using The IE Matrix, SWOT Analysis and Other ToolsDocument20 pagini45c48case Analysis On Wal-Mart Using The IE Matrix, SWOT Analysis and Other ToolsMaroun C. Semaan100% (1)
- Disney ReportDocument12 paginiDisney Reportalhumdulilah100% (1)
- Virgin Media's - Diversification StrategyDocument6 paginiVirgin Media's - Diversification StrategyRachita SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment#11 Diversification StrategyDocument5 paginiAssignment#11 Diversification Strategygian kaye aglagadanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diversification: Strategies For Managing Group BusinessesDocument26 paginiDiversification: Strategies For Managing Group Businessessat444Încă nu există evaluări
- Strategic ManagementDocument14 paginiStrategic ManagementMAXWELL gwatiringaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Virgin Group Strategic Management Case StudyDocument6 paginiVirgin Group Strategic Management Case StudyNguyễn Đặng Phương DungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hidden champions: Lessons from medium-sized highly profitable niche leadersDocument4 paginiHidden champions: Lessons from medium-sized highly profitable niche leadersEmmy SukhÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Corporate Rationale of The Virgin Group Marketing EssayDocument9 paginiThe Corporate Rationale of The Virgin Group Marketing EssayKyaw KyawÎncă nu există evaluări
- VirginDocument2 paginiVirginmichalis72100% (1)
- Virgin Blue AsignmentDocument20 paginiVirgin Blue AsignmentAhmed Nayeemuddin100% (1)
- Strategic Managment AssignmentDocument6 paginiStrategic Managment Assignmentsharad jainÎncă nu există evaluări
- GRAND STRATEGIES AssignmentDocument5 paginiGRAND STRATEGIES Assignmentabayomi abayomiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strategic Management Concepts Competitiveness and Globalization 12Th Edition Hitt Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument55 paginiStrategic Management Concepts Competitiveness and Globalization 12Th Edition Hitt Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFdisfleshsipidwcqzs100% (6)
- Strategic Management Concepts Competitiveness and Globalization 12th Edition Hitt Solutions ManualDocument34 paginiStrategic Management Concepts Competitiveness and Globalization 12th Edition Hitt Solutions Manualedithbellamyhd3a100% (23)
- Acquisition & Mergers 2021Document40 paginiAcquisition & Mergers 2021Sasha MacÎncă nu există evaluări
- PESTEL For HNBDocument16 paginiPESTEL For HNBFazlanMarikkar69% (13)
- PESTEL Factors For EtisalatDocument14 paginiPESTEL Factors For EtisalatFazlanMarikkar50% (2)
- Project Proposal - Fundraising CampaignDocument3 paginiProject Proposal - Fundraising CampaignFazlanMarikkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Enron ScandalDocument5 paginiEnron ScandalFazlanMarikkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 07 - IntelDocument5 paginiAssignment 07 - IntelFazlanMarikkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Managing Communications in WorkplaceDocument27 paginiManaging Communications in WorkplaceFazlanMarikkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 06 - TescoDocument8 paginiAssignment 06 - TescoFazlanMarikkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 05 - Virgin GroupDocument8 paginiAssignment 05 - Virgin GroupFazlanMarikkar100% (1)
- Assignment 05 - Virgin GroupDocument8 paginiAssignment 05 - Virgin GroupFazlanMarikkar100% (1)
- Environmental Analysis at ODELDocument10 paginiEnvironmental Analysis at ODELFazlanMarikkar83% (6)
- Organizational StructureDocument9 paginiOrganizational StructureFazlanMarikkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Executive Decision Making at General MotorsDocument14 paginiExecutive Decision Making at General MotorsGourav Guha100% (2)
- Chap005 - Capacity PlanningDocument25 paginiChap005 - Capacity Planningspchheda4996Încă nu există evaluări
- Mba Digital Retail BankingDocument6 paginiMba Digital Retail BankingalamctcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alka Munjal, Anil Kumar & Pradeep Narwal Alka Munjal, Anil Kumar & Pradeep Narwal Alka Munjal, Anil Kumar & Pradeep NarwalDocument7 paginiAlka Munjal, Anil Kumar & Pradeep Narwal Alka Munjal, Anil Kumar & Pradeep Narwal Alka Munjal, Anil Kumar & Pradeep NarwalDharmendra SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Strategic Management, Really? Inductive Derivation of A Consensus Definition of The FieldDocument21 paginiWhat Is Strategic Management, Really? Inductive Derivation of A Consensus Definition of The FieldM Fharys Arfandhy FÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mediterranean School of BusinessDocument32 paginiMediterranean School of BusinessAnja GuerfalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch8-Planning For New Product-InnovationDocument36 paginiCh8-Planning For New Product-InnovationFajar Aditya PutraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Managerial Accounting Course at Ateneo MBA ProgramDocument37 paginiManagerial Accounting Course at Ateneo MBA ProgramCyn SyjucoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Crafting and Executing CHapter 10Document46 paginiCrafting and Executing CHapter 10DjoaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Charles Keith Marketing Plan FINALDocument63 paginiCharles Keith Marketing Plan FINALlinh kieu haÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reflective Essay, Entrepreneurship, Monika HubenakovaDocument11 paginiReflective Essay, Entrepreneurship, Monika HubenakovaMonika Hubenakova75% (4)
- SM Mod 05Document60 paginiSM Mod 05Kavi_3788Încă nu există evaluări
- Brasil Eggers 2019Document32 paginiBrasil Eggers 2019anon_652192649Încă nu există evaluări
- 9780133995909Document42 pagini9780133995909Omar vicente sanchezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Barriers To Successful NegotationDocument25 paginiBarriers To Successful Negotationmoiliana83% (6)
- Annie Porbeni, PHDDocument6 paginiAnnie Porbeni, PHDAnonymous wqu5Bnvlr4Încă nu există evaluări
- Segmentation Targeting and Positioning of Nestle Marketing EssayDocument7 paginiSegmentation Targeting and Positioning of Nestle Marketing Essayrao hafeez100% (1)
- Business Strategy and Planning: Session 2Document15 paginiBusiness Strategy and Planning: Session 2ALI RAZAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strama Paper FinalDocument31 paginiStrama Paper FinalLauren Refugio50% (4)
- Marketing Planning - MOD004454Document14 paginiMarketing Planning - MOD004454Nicholas ZemuraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Leicestershire County Council: Project Initiation Document Leicestershire Sustainable Community StrategyDocument28 paginiLeicestershire County Council: Project Initiation Document Leicestershire Sustainable Community Strategymanosteel1981Încă nu există evaluări
- McomDocument23 paginiMcomkapilchandan0% (1)
- Original Paper: Business Strategy Analysis-LenovoDocument5 paginiOriginal Paper: Business Strategy Analysis-Lenovosaherhcc4686Încă nu există evaluări
- Mang Inasal 2 PDFDocument109 paginiMang Inasal 2 PDFCharl Justin A. TimoteoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reviewer in Operations ManagementDocument6 paginiReviewer in Operations ManagementZie TanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Innovation Strategy Mapping ValueDocument23 paginiInnovation Strategy Mapping ValueSantanu KararÎncă nu există evaluări
- Worth 4e Test Bank 07Document12 paginiWorth 4e Test Bank 07Nick Inker100% (1)
- Post Merger People IntegrationDocument28 paginiPost Merger People IntegrationDebasish Chakraborty100% (4)
- CH.5 Strategic Analysis of Ben and JerryDocument9 paginiCH.5 Strategic Analysis of Ben and JerryJackie100% (1)
- CIM Original TemplateDocument5 paginiCIM Original Templatekashif4987Încă nu există evaluări