Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Nursing Care Plan
Încărcat de
Tess Barbarona DelacruzDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Nursing Care Plan
Încărcat de
Tess Barbarona DelacruzDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
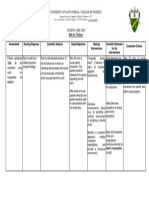
NURSING CARE PLAN
Problem: Ineffective tissue Perfusion Date Identified: June 7, 3013 Cues: Received patient per stretcher with heplock at right arm, with oxygen via nasal prong, with respiratory rate of 36 cpm, restlessness noted. Patient is dyspneic as observed. With the laboratory results of the following: Result Hemoglobin Hematocrit Urea 53 0.17 146.65 Unit g/L L/L mg/dL Reference 120-160 0.37-0.47 7.00-18.68
Analysis of the problem: Hemoglobin in the blood carries oxygen from the respiratory organs such as lungs to the rest of the body (i.e. the tissues) where it releases the oxygen to burn nutrients to provide energy to power the functions of the body, and collects the resultant carbon dioxide to bring it back to the respiratory organs to be dispensed from the body. Decrease in hematocrit level may indicate acute blood loss or anemia. Increased in urea in the blood is an indicator of dehydration, pre-renal or renal failure. Therefore, decrease in hemoglobin and other components of our blood means decrease oxygen supply to other parts of the body. Increase urea in the blood and the dehydration of the body could lead to viscosity of the blood that makes blood flows slowly to other organs and tissues. Due to this, patient has difficulty breathing and restless. Statement of patients care objectives:
After nurse-patient interaction, patient will be able to: Demonstrates adequate tissue perfusion as evidenced by palpable peripheral pulses, warm and dry skin, adequate urinary output, and the absence of respiratory distress Verbalizes knowledge of treatment regimen, including appropriate exercise and medications and their actions and possible side effects Identifies changes in lifestyle that are needed to increase tissue perfusion.
Nursing Actions 1. Assessed patients status and vital signs taken. 2. Assisted patient to moderate high back rest. 3. Maintained on Oxygen theraphy @ 2Lpm 4. Encourage patient to have enough rest and sleep 5. Assisted patient for salbutamol nebulization as order
Rationale Basis for prioritizing patients need and nursing intervention to be given.
Evaluation
To promote circulation
To increase oxygen supply to the body and promote perfusion To conserve energy and to decrease tissue O2 demand
Patient was transported to renal unit for hemodialysis with the following vital signs of Temperature of 37.3, Pulse rate of 88, Blood pressure of 150/90 and Respiratory rate of 30 cpm.
Relaxes bronchial uterine and vascular smooth muscle by stimulatng beta 2 receptors, thus, helps inceasing oxygen supply to the body To determine hydration status of the patient and to watched for hypovolemic shock Restriction of protein limits BUN
6. Monitored intake and output of the patient 7. Advised patient to limit taking protein rich foods such as meat and egg 8. Kept client warm, and had client wear socks. Do not apply heat.
Clients with arterial insufficiency complain of being constantly cold; therefore keep extremities warm to maintain vasodilation and blood supply. Heat application can easily damage ischemic tissues Hemodialysis is used to achieve the extracorporeal removal of waste products such as creatinine and urea and free water from the blood when the kidneys are in a state of renal failure. Thus decreasing viscosity of the blood.
9. Scheduled patient for emergency hemodialysis as ordered.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Mindray BS-120 / BS-200 / BS-300 / BS-380 / BS-400: MTD Diagnostics, SRLDocument40 paginiMindray BS-120 / BS-200 / BS-300 / BS-380 / BS-400: MTD Diagnostics, SRLCarlos SoutoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marilyn K. Gard Recognized As A Professional of The Year by Strathmore's Who's Who Worldwide PublicationDocument3 paginiMarilyn K. Gard Recognized As A Professional of The Year by Strathmore's Who's Who Worldwide PublicationPR.comÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intralesional Pentoxifylline Injection in Localized Alopecia Areata 2018Document6 paginiIntralesional Pentoxifylline Injection in Localized Alopecia Areata 2018maat1Încă nu există evaluări
- Calcium-Phosphate Metabolism: Medical Benchmarking ReportDocument9 paginiCalcium-Phosphate Metabolism: Medical Benchmarking ReportLuis Hernan Guerrero LoaizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amarnath Yatra Compulsory Health Certificate 2017Document1 paginăAmarnath Yatra Compulsory Health Certificate 2017Sneha KerkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prospekt BR 102plusDocument4 paginiProspekt BR 102plusAnonymous zynaalZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Can Oral Sex Cause Throat CancerDocument4 paginiCan Oral Sex Cause Throat CancerjyuldipÎncă nu există evaluări
- Py 16096Document9 paginiPy 16096neviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Procedural Checklist NCM 112 RLE Preparing A Sterile Field Opening A Sterile Pack Adding Items To A Sterile Field Adding Liquids To A Sterile Field Skin PreparationDocument5 paginiProcedural Checklist NCM 112 RLE Preparing A Sterile Field Opening A Sterile Pack Adding Items To A Sterile Field Adding Liquids To A Sterile Field Skin PreparationAbegail Eliah EstalaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cramp Pages 1Document10 paginiCramp Pages 1masi10Încă nu există evaluări
- HTN and Arrh AfzalDocument8 paginiHTN and Arrh AfzalAFA.BLSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmaceuticals 11 00094Document14 paginiPharmaceuticals 11 00094CindyGaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacy Calculations Review: Pharmacy Tech Topics™ Volume 16 Number 3 July 2011Document24 paginiPharmacy Calculations Review: Pharmacy Tech Topics™ Volume 16 Number 3 July 2011Mirumbi Kefa MomanyiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fast Dispersible Tablet-1Document26 paginiFast Dispersible Tablet-1Hely PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medico-Legal Protocols: Dead On Arrival (BROUGHT DEAD)Document3 paginiMedico-Legal Protocols: Dead On Arrival (BROUGHT DEAD)kapindra100% (1)
- Sprain and DislocationDocument9 paginiSprain and Dislocationbhavesh jain100% (1)
- Management of Dry SocketDocument4 paginiManagement of Dry SocketFakhrul ImamÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Lecture) Approach To AscitesDocument48 pagini(Lecture) Approach To AscitesJirayu Puthhai100% (1)
- Producing Clinical Laboratory Shift Tables From Adam Data: Rao Bingi, Octagon Research Solutions, Wayne, PADocument12 paginiProducing Clinical Laboratory Shift Tables From Adam Data: Rao Bingi, Octagon Research Solutions, Wayne, PAlenithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topical Lotion Formulation PDFDocument45 paginiTopical Lotion Formulation PDFMustafa ArarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research Paper Final DraftDocument17 paginiResearch Paper Final Draftapi-740628337Încă nu există evaluări
- (MRCP Study Guides) S. Hughes - Complete Data Interpretation For The MRCP-Churchill Livingstone (2001)Document2 pagini(MRCP Study Guides) S. Hughes - Complete Data Interpretation For The MRCP-Churchill Livingstone (2001)basocdovnch0% (1)
- 100 Hot Topics For Disertations...... (1.1)Document7 pagini100 Hot Topics For Disertations...... (1.1)vsvsuresh2099Încă nu există evaluări
- Dosage Lec - Unit 2 Drug DiscoveryDocument8 paginiDosage Lec - Unit 2 Drug DiscoveryJohn Lorenz BordadorÎncă nu există evaluări
- ACD/Percepta: Overview of The ModulesDocument91 paginiACD/Percepta: Overview of The ModulesTinto J AlencherryÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Self HarmDocument1 paginăNCP Self HarmJoshua ArevaloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eng NCPDocument4 paginiEng NCPima nunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- OFLOXACINDocument3 paginiOFLOXACINfayrouz fathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Next To Normal - Abridged ScriptDocument13 paginiNext To Normal - Abridged Scriptterrify007Încă nu există evaluări
- Palmer Ultrasound ImagingDocument354 paginiPalmer Ultrasound ImagingRajeshPilot100% (13)