Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Basic Piping Design
Încărcat de
Priyanathan ThayalanDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Basic Piping Design
Încărcat de
Priyanathan ThayalanDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
To know piping design basics by going through the following points: Design of pressure components. Pipe Span calculations.
Design of pipe supports & hangers. Stiffness & flexibility. Expansion & stresses. Line expansion & flexibility. Supports & anchorage of piping.
Design of pressure piping Many decisions need be made in the design phase to achieve this successful operation, including:Required process fluid quantity Optimum pressure-temperature Piping material selection Insulation selection (tracing) Stress & nozzle load determination Pipe support standard The codes provide minimal assistance with any of these decisions as the codes are not design manuals.
Design of pressure components Pipe Structure static design, not Layout design.
Limitations: Code, Pressure, Temperature, How long is theplant lifetime, What is the plant reliability, etc.. Piping designed according to B31.3 has less lifetime thanB31.1 due to lower F.S.
Reliability of piping under B31.1 should be higher thanB31.3 Given that the code is a product of pressure technology, one of the concerns is the pressuretemperature ratings of the components. Design of pressure components Each system be it vessel or piping has some base pressure-temperature rating. This is essentially the pressure temperature rating of the weakest member of the system. This can be translated that no minor component (valve,flange, etc) shall be the weakest link. The key components of the design conditions are the design pressure and the design temperature. Design pressure is defined as the most severe sustained pressure which results in the greatest component thickness and the highest component pressure rating. Design temperature is defined as the sustained pipe metaltemperature representing the most severe conditions of coincident pressure and temperature.
Design of pressure components Thus we can try to simplify our stresses into two main categories; Pressure stress is the circumferential stress (primary stress) or hoop stress, which is known to be not self limiting. Temperature stress is the shear or bending stress (Secondary stress), known to be self limiting. In addition VIBRATION, has to be addressed as low cycle high stress named as thermal expansion cycles,
Design of pressure componentsWall Thickness Calculation The code assists the designer in determining adequate pipewall thickness for a given material and design conditions asfollows:Calculate the pressure design thickness t -
Add the mechanical corrosion and erosion allowances c to obtain the thicknesstm=t+c- Add mill tolerance (MT) to tm, then select the nextcommercially available wall thickness.- Provided t<D/6, if not high pressure piping equationsapply.
Design of pressure components Code Equation: tm = PDo /2(SEq + PY) + A = t + A where : P = Internal design pressure Do = pipe outside diameter S = the pipe material allowable stress, S is for thelisted pipe material at hot temperature E = quality factor Y = stress-temperature compensating factor.
Design of pressure components The E FACTOR is a allowable stress penalty based on the method of manufacture of the pipe. It is based on thequality of the weld in seam-welded pipe and will have avalue ranging from E = 0.6 for FURNACE BUTTWELDED (FBW) to E = 1.0 for SEAMLESS PIPE,(SMLS). This FACTOR is a carry-over from the old dayswhere pipe was manufactured using rivets. TheE FACTORfor seam-welded pipe can be improved:increasing this factor from 0.8 to 1.0. TheY FACTORis included to account for effects of creepconsidering the non-linear reduction in ALLOWABLESTRESS at design temperatures above 482 C (900 F).
Design of pressure components Wall thickness problem : P = 4135 KPa (41.35Bar)D = 219.1 mm (8.625 in)S = 130 MPa at 260C (18,900 psi at 500 F), from TABLE A-iE = 0.85 (TABLE A-lB for A53 pipe)Y = 0.4 (TABLE 304.1.1) Convert MPa allowable stress to kPa for consistency of units, then : t = 4135*219.1/2(13000*0.85+0.4*4135)Metric units: t = 4.0 mmthen t m
plus mill under run tolerance is : t m = 4.0 + 1.6 + 1.0 (The 1.0 mm value is 12.5% mill under run tolerance of 8.2 mm nominalwall pipe expected to be purchase).t m = 6.6 mm Design of pressure components U.S. customary units : t =8.625*600/2(18900*0.85+0.4*600)t =0.159 inch t m = 0.159 + 0.063 + 0.040t m = 0.262 in . (The 0.04 inch value is 12.5% mill under run tolerance of 0.322 inch nominal wall expected to be purchase).The next commercially available pipe wall is SCHEDULE40, with a nominal wall of 8.2 mm (0.322 in.).This is the wall to use for these stated conditions.
Design of pressure componentsTest Pressure The hydrostatic test pressure at any point in the systemshould be not less than 1.5 times the design pressure.For Temp. above 650F (343C), the min. test pressure P T isgiven by;P T = 1.5(S T /S)(Design Pressure)S T = allowable stress at 650F,S = allowable stress at design temperature
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Shell and Tube Heat ExchangerDocument19 paginiShell and Tube Heat Exchangerhuangjl33% (3)
- SBES Organization ProfileDocument9 paginiSBES Organization ProfilePriyanathan ThayalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rathish ResumeDocument6 paginiRathish ResumePriyanathan ThayalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organic Solvents Heat Exchanger DesignDocument40 paginiOrganic Solvents Heat Exchanger Designprateek_bhoirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Air Cooler Design Sheiko PDFDocument22 paginiAir Cooler Design Sheiko PDFJason ThomasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sizing Air ReceiverDocument3 paginiSizing Air ReceiverAnkon Mukherjee100% (3)
- EXAMPLE - METHOD 2 (Statistical) Depth of Engagement - Pipe - Pressure ApplicationDocument6 paginiEXAMPLE - METHOD 2 (Statistical) Depth of Engagement - Pipe - Pressure ApplicationdakidofdaboomÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shell & Tube HX Design (Rev1)Document32 paginiShell & Tube HX Design (Rev1)Priyanathan ThayalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermal Expansion CalculatorDocument2 paginiThermal Expansion CalculatorPriyanathan ThayalanÎncă nu există evaluări
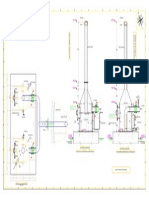
- Surge TankDocument1 paginăSurge TankPriyanathan ThayalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- BeamsDocument21 paginiBeamsSrinivas TanarapuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Base Silencers For Rotary Positive Blowers: Building Sound SolutionsDocument4 paginiBase Silencers For Rotary Positive Blowers: Building Sound SolutionsPriyanathan ThayalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Site FacilitiesDocument1 paginăSite FacilitiesPriyanathan ThayalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 620Document33 pagini620ccricaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clarified Water PumpDocument1 paginăClarified Water PumpPriyanathan ThayalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dolby HomeTheaterSetupGuide 5.1Document5 paginiDolby HomeTheaterSetupGuide 5.1Milan MijailovicÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4) Power Plants 5) Hydraulic Equipments: ManpowerDocument1 pagină4) Power Plants 5) Hydraulic Equipments: ManpowerPriyanathan ThayalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fan SilenserDocument6 paginiFan SilenservrgohilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sbes Profile PDFDocument7 paginiSbes Profile PDFPriyanathan ThayalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- VB and PB GA DrawingDocument1 paginăVB and PB GA DrawingPriyanathan ThayalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- R134 ADocument59 paginiR134 ABing TzuanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 360brake BrakingTips 73564ADDD04FADocument3 pagini360brake BrakingTips 73564ADDD04FAPriyanathan ThayalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- North: 100.30 Avg - GL 100.00 Avg - GL 100.30Document1 paginăNorth: 100.30 Avg - GL 100.00 Avg - GL 100.30Priyanathan ThayalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Steel Grades and Their PropertiesDocument2 paginiTypes of Steel Grades and Their PropertiesPriyanathan ThayalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Calculate Duty and Surface Area of Heat Ex ChangersDocument7 paginiHow To Calculate Duty and Surface Area of Heat Ex ChangersJohn Obidi100% (2)
- Fuel Oils Chemical and Physical DetailsDocument6 paginiFuel Oils Chemical and Physical DetailsPriyanathan ThayalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 14033Document2 pagini14033Priyanathan ThayalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical Guide To Industrial Boiler SystemsDocument375 paginiPractical Guide To Industrial Boiler Systemssumeet0827100% (19)
- Hydro EnggDocument11 paginiHydro EnggPriyanathan ThayalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- UPoles - Paper - Durability of Poles in NESC Grade C Construction by HJ Dagher - 04-23-2001.ashxDocument22 paginiUPoles - Paper - Durability of Poles in NESC Grade C Construction by HJ Dagher - 04-23-2001.ashxVictor JimenezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Confort 125 - Aluminium Sliding Doors - Sapa Building SystemDocument12 paginiConfort 125 - Aluminium Sliding Doors - Sapa Building SystemSapa Building SystemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mba Pom Exam 122019Document6 paginiMba Pom Exam 122019Ped SalvadorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blanco Ku 0099M 13094 DATA 1 PDFDocument96 paginiBlanco Ku 0099M 13094 DATA 1 PDFCm EtcmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kimray 112 SMT (Regulator)Document5 paginiKimray 112 SMT (Regulator)CARLOS SARMIENTOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Performance of Recycled Plastic Waste Modified Asphalt Binder in Saudi ArabiaDocument10 paginiPerformance of Recycled Plastic Waste Modified Asphalt Binder in Saudi ArabiaDiana BecerraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 31000, 32000 Proximity Probe Housings: DescriptionDocument9 pagini31000, 32000 Proximity Probe Housings: Descriptionmehdi227Încă nu există evaluări
- Impact of Covid-19 On The Automotive Industry: By: Raman ATUL (19109029) RohitDocument14 paginiImpact of Covid-19 On The Automotive Industry: By: Raman ATUL (19109029) RohitRaman BansalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lean Manufacturing A1Document14 paginiLean Manufacturing A1Ankita SinhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Install and maintain Indeeco electric duct heatersDocument2 paginiInstall and maintain Indeeco electric duct heatersDoan Tien DoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guide To The Layout Requirements For A Commercial Laundry Room PDFDocument11 paginiGuide To The Layout Requirements For A Commercial Laundry Room PDFTueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Retrofilling Aging Transformers With Natural Ester Based Dielectric Coolant For Safety and Life ExtensionDocument7 paginiRetrofilling Aging Transformers With Natural Ester Based Dielectric Coolant For Safety and Life Extension王阳Încă nu există evaluări
- Power Contactor 1250 A - HubbellDocument4 paginiPower Contactor 1250 A - Hubbellmanuel99a2kÎncă nu există evaluări
- BECE BDT Past Questions 2016Document9 paginiBECE BDT Past Questions 2016Anonymous lnC6IDg67% (3)
- Stone Cladding Fixings Technical StandardsDocument6 paginiStone Cladding Fixings Technical StandardsvtalexÎncă nu există evaluări
- MyDocument61 paginiMynvnrev0% (1)
- Naia Sustainability PresentationDocument54 paginiNaia Sustainability PresentationviathungÎncă nu există evaluări
- AsphaltDocument182 paginiAsphaltEnd EndÎncă nu există evaluări
- MR419X6188A000Document22 paginiMR419X6188A000Ties van RaakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elastomer - WikipediaDocument15 paginiElastomer - WikipediaM Irfan KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- DOE Guidance WBSDocument20 paginiDOE Guidance WBSShowki WaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1507704441084-Aug 2017 - Stock PDFDocument38 pagini1507704441084-Aug 2017 - Stock PDFRakesh Singh0% (1)
- Automatic Priming of PumpDocument4 paginiAutomatic Priming of PumpZeshanÎncă nu există evaluări
- TDS - Superfloc A-100 - ENDocument2 paginiTDS - Superfloc A-100 - ENFrank George Sandoval ParedesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Filtro Bacteriologico Puritan BennetDocument24 paginiFiltro Bacteriologico Puritan BennetRonald David ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Proceso: Lummus Application: Improved Technology To Produce Highest Quality Phenol andDocument5 paginiProceso: Lummus Application: Improved Technology To Produce Highest Quality Phenol andAdrian Copa JÎncă nu există evaluări
- Autonext Study Material 3 (Brakes)Document11 paginiAutonext Study Material 3 (Brakes)SouravÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simulation of SOI PIN Diode for Space Radiation DetectionDocument12 paginiSimulation of SOI PIN Diode for Space Radiation Detectionzuraixoz7967Încă nu există evaluări
- GBDocument6 paginiGBNandor KermeciÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rate Analysis-KalikaDocument35 paginiRate Analysis-KalikaPujan Amit Gurung100% (1)