Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance
Încărcat de
Art Christian RamosDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance
Încărcat de
Art Christian RamosDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Art Christian M.
Ramos BSN 4 - 3
Diagnosis: Muscle Paresis, s/t Motor Neuro Disease, Spinal Cord Injury, Epidural Abcess July 10, 2013 Patient: X
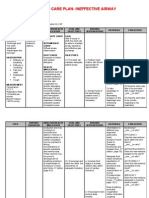
Diagnosis Ineffective Airway Clearance related to accumulation of mucous secretion secondary to Spinal Cord Injury as manifested by: Mucous secretion in the Endotrache al tube. (+) wheezing and crackes on left lobe of the lung noted upon auscultation Inference The presence of a foreign microorganism triggers the B lymphocyte to produce antibodies that are specific to that antigen. These antibodies then attach to mast cells in the lungs. The mast cells with the antibody attaches to the antigen and begins to degranulate. This degranulation causes the release of certain chemical mediators, namely, histamine, bradykinin, prostaglandin, and leukotriene. These chemical mediators cause bronchospasm leading to bronchoconstriction, increased vascular permeability leading to fluid leakage from the lung vasculature and increased mucus production. These lead to swelling of the bronchi, mucus buildup that plugs the airway and decreased bronchial diameter. This causes an Planning After 8 hours of effective nursing intervention, patient will manifest: Maintain and improve airway clearance by decrease in secretion Manifest decrease in wheezing and crackles upon auscultation Vital Signs within Normal Limits. Interventions Auscultate breath sounds q 4. Rationale Breath sounds are normally clear or scattered fine crackles at bases, which clear with deep breathing. The presence of coarse crackles during late inspiration indicates fluid in the airway; wheezing indicates an airway obstruction. Normal respiratory rate for an adult without dyspnea is 12 to 16. With secretions in the airway, the respiratory rate will increase. Normal blood gas values are a PO2 of 80 to 100 mm Hg and a PCO2 of 35 to 45 mm Hg. An oxygen saturation of less than 90% indicates problems with oxygenation. Hypoxemia can result from Evaluation after 8 hours of effective nursing intervention, patient manifested: Improved airway clearance and decrease accumulation of secretion by suctioning and repositioning methods Decreased crackles and wheezes noted upon auscultation Lates vital signs taken @ 9pm, 7/9/13: Temp = 37.7C BP= 110/60 RR = 28A PR= 91 O2Sat = 95%
Assessment Subjective: N/A due to patient can only mouth words when asked or when she needs something. Objective:
Received Sleeping but arousable c Nasogastric tube intact and patent for feeding(NPO temporarily) c endotracheal tube @ 22mm leveled connected to Mechanical Ventilatior c settings @ : Fi02 = 40% TV = 400ml IFR = 55 BUR = 16 18 AC mode c IVF 1L PNSS leveled @ 720cc, infusing @ 80cc/hr. c foley catheter
Monitor respiratory patterns, including rate, depth, and effort.
Monitor blood gas values and pulse oxygen saturation levels as available.
Position client to optimize respiration
Art Christian M. Ramos BSN 4 - 3
Diagnosis: Muscle Paresis, s/t Motor Neuro Disease, Spinal Cord Injury, Epidural Abcess July 10, 2013 Patient: X
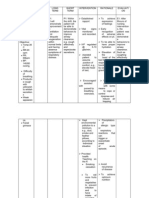
increased airway resistance and a constricted pathway for air. Air cannot pass effectively and this manifests as a whistling sound. Coughing is a way to expel the obstruction (mucus plug) while dyspnea is a manifestation of the increased airway resistance. Irritant during inhalation due to microbial agents Inflammatory Responses Tissue Injury ventilationperfusion mismatches secondary to respiratory secretions. (e.g., head of bed elevated 45 degrees and repositioned at least every 2 hours). An upright position allows for maximal air exchange and lung expansion; lying flat causes abdominal organs to shift toward the chest, which crowds the lungs and makes it more difficult to breathe. Studies have shown that in mechanically ventilated clients receiving enteral feedings, there is a decreased incidence of nosocomial pneumonia if the client is positioned at a 45-degree semirecumbent position as opposed to a supine position
received connected to urine bag noted c yellowish output with adequate amount. c bed sore grade 2 on the lumbar area c estimate 8 10 long c 2 more bed sore grade 3 approximately 1 2 in diameter (+) edema with grade 2 pitting Noted c distended abdomen Hypotonic bowel sound noted upon auscultation Initial Vital signs taken @ 3pm, 7/9/13: T= 39.6C, BP = 100/50 mm/HG RR= 32 A cpm, PR 98 bpm, O2 Sat = 93%
Vascular Responses
Increaseproduction of secretions
Airway constriction
Dyspnea
Art Christian M. Ramos BSN 4 - 3
Diagnosis: Muscle Paresis, s/t Motor Neuro Disease, Spinal Cord Injury, Epidural Abcess July 10, 2013 Patient: X
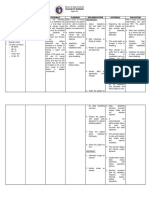
Maintain a semiFowler's position with a lateral position (with a 10- to 15degree elevation and "good lung down") , Gravity and hydrostatic pressure allow the dependent lung to become better ventilated and perfused, which increases oxygenation Normal sputum is clear or gray and minimal; abnormal sputum is green, yellow, or bloody; malodorous; and often copious. To clear or remove mucous secretion of the patient but in a very limited manner of time to prevent patient from hypoxia. Oral care freshens the mouth after respiratory secretions have been expectorated. Research is promising on the use of chlorhexidine oral
Observe sputum, noting color, odor, and volume.
Suctioning of secretion per oral/ Endotracheal tube
Provide oral care every 4 hours.
Art Christian M. Ramos BSN 4 - 3
Diagnosis: Muscle Paresis, s/t Motor Neuro Disease, Spinal Cord Injury, Epidural Abcess July 10, 2013 Patient: X
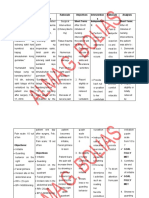
rinses after oral care to reduce bacteria, and possibly reduce the incidence of nosocomial pneumonia Body movement helps mobilize secretions. The supine position and immobility have been shown to predispose postoperative clients to pneumonia Oxygen has been shown to correct hypoxemia, which can be caused by retained respiratory secretions. To treat or prevent bronchospasms and facilitate expectoration of mucus and airway clearance. Used to reduce colonization or prophylactic treatment for localized infection process.
Turn client from side to side at least every 2 hours.
Administer oxygen as ordered.
Administer Salbutamol + Ipratropium nebulizer
Q8Administer Meropenem 1gm IV Q8
Art Christian M. Ramos BSN 4 - 3
Diagnosis: Muscle Paresis, s/t Motor Neuro Disease, Spinal Cord Injury, Epidural Abcess July 10, 2013 Patient: X
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument5 paginiNCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceEmm Estipona HaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP-Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument13 paginiNCP-Ineffective Airway ClearancePaulo Manlangit86% (22)
- Pneumonia-Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 paginiPneumonia-Ineffective Airway ClearanceNursesLabs.com86% (7)
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Excessive Mucus Production COPDDocument7 paginiNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Excessive Mucus Production COPDMa. Elaine Carla Tating67% (3)
- DIAGNOSIS Hyperthermia Related To Increased Metabolic Rate, Illness. ASSESSMENT SubjectiveDocument1 paginăDIAGNOSIS Hyperthermia Related To Increased Metabolic Rate, Illness. ASSESSMENT Subjectivemawel100% (1)
- NCP - Ineffective Airway Clearance PediaDocument2 paginiNCP - Ineffective Airway Clearance PediaAdrian Mallar100% (6)
- Nursing Progress Note.Document2 paginiNursing Progress Note.Art Christian RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Colon CancerDocument2 paginiPathophysiology of Colon CancerArt Christian Ramos67% (15)
- Drug StudyDocument3 paginiDrug StudyBheiatriz de VeraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Where There Is No DoctorDocument503 paginiWhere There Is No DoctorChuck Heston100% (1)
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument6 paginiIneffective Airway Clearanceapi-252726911Încă nu există evaluări
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance For PneumoniaDocument5 paginiNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance For PneumoniaKullin Rain100% (1)
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Presence of Secretion in Trachea-Bronchial Tree Secondary To History of CAPDocument2 paginiNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Presence of Secretion in Trachea-Bronchial Tree Secondary To History of CAPpa3kmedina100% (1)
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 paginiIneffective Airway Clearancemichelle_010379Încă nu există evaluări
- NCP Difficulty of Breathing R/T SecretionDocument3 paginiNCP Difficulty of Breathing R/T Secretionherscentasiascribd50% (8)
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPDocument4 paginiImpaired Gas Exchange NCPkimglaidyl bontuyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP-Ineffective AirwayDocument5 paginiNCP-Ineffective Airwayjava_biscocho1229Încă nu există evaluări
- ANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationDocument2 paginiANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationEdrianne Tui100% (2)
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 paginiNCP - Ineffective Airway Clearancelarapatricia1215Încă nu există evaluări
- Impaired Gas Exchange - NCPDocument4 paginiImpaired Gas Exchange - NCPJaye DangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP CopdDocument4 paginiNCP CopdJoshua ValdrizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 paginiAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationTrisha SuazoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lopez, Maria Sofia B. 10/07/2020 3-BSN-B Prof. Zoleta: Nursing Care Plan: PneumoniaDocument9 paginiLopez, Maria Sofia B. 10/07/2020 3-BSN-B Prof. Zoleta: Nursing Care Plan: PneumoniaSofia Lopez100% (2)
- Ineffective Airway Clearance Nursing Care PlanDocument2 paginiIneffective Airway Clearance Nursing Care Planrois romaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ineffective Airway Clearance Nursing Care PlanDocument5 paginiIneffective Airway Clearance Nursing Care PlanCamille Serrano100% (1)
- NCP CopdDocument2 paginiNCP CopdDanica Salinas100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument1 paginăNursing Care Plan - Ineffective Airway ClearanceLei OrtegaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP PneumoniaDocument3 paginiNCP Pneumoniakaiserdominick100% (2)
- Impaired Gas Exchange-Sample NCPDocument1 paginăImpaired Gas Exchange-Sample NCPKaycee BinanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bronchial Asthma NCPDocument6 paginiBronchial Asthma NCPRacelle DelesÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP BaiaeDocument7 paginiNCP BaiaeJonathan Delos ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP PneumoniaDocument2 paginiNCP Pneumonia_garonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument2 paginiIneffective Breathing PatternJoy Arizala CarasiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ncp-Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument4 paginiNcp-Ineffective Breathing PatternRoxanne Ganayo Claver100% (1)
- NCP HemothoraxDocument3 paginiNCP Hemothoraxroseonabreeze0% (2)
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument8 paginiIneffective Breathing PatternJansen Arquilita Rivera100% (2)
- NCP Self CaRE DeficitDocument1 paginăNCP Self CaRE Deficitnicole pageÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument3 paginiNCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceHyacinth Gallardo Valino50% (2)
- NANDA Page 658Document5 paginiNANDA Page 658Ashley Gaton Alindogan100% (1)
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern - NCPDocument2 paginiIneffective Breathing Pattern - NCPHsintan HsuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument3 paginiIneffective Airway ClearanceDarkCeades83% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan: Ineffective Breathing Pattern Related ToDocument4 paginiNursing Care Plan: Ineffective Breathing Pattern Related ToFrudz OrjalezaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument3 paginiDecreased Cardiac OutputRizalyn QuindipanÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP PediaDocument2 paginiNCP PediaJacinth Rizalino40% (5)
- 1 Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument8 pagini1 Ineffective Breathing PatternNoel MontemayorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pleural Effusion FdarDocument1 paginăPleural Effusion FdarvanessabdeveraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument8 paginiFinal NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceHazel EndayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SAMPLE NCP For PneumoniaDocument3 paginiSAMPLE NCP For Pneumoniakana_mercado100% (6)
- Acute Pain Related To Tissue Trauma and InjuryDocument4 paginiAcute Pain Related To Tissue Trauma and Injuryprickybiik50% (2)
- NCP Format 3 CKD Chronic Kidney Disease DM Diabetes Mellitus NephropathyDocument3 paginiNCP Format 3 CKD Chronic Kidney Disease DM Diabetes Mellitus NephropathyAngie MandeoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument4 paginiImpaired Gas ExchangeShen Paril0% (1)
- Impaired Gas Exchange Care PlanDocument5 paginiImpaired Gas Exchange Care Planjakifer50% (2)
- NCP HyperthermiaDocument3 paginiNCP HyperthermiaPrincess Alane MorenoÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Activity IntoleranceDocument5 paginiNCP Activity IntoleranceRea HashimÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP #1 Acute Pain Related To Decreased Blood Supply Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Interventions Rationale Expected OutcomeDocument22 paginiNCP #1 Acute Pain Related To Decreased Blood Supply Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Interventions Rationale Expected OutcomeAnnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity Intolerance NCPDocument3 paginiActivity Intolerance NCPGen RodriguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP: Acute GastroenteritisDocument3 paginiNCP: Acute GastroenteritishauteanicoleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan Problem: Acute Intermittent Moderate PainDocument1 paginăNursing Care Plan Problem: Acute Intermittent Moderate PainDiana Laura Lei100% (3)
- NCP Impaired Gas Exhange Related To Alveolar Wall Destruction EMPHYSEMADocument5 paginiNCP Impaired Gas Exhange Related To Alveolar Wall Destruction EMPHYSEMAMa. Elaine Carla Tating50% (2)
- BronchiectasisDocument40 paginiBronchiectasisyana jaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ineffective Airway Clearance R/T Tracheobronchial ObstructionDocument23 paginiIneffective Airway Clearance R/T Tracheobronchial ObstructionGuia Rose SibayanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medical Surgical Nursing - RespiratoryDocument15 paginiMedical Surgical Nursing - RespiratoryChristian Esteves75% (4)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument14 paginiNursing Care PlanVin Landicho100% (1)
- Medical Surgical NursingDocument146 paginiMedical Surgical Nursingnisha jomonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effective Communication SkillsDocument7 paginiEffective Communication SkillsArt Christian RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Categories of Network ApplicationsDocument17 paginiCategories of Network ApplicationsArt Christian RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Occupational NeedsDocument2 paginiOccupational NeedsArt Christian RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solutions in CHN BagDocument5 paginiSolutions in CHN BagArt Christian RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Benedict's SolutionDocument2 paginiBenedict's SolutionArt Christian RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- AaaaDocument1 paginăAaaaArt Christian RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Volvulus, Intestinal ObstructionDocument9 paginiVolvulus, Intestinal ObstructionArt Christian RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chole Lithia SisDocument11 paginiChole Lithia SisArt Christian RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bacon BDocument56 paginiBacon BArt Christian RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Systems TheoryDocument2 paginiGeneral Systems TheoryArt Christian Ramos100% (2)
- Anaphy and Patho of AppendicitisDocument3 paginiAnaphy and Patho of AppendicitisArt Christian RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ethical Issues Regarding The Donor and The RecipientsDocument8 paginiEthical Issues Regarding The Donor and The RecipientsArt Christian RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug AnalysisDocument18 paginiDrug AnalysisArt Christian RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Health HistoryDocument5 paginiNursing Health HistoryArt Christian RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anorexia NervosaDocument6 paginiAnorexia NervosaArt Christian RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Close Complete FractureDocument3 paginiNCP Close Complete FractureArt Christian RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and Pathophysiology of CHFDocument7 paginiAnatomy and Pathophysiology of CHFArt Christian RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute and Chronic PancreatitisDocument9 paginiAcute and Chronic PancreatitisArt Christian RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Close Complete Fracture AnxietyDocument2 paginiNCP Close Complete Fracture AnxietyArt Christian RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Metabolic EncephalopathyDocument1 paginăPathophysiology of Metabolic EncephalopathyArt Christian RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Close Complete Fracture Knowledge DeficitDocument2 paginiNCP Close Complete Fracture Knowledge DeficitArt Christian Ramos0% (1)
- Traumatic ConditionsDocument23 paginiTraumatic ConditionsArt Christian RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Health HistoryDocument5 paginiNursing Health HistoryArt Christian RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5 CHNDocument3 paginiChapter 5 CHNArt Christian RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Path o PhysiologyDocument4 paginiPath o PhysiologyArt Christian RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute and Chronic PancreatitisDocument9 paginiAcute and Chronic PancreatitisArt Christian RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Programs and Development Plans of Barangay Project 6Document8 paginiPrograms and Development Plans of Barangay Project 6Art Christian RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bacon BDocument56 paginiBacon BArt Christian RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Certificate of Physical FitnessDocument3 paginiCertificate of Physical Fitnesssreelalitha71% (7)
- DMDudzinski EKG Algorithm4Document1 paginăDMDudzinski EKG Algorithm4nate simmons100% (1)
- Pneumonia Vaccine For ChildrenDocument1 paginăPneumonia Vaccine For ChildrenPrincess Gutierrez RositaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water MicrobiologyDocument15 paginiWater MicrobiologyDayledaniel SorvetoÎncă nu există evaluări
- In Time of PlagueDocument29 paginiIn Time of PlagueterenceTerterÎncă nu există evaluări
- National Nipah Virus Guideline BangladeshDocument77 paginiNational Nipah Virus Guideline BangladeshFaisol KabirÎncă nu există evaluări
- African Adventure: by Margaret Iggulden Streamline Graded Readers Level 3 1000 HeadwordsDocument8 paginiAfrican Adventure: by Margaret Iggulden Streamline Graded Readers Level 3 1000 Headwordsjluis1980Încă nu există evaluări
- History Taking NotesDocument7 paginiHistory Taking NotesZWEASÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nectria CankerDocument6 paginiNectria CankerTate SimpsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diare: Arlinda Silva Prameswari 201810401011044Document28 paginiDiare: Arlinda Silva Prameswari 201810401011044Lilian Rahma AnandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PoemDocument4 paginiPoemJosethÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nihms579455 PDFDocument78 paginiNihms579455 PDFMASIEL AMELIA BARRANTES ARCEÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 66th WHA Provisional AgendaDocument6 pagini1 66th WHA Provisional AgendaRenzo R. GuintoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alendronate SodiumDocument3 paginiAlendronate SodiumGLen Caniedo100% (1)
- What Is A Tzanck Smear?Document5 paginiWhat Is A Tzanck Smear?dsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Influenza GuidelinesDocument1 paginăInfluenza GuidelinesThomas B. FriedmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coronavirus Politics: The Comparative Politics and Policy of Covid-19Document663 paginiCoronavirus Politics: The Comparative Politics and Policy of Covid-19Conceição Lemes100% (2)
- InTech-Molar Incisor Hypomineralization Morphological Aetiological Epidemiological and Clinical ConsiderationsDocument25 paginiInTech-Molar Incisor Hypomineralization Morphological Aetiological Epidemiological and Clinical ConsiderationsNeagu EmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Child Attitude Joward Jllness Scale: EspaňDocument1 paginăChild Attitude Joward Jllness Scale: EspaňAvinash ToraneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hsra Monograph No. 9 FinalDocument51 paginiHsra Monograph No. 9 FinalJeffry AcabaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Boston Globe 30 10 2020 PDFDocument40 paginiThe Boston Globe 30 10 2020 PDFDeadnightvikernesÎncă nu există evaluări
- African Swine Fever: Now in WidespreadDocument2 paginiAfrican Swine Fever: Now in WidespreadMariaGlenda Dellosa Guevara-YusonÎncă nu există evaluări
- EEH - UNIT - I and IIDocument16 paginiEEH - UNIT - I and IIWilliam StainsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Impact of Covid-19Document9 paginiImpact of Covid-19adane yehualawÎncă nu există evaluări
- ONE POINT ACUPRESSURE TREATMENT - TCM Part 1 PDFDocument75 paginiONE POINT ACUPRESSURE TREATMENT - TCM Part 1 PDFshamim hijama83% (6)
- Clinical Microbiology Reviews-2002-Cox-595.full PDFDocument19 paginiClinical Microbiology Reviews-2002-Cox-595.full PDFMUHAMMAD IQBALÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geles Marcela Engleza-Italiana Test Anul Iii - Evaluare Pe Parcurs Limba Engleză Curs PracticDocument3 paginiGeles Marcela Engleza-Italiana Test Anul Iii - Evaluare Pe Parcurs Limba Engleză Curs PracticMarcela GelesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Serocheck TP DevicekkkkDocument4 paginiSerocheck TP DevicekkkkMatibar RahmanÎncă nu există evaluări