Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Tematica Parcial Ingles 1
Încărcat de
20santiago11Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Tematica Parcial Ingles 1
Încărcat de
20santiago11Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
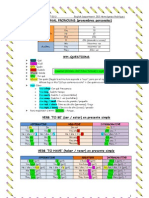
VERB TO BE Las estructuras con el verbo "to be" sirven para poder comunicar varias aspectos muy tiles
como lo son hablar sobre una persona, su nombre, nacionalidad, de dnde es, su profesin, como se siente y describir las caractersticas de personas, animales u objetos, qu es algo, su color y a quien pertenece. TO BE: Ser /Estar /Tener edad /Sensacin Su infinitivo TO BE es equivalente en espaol a la terminacin verbal ar/er/ir/. Se conjuga de esta manera: AFIRMATIVA: SUJETO + VERB TO BE + COMPLEMENTO I am / (Im): Yo soy /estoy / tengo You are / (You re): Tu eres / ests / tienes He is / Hes: l es / est / tiene She is / Shes: Ella es / est / tiene It is / Its: Esto / est / es, tiene We are / We re: Nosotros somos / estamos / tenemos You are / You re: Ustedes son / estn / tienen They are / They re: Ellos son / estn / tienen El pronombre personal sujeto no vara. Lo que si se modifica es la forma del verbo, que pierde la primera slaba y se sustituye por el apstrofe . Cabe resaltar sus formas negativas e interrogativas. NEGATIVA: SUJETO + VERB TO BE + NOT + COMPLEMENTO I am not / (Im not) You are not / (You arent) He is not / He isnt She is not / She isnt It is not / It isnt We are not / We arent You are not / You arent They are not / They arent INTERROGATIVA: VERB TO BE + SUJETO + COMPLEMENTO Am I? Are you? Is he?
Is she? Is it? Are we? Are you? Are they? WH-QUESTIONS + AM / IS /ARE + SUBJECT +COMPLEMENT +? Where are you? When is it? Why is she angry? What is that? Which is your bag? Who am I? How is he? SIMPLE PRESENT USES: Este tiempo verbal se utiliza para expresar hechos o verdades generales. The Sun warms the atmosphere. -> El Sol calienta la armsfera. Tambin lo usamos para hablar de hbitos; en este caso, en la oracin suele aparecer expresiones de frecuencia, como usually o always. We play tennis usually. -> Nosotros jugamos al tenis ocasionalmente. You study always. -> Vosotros estudiais siempre. Tambien lo usamos para expresar horarior o programas (como el programa de un espectculo teatral). The train leaves in an hour. -> El tren llega en una hora. AFFIRMATIVE: SUBJECT + VERB + COMPLEMENT
NEGATIVE: SUBJECT + DONT / DOESNT + VERB + COMPLEMENT En la forma negativa aadimos DOES NOT a la tercera persona del singular (he, She, It) y suprimimos la s del verbo principal. Las dems personas llevan DOES NOT Ex: Jason doesnt play soccer everyday They dont go to the beach every Sunday
INTERROGATIVE: YES / NO QUESTIONS: DO / DOES + SUBJECT + VERB + COMPLEMENT +? Situamos el auxiliar DO, DOES al principio de la oracin. En la tercera persona suprimimos la S del verbo principal, porque ya la hemos utilizado en el verbo auxiliar Ex: Do you have a pink blouse? WH QUESTIONS: WH-QUESTIONS + DO / DOES + SUBJECT +VERB + COMPLEMENT + ? What: Qu? Where: Donde? When: Cuando? Why: Por qu? How: Cmo? Who: Quien (es)? Which: Cual (es)? Whose: De quien (es)? FREQUENCY ADVERBS Los adverbios de frecuencia indican cuntas veces ocurre algo. Los ms importantes son: Always Siempre Almost Always Casi Siempre Usually Normalmente Often - A menudo Sometimes - A veces, Algunas veces Almost Never: Casi Nunca Never Nunca Rarely - Raramente Estos adverbios se colocan generalmente en medio de la frase justo antes del verbo principal. Examples: He always drinks coffee (l siempre bebe caf) She never eats meat (Ella nunca come carne)
We often play tennis on Sunday (A menudo jugamos al tenis el domingo) We sometimes go to the cinema on Wednesday (Nosotros a veces vamos al cine el mircoles) Do you often go to the cinema? (T vas a menudo al cine?) Do they usually speak English? (Ellos normalmente hablan ingls?) I usually arrive late (Yo normalmente llego tarde) A veces pueden colocarse en posicin inicial o final: Examples: Sometimes I listen to the news on the radio (A veces escucho las noticias en la radio) PRESENT PROGRESSIVE USES: Utilizamos el present progressive para una Accin que est ocurriendo en el instante en que se habla. Ex: It is (its) raining I am (Im) having a bath You are drinking soda Para comentar cambios o tendencias que estn ocurriendo en el momento actual Ex: The price of food is rising He is going bald Hes cleaning his room much more regularly these days Con verbos que describen acciones habitualmente repentinas, el uso del presente continuo sugiere que la accin se repita varias veces. Ex: I am jumping she is hitting her brother Adems, podemos utilizar el present progressive para expresar la intencin de hacer algo en el futuro. En estos casos es preciso utilizar una expresin de tiempo para dejar claro que se trata de una accin futura Ex: Im playing golf with Richard on Friday They are arriving on Tuesday We are coming next week Formamos el present progressive con el auxiliar to be y un verbo en la forma ing RULES: Habitualmente aadimos la terminacin ing a la raz del verbo: Ex: Play playing
Cuando la raz termina en consonante + e, la e se sustituye por ing Ex: Love loving Cuando la raz termina en ie, la terminacin pasa a ser ying Ex: Die Diying Cuando la raz tiene una vocal seguida de una sola consonante, duplicamos la consonante Ex: Rob robbing Cuando la raz tiene ms de una slaba y se acenta la ltima, duplicamos la consonante final Ex: Refer referring / Begin Beginning Aunque el verbo to travel no tiene la ltima slaba acentuada, en el ingls Britnico la l duplica. Ex: Travel travelling * En el ingls americano se escribe traveling FORM: AFFIRMATIVE: SUBJECT + AM/IS/ARE + VERB -ING + COMPLEMENT I am playing soccer right now She is working in the Hospital in this moment NEGATIVE: SUBJECT + AM/IS/ARE + NOT + VERB -ING + COMPLEMENT She is not eating a hamburger They are not sleeping in the sofa INTERROGATIVE: AM/IS/ARE + SUBJECT + VERB -ING + COMPLEMENT +? Are you drinking a soda? Yes, I am / No, I am not Is he listening to music? Yes, He is / No, He is not WH-QUESTION + AM/IS/ARE + SUBJECT + VERB -ING + COMPLEMENT +? What are you doing? I am washing my car
Where are you studying? I am studying in Unimetro
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Cuadro ComparativoDocument1 paginăCuadro ComparativoValeria OlmosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tematica Parcial Ingles 3Document11 paginiTematica Parcial Ingles 320santiago11Încă nu există evaluări
- Gramatica Del InglesDocument19 paginiGramatica Del InglesJexhieli CastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Estructura Del Verbo To Be en InglésDocument5 paginiEstructura Del Verbo To Be en InglésHumberto PerezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guía Inglés IDocument18 paginiGuía Inglés IJimmy Angel Herrera RosalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- English Grammar For 3º, 4º ESODocument17 paginiEnglish Grammar For 3º, 4º ESOCancerbero Cancerbe100% (13)
- 2do Vesp Ingles2Document104 pagini2do Vesp Ingles2Erwing MoncadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Material de InglesDocument38 paginiMaterial de InglesAntonio Zarate CanelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Leccion 6Document15 paginiLeccion 6Alexander Urbina BarrientosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tipos de Preguntas en InglésDocument6 paginiTipos de Preguntas en InglésEstefanía SolisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grammar - 2 Auxiliary Verbs 2021Document14 paginiGrammar - 2 Auxiliary Verbs 2021Pablo PuchikÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2017 NuevoDocument97 pagini2017 NuevoAnabell Zapico100% (1)
- Grammar. Present Simple and Present ContinuousDocument3 paginiGrammar. Present Simple and Present ContinuousMaria Jose Rosa Yera33% (3)
- Curso de Inglés OnlineDocument46 paginiCurso de Inglés OnlineEloisa Navas FernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tiempos VerbalesDocument16 paginiTiempos VerbalesJessie GomezÎncă nu există evaluări
- El Verbo To Be Es Ser o EstarDocument7 paginiEl Verbo To Be Es Ser o EstarVictor GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ingles 1 Guia de AyudaDocument46 paginiIngles 1 Guia de AyudaNiki LMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Warm UpDocument14 paginiWarm UpAlejandra OyanederÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spanish Grammar Support - Present TensesDocument16 paginiSpanish Grammar Support - Present TensesEsteban SánchezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presente SimpleDocument34 paginiPresente SimpleRo KaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guia Tiempos VerbalesDocument33 paginiGuia Tiempos VerbalesMery Pedroza0% (1)
- Inglés para PrincipiantesDocument25 paginiInglés para PrincipiantesMarina MesaglioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presente y Pasado Simple Verbo Tobe Auxiliares DoDocument34 paginiPresente y Pasado Simple Verbo Tobe Auxiliares Doyomarcarrillo100% (2)
- Verbo To Be (Verbo Ser o Estar)Document8 paginiVerbo To Be (Verbo Ser o Estar)chongmirthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ingles CandyDocument6 paginiIngles CandyAnny Narvaez ManeiroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guía de Estudio para EER - Inglés I (Primer Grado)Document7 paginiGuía de Estudio para EER - Inglés I (Primer Grado)Fernanda RodríguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ingles Tecnico InformaticaDocument54 paginiIngles Tecnico InformaticaVictoriano Dominguez Henriquez100% (1)
- Greetings and FarewellsDocument18 paginiGreetings and FarewellsPATRICIA QUEVEDOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecciones de InglesDocument7 paginiLecciones de InglesLukeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 07 Gramatica Completa Autor TrasteandoDocument101 pagini07 Gramatica Completa Autor TrasteandoViviana LeonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Estudio para ToeflDocument14 paginiEstudio para Toeflcris_sonricsÎncă nu există evaluări
- PDF InglesDocument14 paginiPDF InglesCeleste ArayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple Present Do DoesDocument4 paginiSimple Present Do DoesMiguel Angel García GilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curso de InglesDocument25 paginiCurso de InglesGilberth CardonaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guìa de Estudio Inglés IDocument18 paginiGuìa de Estudio Inglés Iangelserva96Încă nu există evaluări
- Ingles HeidiDocument9 paginiIngles HeidiVioleta AlguÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grammar Unit 1Document14 paginiGrammar Unit 1keytmoralÎncă nu există evaluări
- Info de InglesDocument15 paginiInfo de InglesShir Gabriel FerreyraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presente SimpleDocument3 paginiPresente SimpleNadia Sandoval de Sánchez100% (1)
- Taller de InglesDocument44 paginiTaller de InglesDiane Tinoco0% (1)
- Cartilla 1Document12 paginiCartilla 1gabriela ruizÎncă nu există evaluări
- ENGLISH ApuntesDocument31 paginiENGLISH ApuntespepititoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Material de Apoyo 1Document5 paginiMaterial de Apoyo 1Yurani arevaloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ingles IDocument61 paginiIngles IrosiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presente Continuo o ProgresivoDocument11 paginiPresente Continuo o ProgresivoJose Pablo Sánchez GutierrezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pronombres PersonalesDocument8 paginiPronombres Personalesyasr22Încă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 6 de InglesDocument6 paginiLesson 6 de InglesClaudiaShimÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2da CLASE DE INGLESDocument4 pagini2da CLASE DE INGLESleomarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curso de Ingles - GramaticaDocument20 paginiCurso de Ingles - GramaticaCristian Lizarazo ZabalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Present ContinuousDocument11 paginiPresent ContinuousmarcoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Estructuras de Los Tiempos en InglesDocument10 paginiEstructuras de Los Tiempos en Inglesvivijara7707Încă nu există evaluări
- El Sistema Verbal Ingles PDFDocument14 paginiEl Sistema Verbal Ingles PDFMaria Jose Cermeno RodriguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Taller Individual Gramatica InglesaDocument13 paginiTaller Individual Gramatica InglesaEudy Arredondo BolivarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subject Pronoun and Verb To BeDocument10 paginiSubject Pronoun and Verb To BePaula Escobar100% (1)
- EL VERBO To BE Es Uno de Los Verbos Más Importantes Del Inglés y También Un Concepto Que Depende Del Contexto en El Que Se EncuentreDocument6 paginiEL VERBO To BE Es Uno de Los Verbos Más Importantes Del Inglés y También Un Concepto Que Depende Del Contexto en El Que Se EncuentregleceidyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mi Blog de Notas Aprendiendo Inglés. Elaborado Por Jennifer Grupo "We Learn English" 2022Document58 paginiMi Blog de Notas Aprendiendo Inglés. Elaborado Por Jennifer Grupo "We Learn English" 2022Joaquin Pinto100% (1)
- Gramática Inglesa A1: Domina la gramática de inglés, #1De la EverandGramática Inglesa A1: Domina la gramática de inglés, #1Încă nu există evaluări
- Curso de Inglés. Learning With the Best: Vocabulary and Easy PronunciationDe la EverandCurso de Inglés. Learning With the Best: Vocabulary and Easy PronunciationEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (3)
- Primeros Pasos en Inglés ¡Sin Gramática!: Un Inicio Rápido y Fácil: Primeros pasos en inglés, #1De la EverandPrimeros Pasos en Inglés ¡Sin Gramática!: Un Inicio Rápido y Fácil: Primeros pasos en inglés, #1Evaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (6)
- Gramatica InglesaDocument27 paginiGramatica InglesaJose Andres Martinez Garcia100% (2)
- Resumen Gramar Ingles Bachillerato PDFDocument29 paginiResumen Gramar Ingles Bachillerato PDFAnonymous iDRq4TÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comple MDocument35 paginiComple M20santiago11Încă nu există evaluări
- Preparación Examen Inglés)Document132 paginiPreparación Examen Inglés)20santiago11Încă nu există evaluări
- Comparatives and SuperlativesDocument5 paginiComparatives and Superlatives20santiago11100% (2)
- FONETICADocument7 paginiFONETICA20santiago11Încă nu există evaluări
- Guia Unidades 9 y 10 I2Document5 paginiGuia Unidades 9 y 10 I220santiago11Încă nu există evaluări
- EB002Document14 paginiEB00220santiago11Încă nu există evaluări
- Guia Unidad 4 Inglés 1Document6 paginiGuia Unidad 4 Inglés 120santiago11Încă nu există evaluări
- Pre Pagado SDocument1 paginăPre Pagado Smariana100% (1)
- Programa Servicio Social Comunitario 2022Document32 paginiPrograma Servicio Social Comunitario 2022Liliana Alvarez VilchisÎncă nu există evaluări
- BehemotDocument5 paginiBehemotJulioAraneda0% (1)
- Filipenses 3-El Gozo en Dios - Una Cuestión de SuguridadDocument5 paginiFilipenses 3-El Gozo en Dios - Una Cuestión de SuguridadEugenia Lopez FernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tarea1 CostumbresDocument4 paginiTarea1 Costumbrestania ddaengÎncă nu există evaluări
- Semiologia PC IVDocument3 paginiSemiologia PC IVMarlenne Bautista Andrade100% (1)
- Condori Mamani Henry Brando El TeatroDocument32 paginiCondori Mamani Henry Brando El TeatroCondori Mamani Henry BrandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1a. Clase INTRODUCTORIO FUNDESUR Enviado FundesurDocument67 pagini1a. Clase INTRODUCTORIO FUNDESUR Enviado FundesurLuis RiestraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modelo Por Necesidades Básicas de Virginia HendersonDocument11 paginiModelo Por Necesidades Básicas de Virginia Hendersonpmsmx4t9fbÎncă nu există evaluări
- Socialización PTI EstudiantesDocument22 paginiSocialización PTI EstudiantesYeKa FelipeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Individuo y Medio AmbienteDocument13 paginiIndividuo y Medio AmbienteMarjorie CaceresÎncă nu există evaluări
- La Sociedad Del Cansancio InfoDocument2 paginiLa Sociedad Del Cansancio InfoMiguel Poveda100% (1)
- Acceso A ScrumStudyDocument5 paginiAcceso A ScrumStudyJuan Carlos Ruiz HonoresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trabajo en Grupo Proyectos Mecanica Industrial Christopher Enriquez 5aDocument6 paginiTrabajo en Grupo Proyectos Mecanica Industrial Christopher Enriquez 5aChris ÊnrïqüëzÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASV Participacion JuvenilDocument2 paginiASV Participacion JuvenilJose E. MartinezÎncă nu există evaluări
- PC1Consigna 23C1MDocument11 paginiPC1Consigna 23C1MShirley ChallcoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Resumen-Introduccion A La FilosofiaDocument28 paginiResumen-Introduccion A La FilosofiaMARIA FABIANA FERNANDEZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exposición Columna VertebralDocument15 paginiExposición Columna VertebralCarlos Javier Fuentes Agudelo100% (1)
- Dos Abejas Amigas para Segundo Grado de PrimariaDocument5 paginiDos Abejas Amigas para Segundo Grado de PrimariaValeska Nicole Cabanillas AlhuayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Triptico Dia Mundial Del CorazonDocument2 paginiTriptico Dia Mundial Del CorazonAlba Palacios100% (1)
- 4 Administracion de EfectivoDocument61 pagini4 Administracion de EfectivoVictor Antonio Lopez CastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- El Estado de Derecho y La Realidad PeruanaDocument34 paginiEl Estado de Derecho y La Realidad PeruanaIncognito18Încă nu există evaluări
- Tabla Periódica y Relacion de Modelos Atomicos.Document4 paginiTabla Periódica y Relacion de Modelos Atomicos.Alirio MendozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- FacebookDocument31 paginiFacebookThonny Sanchez UltimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Semana-2 Estructura SepDocument32 paginiSemana-2 Estructura SepRosa Icela Lozano EncinasÎncă nu există evaluări
- El Comportamiento Colectivo y Sus FormasDocument23 paginiEl Comportamiento Colectivo y Sus FormasArnold Jefferson SanchezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Derecho Procesal CivilDocument99 paginiDerecho Procesal CivilLudith Mozombite TalexcioÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4.-Matrices y DeterminantesDocument5 pagini4.-Matrices y DeterminantesJhymy SanchezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Politicas MonterredondoDocument3 paginiPoliticas MonterredondoKarol Eliana BURBANO BASTIDASÎncă nu există evaluări