Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
05 Nose Anatomy
Încărcat de
Novriefta NugrahaDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
05 Nose Anatomy
Încărcat de
Novriefta NugrahaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Anatomy of Nose & Sinus
1. external nose
- Bony part : 2 nasal bone - Cartilaginous part a. upper lateral cartilage b. lower lateral cartilage (alar cartilage) c. septal cartilage d. accessory cartilage
-Keystone area
-Skeletal Anatomy
Tip support mechanism
Arterial Supply of Nose
-external nose blood supply
Arterial supply 1). External carotid a. - facial a. : angular br., alar br., septal br., external nasal br. 2). Internal carotid a. - ophthalmic a. : dorsal nasal br.
2. nasal septum
- 7 parts 1) the vomer (below) 2) perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone (post) 3) quadriangular(septal) cartilage (ant) 4) nasal crest of maxillary & palatine bone 5) anterior nasal spine : formed by the midline fusion of the palatal processes of maxilla 6) membranous septum : memb. connecting columella to septal cartilage 7) columella : medial crura of the greater alar cartilage
3. lateral nasal wall
Turbinates: inferior, middle, superior, supreme Meatus: inferior, middle, superior Inferior meatus: Hasners valve Middle meatus: opening of frontal, ant. ethmoid, & maxillary sinus Superior meatus: post. ethmoid & sphenoid sinus
4. middle meatus
5. nasal ostium
6. nasal valve
Nasal valve: most resistant portion Upper lateral cartilage, septum, anterior part of inferior turbinate . Septal valve: soft tissue of middle turbinate and septum
7. Acoustic rhinometry Cross section
8. Artery of lateral nasal wall & septum
ICA: anterior and posterior ethmoid artery ECA: sphenopalatine artery- posterior superolateral / posterior inferolateral / anterior inferolateral a. / greater palatine a. / superior labial a. / septal branch
9. Blood Supply of Inf. Turbinate
9. Kiesselbachs area
10. Woodruffs plexus
11. Nerves of nose
Autonomic nerve Sympathetic nerve : vasoconstricture : noradrenaline(NA), neuropeptide Y(NPY), avian pancreaqtic
polypeptide(APP) Parasympathetic nerve : secretion, vvasodilatation : acetylcholine, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide(VIP), peptide histidine isoleucine(PHI),nitro oxide(NO) Sensory nerve trigeminal nerve (C V) : protective reflaex (sneezing, secretion, BP) : substance P, neuropeptide K, calcitonin gene-related peptide(CGRP)
olfactory nerve (C I)
12. paranasal sinus
13
Ostiomeatal Unit(OMU)
14. Development of Paranasal sinus
15. Possible Functions of Sinus Air conditioning Pressure damping Reduction of skull weight Heat insulation
Flotation of skull in water Increasing the olfactory area Mechanical rigidity Vocal resonance and diminution of auditory feedback
16. Lamella
2 5 1 4 3
1st lamella 2nd lamella 3rd lamella 4th lamella 5th lamella
Uncinate process Bulla Middle turbinate Superior turbinate Supreme turbinate
-17. Sphenoid sinus
-18. Optic Nerve & Internal Carotid Artery
Optic nerve
Internal
19. normal CT 1)lacrimal fossa and duct
carotid artey
20. endoscopic finding 1)inferior turbinate
2) middle turbinate -Paradoxical MT
3)uncinate process
4) Ethmoidal bulla
5) Superior turbinate
6) Double middle turbinate
7) Inferior turbinate polyp
8)septal perforation
Physiology of Nose & Sinus
1. Function of nose 1. Respiratory function
2.
Olfactory function
3.
Voice resonance
2. Respiratory function ?
Respiratory passage ( )
Control of inspired air
( ) Maximal distribution
Control of temperate & humidification Air cleaning & protection mucous blanket ciliary movement neural reflex : reflex apnea, sneezing
2. Respiration
Nasal air flow . . . Inspiratory flow: laminar flow Expiratory flow: turbulent flow Velocity of flow: central > lateral
3. Nasal resistance Disturbance of air flow in airway Nose : 50 % of total airway resistance Complex anatomy of nose, mucous seretion Nasal alae Nasal cavum Nasal valve : most resistant portion
4. Nasal resistance increase
Hyperventilation Supine position Cold air Alcohol Rhinitis except atropy Aspirin, diuretics, pill antihypertensive drug Sympathetic antagonist
4. Nasal resistance decreased Exercise Erect position Sympathomimetics Rebreathing Atrophic rhinitis PGE2
5. Nasal cycle Alternative increase or decrease of nasal resistance 80 % of normal adult, short cycle in children Blood volume change of capacitance vessel Controlled by autonomic nerve system
Insensible 0.5 - 3 hours/cycle Allergy, infection, exercise, hormone, pregnancy, emotion, posture
6. Nasal Blood Vessel Resistant vessels (arterioles, precapillary spincter) : control of blood flow to nasal mucosa Exchange(nutrient) vessels (capillary bed, AV anastmosis) : filtration and absorption of fluid Capacitance vessels (AV anastmosis, vein, venous sinusoid) : determines nasal patency by tones of vessels : nasal cycle
7. Paradoxical nasal obstruction Septal deviation Nasal obstruction in concave site Adaptation of convex site Increased resistance in concave site by nasal cycle nasal obstruction in concave site
8. Rhinomanometry (nasal resistance)
9. Acoustic rhinometry (Cross section)
10. Control of temperature & humidification Temperature : 35 0C Humidity : 95% saturation in inspired air 100% in expiration capillary and submucous gland
11. Composition of secretion Mucous mucin Serous lysozyme(LZ), lactoferrin(LF) secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor, s-Ig A, albumin
12. Mucociliary transport
13.
14. Nasal secretion transport
14. Abnormality of cilia
15.
Structure 200 / cell Length : 6 7 m, Diameter : 0.2- 0.3 m Deeper into mucus layer < 0.5 m Axoneme : the structure of a cilium mainly composed of microtubules (9+2 or 9 + 2 structures) surrounded with cell membrane 9+2 VS 9+0
Inner microtubule : direction Inner arm : bending form Outer arm : frequency
16. 17.
Functions of cilia Clearing mucus and debris from airway
Circulate spinal fluid in the ventricle of the brain
Contribute to the movement of the ovum in the fallopian tube
Control left-right asymmetry in embryonic node
Primary ciliary disease Cilia beat frequency : 5 -20 Hz
Primary ciliary dyskinesia (PCD) Cilia microstructure defect Cilia with decreased or total absence of motility Sinusitis, chronic bronchitis, bronchiectasis, and male infertility
Katargener syndrome PCD + Sinus inversus
18. Cilia beat Effective phase maximum velocity : 1 mm/s maximum arc : 110 2-3 X faster than recovery stroke
Resting phase
Recovery phase close to the cell surface clockwise sweep from above
CBF increase : all phase are shortened (especially resting phase)
19. Factors affecting CBF
Increase Purinergic receptor agonist adrenergic receptor antagonist prostaglandin E1, E2, F2a
Decrease Purinergic receptor antagonist Local anesthesia (lidocane) Temperatue (< 5 0C, > 40 0C) Histamine acetylcholine, methacholine topical steroid
20. Olfaction
Cribriform plate , septum, middle & sup. Turbinate
21. Olfactory epithelium PCCE Cribriform plate , septum, middle & sup. turbinate 9+2 dynein arm . Bowmans glands in lamina propria
Bipolar cell, microvilli, supporoting cell, basal cells
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Islamic MedicineDocument16 paginiIslamic MedicineNovriefta NugrahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diabetes Dengan Xanthoma KulitDocument2 paginiDiabetes Dengan Xanthoma KulitNovriefta NugrahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tugas Journal ReadingDocument34 paginiTugas Journal ReadingNovriefta NugrahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Journal of XanthomaDocument5 paginiJournal of XanthomaNovriefta NugrahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pediatrics 2004 Garcia Peña 24 8Document7 paginiPediatrics 2004 Garcia Peña 24 8Novriefta NugrahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Embryology&TeratologyDocument43 paginiEmbryology&TeratologyNovriefta NugrahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dengue Guideline DengueDocument33 paginiDengue Guideline DenguedrkkdbÎncă nu există evaluări
- Results of Case-Control Studies Support Association Between Contact Lens Use andDocument17 paginiResults of Case-Control Studies Support Association Between Contact Lens Use andNovriefta NugrahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory EmergenciesDocument30 paginiRespiratory EmergenciesNovriefta NugrahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Initial Assessment of Respi. Emergency (PKGDI Medan)Document49 paginiInitial Assessment of Respi. Emergency (PKGDI Medan)Novriefta NugrahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- COPD, Asthma, and DM Risk FactorDocument13 paginiCOPD, Asthma, and DM Risk FactorNovriefta NugrahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Journal of Ultrasonography in Acute AppendisitisDocument7 paginiJournal of Ultrasonography in Acute AppendisitisNovriefta NugrahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Newcastle OttawaDocument3 paginiNewcastle OttawaNovriefta NugrahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ankle Brachial Pressure IndexDocument12 paginiAnkle Brachial Pressure IndexNovriefta NugrahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 05 Nose AnatomyDocument28 pagini05 Nose AnatomyNovriefta NugrahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ARITMIA, Gangguan Irama JantungDocument37 paginiARITMIA, Gangguan Irama JantungNovriefta NugrahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- WHO - Surgical Care at The District Hospital (WHO 2003)Document514 paginiWHO - Surgical Care at The District Hospital (WHO 2003)gekriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 05 Nose AnatomyDocument28 pagini05 Nose AnatomyNovriefta NugrahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atypical Bacteria in Adenoids and Tonsils of Children Requiring AdenotonsillectomyDocument7 paginiAtypical Bacteria in Adenoids and Tonsils of Children Requiring AdenotonsillectomyNovriefta NugrahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Handbook of Pathology and Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular Disease 2002 PDFDocument321 paginiHandbook of Pathology and Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular Disease 2002 PDFChavo Delocho100% (1)
- Terminology of The Tonsils: 2011 Blackwell Verlag GMBH - Anat. Histol. Embryol. 40 (2011) 204-209Document7 paginiTerminology of The Tonsils: 2011 Blackwell Verlag GMBH - Anat. Histol. Embryol. 40 (2011) 204-209Novriefta NugrahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Allergic Rhinitis 2Document4 paginiAllergic Rhinitis 2Novriefta NugrahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vertigo PeriferDocument76 paginiVertigo PeriferAstriana IndrawatiÎncă nu există evaluări
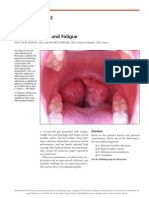
- Photo Quiz: Enlarged Tonsils and FatigueDocument3 paginiPhoto Quiz: Enlarged Tonsils and FatigueNovriefta NugrahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- UPLOAD KE-1 HormDocument47 paginiUPLOAD KE-1 HormNovriefta NugrahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)