Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Participatory Action Research
Încărcat de
Patricia Camille NucumDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Participatory Action Research
Încărcat de
Patricia Camille NucumDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
PARTICIPATORY ACTION RESEARCH (PAR) PROCESS Community-directed process of gathering and analyzing information or issues for the process
rocess of taking actions and making changes Involves research, education and action to empower the people FOCUS generate knowledge to generate actions DRIVING FORCE Positive Social Change ESSENTIAL ELEMENT OF PAR Participation MAIN ACTORS in THE RESEARCH PROCESS People (Beneficiaries)
COPAR PHASES 1. PRE-ENTRY PHASE Gathering important data in the community before entering it Community consultations/dialogues Setting of issues/considerations related to site selection Development of criteria for site selection Preliminary social investigation Site selection SOURCES OF INITIAL DATA: Written community profile Vital statistics consolidated and updated at the RHC Descriptions of the barangay from RHU workers, barangay health workers, and volunteers 2. ENTRY PHASE Integration with the community Sensitization of the community/information campaigns Conduct IEC Methodology for Info campaign Purok meetings and assembly Small group discussion Groundwork General meetings / assemblies c. Deepening social investigation (DSI) / community study
Pointers: Survey questionnaire Train key informants Secondary data Validation of data Gather data-informal
3. Identification of potential leaders Core group formation (CG) development of criteria for selection of CG members; Defining the roles/functions/tasks of the CG Education and Training Core group formation (CG) development of criteria for selection of CG members; Defining the roles/functions/tasks of the CG Education and Training Leadership Training Salt (Self-awareness Leadership Training) Technical skills Organizational skills Supervisory skills Provision of Health Services Purposes : Respond to acute problems Draw out peoples interest Enhances teams integration Focus on health problems
ORGANIZATION BUILDING PHASE Prepare community for CHO Organize CHO Train and educate CHO Setting up CHO
2 Important Preparation :
Legal requirements Technical requirements LEGAL REQUIREMENTS
Constitution & By-laws Registration papers Guidelines for election Board members
TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS Working Committee Health Committee Education & Training Membership Committee
4. SUSTENANCE and STRENGTHENING PHASE Mobilization in health Education and training Networking Livelihood program Developing secondary leaders Phase out
BASIC CO vs. COPAR Phases BASIC CO Specific - Preparation - Organizational - Education and training - Intersectoral linkages - Phase out Role of Organizing Staff BASIC CO Practitioner Leader / Manager Turn over : activities BASIC CO Absolute Periodic COPAR Sustainable relationship COPAR Practitioner Researcher COPAR Comprehensive - Pre entry - Entry - Organizational building - Sustenance and strengthening
IDEAL COPAR vs. PRACTICED COPAR Time Frame Ideal COPAR 3 6 weeks immersion 8 12 hrs / day Practiced COPAR 2 weeks 8 hrs / day or depending on the time allotted by the school
Community Study / Social investigation Ideal COPAR Based on the needs of the community SI - systematic Practiced COPAR Tailor made survey form Record review process
Education and Training
Ideal COPAR Based on community study and TNA Organizational Building Ideal COPAR Set up the CHO
Practiced COPAR Based on concepts mandated by the curriculum
Practiced COPAR Consider the existing non formal organization
Program Implementation Ideal COPAR fishing rod effect Long term Program Evaluation Ideal COPAR sustainability accept reality not all goals are met Practiced COPAR absolute phase out some results are manipulated Practiced COPAR fish effect one time
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Participatory Action ResearchDocument8 paginiParticipatory Action Researchjlfernandezpacheco100% (1)
- 3 Year Developmental PlanDocument13 pagini3 Year Developmental PlanMario HipolitoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Community Assessment: 1/ The Nature of CommunityDocument11 paginiCommunity Assessment: 1/ The Nature of CommunityN NÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.03 Community Based Participatory ResearchDocument2 pagini1.03 Community Based Participatory Researchgene2693Încă nu există evaluări
- Curriculum PlanningDocument26 paginiCurriculum PlanningMarion Agarpao - Piczon100% (1)
- Community Health Course Outline 2014 KingstonDocument11 paginiCommunity Health Course Outline 2014 KingstonJerilee SoCute Watts100% (1)
- Community DiagnsisDocument90 paginiCommunity DiagnsisRigel L. LicmoanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Designing Health Promotion ProgramDocument10 paginiDesigning Health Promotion ProgramThe HoopersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Participatory Action Research PresentationDocument39 paginiParticipatory Action Research Presentationapi-309521519Încă nu există evaluări
- Staff Development ReportDocument18 paginiStaff Development Reportdonnah artiedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guidance Note On District-Level Gap Analysis of RMNCH+A ImplementationDocument49 paginiGuidance Note On District-Level Gap Analysis of RMNCH+A ImplementationJennifer Pearson-ParedesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Functional AssessmentDocument3 paginiFunctional AssessmentRene John FranciscoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Correlational study between social media use and stress levelsDocument26 paginiCorrelational study between social media use and stress levelsQueen ZaportizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction to Capstone ProjectsDocument3 paginiIntroduction to Capstone ProjectsNana MinÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Flexible TeacherDocument4 paginiThe Flexible TeacherMCFÎncă nu există evaluări
- Typhoid Fever: Infectious DiseaseDocument52 paginiTyphoid Fever: Infectious Disease12. Akshit AtwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final EvaluationDocument2 paginiFinal Evaluationapi-396236810100% (1)
- Running Head: Curriculum Development in Nursing Education 1Document15 paginiRunning Head: Curriculum Development in Nursing Education 1api-396212664100% (1)
- 9 Transformative and MultiphaseDocument9 pagini9 Transformative and MultiphaseAC BalioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Public Health PaperDocument36 paginiPublic Health PaperLigia Peña TorresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Community Needs AssessmentDocument39 paginiCommunity Needs AssessmentCid PonienteÎncă nu există evaluări
- CO ContentDocument312 paginiCO ContentJonas Dela Cruz100% (1)
- RHU Situanional ReportDocument8 paginiRHU Situanional ReportErnest AtonÎncă nu există evaluări
- NR222 RUA Health Promotion - Adolescent Suicide Prevention - EditedDocument7 paginiNR222 RUA Health Promotion - Adolescent Suicide Prevention - EditedBridget ParkerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Health Policy and AdministrationDocument90 paginiHealth Policy and AdministrationGengen GolingoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles of Curriculum and Instruction in Nursing SyllabusDocument8 paginiPrinciples of Curriculum and Instruction in Nursing SyllabusLevy DuranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Barriers to Learning and DevelopmentDocument6 paginiBarriers to Learning and DevelopmentEmmanuel Manuel ForbesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Qualitative Research in NursingDocument8 paginiQualitative Research in NursingRoel AbricaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Council On Continuing Professional Education For NursesDocument2 paginiCouncil On Continuing Professional Education For NursesNoel100% (3)
- Assessing Community Health Factors in a Windshield SurveyDocument2 paginiAssessing Community Health Factors in a Windshield SurveyJennifer Loew Barstad100% (1)
- Tools Used in Community Diagnosis Demographyvital and Health Statistics EpidemiologyDocument41 paginiTools Used in Community Diagnosis Demographyvital and Health Statistics EpidemiologyFatmaIbrahim100% (1)
- Nursing Informatics: Unit 1 Introduction To Informatics: The American Nurses Association (ANA)Document3 paginiNursing Informatics: Unit 1 Introduction To Informatics: The American Nurses Association (ANA)Gabbi Kim100% (1)
- Advantages and Disadvantages of The Survey MethodDocument5 paginiAdvantages and Disadvantages of The Survey MethodFiz Iz100% (2)
- The Petilla Health REPORTDocument18 paginiThe Petilla Health REPORTjosejardinianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basics ResearchDocument21 paginiBasics ResearchAurora Marie AlberbaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plenary Ehealth Philippines PDFDocument33 paginiPlenary Ehealth Philippines PDFCarlo Beltran Valerio100% (1)
- Evidence Based Practice A Concept AnalysisDocument7 paginiEvidence Based Practice A Concept Analysissana naazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advantages and DisadvantagesDocument5 paginiAdvantages and DisadvantagesKyla RodriguezaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Resilience and Deaf Children Current Knowledge and Future Directions PDFDocument47 paginiResilience and Deaf Children Current Knowledge and Future Directions PDFJennifer R. BalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Statistics1Document20 paginiWhat Is Statistics1Candy ChocolateÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conceptualizing Tele NursingDocument14 paginiConceptualizing Tele NursingdollyodemboÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hospital Leadership, Management and GovernanceDocument46 paginiHospital Leadership, Management and GovernanceGebre GutetaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.the Advantages and Disadvantages of StatisticsDocument3 pagini1.the Advantages and Disadvantages of StatisticsMurshid IqbalÎncă nu există evaluări
- IMRADDocument60 paginiIMRADKirk Martin MarcosÎncă nu există evaluări
- g7 Research Proposal FinalDocument36 paginig7 Research Proposal FinalChristian Leo Venzon MoringÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles of Planning and Characteristics of A Good PlanDocument16 paginiPrinciples of Planning and Characteristics of A Good PlanArlanosaurus91% (11)
- The Community, Its Organization, and Its HealthDocument27 paginiThe Community, Its Organization, and Its HealthAurian Tormes100% (3)
- Knowledge, Attitude and Practices On Oral Health of Public School Children of Batangas CityDocument10 paginiKnowledge, Attitude and Practices On Oral Health of Public School Children of Batangas CityAsia Pacific Journal of Multidisciplinary ResearchÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCM 113 Midterm Lec Mod 5Document17 paginiNCM 113 Midterm Lec Mod 5desteen klaire montefalcoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research Paper IntroductionDocument6 paginiResearch Paper IntroductionJomar Francisco AvilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MPH Capstone GuideDocument17 paginiMPH Capstone GuideImran KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maternal Knowledge Attitudes and Practices and Health OutcomesDocument195 paginiMaternal Knowledge Attitudes and Practices and Health OutcomesLucky Radita Alma100% (1)
- Aschiana: Afghan Children and New Approach Project ProposalDocument6 paginiAschiana: Afghan Children and New Approach Project Proposalsaher8901100% (1)
- Methodological Dimension of Curriculum DevelopmentDocument10 paginiMethodological Dimension of Curriculum DevelopmentDa LheneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Public Health Needs Assessment Profile and Health Promotion Proposal by Theresa Lowry Lehnen Specialist Nurse Practitioner in Conjunction With Surrey University 2005Document46 paginiPublic Health Needs Assessment Profile and Health Promotion Proposal by Theresa Lowry Lehnen Specialist Nurse Practitioner in Conjunction With Surrey University 2005Theresa Lowry-LehnenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Community Organizing Through Paticipatory Action Researchco ParDocument35 paginiCommunity Organizing Through Paticipatory Action Researchco ParZanesville Lymont L. SubidoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Primitive ManDocument4 paginiPrimitive ManPriti PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study On Support For Persons With DisabilitiesDocument97 paginiStudy On Support For Persons With DisabilitiesadkittipongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Community Health A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDe la EverandCommunity Health A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Common Risk Factors in The Elderly (Elec)Document6 paginiCommon Risk Factors in The Elderly (Elec)Patricia Camille NucumÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Organization For Grooming Adept Nurses (ORGAN)Document2 paginiThe Organization For Grooming Adept Nurses (ORGAN)Patricia Camille NucumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Easy A (Reflection Paper)Document2 paginiEasy A (Reflection Paper)Patricia Camille NucumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Functional Screening Is Important Because When Doing An AssessmentDocument3 paginiFunctional Screening Is Important Because When Doing An AssessmentPatricia Camille NucumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Properties of RadicalsDocument2 paginiProperties of RadicalsPatricia Camille NucumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modern Stratification Systems: SlaveryDocument3 paginiModern Stratification Systems: SlaveryPatricia Camille NucumÎncă nu există evaluări
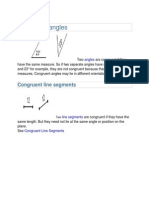
- Congruent AnglesDocument1 paginăCongruent AnglesPatricia Camille NucumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample Resume For NO EXPERIENCEDocument1 paginăSample Resume For NO EXPERIENCEPatricia Camille NucumÎncă nu există evaluări
- JkoDocument3 paginiJkoPatricia Camille NucumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample Resume ONE PAGEDocument1 paginăSample Resume ONE PAGEPatricia Camille NucumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample Resume For ABROADDocument3 paginiSample Resume For ABROADPatricia Camille NucumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Resume for Hotel and Restaurant Management GraduateDocument2 paginiResume for Hotel and Restaurant Management GraduatePatricia Camille NucumÎncă nu există evaluări
- App LetterDocument1 paginăApp LetterPatricia Camille NucumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Therapeutic Communication in Psychiatric NursingDocument6 paginiTherapeutic Communication in Psychiatric NursingPatricia Camille Nucum0% (1)
- Sample Resume For ABROADDocument3 paginiSample Resume For ABROADPatricia Camille NucumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Full Hand Out (Theo)Document11 paginiFull Hand Out (Theo)Patricia Camille NucumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Play TherapyjomelDocument5 paginiPlay TherapyjomelPatricia Camille NucumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Health Problem Family Nursing Problem Goal of Care Objectives of Care Intervention PlanDocument5 paginiHealth Problem Family Nursing Problem Goal of Care Objectives of Care Intervention PlanCel Limbre Rabia100% (10)
- Cost Effectiveness AnalysisDocument14 paginiCost Effectiveness AnalysisPatricia Camille NucumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Corporate Account: Department of Commerce Doctor Harisingh Gour Vishwavidyalaya (A Central University) SAGAR (M.P.)Document6 paginiCorporate Account: Department of Commerce Doctor Harisingh Gour Vishwavidyalaya (A Central University) SAGAR (M.P.)Aditya JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kedudukan Dan Fungsi Pembukaan Undang-Undang Dasar 1945: Pembelajaran Dari Tren GlobalDocument20 paginiKedudukan Dan Fungsi Pembukaan Undang-Undang Dasar 1945: Pembelajaran Dari Tren GlobalRaissa OwenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 00.arkana ValveDocument40 pagini00.arkana ValveTrần ThànhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Leku Pilli V Anyama (Election Petition No 4 of 2021) 2021 UGHCEP 24 (8 October 2021)Document52 paginiLeku Pilli V Anyama (Election Petition No 4 of 2021) 2021 UGHCEP 24 (8 October 2021)Yokana MugabiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 740LIDocument13 pagini740LIm FaisalÎncă nu există evaluări
- TAX & DUE PROCESSDocument2 paginiTAX & DUE PROCESSMayra MerczÎncă nu există evaluări
- BI - Cover Letter Template For EC Submission - Sent 09 Sept 2014Document1 paginăBI - Cover Letter Template For EC Submission - Sent 09 Sept 2014scribdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heidegger - Nietzsches Word God Is DeadDocument31 paginiHeidegger - Nietzsches Word God Is DeadSoumyadeepÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction to History Part 1: Key ConceptsDocument32 paginiIntroduction to History Part 1: Key ConceptsMaryam14xÎncă nu există evaluări
- LTD Samplex - Serrano NotesDocument3 paginiLTD Samplex - Serrano NotesMariam BautistaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ROCKET STOVE DESIGN GUIDEDocument9 paginiROCKET STOVE DESIGN GUIDEfrola5100% (2)
- Virtue Ethics: Aristotle and St. Thomas Aquinas: DiscussionDocument16 paginiVirtue Ethics: Aristotle and St. Thomas Aquinas: DiscussionCarlisle ParkerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Apple NotesDocument3 paginiApple NotesKrishna Mohan ChennareddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Setting MemcacheDocument2 paginiSetting MemcacheHendra CahyanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 1 in 21st CneturyDocument8 paginiTopic 1 in 21st CneturyLuwisa RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- MatriarchyDocument11 paginiMatriarchyKristopher Trey100% (1)
- Business Law Module No. 2Document10 paginiBusiness Law Module No. 2Yolly DiazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mari 1.4v2 GettingStartedGuide PDFDocument57 paginiMari 1.4v2 GettingStartedGuide PDFCarlos Vladimir Roa LunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Statement of The Problem: Notre Dame of Marbel University Integrated Basic EducationDocument6 paginiStatement of The Problem: Notre Dame of Marbel University Integrated Basic Educationgab rielleÎncă nu există evaluări
- IB Theatre: The Ilussion of InclusionDocument15 paginiIB Theatre: The Ilussion of InclusionLazar LukacÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Love? - Osho: Sat Sangha SalonDocument7 paginiWhat Is Love? - Osho: Sat Sangha SalonMichael VladislavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Javascript The Web Warrior Series 6Th Edition Vodnik Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument31 paginiJavascript The Web Warrior Series 6Th Edition Vodnik Test Bank Full Chapter PDFtina.bobbitt231100% (10)
- Belonging Through A Psychoanalytic LensDocument237 paginiBelonging Through A Psychoanalytic LensFelicity Spyder100% (1)
- Operational Risk Roll-OutDocument17 paginiOperational Risk Roll-OutLee WerrellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Art 1780280905 PDFDocument8 paginiArt 1780280905 PDFIesna NaÎncă nu există evaluări
- International Standard Knowledge Olympiad - Exam Syllabus Eligibility: Class 1-10 Class - 1Document10 paginiInternational Standard Knowledge Olympiad - Exam Syllabus Eligibility: Class 1-10 Class - 1V A Prem KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Important TemperatefruitsDocument33 paginiImportant TemperatefruitsjosephinÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4AD15ME053Document25 pagini4AD15ME053Yàshánk GøwdàÎncă nu există evaluări
- Astrology - House SignificationDocument4 paginiAstrology - House SignificationsunilkumardubeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bianchi Size Chart for Mountain BikesDocument1 paginăBianchi Size Chart for Mountain BikesSyafiq IshakÎncă nu există evaluări