Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
HSRP
Încărcat de
Nishant MishraDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
HSRP
Încărcat de
Nishant MishraDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Step-by-Step With Cisco's Hot Standby Router Protocol
Page 1 of 2
The latest network routers, software, management tools and information for enterprise IT administrators. Networking Project Center Network Security Network Software WAN and LAN Data Center Network Management Networking Hardware Unified Communications
Sign In
Register
Get the samples, tools, and support you need to move your iOS or Android Apps to Windows 8. Sponsored
Get the Latest Scoop with Enterprise Networking Planet Newsletter
Home
How-To
Enter Your E-mail Address
Step-by-Step With Cisco's Hot Standby Router Protocol
Cisco's Hot Standby Router Protocol lets you add redundancy, fault tolerance, and load balancing to your network with relative ease. Michael Burton steps you through basic HSRP configuration and troubleshooting. By Michael Burton | Aug 2, 2004 Page 1 of 2 1
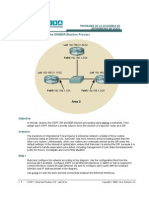
The Hot Swappable Router Protocol (HSRP) is a way to build redundancy into your network by allowing two or more routers to continuously test each other for connectivity, and take over if a router fails. For purposes of discussing a basic HSRP configuration, let's assume we want to make the 10.10.10./24 network dynamically redundant and have two building routers at our disposal. Using HSRP terminology, both building routers together are referred to as a standby group and appear to the subnet as a single default gateway. Through an election process, one router is designated as active and the other router is designated as standby. Both the active and standby router listen to routing updates from the core router, but only the active router processes IP packets as the default gateway for the subnet. The active and standby routers are constantly sending "hello" packets back and forth. If the active router fails, as soon as a predetermined number of "hello" packets from the standby router to the active router go unanswered, the standby router becomes the active router and starts processing IP packets for the subnet. Both routers are configured with standard IP addresses on their interface into the subnet. Each router also has a special virtual IP address which is the same on both routers, configured via standby commands under the specific interfaces.
Go Deeper
802.11ac Action Plan: A Network-Readiness Checklist
Configuring the Routers
Given a standard 24-bit subnet, we can build the following: Network: 10.10.10.0 Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0 Default Gateway: 10.10.10.251 Physical IP Address Building Router A: Building Router B: 10.10.10.252 10.10.10.253
Products based on the upcoming IEEE 802.11ac wireless-LAN (WLAN) standard are indeed going to dominate the enterprise wireless local-area
Best Practices to Ensure Successful Delivery of Unified Communications
The configuration commands are as follows: building router a# interface fa0/2 ip address 10.10.10.252 255.255.255.0 This sets the IP address for the interface standby 100 timers 3 10 100 denotes the HSRP process number as "hot standby group 100". You can have multiple HSRP standby groups on the same interface. The timers command sets the interval to 3 seconds between HELLO messages, and waits 10 seconds before the other router is declared down. standby 100 priority 200 preempt Defines the priority of this router. The highest priority number will win the election. "Preempt" allows the router to take over control even if there is not an election in process if it comes on line with the highest priority. standby 100 authentication fnord Optional - Authentication [word] creates an unencrypted authentication process for each HSRP packet. standby 100 ip 10.10.10.251 Establishes 10.10.10.251 as the virtual interface. This IP address should be the same on both HSRP routers. standby 100 track fa0/0 mhall@internet.com
Deploying unified communications can greatly enhance both employee and business productivity. However, designing and deploying
Mobilize Magazine, Winter/Spring 2013
The power to connect anytime, anywhere is becoming prominent in today's business world. Cisco is using this power to enhance both
29%
Print to PDF without this message by purchasing novaPDF (http://www.novapdf.com/) http://www.enterprisenetworkingplanet.com/netsysm/article.php/1438251/StepbyStep-Wi...
29/05/2013
Step-by-Step With Cisco's Hot Standby Router Protocol
Page 2 of 2
Next Page 5 Comments (click to add your comment) By mithun franciz March 13 2013 00:24 PDT your way of explaining the configuration of hsrp is very helpful. Can u try to include multiple hsrp [m hsrp] configuration details..
Reply to this comment
By Koloz January 07 2013 02:10 PST Great article but please I can't see page 2, same thing seems to be on page 1 and page 2 or am I missing something here? Thanks.
Reply to this comment
By Jerry June 24 2012 19:44 PDT Nice configuration of HSRP.I love the way you explained your configuration.It is a step-bystep configuration which is very straight forward. Thanks for the article.
Reply to this comment
By Abith Basha March 23 2009 10:29 PDT The article is amazing and it is really helped a lot for me to configure the HSRP in my company
Reply to this comment
By Very helpful January 08 2009 06:34 PST What is Priority decrement is set to 20?
Reply to this comment
Comment and Contribute
Your name/nickname Subject (Optional) Comments
Your email
(Maximum characters: 1200). You have
1200
characters left.
Type the two words
Privacy & Terms
Print to PDF without this message by purchasing novaPDF (http://www.novapdf.com/) http://www.enterprisenetworkingplanet.com/netsysm/article.php/1438251/StepbyStep-Wi...
29/05/2013
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Wan Frly 12 4 BookDocument248 paginiWan Frly 12 4 BookNishant MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Google Advanced FeaturesDocument26 paginiGoogle Advanced FeaturesNishant MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- IP Encapsulation, Fragmentation, and Reassembly: Computer Science Prof. MartinsDocument26 paginiIP Encapsulation, Fragmentation, and Reassembly: Computer Science Prof. MartinsNishant MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCIE Notes From ExperienceDocument27 paginiCCIE Notes From Experienceapi-3817990Încă nu există evaluări
- Using OSPF in MPLS VPN EnvironmentDocument52 paginiUsing OSPF in MPLS VPN EnvironmentMauro Ferri100% (1)
- Configuring BGP On Cisco Routers Lab Guide 3.2Document106 paginiConfiguring BGP On Cisco Routers Lab Guide 3.2skuzurov67% (3)
- Iewb-Rs Technology Labs Ipv6: Brian Dennis, Ccie # 2210 (R&S / Isp Dial / Security / Service Provider)Document17 paginiIewb-Rs Technology Labs Ipv6: Brian Dennis, Ccie # 2210 (R&S / Isp Dial / Security / Service Provider)Nishant MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Configuring IP Access Lists: Document ID: 23602Document18 paginiConfiguring IP Access Lists: Document ID: 23602Srikanth ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 026Document3 pagini026frontechaslÎncă nu există evaluări
- Network Engineer CV TemplateDocument2 paginiNetwork Engineer CV TemplatemacumuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Be Prepared - Getting Ready For Job InterviewsDocument97 paginiBe Prepared - Getting Ready For Job InterviewshutsupÎncă nu există evaluări
- For Browse More TCY Network Engineer's Resume, Please VisitDocument1 paginăFor Browse More TCY Network Engineer's Resume, Please VisitNishant MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interview Questionjkndqwjks For System Engineer Net. EngDocument5 paginiInterview Questionjkndqwjks For System Engineer Net. EngNishant MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Betwwen You and DreamDocument13 paginiBetwwen You and DreamNishant MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 001Document4 pagini001Venkata Nagi ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 023Document3 pagini023Nishant MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2523 Full Mesh. 4 3 3Document2 pagini2523 Full Mesh. 4 3 3Nishant MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3600 Hub N SpokeDocument2 pagini3600 Hub N SpokeNishant MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Using OSPF in MPLS VPN EnvironmentDocument52 paginiUsing OSPF in MPLS VPN EnvironmentMauro Ferri100% (1)
- Configuring IP Access Lists: Document ID: 23602Document18 paginiConfiguring IP Access Lists: Document ID: 23602Srikanth ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- TosDocument3 paginiTosNishant MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCNA Subnetting Course MapDocument0 paginiCCNA Subnetting Course Maprick018Încă nu există evaluări
- CCNA GlossaryDocument36 paginiCCNA GlossaryAamir KhalilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cisco IOS Cisco Discovery Protocol Command Reference Cdp-Cr-BookDocument42 paginiCisco IOS Cisco Discovery Protocol Command Reference Cdp-Cr-BookNishant MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neibour RelationshipDocument1 paginăNeibour RelationshipNishant MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Commn Fundamentals DATA and SIGNALDocument13 paginiData Commn Fundamentals DATA and SIGNALapi-3806586100% (1)
- 3600 Hub N SpokeDocument2 pagini3600 Hub N SpokeNishant MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2523 Full Mesh. 4 3 3Document2 pagini2523 Full Mesh. 4 3 3Nishant MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- WWW Careercert InfoDocument1 paginăWWW Careercert InfoNishant MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2523 Hub N SpokeDocument2 pagini2523 Hub N SpokeNishant MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5784)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (890)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (72)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- 2.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes - Swinburne - V1.0Document7 pagini2.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes - Swinburne - V1.0Basit KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8.1.1.8 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Challenge - Documenting The Network Instructions - ILMDocument24 pagini8.1.1.8 Packet Tracer - Troubleshooting Challenge - Documenting The Network Instructions - ILMkaren rocha0% (1)
- 19-1 IGP Fundamentals Configuration Answer KeyDocument5 pagini19-1 IGP Fundamentals Configuration Answer KeyTent DorinÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3G UMTS/WCDMA Drop Call Rate Improvement (DCR CS/PS) in 3G Network HuaweiDocument1 pagină3G UMTS/WCDMA Drop Call Rate Improvement (DCR CS/PS) in 3G Network HuaweiAsmae100% (1)
- CCNA 3 v503 v60 Chapter 5 Exam Answers 2017 100 FullDocument14 paginiCCNA 3 v503 v60 Chapter 5 Exam Answers 2017 100 FullSándor PetrócziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inter-Autonomous System Mpls VPN: Configuration and TroubleshootingDocument41 paginiInter-Autonomous System Mpls VPN: Configuration and Troubleshootingkds850Încă nu există evaluări
- RNC PAT ChecklistDocument41 paginiRNC PAT ChecklistSudipta DasÎncă nu există evaluări
- LTE CELL Reselection ProcedureDocument5 paginiLTE CELL Reselection ProcedureNak SandyÎncă nu există evaluări
- AirScale BB - CellSet Connection Rules - Ed02Document7 paginiAirScale BB - CellSet Connection Rules - Ed02Abdelaziz Boubaker0% (1)
- 3G KPI Analysis ReportDocument64 pagini3G KPI Analysis ReportTryEkoÎncă nu există evaluări
- UCPE (4) UCPE Acting As Remote Inet GWDocument13 paginiUCPE (4) UCPE Acting As Remote Inet GWbike9915Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1Document12 paginiUnit 1ChuntitoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ccnpv7 Route Lab7-1 BGP Config StudentDocument11 paginiCcnpv7 Route Lab7-1 BGP Config StudentplobaredeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Huawei 3g Capacity OptimizationDocument39 pagini1 Huawei 3g Capacity OptimizationCharles W GitahiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Business Objects KPI AnalyzeDocument21 paginiBusiness Objects KPI AnalyzeshethÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 7.7.3 Configuring IS-IS Over Frame Relay: AlternateDocument8 paginiLab 7.7.3 Configuring IS-IS Over Frame Relay: AlternateKishore Reddy KandiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circuit Switched Fallback CSFBDocument6 paginiCircuit Switched Fallback CSFBMalikMDNuraniÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3GPP TS 23.272Document50 pagini3GPP TS 23.272Wong Ting FungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ospf DR BDRDocument5 paginiOspf DR BDRvelramsenÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 8 1 Policy Based Routing PrincipleDocument5 pagini2 8 1 Policy Based Routing PrincipleDaniel Ibarra OÎncă nu există evaluări
- Domande IP RagazziDocument22 paginiDomande IP Ragazziferranti.mÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cisco CCNA Lab 6.7.5 Subnet and Router ConfigurationDocument3 paginiCisco CCNA Lab 6.7.5 Subnet and Router ConfigurationBms Ag0% (1)
- ERNW HITB AMS Mende Rey Attacking Mobile Telecommunication Networks GerDocument70 paginiERNW HITB AMS Mende Rey Attacking Mobile Telecommunication Networks GerMike HortonÎncă nu există evaluări
- OSPFDocument43 paginiOSPFAftab AlamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Collection FormatDocument15 paginiData Collection FormatneerajnepalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ospf Neighbor States Explained With ExampleDocument19 paginiOspf Neighbor States Explained With ExampleMark BrownÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amazon Interview QuestionsDocument2 paginiAmazon Interview Questionsmita-balijaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Airtel Nokia ParameterDocument23 paginiAirtel Nokia ParameterkbgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modular Qos Configuration Guide For Cisco Ncs 540 Series Routers, Cisco Ios XR Release 7.4.XDocument114 paginiModular Qos Configuration Guide For Cisco Ncs 540 Series Routers, Cisco Ios XR Release 7.4.XCCIE RocksÎncă nu există evaluări
- Command Comparison List For Huawei 'S Device and Counterparts'Document93 paginiCommand Comparison List For Huawei 'S Device and Counterparts'hilbert69100% (2)