Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
High Impedance Relay and Low Impedance Relay
Încărcat de
Irfan UllahDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
High Impedance Relay and Low Impedance Relay
Încărcat de
Irfan UllahDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
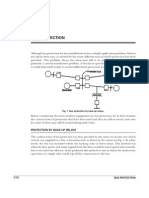
High impedance principle means that protective relay has a such a large series impedance that even the
largest through fault current occuring during transient condition does not start an un-necessary relay operation.High impedance relay is one in which all CTs must have the same ratios. it is employed in The differential protection of generators, bus bars, motors and reactors. Low impedance relays do not have any additional series impedances and are usually employed for transformers differential protection. http://www.allinterview.com/showanswers/104109.html
High impedance bus differential relays are used on most of the busses in North America. The popularity can be explained by the good performance of this scheme in relation to CT saturation and the low cost, if used on a simple bus system. However with the introduction of numerical relays and their low CT burden as well as their ability of measuring several feeder currents, a low impedance bus differential principal could be applied on simple busses also. In addition, the availability of fiber optic communication inside of the substation allows the use of decentralized bus system in which the CT output values becomes transmitted via communication to a centralized unit versus having CT wires running to the control house. Low impedance bus differential protection systems have many positive attributes. Common advantages of all low impedance bus protection schemes are the ability to be able to use CT's of different ratios on respective branch inputs and the fact that the same CT used for the bus protection can be shared with the feeder protection relay. The question needs to be discussed what selection criteria needs to get evaluated for the selection of the appropriate principal. The paper will give an overview on both principles and explain the difference in building and evaluating of the differential current. The effect of CT saturation during external and internal faults will be discussed in details for both schemes as well as the CT requirements. Some advanced numerical techniques employed in low impedance bus differential relays to recognize CT saturation on heavy throughfaults and avoid false tripping are presented. Common guidelines for setting both principles will be reviewed and explained in detail and some examples will be shown. The influence of the complexity of the bus system on the selection will be discussed. Benefits and disadvantages of both systems will be compared. The comparison will also include the difference during the installation, commissioning- , operation and maintenance phase of the different systems. The evaluation will be done technically as well as economically. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/articleDetails.jsp?arnumber=5262334
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Busbar Protection SystemsDocument12 paginiBusbar Protection SystemsAhmed Said GhonimyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Survey On Power Optimization Techniques For Low Power Vlsi Circuit in Deep Submicron TechnologyDocument15 paginiSurvey On Power Optimization Techniques For Low Power Vlsi Circuit in Deep Submicron TechnologyAnonymous e4UpOQEPÎncă nu există evaluări
- Algorithm For Digital Low ImpedanceDocument8 paginiAlgorithm For Digital Low ImpedanceJanen AhujaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparison Between High Impedance and Low Impedance Bus Differential ProtectionDocument15 paginiComparison Between High Impedance and Low Impedance Bus Differential Protectionpop papÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital Busbar Protection - RahafDocument8 paginiDigital Busbar Protection - RahafRahaf WaheepÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cpre 2017 8090038Document19 paginiCpre 2017 8090038Rahaf WaheepÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rahaf Busbar-ModificationDocument9 paginiRahaf Busbar-ModificationRahaf WaheepÎncă nu există evaluări
- Busbar ProtectionDocument4 paginiBusbar Protectiondundi_kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Busbar Protection Systems: Busbars Are A Vital, Yet Often Overlooked, Part of The Power SystemDocument3 paginiBusbar Protection Systems: Busbars Are A Vital, Yet Often Overlooked, Part of The Power SystemKeval VelaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Busbar Protection - A ReviewDocument5 paginiBusbar Protection - A ReviewPrajiWazharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Busbar Differential ProtectionDocument19 paginiBusbar Differential ProtectionVijay KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- A New Differential Protection Scheme For Busbar Considering CT Saturation EffectDocument4 paginiA New Differential Protection Scheme For Busbar Considering CT Saturation EffectMuruganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Testing of Modern Bus Protection SystemsDocument7 paginiTesting of Modern Bus Protection Systemss_banerjeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- BBP ZGDocument17 paginiBBP ZGRahaf WaheepÎncă nu există evaluări
- BB ProtectionDocument38 paginiBB ProtectionMOHAMED KHAMIS0% (1)
- Double Bus With Bus Tie ProtectionDocument4 paginiDouble Bus With Bus Tie ProtectionWoei Song OoiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study Committee B5 Colloquium 2007 October 15-20 Madrid, SPAINDocument13 paginiStudy Committee B5 Colloquium 2007 October 15-20 Madrid, SPAINraghavendran raghuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper 2Document7 paginiPaper 2Hnin HninÎncă nu există evaluări
- Micom P740Document18 paginiMicom P740vsrikala68Încă nu există evaluări
- Distribution System DesignDocument14 paginiDistribution System DesignAhmed0% (1)
- TCSC For Protection PDFDocument9 paginiTCSC For Protection PDFpragatinareshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multi-Terminal DC System Line Protection Requirement and High Speed Protection SolutionsDocument9 paginiMulti-Terminal DC System Line Protection Requirement and High Speed Protection SolutionsMuhammad AftabuzzamanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power System RelayingDocument22 paginiPower System RelayingKhairul AshrafÎncă nu există evaluări
- Busbar Protection Selection and DesignDocument30 paginiBusbar Protection Selection and DesignAdhyartha KerafÎncă nu există evaluări
- Proteccion Diferencial de BarrasDocument19 paginiProteccion Diferencial de BarrasSalvador Gutierrez CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Applications and Characteristics of Differential Relays ANSI 87Document6 paginiApplications and Characteristics of Differential Relays ANSI 87Ricardo A VergaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Current Differential Line Protection Setting ConsiderationsDocument28 paginiCurrent Differential Line Protection Setting ConsiderationskankokwahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Switchgear Application Issues For Mission Critical Power Systems, Part OneDocument12 paginiSwitchgear Application Issues For Mission Critical Power Systems, Part OneMithra Sathish KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paralleling Cts For Line Differential ProtectionDocument15 paginiParalleling Cts For Line Differential ProtectionYeissonSanabria100% (1)
- Eric Moore Switchgears AssignmentDocument10 paginiEric Moore Switchgears AssignmentEmmanuel EsselÎncă nu există evaluări
- Benefits of HVDC and FACTS For Power-Flow Control "Transmission Can Be So Easy"Document5 paginiBenefits of HVDC and FACTS For Power-Flow Control "Transmission Can Be So Easy"rworld999Încă nu există evaluări
- HighImpedanceDifferential 6818 20180209Document14 paginiHighImpedanceDifferential 6818 20180209Babar SaleemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bus ProtectionDocument21 paginiBus ProtectionSoumik DandapatÎncă nu există evaluări
- ANALOG VS DIGITAL BUS DIFFERENTIAL PROTECTIONDocument6 paginiANALOG VS DIGITAL BUS DIFFERENTIAL PROTECTIONratheeshkumardÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report - Next Generation Smart Substation Through GSM TechnologyDocument70 paginiReport - Next Generation Smart Substation Through GSM TechnologyRamsathayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 10: Differential Protection of Bus, Transformer and Generator: Bus ProtectionDocument9 paginiModule 10: Differential Protection of Bus, Transformer and Generator: Bus ProtectionCésar PérezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design HDocument7 paginiDesign HJohn Mark DalidaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coordination of Relays, Reclosers, and Sectionalizing Fuses For Overhead Lines in The Oil PatchDocument8 paginiCoordination of Relays, Reclosers, and Sectionalizing Fuses For Overhead Lines in The Oil PatchluhusapaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 16.prospects ofVoltage-Sourced Converters (VSC) Applications in DCTransmission SystemsDocument5 pagini16.prospects ofVoltage-Sourced Converters (VSC) Applications in DCTransmission SystemsWahyu HarianjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A PAPER On Flexible AC Transmission SystemDocument19 paginiA PAPER On Flexible AC Transmission SystemTeju NookalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture Notes Unit 2 Smart Grid1Document25 paginiLecture Notes Unit 2 Smart Grid1Saurabh BhardwajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Motor Protection Application GuideDocument28 paginiMotor Protection Application Guidekvasquez1979Încă nu există evaluări
- Busbar Protection: Dinesh Kumar Sarda A.Manager (MRSS)Document30 paginiBusbar Protection: Dinesh Kumar Sarda A.Manager (MRSS)karthikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fault Diagnosis in Electric Drives Using Machine Learning ApproachesDocument21 paginiFault Diagnosis in Electric Drives Using Machine Learning ApproachesRaid AbdemezianeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2006paper19 SegregatedbusDocument32 pagini2006paper19 SegregatedbusRahaf WaheepÎncă nu există evaluări
- Improved Power Transformer Protection Using Numerical RelaysDocument17 paginiImproved Power Transformer Protection Using Numerical RelayssegamegaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comprehensive Review and Comparative Analysis of Compensation Networks For Capacitive Power Transfer SystemsDocument7 paginiComprehensive Review and Comparative Analysis of Compensation Networks For Capacitive Power Transfer SystemsAhmed Moh'dÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application of Upfc For The Enhancement of AtcDocument24 paginiApplication of Upfc For The Enhancement of AtcVishnu BasettiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asset ManagementDocument4 paginiAsset ManagementJohan TadlasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transmission Line Fault Detection Methods AnalysisDocument28 paginiTransmission Line Fault Detection Methods AnalysisAvinash ChimkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power System Protection Studies and Relay CoordinationDocument9 paginiPower System Protection Studies and Relay CoordinationJeya Kannan100% (1)
- Congestion Control and Traffic Management in ATM NDocument27 paginiCongestion Control and Traffic Management in ATM Nsurya selvamÎncă nu există evaluări
- k01 000 00 PDFDocument15 paginik01 000 00 PDFomairyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Applications of MatixDocument2 paginiApplications of MatixSugu SukuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Impedance Relays in Distribution NetworksDocument3 paginiImpedance Relays in Distribution NetworksJose Alberto RodriguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Differential Protection for Power Transformers Using RelayDocument5 paginiDifferential Protection for Power Transformers Using RelayChandan DwivediÎncă nu există evaluări
- Methods for Increasing the Quality and Reliability of Power System Using FACTS DevicesDe la EverandMethods for Increasing the Quality and Reliability of Power System Using FACTS DevicesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Joint RES and Distribution Network Expansion Planning Under a Demand Response FrameworkDe la EverandJoint RES and Distribution Network Expansion Planning Under a Demand Response FrameworkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Overcurrent Relay Advances for Modern Electricity NetworksDe la EverandOvercurrent Relay Advances for Modern Electricity NetworksÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spring 2017 - ENG301 - 2Document3 paginiSpring 2017 - ENG301 - 2Irfan UllahÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9 DIFFERENCES BETWEEN MANAGER and LEADERSDocument2 pagini9 DIFFERENCES BETWEEN MANAGER and LEADERSIrfan UllahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conditional Sentences Unit 39-ConditionalsDocument4 paginiConditional Sentences Unit 39-ConditionalsIrfan UllahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gat CurriculumDocument8 paginiGat CurriculumIrfan UllahÎncă nu există evaluări
- WingleDocument7 paginiWingleIrfan UllahÎncă nu există evaluări
- NTS FormDocument1 paginăNTS FormIrfan UllahÎncă nu există evaluări
- NTS FormDocument1 paginăNTS FormIrfan UllahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phiosophy and Operation of Check Zone ProtectionDocument2 paginiPhiosophy and Operation of Check Zone ProtectionIrfan UllahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Characteristic or Intrinsic Impedence of The LineDocument10 paginiCharacteristic or Intrinsic Impedence of The LineIrfan UllahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Have or Get - 2Document2 paginiHave or Get - 2Irfan UllahÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Complain in EnglishDocument3 paginiHow To Complain in EnglishIrfan UllahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conditional Sentences Complete All TypesDocument17 paginiConditional Sentences Complete All TypesIrfan UllahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steps To Ensure Effective Substation GroundingDocument7 paginiSteps To Ensure Effective Substation GroundingIrfan UllahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Personality InformationDocument6 paginiPersonality InformationIrfan UllahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Energy Vs MWDocument21 paginiEnergy Vs MWIrfan UllahÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Choose A TransformerDocument6 paginiHow To Choose A TransformerIrfan UllahÎncă nu există evaluări
- P&i 174Document97 paginiP&i 174Irfan UllahÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Terrorist Prince Murtaza Bhutto 18 QistsDocument18 paginiThe Terrorist Prince Murtaza Bhutto 18 QistsIrfan UllahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organization: A Message From The Chairman Main Activities History Organi Office LocationDocument2 paginiOrganization: A Message From The Chairman Main Activities History Organi Office LocationIrfan UllahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research & Info ActivitiesDocument4 paginiResearch & Info ActivitiesIrfan UllahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fun EnglishDocument34 paginiFun Englishsniju100% (3)
- Operating and Financial DataDocument14 paginiOperating and Financial DataIrfan UllahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test 4Document3 paginiTest 4Irfan UllahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Office Location: A Message From The Chairman Main Activities History Organi Office LocationDocument3 paginiOffice Location: A Message From The Chairman Main Activities History Organi Office LocationIrfan UllahÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of Important Pair of Words From CSS Past PapersDocument23 paginiList of Important Pair of Words From CSS Past PapersIrfan Ullah100% (1)
- Electrical Important McqsDocument1 paginăElectrical Important McqsIrfan UllahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Int'l CooperationDocument2 paginiInt'l CooperationIrfan UllahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Big Large and GreatDocument1 paginăBig Large and GreatIrfan UllahÎncă nu există evaluări
- MM0706 Edition 5Document20 paginiMM0706 Edition 5Irfan UllahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electronics Plus Telecom Paper Without AnswersDocument43 paginiElectronics Plus Telecom Paper Without AnswersIrfan UllahÎncă nu există evaluări