Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Nemo Outdoor 6.41 Manual
Încărcat de
Punky HeroDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Nemo Outdoor 6.41 Manual
Încărcat de
Punky HeroDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
User Manual
Air Interface Measurement Tool
Version 6.41
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
2013 by Anite Finland Ltd. All rights reserved. This manual, as well as the software described in it, is furnished under license and may only be used or copied in accordance with the terms of such license. The information in this manual is intended for informational use only and is subject to change without notice. Anite Finland Ltd assumes no responsibility or liability for any errors or inaccuracies that may appear in this user manual. Except as permitted by such license, no part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, recording, or otherwise, without the prior written permission of Anite Finland Ltd. Windows, Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Outlook, and Internet Explorer are registered trademarks of the Microsoft Corporation in the United States and other countries. MapInfo and MapX are registered trademarks of MapInfo Corporation. CDMA 2000 is a registered trademark of the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA -USA). The license management portion of this Licensed Technology is based on SentinelLM* 1989-2003 Rainbow Technologies, Inc. All rights reserved. POLQA is a registered trademark of OPTICOM GmbH. Used by permission. 2011 by the POLQA Coalition of OPTICOM GmbH, Germany - SwissQual AG, Switzerland - KPN, The Netherlands - TNO, The Netherlands.
Revision 6.41.00, Last edited January 2013
Q UI CK G UI DE
CONTENTS
QUICK GUIDE
SETTING UP THE SYSTEM DATA MEASUREMENTS USING NEMO OUTDOOR Using Nemo Outdoor with Command Line Options
9
9 10 12 12
BEFORE YOU BEGIN
COPY PROTECTION Technical Support Expiration IMPORTANT Nemo Outdoor Laptop Settings Traffic Safety Operating Environment
14
14 17 18 18 21 21
NEMO OUTDOOR SYSTEM OVERVIEW 22
VOICE TESTING CIRCUIT-SWITCHED DATA TESTING PACKET-SWITCHED DATA TESTING NEMO OUTDOOR MULTI NEMO OUTDOOR MULTI LITE NEMO INVEX INDOOR MEASUREMENTS 22 22 23 24 25 26 27
INSTALLING NEMO OUTDOOR SYSTEM28
HARDWARE AND SOFTWARE REQUIREMENTS OTHER HARDWARE REQUIREMENTS NEMO OUTDOOR SOFTWARE INSTALLATION NEMO OUTDOOR DEVICE SET-UP Connecting a GPS Receiver Connecting a Scanner Connecting Voice Quality Devices NEMO INVEX DEVICE SET-UP Two Data Connections on One Measurement Server GENERAL GUIDELINES FOR DRIVE TESTING 28 29 30 31 31 31 31 32 38 39
CONFIGURATION SETTINGS
40
CONFIGURING NEMO OUTDOOR 40 Configuration through Welcome page 40 Configuration through Load Device Configuration Dialog 43 Configuring Nemo Outdoor Manually 46 Use Case 1. Start Measurements Automatically upon Device Startup CONFIGURING TEST MOBILES 49
48
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
CONFIGURATION MANAGER Handler Information User Interface Notifications Scripts Base Station Files Device Configurations Devices View Groups
49 50 51 61 65 66 67 68 73
MEASUREMENT PROPERTIES 74 Measurement Properties General 74 Measurement Properties Measurement Settings 76 Measurement Properties Frequency Scanning with Mobiles Measurement Properties Pilot Scanning with Mobiles 80 Measurement Properties Frequency Scanning with Scanners Measurement Properties Pilot Scanning with Scanners 87 Measurement Properties Spectrum Scanning 99 Measurement Properties - Script 101
77 81
DURING MEASUREMENTS
MAKING SCANNING MEASUREMENTS With a Scanner With a Mobile MAKING VOICE CALLS Voice Call Properties Voice Call Properties TETRA Push-to-Talk (PTT) Testing VOICE QUALITY MEASUREMENTS MAKING VIDEO CALLS DATA TRANSFERS Configuring the Data Connection Configuring the FTP Protocol Configuring the SFTP Protocol Configuring the HTTP(S) Protocol Configuring the (HTTP) Browsing Protocol Configuring the POP3 Protocol Configuring the SMTP Protocol Configuring the IMAP Protocol Configuring the WAP Protocol Configuring the Streaming Protocol Configuring the Trace Route Protocol Making Data Transfers STREAMING VIDEO QUALITY TESTING VOIP CALLS SKYPE CALLS SMS TESTING SMS Testing with CDMA Terminals
103
104 104 104 104 105 107 108 109 109 112 112 117 120 122 124 126 128 131 133 135 136 138 138 139 141 145 146
Q UI CK G UI DE
MMS TESTING Packet Session Settings for MMS MMS Editor Making MMS Measurements MMS Settings for Nokia 6630, 6680, and N80 MMS Settings for Nokia N95, 6120, and 6121 USSD TESTING START EXTERNAL APPLICATION ICMP PING IP PACKET CAPTURING MAKING SCRIPT FILES Script Transfer Stop Commands Add Menu Wait Settings Advanced Script Settings Running Scripts MEASUREMENT LISTS FORCING FUNCTIONS Channel Locking Band Locking Handover Control Cell Barring Set Terminal Radio On/Off (Airplane Mode) CELL TESTING
147 148 149 149 150 152 156 157 159 160 162 164 167 168 171 176 177 179 179 181 182 187 187 188
MISSING NEIGHBOR DETECTION 189 Missing Neighbor Detection with a Mobile 190 Missing Neighbor Detection with a Scanner/Scanner and Mobile 191 PILOT POLLUTION ANALYSIS 192 UMTS Pilot Pollution Analysis on Mobile Phone 194 UMTS Pilot Pollution Analysis Based on Scanner Measurements 195 CDMA/EVDO Pilot Pollution Analysis - Mobile Phones 195 CDMA/EVDO Pilot Pollution Analysis - Scanners 196 GSM INTERFERENCE ANALYSIS BAND SCAN TIMESLOT TESTING 196 199 201
VIEWING GRAPHS 203 Graph Popup Menu 204 Zoom - Scatter Graph 208 Graph Side Panel - Layers 209 Graph Side Panel Values & Parameter 217 Graph Layer Color Configuration 219 How to Read MIMO Parameters in Bar Graph Data View224 VIEWING GRIDS 225 Find Function in Signaling Grid Based on Decoded Message Grid Popup Menu 226 VIEWING MAPS 253 226
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Base Stations on a Map MapX Maps Map Side Panel Route Plans Map Popup Menu Color Set Editor Map Example 1 Map Example 2 Map Example 3 Map Example 4 Map Example 5 Map Example 6 VIEWING INDOOR MAPS Floorplans and BTS Files Multiple Routes and Floorplans Indoor Route Planning iBwave Maps Indoor Map Popup Menu
254 257 257 259 264 284 286 287 288 289 290 292 295 297 299 300 301 306
ENDING MEASUREMENTS
MEASUREMENT REPORT
314
315
MEASUREMENT RESULTS
ANALYZING MEASUREMENT RESULTS PLAYING BACK MEASUREMENT FILES Selecting Playback Files During Playback Viewing and Moving Markers Closing Playback Files
317
317 317 317 318 319 320
UPLOADING MEASUREMENT FILES TO AN FTP SERVER321 EXPORTING MEASUREMENTS 322
USER INTERFACE
VIEW GROUPS MENU BAR TOOLBAR STATUS BAR NEMO OUTDOOR MENUS File Menu Edit Menu View Menu Measurement Menu Playback Menu Data Menu Window Menu Help Menu CUSTOMIZING MENUS AND TOOLBARS NEMO OUTDOOR WINDOWS
326
326 327 327 327 328 328 329 329 330 332 332 334 334 335 339
Q UI CK G UI DE
Custom Windows Parameter Tree Search Functionality Devices View Device Status View Server Status View Output Window Script Status Window Controlling Windows
339 340 341 343 345 346 346 346
TROUBLESHOOTING
LOW THROUGHPUT All Windows Versions Windows XP Windows Vista/Windows7 DEVICE STATUS VIEW CANNOT ADD DEVICES CANNOT MAKE CALLS/PACKET TRANSFERS PROBLEMS WITH GPS RECEIVERS MEASUREMENT FILE CHECKSUM NOTIFICATION
348
348 349 350 350 352 352 353 353 353
NEMO OUTDOOR BUTTONS
TOOLBAR BUTTONS DIALOG BUTTONS GRAPH TOOLBAR BUTTONS MAP TOOLBAR BUTTONS
354
354 355 356 357
SHORTCUT KEYS NOTIFICATION SYMBOLS NEMO OUTDOOR SUPPORT
INTERNET SUPPORT USER CLUB PHONE, EMAIL, AND FAX SUPPORT
359 360 363
363 363 363
APPENDIX 1
MAKING MAPINFO RASTER MAPS Registering a Raster Map with MapInfo SW
365
365 365
APPENDIX 2
367
CDMA SETTINGS AND PRL EDITING IN NEMO OUTDOOR367
APPENDIX 3 - TROUBLESHOOTING DATA TRANSFER ISSUES 371
PS CONNECTION WORKS BUT NO DATA UAC Settings Antivirus Filtering Low Data Throughputs 371 371 371 371
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
APPENDIX 4
END-USER LICENSE AGREEMENT
376
376
Q UI CK G UI DE
QUICK GUIDE
This quick guide will explain briefly how to set up the Nemo Outdoor measurement system and how to start the actual measurements. Check the cross-references for more detailed explanations on using Nemo Outdoor.
SETTING UP THE SYSTEM
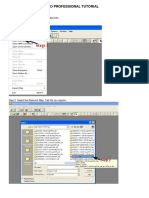
From Nemo Outdoor 5.8 onwards the software is protected with a copy protection module and it is not possible to install Nemo Outdoor without it. Software-based copy protection licenses are no longer valid. Installing and running Nemo Outdoor requires administrator rights. 1. Installing the software. Check the manual for hardware requirements if necessary (see Hardware and Software Requirements). Run the Nemo Outdoor installation program Nemo Outdoor 6.xx.xx.exe from the Nemo Outdoor CD-ROM. The Nemo Outdoor SW and handlers are installed in the same setup. 2. During the installation, Nemo Outdoor will ask you to insert the copy protection module on the computer on which you are running Nemo Outdoor (see Copy Protection). Please insert the copy protection module and wait until Windows has completed installing the device drivers. Press OK to continue the setup. 3. When the installation is finished, restart the computer. 4. The measurement mobiles, GPS receiver, and scanner are connected to the computers USB ports. 5. If you are making a data measurement, you need to create a dial-up connection. Follow the instructions in the Dial-Up Networking Setup Guide provided in the Nemo Outdoor package to set up a dial-up connection and to configure the measurement mobile. Choose one of the following steps: Select step 5 if you are a first-time user of Nemo Outdoor. Go to step 6 if you are an older user of Nemo Outdoor and would like to use the Load Device Configuration dialog. Go to step 7 if you would like to set up the system manually. 6. On the Welcome page, the Load a Measurement tool enables you to open a previously viewed measurement with the attached devices for playback. In the Open a Device Configuration tool you can select saved device configurations, and start the devices in online mode, or decide to work offline first and connect and start them later by clicking the work offline button in Nemo Outdoor. In addition, the Automatic device detection functionality in the Create New Device Configuration tool automatically detects devices connected to the computer and assigns the appropriate, previously created COM port and dial-up information to them. 7. To view the Load Device Configuration dialog, click the Other.. button in the Open a Device Configuration field in the Welcome to Nemo Outdoor dialog (see Configuration through Load Device Configuration Dialog).
10
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
8. If you have used Nemo Outdoor before and would like to start in online mode, select a premade device configuration and click Start Devices. All the devices included in the device configuration file will be activated and you are ready to start measurements. If you prefer setting up the measurement configuration offline, that is, without connecting and starting the measurement devices, select a pre-made device configuration and click the Work Offline button. You can change the measurement configurations in the offline mode and activate the device later. When you want to activate the devices, connect the devices to the measurement system and click the work offline button in the Nemo Outdoor toolbar. 9. If you want to configure Nemo Outdoor manually, close the Welcome page or Load Device Configuration dialog when you start Nemo Outdoor. You can go to File | Open Measurement, and select a saved measurement for playback, or you can open a saved device configuration in File | Open Device Configuration and start a measurement in online of offline mode. Alternatively, you can go to Measurement | Add New Device, select a device and configure it for measurements. You can also do this from the configuration manager (Ctrl+M) (see step 9). In addition, you can also use the Autodetect devices functionality by going to Measurement | Autodetect Devices, which automatically detects a previously added device and its assigned COM ports and dial-up connection. 10. Open the Configuration Manager dialog (Ctrl+M) to add measurement devices manually. Select the Device item and click the Add button . Select the device type (phone, scanner, GPS) that you want to add and select the device model from the list. Click Next. In the Device Configuration dialog, select the correct COM ports and click OK. 11. If you are using a GPS receiver, you will also need a map. Use the Windows Explorer to copy all the required map files to the maps folder, for example, C:\Nemo Tools\maps. Define the default map file and map folder as follows: open the Configuration Manager dialog, double-click the User Interface item and select the Paths tab. In the Map field, browse the folder where map files are stored. In the Default map field, browse the default map file (see User Interface Properties Paths). 12. If you have base station files (.nbf), copy them to the BTS files folder, for example, C:\Nemo Tools\BTS files. When you want to view a BTS file on a map, open the Measurement Properties dialog for the measurement mobile used, and browse a file in the BTS File field. Click OK. Open a map through the Data menu and the BTS icons should appear on the map.
DATA MEASUREMENTS
A PPP compatible dial-up server is required for CS data testing. Settings related to the dial-up server (number, username, and password) are operator-specific. Follow the instructions in the Dial-Up Networking Setup Guide to set up a dial-up connection and to configure the measurement mobile.
Setting up data measurements:
1. Configure the measurement device in the Device Configuration dialog (see Device Configuration for Mobiles and Modems). Define the Trace and Modem Ports and select a Dial-Up Connection.
Q UI CK G UI DE
11
2. Open the Measurement Properties, Measurement settings dialog (see Measurement Properties Measurement Settings). Please note that the selection is device-specific.
3. For circuit-switched data measurements, double-click the Circuit-Switched Data Call item to define Data Call Properties. For packet-switched data calls, double-click the Packet Session item to define Packet Session Settings. 4. Select a data protocol in the Selected Data Protocol field. Then define properties for the selected data protocol by double-clicking the respective item under Supported Data Protocols: Browsing (see Browser Transfer Properties), FTP (see FTP Transfer Properties), SFTP (see SFTP Transfer Properties), HTTP (see HTTP(S) Transfer Properties), ICMP Ping (see ICMP Ping), POP3 (see Configuring the POP3 Protocol), SMTP (see Configuring the SMTP Protocol), IMAP (see Configuring the IMAP Protocol), TCP/UDP (Iperf) (see TCP/UDP Protocol Configuration (Iperf)), Trace Route (see Configuring the Trace Route Protocol), WAP (see Configuring the WAP Protocol), or Streaming (see Configuring the Streaming Protocol).
5. To set up ICMP Ping measurements (can be performed simultaneously with the data measurements), double-click the ICMP Ping field and define the Ping Settings (see ICMP Ping).
12
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
6. To set up SMS measurements (can be performed simultaneously with the data measurements), double-click the Short Messaging Service field and define the SMS Testing Settings (see SMS Testing). 7. To set up MMS measurements (can be performed simultaneously with the data measurements), double-click the Multimedia Messaging Service field and define the MMS Settings (see MMS Testing). 8. To set up USSD measurements (can be performed simultaneously with data measurements), double-click the USSD Message field and define the USSD Message Settings (see USSD Testing). 9. Click OK. You can now start data measurements.
USING NEMO OUTDOOR
When a green light is blinking in the Device Status window, the device is connected properly and is ready for measurements. 1. First, open some measurement windows through the Data menu for monitoring the measurement. Alternatively you can open a workspace (File | Open Workspace) that contains some predefined views (graphs, grids, maps, etc.). 2. You can use Scripts (see Scripts) to generate a sequence of actions that Nemo Outdoor will execute automatically. Click the Device script settings button in the Devices view. Select an existing script in the Script File field or create a new one by clicking the Script Editor button. 3. If you want to be notified about certain events during the measurement, use the Notifications function (see Notifications). Click the Device notification settings button in the Devices view to access the Notifications dialog. 4. Run a script by clicking the Start/Stop Scripts button . Nemo Outdoor will start the recording automatically. To stop running the script, click the button again. To finish both the recording and the script, click the Stop button . 5. To perform measurements manually, select the appropriate actions, such as, start voice call or send MMS message, from the Measurement control menu. 6. Stop the recording by clicking the Stop button . Nemo Outdoor has recorded a measurement file of the performed test calls/scan on the computers hard disk. You can playback the measurement file by clicking the Playback button in the Report dialog. Click the Rename button to change the file name. 7. Click the Start Playback button to playback a file. During playback use the Pause button to freeze the playback and observe the different measurement windows for that particular point in time.
Using Nemo Outdoor with Command Line Options
Outdoor supports the following command-line options. These command lines will enable the user to enter a certain profile in Nemo Outdoor. You can enter the command lines either with Command Prompt through Start | Run | cmd, or you can create a shortcut to Nemo Outdoor on the desktop and enter the command line to the shortcuts Properties | Shortcut |Target field. /W <workspace> will directly open the specified workspace in Nemo Outdoor /H <hw config> will directly open the given hardware configuration in Nemo Outdoor
Q UI CK G UI DE
13
/M SIMPLE will open Nemo Outdoor in limited mode, in which the user is not able to save any changes made to the hardware configuration or workspace /DEBUGBIN will start debug logging
For example, the command line below will start Nemo Outdoor, load the test.wor workspace, N95.hwc hardware configuration, and prevent any changes possibly made to them from taking effect. Outdoor6 /W test.wor /H N95.hwc /M SIMPLE
14
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
BEFORE YOU BEGIN
This manual explains how to set up and operate the Nemo Outdoor Air Interface Measurement Tool Software for Windows XP Professional and Windows 7 developed by Anite Finland Ltd. Nemo Outdoor is a portable engineering tool for measuring and monitoring the air interface of digital networks. The supported network standards are: cdmaOne 450, 800,1900 MHz CDMA2000 1xEVDO AMPS DVB-H EGPRS GSM 850, 900, 1800, 1900 MHz GPRS HSDPA HSUPA HSPA+ LTE TD-SCDMA TETRA iDEN UMTS (FDD mode) WiMAX Nemo Outdoor is an effective tool for tracing digital networks. Nemo Outdoor collects measurement results and geographical coordinates (when used with a GPS receiver) and stores them on a hard disk. Measurement results provide useful information for network optimization, verification, and maintenance purposes. Results can be efficiently and easily viewed with the Nemo analysis tool Nemo Analyze. Nemo Outdoor uses licensed technology from various manufacturers. For a complete list of supported devices, see the Nemo Outdoor product description and data sheet.
COPY PROTECTION
From Nemo Outdoor 5.8 onward, only hardware-based copy protection is used. A USB copy protection dongle will be delivered in the Nemo Outdoor package. Plug in the copy protection dongle in a USB port on your PC. Note that the new dongle introduced in Nemo Outdoor 5.80 will not be backwards compatible with the older versions of Nemo Outdoor. A new dongle with a valid technical support and maintenance agreement option will be in use with Nemo Outdoor 5.80 and later versions. If the following error message appears, please contact Nemo Technical Support at nemosupport@anite.com. The dongle battery has run out and needs to be changed.
BEFO RE Y O U BEG I N
15
No Valid License Detected
If the error message Error: No valid license detected. appears when the application is started, either the dongle key is not plugged in or the dongle key is an unsupported model.
Please follow the instructions for how to read the license information from the existing dongle key. To be able to use the Nemo Outdoor application supported by the old dongle key, it is recommended that you uninstall Nemo Outdoor version 5.4. After un-installation reboot the computer and re-install the previous version. The example above is seen, e.g. when the SPS 00868 dongle key is in use.
No Valid Technical Support Agreement
If the error message below appears, it means that the dongle key type is correct, but that the dongle key is missing valid technical support & maintenance agreement information.
Please follow the instructions for how to read the license information from the existing dongle key with the Remote Update Utility. To be able to use the Nemo Outdoor application supported by the dongle key without information about the technical support agreement, it is recommended that you uninstall Nemo Outdoor version 5.80. After un-installation reboot the computer and re-install the previous version.
The old dongle key
The new dongle key
The dongles are updated using the Remote Update Utility software. Before updating Nemo Outdoor application please make sure that new dongle key is available. Note that you must use the latest version of the software which comes with Nemo Outdoor version 5.80, or it can alternatively be downloaded from Nemo User Club. See the instructions below for updating your Nemo Outdoor dongle.
16
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Updating the dongle (Nemo Outdoor version 5.80 and later)
1. Connect your copy protection module and start the SecureUpdate by selecting Start | All Programs | Nemo Tools | Remote Update Utility. 2. The Collect Key Status Information tab opens.
3. Click Collect Information. If the Select HASP Key dialog appears, select the HASP HL item and click OK.
4. Define the location where the C2V file is saved and send the C2V file to Nemo Technical Support at nemosupport@anite.com. Please add the following information to the e-mail using the following subject Nemo Outdoor dongle update: Company name First name Surname Street address Zip/ Postal Code
BEFO RE Y O U BEG I N
17
Country Telephone number Mobile number
5. After you have received the V2C file containing the update, select the Update File in the Apply License Update tab and click Apply Update.
6. The dongle is now updated. Nemo Outdoor can be installed and is ready for use.
Technical Support Expiration
The new dongle keys used with Nemo Outdoor 5.80 and later versions include a compulsory technical support and maintenance agreement option. The technical support expiration date defines the date the agreement ends. After this date it is not possible to start the new version of the Nemo Outdoor application. Example: A customer has purchased Nemo Outdoor version 5.80 with a 1-year technical support maintenance agreement in April 2011. The customer is entitled for free updates until April 2012. Nemo Outdoor versions released after April 2012 cannot be used with the dongle key without renewing the technical support & maintenance agreement. After the technical support & maintenance agreement is renewed, the dongle key can be updated remotely and the customer can update the application to the latest version.
18
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
IMPORTANT
Installing and running Nemo Outdoor requires administrator rights. The Nemo Outdoor user must be appropriately trained and should be familiar with the signaling behind wireless technologies. The Qualcomm handlers enables the use of Qualcomm CDMA2000, MSM6500, MSM6800, TM6200, TM6250, TM6275, TM6275US, TM7200, and TM8200 chipset-based terminals that have not been verified by Anite Finland. These terminals can be used with Nemo Outdoor but Anite Finland does not guarantee that the terminals will work flawlessly. Please check the Nemo Outdoor product description or the compatibility list in the user manual for a list of measurement terminals verified and approved by Anite Finland. Do not use the Nemo Outdoor test mobiles keypad to make or answer calls when the Nemo Outdoor system is running. With Samsung terminals the key tone volume should be turned off. Otherwise, the mobile can dial a wrong number. With Nokia GSM, GPRS, and EDGE terminals the test display (Net Monitor) must not be activated. In voice quality measurements the volume of the mobile headset must be adjusted to correct levels. Please refer to the Nemo Voice Quality Guide document. Do not place stickers containing metal on the mobile because it may lower the transmission power of the mobile. After the measurements have been completed and it is desired to take the Nemo Outdoor test mobile into normal use, it must be powered off and on again to deselect/deactivate the Nemo Outdoor triggered events in the mobile. Use only the supplied connecting cable, included with the Nemo Outdoor, for connecting the Nemo Outdoor test devices to the computers USB port. When using the Nemo Outdoor test mobile for measurement use, the battery operation time is reduced from normal use. The best operation times will be achieved when the batteries are regularly charged and discharged as instructed in the mobile user manual.
Nemo Outdoor Laptop Settings
The laptops used for running Nemo Outdoor need to be set up before measurements. Below are described the most important settings that may have an effect on the measurement results.
BEFO RE Y O U BEG I N
19
Power Options
Before you begin using Nemo Outdoor, you need to set the power management options of the laptop to High performance to avoid disruptions in the performance of Nemo Outdoor. Go to Control Panel | System and Security | Power Options. Select the High performance power plan.
20
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Active Protection System
If there is a system that detects acceleration in the laptop and causes the hard disk to stop when jolted, it should be turned off. Otherwise, there may be breaks in measurement data. In voice quality testing there may be missing MOS scores, and with other test devices, gaps in the measurement data. With Lenovo laptops, select Control Panel | System and Security | Lenovo Airbag Protection. On the Configuration page, deselect the Enable Active Protection System option.
BEFO RE Y O U BEG I N
21
USB Hub Properties
Also, check the generic USB hub properties. Go to Device Manager, expand the Universal Serial Bus controllers item, right-click the Generic USB Hub item and select Properties. Open the Power Management tab and check that the Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power option is deselected. Repeat this for all the Generic USB Hub items.
Traffic Safety
Do not operate Nemo Outdoor and drive (or walk) at the same time. Remember, traffic safety comes first. Note that in some countries it is illegal to drive a car and operate a computer at the same time. Please observe the legislation of the country where the measurements are performed. Finland assumes no responsibility or liability arising from the failure to comply with local legislation.
Operating Environment
Do not operate Nemo Outdoor without reading the User Manual, including its warnings, for the devices used by Nemo Outdoor. Always stop using Nemo Outdoor and switch off the Nemo Outdoor test device(s) when it is forbidden to use radio equipment or when it may cause interference or danger. Do not use the Nemo Outdoor test device(s) in a hospital. It may interfere with nearby electronic devices. Never use Nemo Outdoor in an aircraft. The use of mobiles in an aircraft may be dangerous. Observe restrictions on the use of radio equipment in gas stations, fuel depots, chemical plants, or sites where blasting operations are in progress.
22
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
NEMO OUTDOOR SYSTEM OVERVIEW
VOICE TESTING
The voice testing environment consists of Nemo Outdoor compatible mobiles and a PC (user provided or, optionally, provided by Anite Finland with all the software installed) with the Windows XP Professional or Windows 7 operating system. The package also includes the necessary connecting cables, serial or USB port adapters, a GPS receiver, and fast frequency scanners if applicable. Also the Nemo Voice Quality option is available.
CIRCUIT-SWITCHED DATA TESTING
The circuit-switched (CS) data testing environment consists of three parts: a measurement unit (Nemo Outdoor), an application server, and a dial-up server. The dial-up server is used to establish a data connection between the measurement unit and the application server. Nemo Data Test Server can be used as the application server. It is a Linux-based administration-free server having up to four public IP addresses and it can serve multiple simultaneous TCP/IP connections from test terminals. Nemo Data Test Server supports FTP, SFTP, HTTP, POP3, SMTP, IPerf for UDP/TCP, Ping, Trace route testing and RTSP (video streaming). CS data testing is possible on all cellular technologies that support circuit-switched data. The data measurement system has two modes: Send and Receive. In the Send mode, the measurement unit sends data packets to the application server; in the Receive mode vice versa. If you are using a FTP server, the measurement unit uploads (Send mode) or downloads (Receive mode) test files to or from the FTP server. If you are using an HTTP server, the measurement unit can only receive files. The user can define the number of timeslots and the coding schemes, which in turn define the desired transfer rate. During the measurement, the user will be able to monitor data throughputs and error rates on different network layers, as well as certain parameters, such as coding scheme and number of timeslots.
NEM O O UTDO O R SY STEM O VERVI EW
23
PACKET-SWITCHED DATA TESTING
The packet-switched (PS) data testing environments consist of two ends: the measurement unit and an application server. Nemo Data Test Server can be used as the application server. It is a Linuxbased administration-free server having up to four public IP addresses and it can serve multiple simultaneous TCP/IP connections from test terminals. Nemo Data Test Server supports FTP, SFTP, HTTP, POP3, SMTP, IPerf for UDP/TCP, Ping, Trace route testing, and RTSP (video streaming). PS data testing is possible on all cellular technologies that support packet-switched data. The data measurement system has two modes: Send and Receive. In the Send mode, the measurement unit sends data packets to the application server; in the Receive mode vice versa. If you are using an FTP server, the measurement unit uploads (Send mode) or downloads (Receive mode) test files to or from the FTP server. If you are using an HTTP server, the measurement unit can only receive files. During the measurement, the user will be able to monitor data throughputs and error rates on different network layers, as well as certain parameters such as coding scheme and number of timeslots.
24
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
NEMO OUTDOOR MULTI
The 3rd generation Nemo Outdoor Multi is a compact and cost-effective benchmarking solution to be used with Nemo Outdoor. The system in combination with Nemo Outdoor Multi-option allows benchmarking measurements to be performed on different system technologies such as GSM, EDGE, WCDMA, HSDPA, CDMA2000, and WiMAX, and different combinations of measurement modes such as voice calls and data transfers. Nemo Outdoor Multi supports a total of seven test devices, i.e. up to five test mobiles, scanners, and a GPS device. The Multi-Data functionality in Nemo Outdoor allows up to five concurrent data measurements to be performed simultaneously while the system is connected to a single laptop, saving space in the test vehicle during drive testing and adding to the ease of use of the system. Combined with Nemo Server, Nemo Outdoor Multi-Data makes it easy to carry out, not only casual data benchmarking test cases that can be used to compare the performance of different technologies or operators, but also long-term network performance measurements. All test devices can be connected to Nemo Outdoor Multi through an onboard USB port while sharing a cars +12VDC power output. The Nemo Outdoor multi unit includes a built-in 2500 mAh battery pack which makes it possible to continue measurements during short power failures without stopping the measurements. With the professional high-quality lockable USB data cable connection the system is very reliable to use, preventing loose connections between test devices and the main unit. Nemo Outdoor Multi can also be delivered with an optional tough roll-around carrying case. The system is by default delivered with a car mounting kit that allows the unit to be semi-permanently mounted into a test car. The Multi system also includes a DC to AC pure sine wave power inverter to supply power for the laptop.
NEM O O UTDO O R SY STEM O VERVI EW
25
NEMO OUTDOOR MULTI LITE
The 4th generation Nemo Multi Lite is a compact and cost-effective benchmarking solution for use with Nemo Outdoor. Benchmarking measurements can be performed on various system technologies and networks with support for up to six test mobiles/data cards, a scanner and a sound card. In addition, the system in combination with Nemo Outdoor Multi-option allows the use of different combinations of measurement modes such as voice calls, voice quality calls and data transfers simultaneously. The system is connected to a single laptop, saving space in the test vehicle during drive testing and adding to the ease of use of the system.
26
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
NEMO INVEX
Nemo Invex system combines powerful intuitive software and scalable military grade hardware design to create superior drive-test systems for wireless networks. Quick and easy to deploy, Nemo Invex provides critical quality-of-service (QoS) measurements and a wide variety of quality-of-experience (QoE) service testing, including the latest voice and video quality measurement algorithms. Nemo Invex is flexible and scalable, capable of evolving as the network evolves providing the lowest effective total cost of ownership available. The Nemo Outdoor software application that runs on the Nemo Invex chassis for benchmarking is also widely known as a tool for network optimization. With other benchmarking tools QoS statistics can be collected but no actual reasons for possible issues, such as, low data rates can be seen without a cause identified. Often the network issue is interference and other benchmarking tools are collecting quality parameters but no real time analysis is performed. The Nemo solutions allow the user to activate different interference analysis measurements, such as, WCDMA pilot pollution, GSM cochannel/ adjacent channel interference and GSM/ WCDMA missing neighbor detection. These enhanced capabilities help to save time and money and provide additional value added information also to benchmarking campaigns. Furthermore, significant cost savings can be realized by bundling the data collection solution with a post-processing solution as Anite has a comprehensive postprocessing solution, Nemo Analyze.
NEM O O UTDO O R SY STEM O VERVI EW
27
INDOOR MEASUREMENTS
Nemo Outdoor has an indoor measurement option in which case Nemo Outdoor can be installed on a Tablet PC. Alternatively, a regular laptop can be used as well. As GPS receivers cannot be used indoors, the indoor option offers a marker function to store location data. Just click markers along the measurement route and the route will be drawn on the map. It is also possible to use BTS files with floorplans. With Nemo Walker, test equipment can be easily taken inside buildings.
28
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
INSTALLING NEMO OUTDOOR SYSTEM
This section provides the basic instructions for installing Nemo Outdoor software and devices. Make sure you have all the listed equipment before starting the software installation. Use the Nemo Outdoor setup program to install Nemo Outdoor; that is, do not just copy the Nemo Outdoor files onto your computer.
HARDWARE AND SOFTWARE REQUIREMENTS
PC (Lenovo or Dell recommended) with Windows XP (32- bit) Professional or Windows 7 Professional (32-/64-bit). Pentium III processor, minimum 1GHz, preferably 1.7 GHz for single mobile measurements For multi data measurements Intel Core Duo processor T2500 2.00GHz or higher required For voice quality measurements with up to four channels with USB sound card Intel Core Duo processor T2500 2.00GHz or higher required For up to six channel voice quality measurements with USB sound card Intel Quad Core processor Q9100 2.26GHz or higher required 512MB RAM minimum, 1GB RAM recommended For multi data measurements with HSPA+ devices Intel Quad Core processor Q9100 2.26GHz or higher required 100 MB of free hard disk space for installation and use; 1 GB recommended One USB port for copy protection module One USB port per mobile Depending on the scanner used, one USB port or serial port or RJ45 or FireWire port per scanner One serial port for each voice quality audio module or one USB port per sound card One USB port for an external GPS receiver Display resolution 1400 x 900 recommended Internet Explorer for viewing the help file
I NS TALLI NG NEM O O UTDO O R SY STEM
29
OTHER HARDWARE REQUIREMENTS
The following hardware is also supported for using Nemo Outdoor. Please note that the scanning receivers and many of the GPS receivers require also +12 V DC power supply (e.g., from cigarette lighter plug). External power supply recommended for computer if vehicle mounted GPS receiver: (optional, following types are supported) Garmin GPS II Garmin GPS II Plus Garmin GPS III/III+ Garmin GPS 35 Garmin V Garmin 18 USB Trimble Placer 450/455 (TAIP) and GPS antenna unit Most other GPS receivers with NMEA 0183 compatible output
DKU-2 USB cable and a free USB port for the following Nokia mobiles: Nokia 6230i Nokia 6630 Nokia 6680
DKU-2 or CA-53 cable and a free USB port for the following Nokia mobiles: Nokia N80 Nokia 6136 Nokia N92
DKE-2 or mini USB cable and a free USB port for the following Nokia mobiles: Nokia 7376
Datang DTM8101 or DTM8120 mobile with the 18Pin SDTM 4.370.010 data cable and a free USB port Leadcore LC8310E mobile with the 18Pin SDTM 4.370.010 data cable and a free USB port Nokia N75 mobile with the DKE-2 or the DKU-2 connectivity cable and a free USB port Nokia N95, N95 US, 6120, 6121, or 3500 mobile with the mini USB cable and a free USB port Nokia C5, C5-03, C7-00, 6720, 6720US, N85, N85US, N96, N96US, N97 and N97US mobile with the micro USB cable and a free USB port Motorola V3X, V9 or V9US mobile with the mini USB cable and a free USB port
30
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Huawei C7600 mobile with the mini USB cable and a free USB port Samsung SGH-Z105, Z107, Z140, Z500, ZV10, or P920mobile with the PCB157ULE USB cable and a free USB port Samsung Z560 or ZX20 mobile with the mini USB cable and a free USB port Samsung Z720, or A707 mobile with the PCB200BBE USB cable and a free USB port Qualcomm CDMA2000 Compatible, MSM6500 Compatible, MSM6800 Compatible, TM6200, TM6250, TM6275, TM6275US or TM7200 mobile with a USB cable and a free USB port LG U800 or KU950 mobile with a mini USB cable and a free USB port LG KX260, C270, C680, C676, and LHD-200E mobile with a LG VX6100/VX7000, KQ-U8A cable and a free USB port
Nemo Outdoor software is protected with a copy protection dongle (see Copy Protection)
NEMO OUTDOOR SOFTWARE INSTALLATION
To install or upgrade Nemo Outdoor:
If you have a previous version of Nemo Outdoor installed, please remove it before installation. Go to Control Panel and select Programs | Uninstall a program. Righ-click on Nemo Outdoor and select Uninstall. 1. Start Windows and insert the Nemo Outdoor CD-ROM in your CD drive (e.g., drive D). Note that for Windows XP and Windows 7, installation must be run under Administrator account or other user account with administrative privileges. 2. Select Start | Run in the Windows Status bar. Type D:\Nemo Outdoor 6\Nemo Outdoor x.xx.xx in the Open field (xx refers to the version number) and click the OK button. When the Installation program starts, follow the instructions on your screen. We recommend that you select the Complete setup type. 3. When the Nemo Outdoor software installation is complete, you will need to restart the computer.
To uninstall Nemo Outdoor:
1. Go to Control Panel and select Programs | Uninstall a program. Righ-click on Nemo Outdoor and select Uninstall. Note that for Windows XP and Windows 7, uninstallation must be run under Administrator account or other user account with administrative privileges.
I NS TALLI NG NEM O O UTDO O R SY STEM
31
NEMO OUTDOOR DEVICE SET-UP
Below you will find instructions for connecting devices to the Nemo Outdoor measurement system. However, instructions for devices that require a dial-up connection can be found in the Dial-Up Networking Setup Guide.
Connecting a GPS Receiver
1. Plug the GPS USB cable into a USB port on your computer. 2. Windows will automatically detect the new device and install the necessary drivers. 3. Start Nemo Outdoor. Open the Configuration Manager, select Device and click the Add button . 4. Click on GPS. Select your GPS model from the list and click Next. 5. Select the USB port to which your GPS receiver is connected. The program automatically sets the other parameters to match your navigator selection according to the following table:
Navigator Type Garmin 18 USB Baud rate 9600 Data bits 8 Parity None Stop bits 1
6. Click OK. Your GPS receiver is now ready for measurements.
Connecting a Scanner
See the Nemo Scanner Guide document for information on how to connect and start scanners with Nemo Outdoor.
Connecting Voice Quality Devices
Please refer to the Nemo Voice Quality Guide document for complete installation and configuration instructions.
32
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
NEMO INVEX DEVICE SET-UP
After the Nemo Invex chassis has been set up and configured, you can connect the measurement servers (UIC modules in the Nemo Invex chassis) and devices to Nemo Outdoor. Start Nemo Outdoor with the Nemo Invex license option. Click the Measurement servers button in the Devices view. A list of available measurement servers is displayed. Select Add | Autodetect Measurement Servers to find all measurement servers connected to the system. If a measurement server is missing from the list, click the Add button and select Add Measurement Server Name. Enter the server name (IP address) and click OK. Nemo Outdoor will try to connect to the server.
To connect to a measurement server, select the server and click Connect. The State will change to Connected. Repeat this for each measurement server that you want to connect with Nemo Outdoor. Finally, click Close.
I NS TALLI NG NEM O O UTDO O R SY STEM
33
The Devices view will display all connected measurement servers. The Local item refers to devices connected directly to the Nemo Outdoor laptop. Click the Autodetect button to detect devices connected to the measurement servers.
A list of devices connected to each measurement server is displayed. In the Mode column, define whether the device will be used for voice, data, or voice and data measurements. Read chapter Two Data Connections on One Measurement Server for more information on having two active data connections on a single measurement server.
34
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
If you are adding a scanner, click the scanner name and select the frequency configuration supported by the scanner.
Finally click Add Devices. The devices will be added to Nemo Outdoor. Depending on the number of devices, this may take a few minutes. The Nemo FSR1 scanner needs to be added manually. Click the Add or remove devices button in the Devices view and select Add New Device. In the Add New Device dialog, select the Nemo FSR1 and select a UIC in the field at the bottom of the dialog.
I NS TALLI NG NEM O O UTDO O R SY STEM
35
Click the Group devices by type/server button by server.
to group the devices by type (phone or scanner) or
36
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
The Device Status view displays all the connected devices and their status. By resizing the view, you can change how the devices are organized.
I NS TALLI NG NEM O O UTDO O R SY STEM
37
Right-click on the Device Status view and select Toggle Status Window Docking Area to dock the Status view to the top of the main view.
Right-click on the Device Status view and select Reorder Devices to change the order of the devices in the Device Status and Devices views. Drag and drop the devices in the correct order and finally click OK.
It is possible to save the hardware configuration by selecting File | Save Device Configuration As. This way all the devices can be loaded automatically the next time you start Nemo Outdoor.
38
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
To disconnect measurement servers, click the Measurement servers button, select a measurement server and click Disconnect.
Two Data Connections on One Measurement Server
You can have two active data connections on a single measurement server. For example, MMS can be tested with one test device while another device is performing an FTP transfer. The data routing option is enabled by default with Nemo Invex allowing more than one active data connection. However, when routing table modifications is enabled, there are some limitations with data testing. For example, it is required that different source IP addresses for data testing are used. This means that the host IP address or URL must be different for each test device. Routing table modification should be disabled when only one active data connection is required. Select View | User Interface Properties and set Enable routing table modifications for devices to No.
If routing table modification is disabled when performing multi (dual) data testing with one measurement server, problems may be caused when several dial-up connections are opened from one host computer to the terminals. All data connections to be established travel along one connection between the host computer and the terminal, i.e. all dial-up connections are routed via one terminal, not via different terminals and their interfaces. This will distort the test results.
I NS TALLI NG NEM O O UTDO O R SY STEM
39
GENERAL GUIDELINES FOR DRIVE TESTING
Check the condition of all antennas, cables, and connectors: there should be no tight curves, no slashes or cuts. Check that connectors are properly connected. Loose connections cause unstable measurements or wrong attenuation of field strength. Place antennas properly on the roof of the vehicle. Antennas should be installed as symmetrically as possible and at least one wavelength from the corners and roof windows, and two wavelengths from each other. If antennas are too close to each other, it may cause interference.
=c/f c = 300E6 (m/s) f = frequency (Hz) 450 MHz, = 66 cm 900 MHz, = 33 cm 1800 MHz, = 17 cm 1900 MHz, = 16 cm GPS antenna 1565-1575MHz, = 19 cm
Check the configuration before starting the measurement. Individual antennas and the mobile holder antenna couplers may have different performance. When removing antennas after a drive test, DO NOT pull antennas from the antenna cables. Hold the antenna from the base and tilt the antenna away from the cable.
40
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
CONFIGURATION SETTINGS
After you have installed Nemo Outdoor, you will need to configure the system for your environment before you will be able to use the measurement functions. The following instructions will help you in this initial configuration.
CONFIGURING NEMO OUTDOOR
You have three different ways to start using Nemo Outdoor. For a first-time user the most convenient way is to start with the Welcome page and proceed from there. Older users of Nemo Outdoor may want to use the Load Device Configuration dialog, and more advanced users may want to configure Nemo Outdoor manually.
Configuration through Welcome page
1. The Nemo Outdoor Welcome page offers an easy way to configure the system for a first-time user, and also helps more advanced users to add new devices. It appears on the screen when you start Nemo Outdoor. If you do not want to view this window in the future when opening Nemo Outdoor, select the Do not show this again option.
2. With the Automatic device detection functionality, you can automatically add devices to Nemo Outdoor without needing to manually set up the system. This functionality automatically searches the Device Manager for the assigned modem and trace COM port information, and matches a dialup connection with the assigned modem port for the device. Please note that the automatic detection is only available for devices connected with a USB cable. Furthermore, you may need to select the correct device model from the drop-down menu.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
41
Note that this functionality varies depending on the device vendor. In addition, you may need to create a dial-up connection for the device before connecting it to Nemo Outdoor. The COM ports are created with the dial-up connection. Please refer to the Nemo Outdoor Dial-Up Networking Setup Guide for instructions on how to do this. The device may also require additional configurations in its modem settings. 3. You can start the devices in online mode by clicking the Start Devices button below, start them in offline mode by clicking the Work Offline button, or refresh the device configuration by clicking the Refresh button on the bottom right-hand corner of the window. This is useful, e.g., when you accidentally unplug a device and plug it in again. 4. You can also open a workspace file from the Welcome dialog.
42
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
5. With the Open a Device Configuration tool you can select saved device configurations. This includes the dial-up connection and the trace and modem COM ports assigned to the device. If you would like to start Nemo Outdoor in online mode, select a pre-made device configuration and a workspace and click Start Devices. All the devices included in the device configuration file will be activated and you are ready to start measurements.
6. If you prefer setting up the measurement configuration offline, that is, without connecting and starting the measurement devices, select a pre-made device configuration and click the Work Offline button. If you want, you can configure the devices manually and activate them. When you want to activate the devices, connect the devices to the measurement system and click the Work Offline button in the Nemo Outdoor toolbar. 7. The Load a Measurement tool enables you to open a previously viewed measurement with the attached devices for playback. In the Workspace field you can select a workspace for the measurement. Click Load Selected Files.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
43
Configuration through Load Device Configuration Dialog
To view the Load Device Configuration dialog, click Other in the Open a Device Configuration field in the Welcome to Nemo Outdoor window. 1. If you have used Nemo Outdoor previously and saved a device configuration and a workspace, Nemo Outdoor will ask if you would like to load a device configuration and a workspace. If you are a first-time user of Nemo Outdoor, go to step 4.
44
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
2. If you have used Nemo Outdoor before and would like to start in online mode, select a pre-made device configuration and a workspace and click Online. All the devices included in the device configuration file will be activated and you are ready to start measurements.
3. If you prefer setting up the measurement configuration offline, that is, without connecting and starting the measurement devices, select a pre-made device configuration and click the Offline button in the Load Device Configuration dialog. You can change the measurement configurations in the offline mode and activate the device. When you want to activate the devices, connect the devices to the measurement system and click the Work Online button in the Nemo Outdoor toolbar. 4. In the Load Device Configuration dialog, select Empty Device Configuration and click Start Devices. An empty Nemo Outdoor main window appears.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
45
5. Add a device by selecting Measurement | Add New Device or by clicking the Add or remove devices button in the Devices view. Choose the appropriate phone, scanner, or GPS receiver from the list and click Next. 6. All Qualcomm terminals are unified into one Qualcomm handler. Nemo Outdoor application detects the chipset of the test device and activates traces accordingly. For example, if device supports MDM8200 chipset (HSPA+) these trace messages are automatically activated. Before trace message activation application is checking is the licence valid for such a device. If license do not cover e.g. MDM8200 devices (HSPA+ devices), device is added to Nemo Outdoor application with an other chipset support e.g. MDM7200 (HSUPA) and HSPA+ trace messages are not activated. The following Qualcomm chipsets are supported: Qualcomm TM6200 Qualcomm TM6250 Qualcomm TM6275 - Compatible with Qualcomm HSDPA devices Qualcomm TM6275 US - Compatible with Qualcomm HSDPA devices Qualcomm TM6280 - Compatible with Qualcomm HSDPA devices Qualcomm TM7200 - Compatible with Qualcomm HSUPA devices Qualcomm TM8200 - Compatible with Qualcomm HSPA+ devices Qualcomm TM8220 - Compatible with Qualcomm HSPA+ dual carrier devices Qualcomm MDM9200 - Compatible with Qualcomm LTE devices Qualcomm MDM9600 - Compatible with Qualcomm LTE devices
7. A properties dialog will be opened for the selected device. Set the appropriate values.
46
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
8. Click on Measurement Properties in the Device Configuration dialog to enter the Measurement Properties dialog. Here you will find device-specific measurement settings. Set the appropriate parameters and click OK. 9. Double-click the User Interface item in the Configuration Manager (alt+M) to open the User Interface Properties dialog. Here you will find general measurement settings that affect all devices. Set the appropriate parameters and click OK. You can now start the measurements.
Configuring Nemo Outdoor Manually
If you want to configure Nemo Outdoor manually, close the Welcome page or Load Device Configuration dialog when you start Nemo Outdoor. You can go to File | Open Measurement, and select a saved measurement for playback, or you can open a saved device configuration in File | Open Device Configuration and start a measurement in online or offline mode. Alternatively, you can go to Measurement | Add New Device, select a device and configure it for measurements. In addition, you can use the Autodetect devices functionality which automatically detects a previously added device and its assigned COM ports and dial-up connection for network measurements. Click the Autodetect Devices button in the toolbar.
A dialog with a list of previously added devices and their dial-up connection appears. Select the devices you want to add, and click the Add Devices tab at the bottom of the Autodetect Devices dialog. Select Add Devices in Specific Order to select the order of the added devices.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
47
In the Add Devices dialog you can select a device and move it up or down in the list to define the device order with the arrow buttons on the right-hand side of the dialog.
Click Add Devices to add the devices to Nemo Outdoor.
48
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Use Case 1. Start Measurements Automatically upon Device Startup
The following example case exemplifies the process of setting up Nemo Outdoor to start recording automatically when devices are connected and started. In the Nemo Outdoor main view, perform the following configurations. 1. Go to View | User Interface Properties. 2. On the Measurement page, set the Start recording automatically when devices are started and Start scripts automatically options to Yes.
3. Click OK. 4. Save the workspace and hardware configuration files by selecting File | Save Workspace As, and File | Save Device Configuration As. 5. Close Nemo Outdoor. The next time you start Nemo Outdoor, measurements will start automatically as long as the correct device configuration file and workspace are selected.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
49
CONFIGURING TEST MOBILES
The Phone Settings of the Nemo Outdoor test mobile can be user defined. However, the PIN Code Request and Automatic Redial options must be turned OFF. Please consult the mobile user manual to find these options from the mobile. To configure the Nemo Outdoor test mobiles for PS data testing purposes, see the Dial-Up Networking Setup guide provided by Anite Finland. Always keep the test mobile connected to a charger, if possible, when carrying out measurements. Net Monitoring must be switched off with the Nokia mobiles listed below: Nokia 6230i
CONFIGURATION MANAGER
Configuring Nemo Outdoor for your environment is accomplished in the Configuration Manager. You can access the view either by pressing Ctrl+M or by clicking the Configuration Manager toolbar button . The Configuration Manager view consists of several items. Select an item from the list and click the Properties button (if applicable) to edit the item.
The System Properties view shows the general system properties for Nemo Outdoor.
50
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Under Measurement Servers are listed all Nemo Invex measurement servers connected to the system. Select a server to view some hardware status information for the server.
Handler Information
Under Handler Information, you will find a list of handlers that have been installed on your computer. All the handlers that you have purchased can be found on the Nemo Outdoor installation CD-ROM. Each device has its own handler, and in order to use them in Nemo Outdoor, you must have the corresponding handler installed.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
51
User Interface
Under the User Interface item, you will find several items: User Interface Properties, Custom Windows, Notifications, Scripts, Color Palettes, Color Sets, and Presentation Modes. The Custom Windows folder contains premade measurement windows for quick startup. Under Color Palettes you will find colors used in the views (see User Interface Properties Colors). Clicking on Color Sets will display the available color sets in the Configuration Manager view. For further information on how to create color sets, see chapter Color Set Editor. You can define the format in which various parameter values are presented through the Presentation modes item (see User Interface Properties Presentation). Double-click on the User Interface Properties item to open the User Interface Properties dialog.
52
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
User Interface Properties General
Save workspace settings on exit option defines whether the workspace settings are saved when you exit the SW so that they will be activated automatically, for example, windows will be opened the next time you start the SW. Selecting the Show a dialog for critical errors option will display a message box when there is a problem with one of the devices or with the measurement file writing. Select the Open Script Status window when script is started option to automatically open the Script Status window when script files are used in measurements. Select the Play audio quality samples during playback option to play the audio samples used in audio quality measurements also during playback. When the Show welcome window when application is launched option is selected, the Welcome to Nemo Outdoor window is displayed. Selecting the Show Close Full Screen window in Full Screen mode option will enable you to exit the Full Screen mode through an UI button. With the Show 'Debug log file management' dialog on exit option selected, a debug file will be generated when Nemo Outdoor is closed. With the Load workspace on startup option you can define which workspace is loaded when Nemo Outdoor is started. With the Load hardware configuration on startup option you can define which hardware configuration is loaded when Nemo Outdoor is started. With the Start measurement list on startup option you can define which measurement list is loaded and started when Nemo Outdoor is started.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
53
User Interface Properties Measurement
By double-clicking the Measurement item in the Configuration Manager window you will access the Measurement tab in the User Interface Properties dialog. Here you can make settings affecting all measurements.
Filename defines the filename format. The default format is %y%b%d %H%M%S (year-month-day hours-minutes-seconds, e.g., 06May31 165246) but you can use any combination of the items below. For example, "%y%b%d_%n means that the filename looks as follows: 06May31_1. The last number (%n) is the sequence number for measurement files recorded that day. You can also create custom filename templates. See chapter Creating Filename Templates. %a %A %b %B %d %H %I %j Abbreviated weekday name Full weekday name Abbreviated month name Full month name Day of month as decimal number (01 31) Hour in 24-hour format (00 23) Hour in 12-hour format (01 12) Day of year as decimal number (001 366)
54
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
%m %M %n %N %p %S %U %w %W %y %Y %z
Month as decimal number (01 12) Minute as decimal number (00 59) Sequence number (1 ) Sequence number (1 ) Current locale's A.M./P.M. indicator for 12-hour clock Second as decimal number (00 59) Week of year as decimal number, with Sunday as first day of week (00 53) Weekday as decimal number (0 6; Sunday is 0) Week of year as decimal number, with Monday as first day of week (00 53) Year without century, as decimal number (00 99) Year with century, as decimal number Either the time zone name or time zone abbreviation, depending on registry settings; no characters if time zone is unknown Either the time zone name or time zone abbreviation, depending on registry settings; no characters if time zone is unknown
%Z
With the Start scripts automatically option, you can order Nemo Outdoor to start executing the script file when you click the Start Recording button in the main window.
With the Force idle mode when stopping scripts option you can force the measurement mobile to return to idle mode if the script is interrupted. When the option is set to No, the mobile will stay in the current state when script is stopped. You can use this option to keep a GPRS mobile in active state when toggling a script on and off. With the Force detach when entering idle mode option selected, a GPRS detach is forced when the measurement device enters idle mode. Please note that it is recommended that with LTE devices this option is set to No. If attach/ detach commands are needed frequently, for example, with script files it is suggested that radio off/radio on commands are used instead of attach/detach. Select the Stop measurement after script is finished option to force Nemo Outdoor to stop recording after the script is finished. If you are making measurements with multiple devices and multiple scripts, select the Synchronize script repeats option to force Nemo Outdoor to wait until all scripts for all devices are finished before repeating the scripts. Select the Prevent script stopping during connection establishment option to delay the script stopping if any of the devices has a call or connection attempt ongoing. With the Use time from GPS option you can order Nemo Outdoor to use GPS time at the start of the measurement. During measurements, Nemo Outdoor will use PC time. Select the Wait for GPS fix before starting measurement option if you would like to start measuring only after there is a GPS fix.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
55
GPS time offset value specifies the difference between GPS UTC time and local time. This offset is used by handlers when GPS time synchronization is performed. Incoming call mode defines how incoming calls are handled. The options are answer, reject and ignore. Select the Redial after dropped call option to automatically make a new call if a call is dropped during measurements. Also define the time in seconds after which the call will be redialed. Remove all forcing functions when device is started option deactivates all forcing functions from the device when the device is started. When the Use ETSI compatible call connection trigger option is set to Yes, Outdoor uses the ETSI specification-based definition of the start and end time of a call. With the Enable routing table modifications for local devices option users can enable and disable routing table modification. The option is selected by default. Routing table modification should be disabled only with single data testing. If routing table modification is disabled with multi data testing, it can cause problems when several dial-up connections are opened from one host computer to terminals. All data connections to be established travel along one connection between the host computer and the terminal, i.e. all dial-up connections are routed via one terminal, not via different terminals and their interfaces. This distorts the test results. Buffer size specifies the number of events stored in the history buffer of the user interface. The size of the buffer affects how far back you can view a file during measurement. Selecting the Start recording automatically when devices are started option enables Nemo Outdoor to start recording automatically at device startup, and also when changing from offline mode to online mode. Selecting the Show report after measurement ends option will display a summary of all test calls after the measurement is ended. Selecting the Show 'Pause' dialog when measurement is paused option will display a message when the measurement has been paused. With the Show Stop Recording Query dialog before recording is stopped option selected, a dialog appears at the end of the measurement to make sure you really want to stop recording. When the Show Enable Missing Neighbor Query dialog when recording is started option is selected, a notification dialog will appear reminding you to enable missing neighbor detection when a scanner and a test terminal are connected to Nemo Outdoor and missing neighbor detection is not currently enabled. If you agree to enable the missing neighbor detection functionality through the dialog, the Missing Neighbor Detection dialog will appear. However, note that you are not able to enable the missing neighbor functionality if active measurement properties do not support missing neighbor detection. In that case recording must be stopped and measurement properties changed before the missing neighbor functionality can be enabled. Selecting the Start recording when incoming call is received option enables Nemo Outdoor to start recording automatically when a test call is received.
Creating Filename Templates
You can create templates for naming measurement log files. The template includes parameters (tags) and a list of allowed values for each parameter. The template also specifies the filename format which defines how the tags are used in the filename. The templates can be exported and imported.
56
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Double-click the Filename item on the User Interface Properties Measurement page to open the Filename Editor. Click the Add button to add a custom parameter.
In the Parameter Editor dialog, type a name for the new parameter. Then click the New button to add the possible values for the parameter. For example, add a parameter called city and then add a list of cities where you conduct measurements. Finally click OK to return to the Filename Editor.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
57
The new parameter is listed in the Parameters table. You can add as many parameters as needed. In the Filename field, define the filename format where you can now use your custom parameters. Below the Filename field you can see what the filename will look like with the selected parameters.
When you start logging, you will be asked to select a value for the custom parameter. This value will be used in the filename.
58
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
User Interface Properties Paths
In the Paths tab you can define locations for different files. In the picture above, you can see the default values. To change the default paths, click on the button and browse for a new location. In the Default Map field, you can enter a map file that will be opened by default. A World.tab map file is provided by Anite Finland in the installation package. Local Files refers to the files that are used in FTP testing. Report Files are the files created during timeslot testing. Default Color Set refers to the color set that is opened by default on the map. For instructions on making new color sets, see chapter Color Set Editor. Nemo Outdoor offers male and female sound files for notifications In the Sounds field, select C:\Nemo Tools\Nemo Shared Files\Sounds\Female if you want to use female sounds or C:\Nemo Tools\Nemo Shared Files\Sounds\Male if you want to use male sounds. Note that BTS files and script files do not apply to scanners.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
59
User Interface Properties Presentation
In the Presentation tab you can define the format in which various parameter values are presented.
60
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
User Interface Properties Colors
In the Colors page you can define colors used for devices, graph lines, and map routes. The first eight colors are reserved for devices. The other colors are used to draw graph lines and map routes. To make new palettes, click the New button, type a name for the new palette, and define all the colors. To change the palette, select a palette from the Color palette list.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
61
Notifications
Notifications are graphical, textual, and audio notifications marking certain events. Nemo Outdoor includes some premade notifications, but you can also add your own notifications. The notifications come in handy when you are looking for certain events, parameters, or values in the measurement file. Depending on your configuration, Nemo Outdoor will either play a sound or display a .png image in a graph/map when the defined event occurs during measurements. A textual notification is displayed in the Output window by default. By double-clicking a notification, the Notifications window appears. There you can make changes to, for example, sound files and icons associated with the notification.
62
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Notification Configuration
To make your own notifications, select the Notifications item in the Configuration Manager window and double-click any notification to open the Notifications dialog. Alternatively select View | Notification Manager. The dialog displays all existing notifications. From the table you can see the notification title and the selected sound and bitmap file for each notification. Activate a sound and/or bitmap file for a notification by selecting and clearing the options in the list.
Sound file defines an audio file for the selected notification. Browse a sound file in the field or use the default file. Nemo Outdoor offers male and female sound files. In the User Interface Properties Paths dialog, define which one you would like to use. Use the Play button to listen to the file. If you want to attach your own sound files (.wav) to the notifications, you should create the sound files and add them in the folder C:\Nemo Tools\Nemo Shared Files\Sounds\Male or C:\Nemo Tools\Nemo Shared Files\Sounds\Female. Bitmap file defines a graphical notification for the selected notification. Browse a bitmap file in the field or use the default file. The button will display a preview of the selected image. If you want to attach your own bitmaps to the notifications, you should create the files and add them in the folder C:\Nemo Tools\ Nemo Shared Files \Images.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
63
Click the Add button to create new notifications in the Notification Criteria dialog.
Title defines a name for the notification. Notify when these criteria are met table displays the criteria for the selected notification. Select the Notify only once when criteria are met option when you want be notified about certain events only once. Select the parameter that you want to use in the notification. Then define the Condition and Value for the selected parameter and click Add to list to add the new criteria for the notification. You can add several criteria for each notification. Finally click OK and the notification is saved and added in the Notifications dialog where you can attach sound and bitmap files to the notification. The notification is also available in the Measurement Properties | Notifications dialog where you can activate the notification for a specific device. Click the Device notification settings button in the Devices view to open the dialog.
64
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
To activate a notification for a particular device, click the Device notification settings button in the Devices view. This will open the Measurement Properties, Notifications dialog. Select the notifications you would like to use in the measurement and click OK.
The table displays a list of notifications that can be activated for the selected device. Select the notification from the list and select how you would like to be notified. The Notification Properties button will open the Notification Configuration dialog where you can edit the notification settings (see chapter Notification Configuration for more information). By clicking the Select All and Clear All buttons, you can select and clear all items in the list.
To make user-configurable notifications:
1. Open the Notifications dialog (View | Notification Manager) and click Add. 2. In the Notification Criteria dialog, define the notification criteria and click OK. 3. In the Notifications dialog, select the notification that you just created. Define sound and bitmap files for the notification and activate them by selecting the options in the notifications table. 4. Click OK to save the settings.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
65
Scripts
Note that you cannot use scripts with scanners. Under the Scripts item you will find premade scripts and user-defined scripts. Scripts can be used to perform measurements automatically instead of performing manual calls or data transfers. Select the Scripts item to open a list of scripts in the Configuration Manager view. Double-click on any of these scripts to open the Script Editor dialog. In order to select a script file to be used in a measurement, click the Device script settings button in the Devices view. Creating Script files is described in more detail in chapter Making Script Files.
66
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Base Station Files
Under the Base Station Files item you will find loaded base station files. Select a BTS file to view the BTS information in the Configuration Manager view. Click the button to remove the BTS file.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
67
Device Configurations
Under Device Configurations, you will find a list of device configuration files (.hwc). A device configuration contains information on devices and their measurement configurations. You can use the device configurations to quickly start measurements with Nemo Outdoor without having to detect and configure the measurement devices each time you start Nemo Outdoor. You can load a .hwc file by selecting File | Open Device Configuration. Alternatively, you can load a device configuration when you start Nemo Outdoor by selecting it in the Load device Configuration dialog. To make new device configurations, add devices manually in Nemo Outdoor and configure them. When everything is ready, select File | Save Device Configuration As and type a name for the saved file. The new .hwc file will appear in the Configuration Manager, Device Configurations folder. To rename a device configuration, double-click the respective item in the Configuration Manager and type a new name in the Rename HW Config dialog.
68
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Devices
Under the Devices item are listed all the devices that you have connected to Nemo Outdoor. Note that you can add a new device from the plus icon , and remove a device by selecting the device and clicking on the minus icon . The table on the right displays information about the selected device. Each device (mobile, GPS, and scanner) has its own configuration dialog. Double-clicking on the device will open the applicable device configuration dialog. These dialogs are presented next.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
69
Device Configuration for Mobiles and Modems
The Label field allows you to give a label such as a comment or a name for the phone, and makes it easier to identify devices during measurement and post processing. The label can be seen in the Nemo Outdoor user interface during a measurement and playback, and the information is also stored in the log file header. Trace port and Modem port selections are device-specific. Please refer to the Dial-up Networking Setup Guide for more detailed information. Circuit switched dial-up connection list box gives a list of all the dial-up connections that have been configured on your computer. If you are making CS data measurements, select a dial-up connection here. See the Dial-Up Networking Setup guide provided by Anite Finland for detailed instructions for configuring dial-up connections. Packet switched dial-up connection list box gives a list of all the dial-up connections that have been configured on your computer. If you are making PS data measurements, select a dial-up connection here. See the Dial-Up Networking Setup guide provided by Anite Finland for detailed instructions for configuring dial-up connections. Antenna gain and Cable loss are antenna-related parameters and they are used in the conversion from dBm to dBuV/m. This parameter is needed only if you are using external antennas. If you are using the internal antenna of each phone, leave these values blank.
70
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Antenna type 1140.27
Frequency range 824 894/1710 1880/ 18502170 MHz
Antenna gain (dBd) 0 dBd
Impedance
VSWR 1
Max power
Polarization
Cable loss
Cable & connector Mini Low Loss 2.5 m, SMA male
50 ohm
2:1 @ specified freq.
10 W
Linear vertical
-0.55/ 0.82 dB/m
1140.26
890 960/1850 1990/ 17102170 MHz
0 dBd
50 ohm
2:1 @ specified freq.
10 W
Linear vertical
Mini Low Loss 2.5 m, SMA male
The above examples can only be used with antennas received from Anite Finland Ltd. or Smarteq. If you are using antennas from other antenna manufacturers, you will have to ask the antenna gain and cable loss information from the manufacturer.
Voice quality algorithm defines whether PESQ or POLQA algorithm is used in voice quality measurements. If you select the Invex isolation module option, you can also make echo measurements. Select the Enable echo measurement option to start logging the echo-related parameters. With the Advanced echo OEM library provided by Opticom it is possible to measure echo from audio with both PESQ and POLQA algorithms. Echo measurements require an additional license and it is available with Nemo Invex using a handset isolation module. Echo measurements are not supported with commercial sound cards, such as, Terratec DMX6 Fire or Maya44. Select the Nemo audio module option to use the Nemo audio module for voice quality measurements. You can define the port where the Nemo voice quality unit is connected in the dropdown menu. Select the Sound card channel option to use the USB sound card for voice quality measurements. Select the applicable sound card channel in the drop-down menu.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
71
Select the Invex isolation module option to use a terminal with an Invex isolation module for voice quality measurements. Select the VoIP only option to make voice quality measurements (POLQA) over a VoIP connection. If you select this option make the appropriate settings in the VoIP Call Configuration dialog (see VoIP Calls). Select Disabled when you do not wish to carry out voice quality measurements. After you have configured the device, click the Apply button to check that the device is working properly. To exit the dialog, click OK. Clicking on the Measurement Properties button will lead to the Measurement Properties dialog where you can make device-specific measurement settings. You can also enter the Measurement Properties dialog through Measurement | <device name> | Measurement Properties in the menu bar.
Device Configuration for Scanners
In the Label field you can define a suitable label for the device, for example, a name or a usage purpose, making it easier to identify the device during measurement and post processing. The label can be seen in the Nemo Outdoor user interface during a measurement and playback, and the information is also stored in the log file header. Port refers to the port to which the scanner is connected. Baud rate refers to the communication speed. Antenna gain and Cable loss are antenna-related parameters and they are used in the conversion from dBm to dBuV/m. This parameter is needed only if you are using external antennas. If you are using the internal antenna of each phone, leave these values blank.
72
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Antenna type 1140.27
Frequency range 824 894/1710 1880/ 18502170 MHz
Antenna gain (dBd) 0 dBd
Impedance
VSWR 1
Max power
Polarization
Cable loss
Cable & connector Mini Low Loss 2.5 m, SMA male
50 ohm
2:1 @ specified freq.
10 W
Linear vertical
-0.55/ 0.82 dB/m
1140.26
890 960/1850 1990/ 17102170 MHz
0 dBd
50 ohm
2:1 @ specified freq.
10 W
Linear vertical
Mini Low Loss 2.5 m, SMA male
The above examples can only be used with antennas received from Anite Finland Ltd. or Smarteq. If you are using antennas from other antenna manufacturers, you will have to ask the antenna gain and cable loss information from the manufacturer. Clicking on the Measurement Properties button will lead to the Measurement Properties dialog where you can make device-specific measurement settings (see Measurement Properties). After you have configured the device, click the Apply button to check that the device is working properly. To exit the dialog, click OK.
Device Configuration for GPS Receivers
In the Label field you can define a label for the GPS device, for example, a name or a usage purpose, making it easier to identify devices during measurement and post processing. The label can be seen in the Nemo Outdoor user interface during a measurement and playback, and the information is also stored in the log file header. Serial port refers to the port to which the GPS receiver is connected. Baud rate refers to the communication speed. The available values are 1200, 2400, 4800, and 9600.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
73
Data bits, Parity and Stop bits are other communication-related parameters. The available values for Data bits are 5, 6, 7, and 8, the options for Parity are Even, None, and Odd. The default value for Stop bits is 1. You should set these values the same as in your GPS. Check your GPS receiver documentation. After you have configured the device, click the Apply button to check that the device is working properly. To exit the dialog, click OK.
View Groups
Under the View Groups item are listed all the view groups that are currently loaded. View groups are sets of windows that are open at the same time. You can add a new view group from the plus icon , and remove a view group by selecting the item and clicking on the minus icon . When you select a view group in the Configuration Manager, the right-hand panel displays the views that are saved in the view group. You can define properties for each view by double-clicking the view name. See chapter View Groups for more information on using the view groups.
74
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
MEASUREMENT PROPERTIES
The Measurement Properties dialog contains several pages and the contents depend on the device type (mobile or scanner), on the device model, and on the technologies supported by the device.
Measurement Properties General
Network name field can be used for stating the friendly name for the network (operator) that Nemo Outdoor measures with the respective test mobile. Note that you should enter the name yourself, as Nemo Outdoor does not recognize the network that each mobile is using. The network name is presented in the output files and helps you to recognize which network you have been monitoring. BTS file defines the base station file that will be displayed on the map. If you have a GPS receiver connected to the system, you can view the measurement vehicle on the map and a line will be drawn from the measurement vehicle to the active base station. Click the button to browse for a BTS file (.nbf).
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
75
By clicking the Advanced button, you will access the Advanced Properties dialog. Here you can enable and disable various measurement options such as layer messages. If you disable some of the options, the disabled messages will not be recorded in the measurement file. This will decrease output file size. The selection depends on the measurement device used. The parameters in the Measurement Options list vary depending on the device. These options are also accessible through the Devices view.
Note that the Enable RLC Data messages item should not be enabled with data connections 384kbit/s or higher as this may cause instability in the measurement terminal. To view data in Packet decoder grids during playback, you need to enable the packet decoding function prior to performing data measurements. Select Full or Partial in the Enable IP Capture field. A separate .pcap-file will be generated for the measurement. This file needs to accompany the measurement file in the same folder when viewing and decoding packet capture information in Packet Decoder grids in Nemo Outdoor. Please note that when measuring with a LX GSM/WCDMA scanner in a WCDMA network, the internal GPS receiver should be activated.
76
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Measurement Properties Measurement Settings
You are able to make measurement type specific configurations by clicking the corresponding field in the dialog. The Measurement Settings page of the Measurement Properties dialog is available for mobiles only.
Voice Call opens the Voice Call Properties dialog. DTMF characters field can be used to send DTMF (dual-tone multi-frequency) tones during a voice call. Short Messaging Service button opens the SMS Testing dialog. See chapter SMS Testing for more information on SMS testing. USSD Message button opens the USSD Testing dialog. See chapter USSD Testing for more information on USSD testing. Multimedia Messaging Service button opens the Packet Session Settings, MMS dialog. See chapter MMS Testing for more information on MMS testing. Circuit-Switched Data Call opens the Data Call Properties dialog. Video Call button opens the Video Call Properties dialog. See chapter Making Video Calls for more information. Packet Session opens the Packet Session Settings dialog. Selected Data Protocol defines which data protocol is used to perform data transfers. Clicking the Supported Data Protocols field opens a list of supported data protocols. Clicking the field of a selected data protocol will open a dialog for configuring the selected data protocol. Enable VoIP Measurements option, when selected, opens the SIP server and VoIP call dialogs. See chapter VoIP Calls for more information.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
77
Custom AT Commands offers the possibility to run custom AT commands with certain test terminals. The available commands are device-specific. Type in the AT command and click Send Command. The AT commands and responses are saved in the measurement file.
Measurement Properties Frequency Scanning with Mobiles
Note that this page is only visible in a phone's Measurement Properties dialog if the terminal supports frequency scanning.
Enable frequency scanning option must be selected to activate frequency scanning for the mobile. The Top-N scanning functionality can be used for scanning the strongest channels in GSM. With TopN scanning it is possible to get Top-N channel results for each band, e.g. for EGSM, GSM900 and GSM1800. The benefits also include the possibility to benchmark different operators.
78
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Selecting the BSIC decoding option displays BSIC value in a measurement window. BSIC threshold defines the minimum BSIC level that the scanner reports. When the Missing neighbor detection option is selected, the missing neighbor information event (NMISS) is written in the log file. You can view the missing neighbor information, for example, in a grid view. If you select BSIC decoding or Missing neighbor detection, click the Select Channels button to define the channels to be scanned.
Select the Show channels as frequencies option to view the channels in MHz. In the Band drop-down menu you can select a band from which to view channels from in the Available view. If you select All in the Band drop-down menu, channels from all bands will be viewed. You can also select one band at a time and add the bands you want to scan. The Available view provides a list of channels that are available for scanning. To add channels to the Selected list, click on a number in the Available list and then click the Add button or simply doubleclick a channel to add it to the Selected list. To select all available channels for scanning, click the Add All button. An alternative method to select channels is to type the channel numbers in the field at the bottom of the dialog and to click Add. If all bands are selected, you have the possibility to select Remove All | ... items from every band. Alternatively, if only one band is selected you can remove only items from the current band through Remove All | ...items from current band.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
79
If you select the Top-N option, click the Top-N Configuration button to select channels.
In the Top-N Configuration dialog you can set the Start and Stop ARFCN range between which the Top-N channels are recorded. Define the number of strongest channels to be searched in the Top-N field. The maximum number of Top-N channels is 32. You can click on the Clear all button to clear the table.
80
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Measurement Properties Pilot Scanning with Mobiles
Note that this page is only visible in a phone's Measurement Properties dialog if the terminal supports pilot scanning.
The Enable pilot scanning option must be selected to activate pilot scanning for the mobile. Select a value for the CPICH RSCP threshold field. The device will only report cells with CPICH RSCP above the set value. The Top-N scanning functionality can be used for scanning the strongest pilots in UMTS. With Top-N scanning it is possible to get Top-N channel results for each band. The benefits also include the possibility to benchmark different operators. When the Missing neighbor detection option is selected, the missing neighbor information event (NMISS) is written in the log file. You can view the missing neighbor information, for example, in a grid view. Click the Top-N Configuration button to enter the Select Channels dialog.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
81
Measurement Properties Frequency Scanning with Scanners
The Frequency scanning page of the Measurement Properties dialog is further divided into sub-pages based on the cellular technology supported by the scanner. The contents of the sub-pages are technology-specific.
Frequency Scanning with GSM Scanners
Note that the available options are device specific.
Channel style defines the style of the measured channel. For GSM the options are 200 kHz and 30 kHz narrow. Data mode defines the type of measurement data computed from each sample. Note that the available selection depends on the scanner type. RX level average: the data reported is the average RX level, in dB, of the number of samples.
Measurement period defines the time in milliseconds for which the scanner measures and then reports the result. Sample size defines the number of samples taken from each channel before a measurement result is written to file.
82
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
The Top-N scanning functionality can be used for scanning the strongest pilots in UMTS. With Top-N scanning it is possible to get Top-N channel results for each band. The benefits also include the possibility to benchmark different operators. Selecting the BSIC decoding option displays BSIC value in a measurement window. BSIC threshold defines the minimum BSIC level that the scanner reports. Select the BCCH C/I option to activate C/I measurements for the BCCH channel. Cell information decoding. Mobile Network Code, Mobile Country Code and Cell ID information can be decoded from BCCH messages. Note that this is only enabled in online mode and if the option has been purchased with the scanner. When the System information decoding option is selected, L3 messages are written in the log file. By clicking the Select Channels button, you can access a dialog where you select the channels that will be scanned.
Frequency Scanning with UMTS Scanners
Note that the available options are device specific.
Channel style refers to the style of the channel. Data mode defines the type of measurement data computed from each sample. Note that the available selection depends on the scanner type.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
83
RX level average: the data reported is the average RX level, in dB, of the number of samples.
Measurement period defines the time in milliseconds for which the scanner measures and then reports the result. Sample size defines the number of samples taken from each channel before a measurement result is written to file. By clicking the Select Channels button, you can access the Select Channels dialog.
Frequency Scanning with LTE Scanners
Note that the available options are device specific.
Channel style refers to the style of the channel. Measurement period defines the time in milliseconds for which the scanner measures and then reports the result. Data mode defines the type of measurement data computed from each sample. Note that the available selection depends on the scanner type. RX level average: the data reported is the average RX level, in dB, of the number of samples.
Sample size defines the number of samples taken from each channel before a measurement result is written to file.
84
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
By clicking the Select Channels button, you can access the Select Channels dialog.
Frequency Scanning with CDMA/EVDO Scanners
Note that the available options are device specific.
Channel style refers to the style of the channel. Data mode defines the type of measurement data computed from each sample. Note that the available selection depends on the scanner type. RX level average: the data reported is the average RX level, in dB, of the number of samples.
Sample size defines the number of samples taken from each channel before a measurement result is written to file. By clicking the Select Channels button, you can access the Select Channels dialog.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
85
Frequency Scanning with WiMAX Scanners
Note that the available options are device specific.
Channel style refers to the style of the channel. Data mode defines the type of measurement data computed from each sample. Note that the available selection depends on the scanner type. RX level average: the data reported is the average RX level, in dB, of the number of samples.
Sample size defines the number of samples taken from each channel before a measurement result is written to file. By clicking the Select Frequencies button, you can access the Select Frequencies dialog.
86
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Frequency Scanning with TD-SCDMA Scanners
Note that the available options are device specific.
Channel style refers to the style of the channel. Data mode defines the type of measurement data computed from each sample. Note that the available selection depends on the scanner type. RX level average: the data reported is the average RX level, in dB, of the number of samples.
Sample size defines the number of samples taken from each channel before a measurement result is written to file. By clicking the Select Channels button, you can access the Select Channels dialog.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
87
Measurement Properties Pilot Scanning with Scanners
The Pilot scanning page of the Measurement Properties dialog is further divided into sub-pages based on the cellular technology supported by the scanner. The contents of the sub-pages are technologyspecific.
Pilot Scanning with UMTS Scanners
Note that the available options are device specific.
CPICH Ec/No threshold defines the minimum level for the CPICH Ec/No. If the values are below the threshold, the pilots are not reported. Channel style refers to the style of the channel. Data processing method defines how the scanned data is processed by the scanner. In aggregate method, the sum of all peak pilot Ec/Io values above the PN threshold is calculated. If there are no peaks above the PN threshold, value -30 dB is returned for WCDMA.
88
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Pilot measurement mode defines the measurement mode for pilot scanning. In High speed mode scanning speed is higher but sensitivity is lower. In high speed mode, weak pilots may be undetected. In High dynamic mode scanning speed is lower but sensitivity is higher.
Measurement period defines the time in milliseconds for which the scanner measures and then reports the result. Number of fingers defines the maximum number of fingers used for RAKE in measurement. Selective level determines a valid path. Set a value (in dB) to decide a valid path from the noise floor (average value). Rake threshold determines a valid path (in dB). Subtracting the set value from a path with a maximum correlation value gives the lower limit of the valid path. Top-N option enables/disables Top-N scrambling code scanning. If enabled, scanner will report results from N best scrambling codes. Number of pilots field defines how many pilots are reported by scanner in Top-N mode. Time of arrival defines if the selected scanner will measure the time of arrival for each scrambling code. The time of arrival value is relative to GPS time and is measured in chips. Delay spread defines if the selected scanner will also measure the delay spread value (in chips) for each scanned scrambling code. Delay spread is determined as the difference between the last and first component to break the threshold set in PN Threshold. When the Missing neighbor detection option is selected, the missing neighbor information event (NMISS) is written in the log file. You can view the missing neighbor information, for example, in a grid view. When the Neighbor list decoding option is selected, the NLIST (neighbor list) event is written in the log file for both GSM and WCDMA. Delay profile option enables/disables delay profile scanning. The Channel number field provides a list of channels that can be selected for scanning. Finger option enables and disables Finger measurements for the scanner. P-SCH defines if the selected scanner will measure the P-SCH Ec/N0 value for each scrambling code. SIR (signal to interference ratio) defines if the selected scanner will measure the SIR value for each scrambling code. S-SCH defines if the selected scanner will measure the S-SCH Ec/N0 value for each scrambling code. When the System information decoding option is selected, L3 messages are written in the log file.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
89
The Top-N Configuration button will open the Select Channels dialog where you can select channels for pilot scanning. If you press the arrow, a drop-down menu will appear from where you can select Top-N Search Configuration.
Please note that the Top-N Search Configuration dialog is available for Anritsu UMTS scanners only. In the Top-N Search Configuration dialog you can limit the search performed by the scanner and consequently speed up the search.
Group specifies the group number for the primary scrambling code in the range of 0 to 63. Cell specifies the cell number for the primary scrambling code in the range of 0 to 7. Secondary code specifies the secondary scrambling code. Limit range should be set from 0 to 0. Channelization code specifies the channelization code. Limit range should be set from 0 to 0. Search method defines how the search is performed. P-CPICH (primary common pilot channel) searches with P-CPICH. SCH performs a three-step search with P-SCH and S-SCH.
90
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Pilot Scanning with LTE Scanners
Note that the available options are device specific.
Channel style refers to the style of the channel. Cyclic prefix defines the type of signal the scanner is set to measure. With Autodetect selected, the scanner will automatically detect the appropriate signal type. Data processing method defines how the scanned data is processed by the scanner. In aggregate method, the sum of all peak pilot Ec/Io values above the PN threshold is calculated. If there are no peaks above the PN threshold, value -30 dB is returned for WCDMA. Please note that this option is not available with PCTEL EX LTE scanners. Sampling ratio option is available for PCTEL EX scanners only. The available options are 1:1, 1:2, 1:4 and 1:8. With ratio 1:1 all samples (Pilotscan events) are logged, with ratio 1:2 every second sample is logged, with ratio 1:4 every 4th sample is logged, and with ratio 1:8 every 8th sample is logged. By decreasing the sampling ratio you can decrease the output file size, but the scanning accuracy will be diminished. RSSI threshold determines a valid path (in dB). Subtracting the set value from a path with a maximum correlation value gives the lower limit of the valid path. Top-N option enables/disables Top-N scrambling code scanning. If enabled, scanner will report results from N best cells. Number of cells field indicates the number of best cells you want the scanning to notify you of. Up to 16 sectors are reported with specific cell ID.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
91
CINR option activates/deactivates Carrier to Interference and Noise Ratio measuring. Carrier refers to either reference signal power or sync signal power depending on the selected signal type. Time offset refers to the number of samples between P-SCH Primary Synchronization Signal arrival time with respect to receiver frequency reference that is derived from GPS reference time. Sync signal refers to the ratio between the synchronization channel, i.e., primary and secondary signal received power and the interference and noise from the same synchronization signal set. Reference signal refers to the ratio between the reference signal received power (RSRP) and the interference and noise from the same reference signal set. The Top-N Configuration button will open the Select Channels dialog where you can select channels for pilot scanning. The maximum number of channels that can be selected is device specific. When you select LTE channels, you can also define some channel-specific settings. In the LTE Channel Specific Settings dialog, select the channel from the Selected channels list and define the settings. Note that the available options are device specific.
Uplink-downlink configuration refers to LTE TDD frame structure. Frame structure type 2 is applicable to TDD. Each radio frame of length Tf = 307200 Ts = 10 ms consists of two half-frames of length 153600 Ts = 5 ms each. Each half-frame consists of five subframes of length 30720 Ts = 1 ms . The supported uplink-downlink configurations are listed in the table below where, for each subframe in a radio frame, D denotes the subframe is reserved for downlink transmissions, U denotes the subframe is reserved for uplink transmissions and S denotes a special subframe with the three fields DwPTS, GP and UpPTS.
92
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
One radio frame, Tf = 307200Ts = 10 ms One half-frame, 153600Ts = 5 ms
One slot, Tslot=15360Ts Subframe #0 One subframe, 30720Ts DwPTS
30720Ts
Subframe #2
Subframe #3
Subframe #4
Subframe #5
Subframe #7
Subframe #8
Subframe #9
GP
UpPT S
DwPTS
GP
UpPT S
Frame structure type 2 (for 5 ms switch-point periodicity):
Uplink-downlink configuration 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 Downlink-to-Uplink Switch-point periodicity 5 ms 5 ms 5 ms 10 ms 10 ms 10 ms 5 ms 0 D D D D D D D 1 S S S S S S S 2 U U U U U U U Subframe number 3 4 5 6 7 U U D S U U D D S U D D D S U U U D D D U D D D D D D D D D U U D S U 8 U U D D D D U 9 U D D D D D D
Pilot Scanning with EVDO Scanners
Note that the available options are device specific.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
93
Channel style refers to the style of the channel. Data processing method defines how the scanned data is processed by the scanner. In aggregate method, the sum of all peak pilot Ec/Io values above the PN threshold is calculated. If there are no peaks above the PN threshold, value -30 dB is returned for WCDMA. Pilot window mode defines the position of the chips that are searched for pilot across in regard to the ideal pilot position (0 chip delay for a given pilot). For Pilot window search mode the options are Standard, Wide and Very Wide. The Wide and Very Wide options can be used to detect pilots far away from the base stations. The sensitivity will not be affected but the scanning speed will be slower as the search window is increased. Sampling ratio option is available for PCTEL EX scanners only. The available options are 1:1, 1:2, 1:4 and 1:8. With ratio 1:1 all samples (Pilotscan events) are logged, with ratio 1:2 every second sample is logged, with ratio 1:4 every 4th sample is logged, and with ratio 1:8 every 8th sample is logged. By decreasing the sampling ratio you can decrease the output file size, but the scanning accuracy will be diminished. Pilot Ec/I0 threshold defines the threshold level for the pilot Ec/I0. If the values are below the threshold, the pilots are not scanned. Top-N option enables/disables Top-N scrambling code scanning. If enabled, scanner will report results from N best scrambling codes. Number of pilots field defines how many pilots are reported by scanner in Top-N mode. Delay option enables/disables delay profile scanning. Delay is defined as the measured difference between the expected arrival time (GPS time) and the actual arrival time of the maximum peak above the PN threshold. It is reported in chips. Overhead message decoding, when selected, enables the scanner to decode PCH messages. The Top-N Configuration button will open the Select Channels dialog where you can select channels for pilot scanning. The maximum number of channels that can be selected is device specific.
94
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Pilot Scanning with CDMA Scanners
Note that the available options are device specific.
Channel style refers to the style of the channel. Chip window size defines the length of pilot window in chips from 1 to 64. This value is used to establish the number of chips to be searched for pilot across (Pilot Window Length) and to define the position of these chips Pilot Window Mode in regard to the ideal pilot position (0 chip delay for a given pilot). Correlator affects how the scanner works. Bigger correlator size enables the scanner to detect and measure Pilot channels with better dynamic but makes scanning speed slower. For example, when using correlator size 2048 versus 512, the dynamic range for pilot measurement changes from 21db to 17db. Data processing method defines how the scanned data is processed by the scanner. In aggregate method, the sum of all peak pilot Ec/Io values above the PN threshold is calculated. If there are no peaks above the PN threshold, value -30 dB is returned for WCDMA. Pilot window mode defines the position of the chips that are searched for pilot across in regard to the ideal pilot position (0 chip delay for a given pilot). Pilot Ec/I0 threshold defines the threshold level for the pilot Ec/I0. If the values are below the threshold, the pilots are not scanned.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
95
TOP-N mode option enables/disables TOP-N scrambling code scanning. If enabled, scanner will report results from N best pilots. Number of pilots field defines how many pilots are reported by the scanner in TOP-N mode. Delay option enables/disables delay profile scanning. Delay is defined as the measured difference between the expected arrival time (GPS time) and the actual arrival time of the maximum peak above the PN threshold. It is reported in chips. Overhead message decoding, when selected, enables the scanner to decode PCH messages. The Top-N Configuration button will open the Select Channels dialog where you can select channels for pilot scanning. The maximum number of channels that can be selected is device specific.
Pilot Scanning with WiMAX Scanners
Note that the available options are device specific.
Channel style refers to the style of the channel. Data processing method defines how the scanned data is processed by the scanner. In aggregate method, the sum of all peak pilot Ec/Io values above the PN threshold is calculated. Top-N option enables/disables TOP-N scrambling code scanning. If enabled, scanner will report results from N best preambles. Number of preambles field defines how many preambles are reported by the scanner in TOP-N mode.
96
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
CINR refers to the Carrier to Interference and Noise ratio value, in dB *100 (e.g., -16.34). It is based on the requested reuse factor. Preamble delay refers to the number of samples between expected arrival time and actual arrival time of preamble with respect to GPS time reference. The values range from 0 to 1023+32. Each sample corresponds to 89.285 nanoseconds. Reuse factor refers to a system design parameter that can be manipulated to achieve the desired balance between the interference and the network coverage. The WiMAX air interface modulating waveform has been divided into three segments (Segment 0, 1 and 2). The allocation of frequency sub-carrier into these three segments is done in such a way that e.g. a downlink signal on segment 0 will not interfere with the downlink signal on segment 1. In a Reuse Factor 1 measurement, contributions from all the three segments are considered in the measured parameters, so that the CINRs are calculated from all the three segments. When Reuse Factor 3 is selected, only the contribution of the desired segment is considered, and the CINRs are calculated only from the same segment. As a broad guideline, measurements performed with Reuse Factor 1 will provide the signal quality of the all the detected preambles relative to each other, whereas the Reuse Factor 3 category of measurements will provide the signal quality of preambles within the same segment. Delay spread defines if the selected scanner will also measure the delay spread value (in chips) for each scanned scrambling code. Delay spread is determined as the difference between the last and first component to break the threshold set in PN Threshold. The Top-N Configuration button will open the Select Frequencies dialog where you can select frequencies for scanning. The maximum number of frequencies that can be selected is device specific.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
97
Pilot Scanning with TD-SCDMA Scanners
Note that the available options are device specific.
Channel style refers to the style of the channel. Data processing method defines how the scanned data is processed by the scanner. In aggregate method, the sum of all peak pilot Ec/Io values above the PN threshold is calculated. Sampling ratio option is available for PCTEL EX scanners only. The available options are 1:1, 1:2, 1:4 and 1:8. With ratio 1:1 all samples (Pilotscan events) are logged, with ratio 1:2 every second sample is logged, with ratio 1:4 every 4th sample is logged, and with ratio 1:8 every 8th sample is logged. By decreasing the sampling ratio you can decrease the output file size, but the scanning accuracy will be diminished. Top-N option enables/disables TOP-N scrambling code scanning. If enabled, scanner will report results from N best pilots. Number of pilots field defines how many pilots are reported by the scanner in TOP-N mode. Time offset refers to the number of samples between P-SCH Primary Synchronization Signal arrival time with respect to receiver frequency reference that is derived from GPS reference time. SIR (signal to interference ratio) defines if the selected scanner will measure the SIR value for each scrambling code.
98
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
The Top-N Configuration button will open the Select Frequencies dialog where you can select frequencies for scanning. The maximum number of frequencies that can be selected is device specific.
Pilot Scanning with DVB-H Scanners
Note that the available options are device specific.
Frequency defines the frequency scanned.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
99
Measurement Properties Spectrum Scanning
In the Spectrum scanning page you can define frequencies that will be scanned.
Use preamplifier option should be selected if the signal level is less than -50 dB. This will increase the scanner sensitivity, hence slightly decreasing background noise. However, it is recommended that it is not selected when signal volume is higher than -50dBm. Select the Enable spectrum scanning option and click Add.
100
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Set start and stop frequencies defines the frequency range that will be scanned. Define the start and stop frequencies within which the measurement will be performed. If you manually define the start and stop frequencies, you can either select to add the frequencies to the scanning list or save them as a predefined set. Select your option by pressing the Add to Scanning List button. Set center frequency and bandwidth defines the frequency range that will be scanned. Define the center frequency and the bandwidth. If you manually define the center frequency and bandwidth, you can either select to add them to the scanning list, or save them as a predefined set. Select your option by pressing the Add to Scanning List button. Sample count determines the sample count measured for the given frequency range. You can define Predefined scanning sets which you can use to quickly select the frequency range to be scanned. Just double-click a set from the list and the predefined values will be selected. To create new scanning sets, define the scanning frequencies at the top of the dialog, press the Add to Scanning List button and select Save as Predefined Set.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
101
Define a name for the set in the Enter Frequency Set Name dialog and click OK.
Measurement Properties - Script
In order to select a script file to be used in a measurement, click the Device Settings button Devices window and select Script Properties. in the
In the Script File field, browse the script file that you want to use. There are some premade script files available but you can also create your own in the Script Editor (see chapter Making Script Files). With Nemo Outdoor you can define multiple script synchronization groups. The scripts in the same group are synchronized with each other. Devices can be assigned for certain script groups. By default the script group is selected as <None>, but the user can also create new script groups by selecting <New group> in the Script group drop-down menu, and typing the name of the new script group in the field. A script group can be also saved with a specific name. To be able to use script groups, the Synchronize script repeats option must be selected in the User Interface Properties (see User Interface Properties Measurement). When a script group is selected as <None>, but Synchronize script repeats option is selected, all script files that belong to the same <None> group are synchronized.
102
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Script groups can be used, e.g., with Nemo Outdoor multi configuration including two voice quality terminals and two USB modems performing PS data transfers simultaneously. For example, script files used with voice quality terminals belong to the same script group, and their script files are synchronized with one another, whereas the PS data scripts belong to the second script group. The script synchronization settings need to be configured separately for each device.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
103
DURING MEASUREMENTS
When Nemo Outdoor is performing the user defined test measurement, you can view the process in a number of graphs, grids, and maps. The graph and grid windows are fully user configurable. In the following chapters, the most common tasks are presented in more detail and some examples are given to illustrate their use. If you have any problems in starting the measurements, see chapter Troubleshooting.
104
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
MAKING SCANNING MEASUREMENTS
With a Scanner
In order to measure with a scanner, just start the recording by clicking the Start Recording Nemo Outdoor will start writing the measurement data in a file. button.
With a Mobile
To carry out frequency scanning with a mobile phone, first make sure that the terminal model supports the scanning feature. To do frequency scanning, select Measurement control | Start Single Shot Scanning, or Measurement control | Start Continuous Scanning.
To end a scanning measurement, select Measurement control | Stop Scanning.
MAKING VOICE CALLS
To make voice calls:
1. In the Measurement Properties, Measurement settings page (see Measurement Properties Measurement Settings), insert the phone number that you wish to use in the test call in the Voice Call field. Click OK. 2. Select Start Voice Call from the Device Commands menu or from the Measurement menu. Alternatively, you can activate a script by clicking the Start/Stop Scripts button. Note that after you have activated the script, you cannot control the measurement manually until the script is finished or you interrupt the script by clicking the Start/Stop Scripts button. 3. When you wish to finish the call in manual mode, select Stop Voice Call from the Device Commands menu . If you are running a script, wait until the script is finished.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
105
Voice Call Properties
Voice call properties are needed to establish the voice calls and to make voice quality measurements. Click the Voice Call button in the Measurement Properties, Measurement Settings dialog and the Voice Call Properties dialog will be opened.
Number defines the number to be called. It must be a valid phone number. The number must be such that the line stays open for a user-defined time and some speech or sound is transferred on the line. The Number field can contain up to 17 characters. When Request voice call callback is selected, the application sends callback command to Nemo Server using DTMF tones. DTMF tones are sent separately from audio so naturally DTMF tones do not affect to MOS score. If Nemo server is connected to analog telephone lines (PSTN) user must define the correct callback number on the server side using Nemo Server manager application. If ISDN lines are used with Nemo Server and test terminals are selected to be sent also caller id to Nemo server, callback number is recognized automatically. Note that this functionality requires Nemo Server version 2.5.0 or later. Select the Voice quality option to activate the voice quality settings. Note that the voice quality settings are available only if your license supports voice quality measurements.
106
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Reference sample filename defines the reference sample to which the received audio sample is compared. If you want to use your own test samples, make sure that the samples are of 8KHz sampling rate, 16-bit linear coded .wav files that are no longer than six seconds in length. With the Terratec sound card, sampling rate can be 8kHz or 16 kHz (for WB-AMR testing) and sample length a maximum of 30 seconds. For ECHO measurements, use one of the following samples: 10s.wav, 4s_m.wav, 8s.wav, ru_6s.wav, and ru_6s_wb.wav. Select the Save sample files option to save the received voice quality sample files. Prefix for received sample files refers to the prefix that is added to the file names of received audio sample files. If you leave this field empty, the received audio files are not stored. When a prefix is defined, Nemo Outdoor names the files as follows: prefix_mos_date_time.wav where prefix is the user-defined prefix, mos the voice quality score on a MOS scale with one decimal precision but without decimal point, date in DDMMYYYY format, and time in HHMMSS format. For example: terminal1_34_15112004_143045.wav. Save only samples below threshold determines the value below which the samples are saved. The threshold values range from 0-5, 0 being the worst and 5 the best value. The default threshold value is 5, which means that all samples are saved. Note that the Script Settings table is activated only if you access this dialog through the Script Editor. See chapter Making Script Files for more information on making scripts. Note that with voice quality measurements when calling the Nemo audio server, the delay time between a new call attempt and the previous call disconnect must be at least 10 seconds. CDMA specific settings, Service option defines the service option used for the test call. Note that the CDMA specific setting is activated only if you are measuring with a CDMA mobile. Call duration determines the time that the call lasts in seconds. The duration timer is started from the channel assignment. The range of duration values is from 1 to 1,000,000 seconds. Note that the maximum value of this parameter is the same as the value you have set as the Delay Between Call Attempts parameter. Call attempt timeout value determines the maximum duration of the call attempt. If the call attempt timeout value is exceeded before the cellular system has assigned a traffic channel, the call attempt will be stopped and the attempt will be marked as a failure. The range of the Call Attempt Timeout values is from 5 to 60 seconds. The value is recommended to be at least 10 seconds.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
107
Voice Call Properties TETRA
Note that the TETRA tab is visible only if you are measuring with a TETRA mobile. Voice call properties are needed to establish the voice calls. Click the Voice Number Properties button in the Measurement Properties dialog and the Voice Call Properties dialog will be opened.
Number defines the number to be called. It must be a valid phone number. The number must be such that the line stays open for a user-defined time and some speech or sound is transferred on the line. The Number field can contain up to 17 characters. Call type defines what kind of calls will be made. There are five different options in TETRA networks: duplex, semiduplex, group, direct, and PSTN. Duplex: Normal call between two terminals; both parties can speak at the same time Semiduplex: Call between two terminals, but only one party can speak at a time by pressing the PTT (Press-to-Talk) button Group: Call from one terminal to a group; all terminals having that group active can listen, and by pressing the PTT button, also speak Direct: Call between terminals which bypasses the network, by means of the PTT button
108
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
PSTN: Call from terminal to fixed line or to another cellular mobile
Note that the Script Settings table is activated only if you access this dialog through the Script Editor. See chapter Making Script Files for more information on making scripts. Call duration determines the time that the call lasts in seconds. The duration timer is started from the channel assignment. The range of duration values is from 1 to 1,000,000 seconds. Note that the maximum value of this parameter is the same as the value you have set as the Delay Between Call Attempts parameter. Call attempt timeout value determines the maximum duration of the call attempt. If the call attempt timeout value is exceeded before the cellular system has assigned a traffic channel, the call attempt will be stopped and the attempt will be marked as a failure. The range of the Call Attempt Timeout values is from 5 to 60 seconds. The value is recommended to be at least 10 seconds.
Push-to-Talk (PTT) Testing
Nemo Outdoor supports QChat, a Push-to-Talk (PTT) technology developed by Qualcomm. Push-to-Talk (PTT) calls must be performed using the keypad of the phone when used with Nemo Outdoor. Normal call events and statistics are written when attempting or ending PTT calls. Different states of PTT calls, such as idle, getting ready to receive, receiving, transmitting are written to VCHI event. Please see the file format specification for further information. RTP packets are recorded and decoded with Nemo Outdoor. Qchat is an optional feature in Nemo Outdoor and requires a license option.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
109
VOICE QUALITY MEASUREMENTS
Nemo Outdoor supports mobile-to-mobile and mobile-to-fixed-to-mobile voice quality measurements in GSM, WCDMA, CDMA2000, and TD-SCDMA. Please refer to the Nemo Voice Quality Guide document for complete instructions on setting up and making voice quality measurements.
MAKING VIDEO CALLS
Click the Video Call button in the Measurement Properties, Measurement Settings dialog to access the Video Call Properties dialog. These settings are needed for making video calls.
Number defines the number where the video call will be made. When Request voice call callback is selected, the application sends callback command to Nemo Server using DTMF tones. DTMF tones are sent separately from audio so naturally DTMF tones do not affect to MOS score. If Nemo server is connected to analog telephone lines (PSTN) user must define the correct callback number on the server side using Nemo Server manager application. If ISDN lines are used with Nemo Server and test terminals are selected to be sent also caller id to Nemo server, callback number is recognized automatically. Note that this functionality requires Nemo Server version 2.5.0 or later. Select the Voice quality option to activate the voice quality settings. Note that the voice quality settings are available only if your license supports voice quality measurements.
110
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Reference sample filename defines the reference sample to which the received audio sample is compared. If you want to use your own test samples, make sure that the samples are of 8KHz sampling rate, 16-bit linear coded .wav files that are no longer than ten seconds in length. With the Terratec sound card, sampling rate can be 8kHz or 16 kHz (for WB-AMR testing) and sample length a maximum of 30 seconds. Select the Save sample files option to save the received voice quality sample files. Prefix for received sample files refers to the prefix that is added to the file names of received audio sample files. If you leave this field empty, the received audio files are not stored. When a prefix is defined, Nemo Outdoor names the files as follows: prefix_mos_date_time.wav where prefix is the user-defined prefix, mos the voice quality score on a MOS scale with one decimal precision but without decimal point, date in DDMMYYYY format, and time in HHMMSS format. For example: terminal1_34_15112004_143045.wav. Save only samples below threshold determines the value below which the samples are saved. The threshold values range from 0-5, 0 being the worst and 5 the best value. The default threshold value is 5, which means that all samples are saved. Note that the Script Settings view is activated only if you access this dialog through the Script Editor. See chapter Making Script Files for more information on making scripts. Note that with voice quality measurements when calling Nemo Server, the delay time between a new call attempt and the previous call disconnect must be at least 10 seconds. CDMA specific settings, Service option defines the service option used for the test call. Note that the CDMA specific setting is activated only if you are measuring with a CDMA mobile. Call duration determines the time that the call lasts in seconds. The duration timer is started from the channel assignment. The range of duration values is from 1 to 1,000,000 seconds. Note that the maximum value of this parameter is the same as the value you have set as the Delay Between Call Attempts parameter. Call attempt timeout value determines the maximum duration of the call attempt. If the call attempt timeout value is exceeded before the cellular system has assigned a traffic channel, the call attempt will be stopped and the attempt will be marked as a failure. The range of the Call Attempt Timeout values is from 5 to 60 seconds. The value is recommended to be at least 10 seconds. Note that video calls with the generic Qualcomm handler require some further settings to be made prior to making the call. Go to Measurement Properties | General, and press the Advanced button. In the Advanced Properties dialog, you need to select the applicable video call method for the measurement from the drop-down menu.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
111
Select the method based on the list below, or try each Method separately and select the one that works. The selected method is saved to the device configuration file. Method 1 - Samsung Z105 Method 2 - Samsung Z107 Method 3 - Samsung Z140, Samsung Z500, Samsung P920, Samsung Z560, Samsung ZX20 Method 4 - Samsung ZV10 Method 5 - Qualcomm TM 6250 reference mobile Method 6 - Qualcomm TM 6250 reference mobile Method 7 - LG KU950 , LG KF700 Method 8 - Samsung U800 (always required to first make a video call using the terminal keypad) Method 9 - Samsung G800
To make video calls and video quality calls:
1. In the Measurement Properties, Configuration dialog, insert the phone number that you wish to use in the test call in the Video Number field. Click OK. 2. Select Make Video Call from the Device Commands menu or from the Measurement menu. Alternatively, you can activate a script by clicking the Start/Stop Scripts button. Note that after you have activated the script, you cannot control the measurement manually until the script is finished or you interrupt the script by clicking the Start/Stop Scripts button.
112
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Note that video quality parameters are supported only with certain Motorola test terminals. 3. When you wish to finish the call in manual mode, select Stop Video Call. If you are running a script, wait until the script is finished.
Note! Video call testing is supported on any video call capable terminal based on Qualcomm chipset. However, the user must remember to select the correct method from Measurement Properties | General | Advanced Properties prior to making the call. The selected method is saved to the device configuration file. Terminals verified by Anite Finland support video calls. It is possible that if the device is not included in the list of supported terminals, the video call functionality does not work.
DATA TRANSFERS
With mobiles supporting CS and PS data, you can make data transfers. In Nemo Outdoor, you have several data protocol options for making data transfers: you can use the Iperf for TCP/UDP, FTP, SFTP, HTTP, HTTP Browsing, POP3, SMTP, IMAP, WAP, or streaming. The Nemo Outdoor Multi system enables multiple simultaneous data connections. Each data transfer needs to be set up and configured individually. To view data in Packet decoder grids during playback, you need to enable the packet decoding function (Measurement settings button General Properties, Advanced button) prior to performing data measurements. Select Full or Partial in the Enable IP Capture field. A separate .pcap-file will be generated for the measurement, and this file needs to accompany the measurement file under the same folder when viewing and decoding packet capture information in Packet Decoder grids in Nemo Outdoor.
Configuring the Data Connection
Before you can start making data transfers you need to define the actual connection that is used for the transfer. The setup is different for CS and PS data transfers. If you are making CS data transfers, see chapter Data Call Properties. If you are making PS data transfers, see chapter Packet Session Settings.
Data Call Properties
Data Call properties are needed to establish the circuit-switched data connection. Open the Data Call Properties dialog by double-clicking the Circuit-Switched Data Call item in the Devices view. There are separate views for GSM, UMTS, and CDMA. The parameters are the same. The UMTS and CDMA views just have fewer parameters. A PPP compatible dial-up server is required for CS data testing. Settings related to the dial-up server (number, username, and password) are operator-specific.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
113
Number defines the number to be called of the dial-up server. Username refers to the dial-up server username. Password refers to the dial-up server password. Transparent mode defines whether transparent or non-transparent mode is used in the CS data call. Compression defines if no compression or v.42bis compression is used. Modem type refers to the modem type that the dial-up server is using. The alternatives are Analog (v.34) and ISDN (v.110 and v.120). Timeslots (UL/DL) defines the number of timeslots for each direction. Coding defines the coding scheme used in the air interface. Enable automatic link adaptation option allows you to disable and enable Automatic Link Adaptation (ALA). The ALA technology controls power levels and automatically selects the best channel coding.
114
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Packet Session Settings
Packet session settings are needed to establish the packet switched data connection. Double-click the Packet Session item in the Devices view to access the Packet Session Settings dialog.
All the parameters in this dialog are operator specific. You must select the correct parameters to make the packet transfer function. Contact the operator of the network that you are measuring.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
115
TCP/UDP Protocol Configuration (Iperf)
Note that it is required that Nemo Server be used with Iperf testing as the original Iperf service is slightly modified for optimal performance. Open the TCP/UDP Protocol Configuration dialogs by double-clicking the TCP (IPerf) and UDP (IPerf) items in the Devices view.
Host name is the IP address used in Nemo Server. Note that if you have multiple simultaneous data connections on different terminals, each connection must have its own IP address. Note that if you are doing multiple simultaneous data transfers on a single terminal, the same IP address can be used. Note that Firewall should be turned off. Host port refers to the port used by Nemo Server. For TCP and UDP protocols, the default port is 5001. Connection timeout defines the time in seconds for how long Nemo Outdoor waits for the connection to be established. If a connection is not established within the defined time, connection attempt will fail. Listen port refers to the port used by the client. For TCP and UDP protocols, the default port is 6015. Direction defines whether you are sending or receiving data, or both.
116
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Transfer timeout determines the maximum waiting time after data connection. If the transfer attempt timeout value is exceeded before data connection, the data connection attempt will be stopped and the attempt will be marked as a failure. The range of Transfer timeout values is from 0 to 60 seconds. The value is recommended to be at least 10 seconds. TCP window size defines the size of the receive window during TCP/IP transmission. If it is too small, it can decrease the maximum data throughput, and if it is too high it can increase the retransmission round-trip time (RTT). To be able to avoid decrease of data throughput, the window size should be at least the maximum throughput multiplied by RTT. For example, with HSDPA with category 8 the maximum throughput is about 7.3 Mbit/s and RTT is about 100 ms. To avoid reduction of the throughput the TCP window size should be set at least to 7.3 Mbit/s * 0.1 s = 730 kbit = 91.25 kB. Downlink testing (these values are indicative only):
Max. throughput 64 kbps (GPRS/ EDGE) 128 kbps (GPRS/ EDGE) 256 kbps (GPRS/ EDGE) 384kbps (Rel. 99) HSDPA 1.8Mbps UE category 3 & 4 HSDPA 3.6Mbps UE category 5 & 6 HSDPA 7.3Mbps UE category 7 & 8 HSDPA 10.2Mbps UE category 9 HSDPA 14.4Mbps UE category 9 ~RTT (ms) 600 600 600 200 100 TCP window size (kbit) 38.4 76.8 153.6 76.8 180 TCP window size (kB) 4.8 9.6 19.2 9.6 22.5
100
360
45
100
730
91.25
100
1020
127.5
100
1440
180
TCP buffer size is the amount of data that can be buffered during a connection without a validation from the receiver. It can be between 1 and 8291 kbytes. UDP buffer size is the amount of data that can be buffered during a connection without a validation from the receiver. It can be between 1 and 8291 kbytes. UDP bandwidth defines how much data is attempted to be transmitted. Since UDP does not guarantee successful data transmission, it is not limited by maximum throughput of the lower layers. If higher data transmission rate is used, the packet error rate (PER) increases. For example, if lower layers are capable of transmitting 100kbit/s and UDP bandwidth is configured to 400kbit/s, there should be a 75% packet error rate (only every fourth packet has been able to transmit successfully). Naturally UDP bandwidth should not be configured too small since it limits the maximum throughput that is not normally desired.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
117
UDP datagram size defines the size of the UDP packet in bytes. It should be smaller than the maximum packet size of the lower layers to be able to avoid packet fragmentation in the lower layers. Packet fragmentation has a huge negative impact to the achieved data throughput and it should be avoided. On the other hand if too small UDP packet size is used the portion of the UDP and IP header increases which decreases the amount of transmitted user data with the result of smaller data throughput. Normally good maximum value for UDP datagram is a little bit less than maximum Ethernet packet size which is 1,500 bytes. A good default value for the UDP datagram size is 1,460 bytes. Number of threads defines the number of parallel Iperf data transfers. Transfer duration defines the length of the data transfer in seconds. Transfer data size defines the length of the total data transfer in kilobytes; that is, the transfer finishes when the defined amount of data has been transferred. The size of the individual data packages is defined in the Packet Size field. Note that if you have chosen Transfer data size from the Packet Transfer Properties dialog, the Transfer duration option will be disabled. This is because when the Transfer data size option is used, the transmission will end after a certain amount of data has been transferred. It is not limited by time. Next, click OK to return to the Measurement Properties dialog. Click the PDP Context Properties button.
Configuring the FTP Protocol
Nemo Outdoor has an integrated FTP client, which can be used to measure data transfer rates between Nemo Outdoor and the FTP server. The server can be any standard FTP server. Current data throughput and transferred data size are reported during transfer. The FTP module supports firewall-friendly passive mode transfers. Normally when a data transfer is initialized, the server opens a new connection to the client and then data is transferred through this connection. Some firewalls may be configured to refuse any incoming connection requests, and in that case the data transfer would fail. With passive mode, the client always opens those new connections so the firewall does not block the connection. A PPP compatible dial-up server is required for CS data testing. Settings related to the dial-up server (number, username, and password) are operator-specific. If you encounter problems with the data transfer, deactivate the firewall on the computer where you are running Nemo Outdoor.
To set up data measurements using FTP
1. Follow the instructions in the Dial-Up Networking Setup Guide to set up a dial-up connection and to connect and configure the measurement devices. 2. Define measurement-related settings in the Measurement Properties dialog (see Measurement Properties Measurement Settings) 3. Configure the data connection for CS data (see Data Call Properties) or PS data (see Packet Session Settings). 4. Define FTP transfer-related settings in the FTP Transfer Properties dialog. 5. Create a script (optional) (see Making Script Files).
118
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
6. After you have completed the setup, you can start the actual data transfer (see Making Data Transfers).
FTP Transfer Properties
Open the FTP Transfer Properties dialog by double-clicking the FTP item in the Devices view.
Host name is the IP address of the FTP server used. Note that if you have multiple simultaneous data connections on different terminals, each connection must have its own IP address. Note that if you are doing multiple simultaneous data transfers on a single terminal, the same IP address can be used. If you encounter problems with the data transfer, deactivate the firewall on the computer on which you are running Nemo Outdoor. Port refers to the port used by the FTP server. In the Username field you must enter a valid username for the FTP server. In the Password field you must enter a valid password for the FTP server. Some firewalls may be configured to refuse any incoming connection requests, and in that case the data transfer would fail. With passive mode, the client always opens those new connections so the firewall does not block the connection. Select the Passive mode option to activate passive mode.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
119
Connection timeout defines the time in seconds for how long Nemo Outdoor waits for the connection to be established. If a connection is not established within the defined time, connection attempt will fail. Proxy type defines the type of the proxy used in the measurements. Supported types are Tunneling, SOCKS4, and SOCKS5. Address refers to the address of the proxy. Port refers to the port used by the proxy. In the Username field you must enter a valid username for the proxy. In the Password field you must enter a valid password for the proxy. Direction defines whether you are sending or receiving data. Buffer size defines the transmit/receive buffer used with the transfer protocol in kilobytes. Transfer timeout defines the time in seconds for how long Nemo Outdoor waits during a transfer if there is a break in the data flow. If the transfer does not continue within the defined time, transfer will fail. Transfer attempts defines how many times an interrupted data transfer is resumed during one FTP session. Number of threads defines in how many threads the test file is split during an FTP transfer. For example, the size of the downloaded file is 10MB. The number of threads is set to five. Nemo Outdoor splits the 10MB file into five fragments with the size of 2MB each. All five FTP transfer sessions are started simultaneously. Each thread creates a new FTP session and transfers a fragment of the file. Total application data throughput is recorded including all threads. Resume is not supported with multi threaded FTP transfers. In case of a data drop, all threads will start from the beginning. Remote file defines the name and location of the file that is on the FTP server. If you are receiving data, this is the source file. If you are sending data, this is the destination file. Note that if you have multiple simultaneous data connections and the direction is set to send for all of them, you must define a different remote file for each connection. Otherwise the different data connections will try to write in the same file. Also note that if there are several testing units using the same FTP server, we recommend that you use a unique file name extension (e.g., filename_tester1.txt, filename_tester2.txt, etc.) for each unit to avoid a situation where two testing units are trying to write in the same file. Local file defines the name and location of the file that is on your laptop. If you are receiving data, this is the output file. If you are sending data, this is the source file. The default location for these files is defined in the User Interface Properties Paths dialog. Generate local file allows you to generate random binary files with user-specified file size. This functionality is available with FTP upload testing. The file is named with following format <IMEI>_<file size in kB>.bin. Select the Write local file to disk option to save the downloaded file on disk. Note that if you have multiple simultaneous data connections and the direction is set to receive for all of them, you must define a different local file for each connection. Otherwise the different data connections will try to write in the same file.
120
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Configuring the SFTP Protocol
Nemo Outdoor has an integrated SFTP client, which can be used to measure data transfer rates between Nemo Outdoor and the SFTP server. The server can be any standard SFTP server. Current data throughput and transferred data size are reported during transfer. The SFTP module supports firewall-friendly passive mode transfers. Normally when a data transfer is initialized, the server opens a new connection to the client and then data is transferred through this connection. Some firewalls may be configured to refuse any incoming connection requests, and in that case the data transfer would fail. With passive mode, the client always opens those new connections so the firewall does not block the connection. A PPP compatible dial-up server is required for CS data testing. Settings related to the dial-up server (number, username, and password) are operator-specific. If you encounter problems with the data transfer, deactivate the firewall on the computer where you are running Nemo Outdoor.
To set up data measurements using SFTP
1. Follow the instructions in the Dial-Up Networking Setup Guide to set up a dial-up connection and to connect and configure the measurement devices. 2. Define measurement-related settings in the Measurement Properties dialog (see Measurement Properties Measurement Settings) 3. Configure the data connection for CS data (see Data Call Properties) or PS data (see Packet Session Settings). 4. Define SFTP transfer-related settings in the SFTP Transfer Properties dialog. 5. Create a script (optional) (see Making Script Files). 6. After you have completed the setup, you can start the actual data transfer (see Making Data Transfers).
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
121
SFTP Transfer Properties
Open the SFTP Transfer Properties dialog by double-clicking the SFTP item in the Devices view.
Host name is the IP address of the SFTP server used. Note that if you have multiple simultaneous data connections on different terminals, each connection must have its own IP address. Note that if you are doing multiple simultaneous data transfers on a single terminal, the same IP address can be used. If you encounter problems with the data transfer, deactivate the firewall on the computer on which you are running Nemo Outdoor. Port refers to the port used by the SFTP server. In the Username field you must enter a valid username for the SFTP server. In the Password field you must enter a valid password for the SFTP server. Connection timeout defines the time in seconds for how long Nemo Outdoor waits for the connection to be established. If a connection is not established within the defined time, connection attempt will fail. Proxy type defines the type of the proxy used in the measurements. Supported types are Tunneling, SOCKS4, and SOCKS5. Address refers to the address of the proxy. Port refers to the port used by the proxy.
122
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
In the Username field you must enter a valid username for the proxy. In the Password field you must enter a valid password for the proxy. Direction defines whether you are sending or receiving data. Buffer size defines the transmit/receive buffer used with the transfer protocol in kilobytes. Transfer timeout defines the time in seconds for how long Nemo Outdoor waits during a transfer if there is a break in the data flow. If the transfer does not continue within the defined time, transfer will fail. Transfer attempts defines how many times an interrupted data transfer is resumed during one SFTP session. Remote file defines the name and location of the file that is on the SFTP server. If you are receiving data, this is the source file. If you are sending data, this is the destination file. Note that if you have multiple simultaneous data connections and the direction is set to send for all of them, you must define a different remote file for each connection. Otherwise the different data connections will try to write in the same file. Also note that if there are several testing units using the same SFTP server, we recommend that you use a unique file name extension (e.g., filename_tester1.txt, filename_tester2.txt, etc.) for each unit to avoid a situation where two testing units are trying to write in the same file. Local file defines the name and location of the file that is on your laptop. If you are receiving data, this is the output file. If you are sending data, this is the source file. The default location for these files is defined in the User Interface Properties Paths dialog. Generate local file allows you to generate random binary files with user-specified file size. This functionality is available with SFTP upload testing. The file is named with following format <IMEI>_<file size in kB>.bin. Select the Write local file to disk option to save the downloaded file on disk. Note that if you have multiple simultaneous data connections and the direction is set to receive for all of them, you must define a different local file for each connection. Otherwise the different data connections will try to write in the same file.
Configuring the HTTP(S) Protocol
The HTTP(S) testing functionality offers the possibility to test how data is transferred through the HTTP(S) protocol. The HTTP(S) protocol is used in web browsing. In HTTP(S) testing, the user selects one file that will be downloaded or uploaded through the HTTP(S) protocol and this data transfer is measured. A PPP compatible dial-up server is required for CS data testing. Settings related to the dial-up server (number, username, and password) are operator-specific.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
123
To set up data measurements using HTTP(S)
1. Follow the instructions in the Dial-Up Networking Setup Guide to set up a dial-up connection and to connect and configure the measurement devices. 2. Define measurement-related settings in the Measurement Properties dialog (see Measurement Properties Measurement Settings) 3. Configure the data connection for CS data (see Data Call Properties) or PS data (see Packet Session Settings). 4. Define HTTP transfer-related settings in the HTTP(S) Transfer Properties dialog. 5. Create a script (optional) (see Making Script Files). 6. After you have completed the setup, you can start the actual data transfer (see Making Data Transfers).
HTTP(S) Transfer Properties
Open the HTTP Transfer Properties dialog by double-clicking the HTTP item in the Devices view. The same dialog is used for defining HTTPS transfer properties.
In the HTTP Transfer Properties dialog, you can define the required data transfer settings. Proxy Type defines the type of the proxy used in the measurements. Supported types are Tunneling, SOCKS4, and SOCKS5. Address refers to the address of the proxy. Port refers to the port used by the proxy. Connection timeout defines the time in seconds for how long Nemo Outdoor waits for the connection to be established. If a connection is not established within the defined time, connection attempt will fail. In the Username field you must enter a valid username for the proxy. In the Password field you must enter a valid password for the proxy.
124
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Direction defines whether the HTTP file is sent or received. Buffer size defines the transmit/receive buffer used with the transfer protocol in kilobytes. Transfer timeout defines the time in seconds for how long Nemo Outdoor waits during a transfer if there is a break in the data flow. If the transfer does not continue within the defined time, transfer will fail. Number of threads enables all the threads to be started simultaneously with the same time stamp. The number of threads can be defined by the user. Each thread transfers the entire file. URL defines the IP address of the test file that will be downloaded when data is received. For example, http://www.yourcompany.com/testfile.htm. Only one file will be downloaded at a time. If you are sending HTTP data, URL defines the destination. To define a port for the transfer, type the port number after the URL, for example, http://www.yourcompany.com:85. Note that if you have multiple simultaneous data connections on different terminals, you must define a different URL from different servers for each of them. Note that if you have multiple simultaneous data connections on a single terminal, you can use the same URL for all of them. If you encounter problems with the data transfer, deactivate the firewall on the computer where you are running Nemo Outdoor. To make consecutive transfers, create a script with several HTTP transfers. See chapter Making Script Files for instructions on making scripts. Local File defines the output file and location for HTTP testing. The default location for these files is defined in the User Interface Properties Paths dialog. Note that if you have multiple simultaneous data connections and the direction is set to receive for all of them, you must define a different local file for each connection. Otherwise the different data connections will try to write in the same file. Generate local file allows you to generate random binary files with user-specified file size. This functionality is available with HTTP upload testing. The file is named with following format <IMEI>_<file size in kB>.bin. Select the Write local file to disk option to save the downloaded file on disk. Select the Use SSL encryption option to transfer the files over a HTTPS connection.
Configuring the (HTTP) Browsing Protocol
The HTTP Browser testing functionality offers the possibility to test how data is transferred through the HTTP Browsing protocol. The HTTP protocol is used in web browsing. In HTTP testing, the user selects one URL address that will be downloaded through the HTTP protocol and this data transfer is measured. If you are experiencing problems with HTTP browsing testing, such as, the page downloading time is increased, disable the following LAN settings: Automatically detect settings and Proxy server.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
125
To set up data measurements using HTTP browsing protocol
1. Follow the instructions in the Dial-Up Networking Setup Guide to set up a dial-up connection and to connect and configure the measurement devices. 2. Define measurement-related settings in the Measurement Properties dialog (see Measurement Properties Measurement Settings) 3. Configure the data connection for CS data (see Data Call Properties) or PS data (see Packet Session Settings). 4. Define HTTP browsing-related settings in the Browser Transfer Properties dialog. 5. Create a script (optional) (see Making Script Files). 6. After you have completed the setup, you can start the actual data transfer (see Making Data Transfers).
Browser Transfer Properties
Open the Browser Transfer Properties dialog by double-clicking the Browsing item in the Devices view.
URL defines the IP address of the test page that will be downloaded. For example, http://www.yourcompany.com/testbrowser.htm. Transfer timeout defines the time in seconds for how long Nemo Outdoor waits during a transfer if there is a break in the data flow. If the transfer does not continue within the defined time, the transfer will fail.
126
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
If Decode content information is selected, information about the images, texts and links are written to measurement file including the number of content elements and size information. Close window after transfer closes the browser window after the data transfer. The downloaded page can be seen during the measurement and the total time to download the whole page is written to the measurement file. The cache and cookies information is cleared after every download. PPP and RLC layer data throughputs are logged during the browser testing. The average PPP and RLC data throughputs are also available. Average results are calculated from the time PDP context was active (PAC- PAD). The connection setup time and the download time can be seen in Nemo Outdoor or calculated with Nemo Analyze For multi browser testing with single computer it is recommended that Nemo Server be used for multiple simultaneous data connections, e.g. for benchmarking purposes as each connection must have its own IP address. If you encounter problems with the data transfer, deactivate the firewall on the computer where you are running Nemo Outdoor.
Configuring the POP3 Protocol
POP3, SMTP, and IMAP testing offers the possibility to send emails through Nemo Outdoor and to monitor how the message is transferred. POP3 and IMAP protocols are used for receiving and SMTP protocol for sending emails. A PPP compatible dial-up server is required for CS data testing. Settings related to the dial-up server (number, username, and password) are operator-specific.
To set up data measurements using POP3
1. Follow the instructions in the Dial-Up Networking Setup Guide to set up a dial-up connection and to connect and configure the measurement devices. 2. Define measurement-related settings in the Measurement Properties dialog (see Measurement Properties Measurement Settings) 3. Configure the data connection for CS data (see Data Call Properties) or PS data (see Packet Session Settings). 4. Define POP3 Server settings in the E-Mail Settings POP3 dialog. Also define the test e-mails that are used in the measurement. 5. Create a script (optional) (see Making Script Files). 6. After you have completed the setup, you can start the actual data transfer (see Making Data Transfers).
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
127
E-Mail Settings POP3
Open the E-Mail Settings (POP3) dialog by double-clicking the POP3 item in the Devices view.
POP3 Server Settings define settings for the POP3 server used in the measurements. Server name defines a name or an IP address for the POP3 server. Note that if you have multiple simultaneous data connections on different terminals, each connection must have its own IP address. Note that if you have multiple simultaneous data connections on a single terminal, the same IP address can be used. Port refers to the port used by the POP3 server. In the Username field you must enter a valid username for the POP3 server. In the Password field you must enter a valid password for the POP3 server. Select the Use SSL encryption option to apply SSL encryption to the test email. Connection timeout defines the time in seconds for how long Nemo Outdoor waits for the connection to be established. If a connection is not established within the defined time, connection attempt will fail. Proxy server settings define settings for the proxy server used in the measurements. Proxy type defines the type of the proxy used in the measurements. Supported types are Tunneling, SOCKS4, and SOCKS5. Address refers to the address of the proxy. Port refers to the port used by the proxy.
128
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
In the Username field you must enter a valid username for the proxy. In the Password field you must enter a valid password for the proxy. POP3 receiving options define how the test e-mails are received and handled by Nemo Outdoor. Transfer timeout defines the time in seconds for how long Nemo Outdoor waits during a transfer if there is a break in the data flow. If the transfer does not continue within the defined time, transfer will fail. Buffer size defines the transmit/receive buffer used with the transfer protocol in kilobytes. Maximum number of messages to receive defines the maximum number of messages received from the e-mail server. Select the Delete messages after receiving option to delete all received test e-mails. This will save disk space. The View button opens a received test message in the E-Mail Editor dialog.
Configuring the SMTP Protocol
POP3, SMTP, and IMAP testing offers the possibility to send emails through Nemo Outdoor and to monitor how the message is transferred. POP3 and IMAP protocols are used for receiving and SMTP protocol for sending emails. A PPP compatible dial-up server is required for CS data testing. Settings related to the dial-up server (number, username, and password) are operator-specific.
To set up data measurements using SMTP
1. Follow the instructions in the Dial-Up Networking Setup Guide to set up a dial-up connection and to connect and configure the measurement devices. 2. Define measurement-related settings in the Measurement Properties dialog (see Measurement Properties Measurement Settings) 3. Configure the data connection for CS data (see Data Call Properties) or PS data (see Packet Session Settings). 4. Define SMTP Server settings in the E-Mail Settings SMTP dialog. Also define the test e-mails that are used in the measurement. 5. Create a script (optional) (see Making Script Files). 6. After you have completed the setup, you can start the actual data transfer (see Making Data Transfers).
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
129
E-Mail Settings SMTP
Open the E-Mail Settings (SMTP) dialog by double-clicking the SMTP item in the Devices view.
SMTP Server Settings define settings for the SMTP server used in the measurements. Server name defines a name or an IP address for the SMTP server. Note that if you have multiple simultaneous data connections, each connection must have its own IP address. Note that if you have multiple simultaneous data connections on a single terminal, the same IP address can be used. Note that some operators prevent accessing SMTP services other than their own. Therefore, it is not possible to test SMTP against the Nemo server with those operators' SIM cards. Port refers to the port used by the SMTP server. In the Username field you must enter a valid username for the SMTP server. In the Password field you must enter a valid password for the SMTP server. Connection timeout defines the time in seconds for how long Nemo Outdoor waits for the connection to be established. If a connection is not established within the defined time, connection attempt will fail. Select the Use SSL encryption option to apply SSL encryption to the test email. Proxy server settings define settings for the proxy server used in the measurements.
130
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Proxy type defines the type of the proxy used in the measurements. Supported types are Tunneling, SOCKS4, and SOCKS5. Address refers to the address of the proxy. Port refers to the port used by the proxy. In the Username field you must enter a valid username for the proxy. In the Password field you must enter a valid password for the proxy. Transfer timeout defines the time in seconds for how long Nemo Outdoor waits during a transfer if there is a break in the data flow. If the transfer does not continue within the defined time, transfer will fail. Buffer size defines the transmit/receive buffer used with the transfer protocol in kilobytes. Messages to be sent defines the test messages used in the SMTP test. Click the Edit button to open the E-Mail Editor where you can type the test message and attach files to the message.
E-Mail Editor
Use the E-Mail Editor dialog to type and edit test messages. You can attach files to the test messages and save messages for later use.
New E-Mail Message button saves the current changes and opens an empty E-Mail Editor. Open E-Mail Message button opens an Open dialog where you can open premade e-mail messages.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
131
Save E-Mail Message button saves the current e-mail message for later use. Save As button saves the current e-mail message with a different name for later use. Save Attachments button saves the files attached to the test message to a selected location. Attachments field displays a list of attachments in the test e-mail. Add button opens an Open dialog for adding an attachment to the test message. Remove button removes the selected attachment from the test message.
Configuring the IMAP Protocol
POP3, SMTP, and IMAP testing offers the possibility to send emails through Nemo Outdoor and to monitor how the message is transferred. POP3 and IMAP protocols are used for receiving and SMTP protocol for sending emails. A PPP compatible dial-up server is required for CS data testing. Settings related to the dial-up server (number, username, and password) are operator-specific.
To set up data measurements using IMAP
1. Follow the instructions in the Dial-Up Networking Setup Guide to set up a dial-up connection and to connect and configure the measurement devices. 2. Define measurement-related settings in the Measurement Properties dialog (see Measurement Properties Measurement Settings) 3. Configure the data connection for CS data (see Data Call Properties) or PS data (see Packet Session Settings). 4. Define IMAP Server settings in the E-Mail Settings IMAP dialog. Also define the test e-mails that are used in the measurement. 5. Create a script (optional) (see Making Script Files). 6. After you have completed the setup, you can start the actual data transfer (see Making Data Transfers).
132
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
E-Mail Settings IMAP
Open the E-Mail Settings (IMAP) dialog by double-clicking the IMAP item in the Devices view.
IMAP server settings define settings for the IMAP server used in the measurements. Server name defines a name or an IP address for the server. Note that if you have multiple simultaneous data connections, each connection must have its own IP address. Note that if you have multiple simultaneous data connections on a single terminal, the same IP address can be used. Port refers to the port used by the server. In the Username field you must enter a valid username for the server. In the Password field you must enter a valid password for the server. Connection timeout defines the time in seconds for how long Nemo Outdoor waits for the connection to be established. If a connection is not established within the defined time, connection attempt will fail. Select the Use SSL encryption option to apply SSL encryption to the test email. Proxy server settings define settings for the proxy server used in the measurements. Proxy type defines the type of the proxy used in the measurements. Supported types are Tunneling, SOCKS4, and SOCKS5. Address refers to the address of the proxy.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
133
Port refers to the port used by the proxy. In the Username field you must enter a valid username for the proxy. In the Password field you must enter a valid password for the proxy. IMAP receiving options define how the test e-mails are received and handled by Nemo Outdoor. Transfer timeout defines the time in seconds for how long Nemo Outdoor waits during a transfer if there is a break in the data flow. If the transfer does not continue within the defined time, transfer will fail. Buffer size defines the transmit/receive buffer used with the transfer protocol in kilobytes. Maximum number of messages to receive defines the maximum number of messages received from the e-mail server. Select the Delete messages after receiving option to delete all received test e-mails. This will save disk space. The View button opens a received test message in the E-Mail Editor dialog.
Configuring the WAP Protocol
The WAP testing functionality offers the possibility to test how data is transferred through the WAP protocol. The WAP protocol is used, for example, in web browsing. In the WAP testing, the user selects one file that will be downloaded through the WAP protocol and this data transfer is measured. A PPP compatible dial-up server is required for CS data testing. Settings related to the dial-up server (number, username, and password) are operator-specific.
To set up data measurements using WAP
1. Follow the instructions in the Dial-Up Networking Setup Guide to set up a dial-up connection and to connect and configure the measurement devices. 2. Define measurement-related settings in the Measurement Properties dialog (see Measurement Properties Measurement Settings) 3. Configure the data connection for CS data (see Data Call Properties) or PS data (see Packet Session Settings). 4. Define WAP Gateway settings in the WAP Transfer Properties dialog. 5. Create a script (optional) (see Making Script Files). 6. After you have completed the setup, you can start the actual data transfer (see Making Data Transfers).
134
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
WAP Transfer Properties
Open the WAP Transfer Properties dialog by double-clicking the WAP item in the Devices view.
WAP transfer properties define settings for the WAP gateway used in the measurements. WAP gateway host defines a name or an IP address for the WAP gateway. Note that if you have multiple simultaneous data connections, each connection must have its own IP address. WAP gateway port refers to the port used by the WAP gateway. Connection timeout defines the time in seconds for how long Nemo Outdoor waits for the connection to be established. If a connection is not established within the defined time, connection attempt will fail. Transfer timeout defines the time in seconds for how long Nemo Outdoor waits during a transfer if there is a break in the data flow. If the transfer does not continue within the defined time, transfer will fail. URL defines the IP address of the test file that will be downloaded. For example, http://www.yourcompany.com/testfile.htm. Only one file will be downloaded at a time. Note that if you have multiple simultaneous data connections on different terminals, you must define a different URL from different servers for each of them. Note that if you have multiple simultaneous data connections on a single terminal, the same URL can be used. If you encounter problems with the data transfer, deactivate the firewall on the computer where you are running Nemo Outdoor. To make consecutive downloads, create a script with several WAP transfers. See chapter Making Script Files for instructions on making scripts. Local file defines the output file and location for WAP testing. The default location for these files is defined in the User Interface Properties Paths dialog.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
135
Note that if you have multiple simultaneous data connections and the direction is set to receive for all of them, you must define a different local file for each connection. Otherwise the different data connections will try to write in the same file.
Configuring the Streaming Protocol
Please note that video streaming with rtsp links and IP packet capturing are not supported on 64-bit Windows. HTTP streaming can be performed with both 32 and 64-bit operating systems. Note that to make video streaming quality measurements, Microsoft Network Monitor must be installed and IP packet capturing must be enabled. Refer to chapter IP Packet Capturing for more information. The Streaming testing functionality offers the possibility to test how data is transferred through the streaming protocol. The streaming protocol is used, for example, in video streaming. In the streaming testing, the user selects one file that will be downloaded through the streaming protocol and this data transfer is measured. A PPP compatible dial-up server is required for CS data testing. Settings related to the dial-up server (number, username, and password) are operator-specific. In order to make streaming measurements with Nemo Outdoor version 6.40 and onwards, you need to have VLC player v. 2.0.4 or newer (32-bit) installed on the computer. You can download VLC from Nemo User Club www.nemotechnologies.com/index (Nemo Outdoor - Drivers for Test Mobiles and Other Devices) or from http://www.videolan.org/vlc. With Nemo Outdoor 6.2 and older versions, you need to have RealPlayer version 11 installed on the computer. You can download RealPlayer 11 from Nemo User Club www.nemotechnologies.com/index (Nemo Outdoor - Drivers for Test Mobiles and Other Devices).
To set up data measurements using streaming:
1. Install VLC. 2. Install Microsoft Network Monitor. 3. Follow the instructions in the Dial-Up Networking Setup Guide to set up a dial-up connection and to connect and configure the measurement mobile. 4. Define measurement-related settings in the Measurement Properties Measurement Settings dialog. Also define the test files that are used in the measurement. 5. Configure the data connection for CS data (see Data Call Properties) or PS data (see Packet Session Settings). 6. Define Streaming properties (see Streaming Properties). 7. Create a script (optional) (see Making Script Files). 8. After you have completed the setup, you can start the actual data transfer (see Making Data Transfers).
136
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Streaming Properties
Open the Streaming Properties dialog by double-clicking the Streaming item in the Devices view. Note that if the Streaming item is not available in the Devices view, VLC is not installed on the computer. You can download a free player from http://www.videolan.org/vlc. Note that version 2.0.4 is supported in Nemo Outdoor 6.40.
URL defines the IP address (http or rtsp) of the video file that will be streamed. For example, rtsp://yourcompany.com/testfile.rm or videos from YouTube. Only one file will be downloaded at a time. Note that if you have multiple simultaneous data connections, you must define a different URL from different servers for each of them. To make consecutive downloads, create a script with several streaming sessions. See chapter Making Script Files for instructions on making scripts. Connection timeout defines the time in seconds for how long Nemo Outdoor waits for the connection to be established. If a connection is not established within the defined time, connection attempt will fail. Transfer timeout defines the time in seconds for how long Nemo Outdoor waits during a transfer if there is a break in the data flow. If the transfer does not continue within the defined time, transfer will fail. Rebuffering timeout defines the maximum allowed buffering duration during video playback. Select the Display video stream option if you would like to view the test clip during the streaming. Select the Streaming quality option to activate streaming video quality measurements.
Configuring the Trace Route Protocol
By conducting Trace Route testing functionality, you can trace the servers pinged along the way to the target server. Ping trace route testing can be used to help troubleshooting network or Internet connections. The ping utility tests responsiveness between two hosts, etc. With ping trace route testing it is also possible to check responsiveness and trace the path of the packet from one host to another. In case the network does not respond to ping or trace route requests with trace route testing, it is possible to show the location right before the host that is not responding. A PPP compatible dial-up server is required for CS data testing. Settings related to the dial-up server (number, username, and password) are operator-specific.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
137
To set up data measurements using the Trace Route Protocol
1. Follow the instructions in the Dial-Up Networking Setup Guide to set up a dial-up connection and to connect and configure the measurement devices. 2. Define measurement-related settings in the Measurement Properties dialog (see Measurement Properties Measurement Settings) 3. Configure the data connection for CS data (see Data Call Properties) or PS data (see Packet Session Settings). 4. See below how to define Trace Route properties. 5. Create a script (optional) (see Making Script Files). 6. After you have completed the setup, you can start the actual data transfer (see Making Data Transfers).
Trace Route Properties
Open the Trace Route Properties dialog by double-clicking the Trace Route item in the Devices view.
The Remote host field defines the IP address or URL of the target server of the trace route measurement, for example, www.anite.com. You can use Packet Data Tester or any IP server. Just make sure that the IP server used will respond to the ping. Note that if you have multiple simultaneous data connections with different terminals, each connection must be given its own, separate IP address! Note that if you are doing multiple simultaneous data transfers on a single terminal, the same IP address can be used! If you encounter problems with the data transfer, deactivate the firewall on the computer on which you are running Nemo Outdoor. Transfer timeout determines the maximum timeout seconds since the beginning of the operation. HOP timeout defines the maximum amount of time to wait for an individual hop to complete. HOP limit defines the maximum number of servers to be pinged along the way to the target server. By selecting the Resolve host names item, the names of the pinged servers will be reported by Nemo Outdoor.
138
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Making Data Transfers
After you have configured the data connection (CS or PS data) and selected and configured the data protocol (Iperf (TCP/UDP), FTP, SFTP, HTTP, Browsing, POP3, SMTP, IMAP, WAP, or streaming), you can start making the data transfers. Note! Firewall must be deactivated when making data transfers.
To make data transfers:
1. Activate the script by clicking the Start/Stop Scripts button.
Note that after you have activated the script, you cannot control the measurement manually until the script is finished or you interrupt the script by clicking the Stop Scripts button. 2. To make manual CS data calls, click the Measurement control button in the Devices view and select Start Data Call. Wait until the call is connected and dial-up connection established. Then select 3. To make manual PS data calls, click the Measurement control button in the Devices view and select Start Packet Session. Nemo Outdoor will automatically activate the PDP context and make the GPRS attach. 4. To end the data transfer/data call, select Stop Packet Session/ Stop Data Call.
STREAMING VIDEO QUALITY TESTING
Streaming video quality testing allows you to monitor how streaming video is transferred in the network. Data streaming can be made manually and with scripts. Nemo Outdoor supports Opticom PVI streaming video quality testing, and measures video quality type, jitter, packet error rate, and MOS. A video preview can also be seen during the measurement in Nemo Outdoor. Note that it is only possible to make single video quality measurements. In order to be able to make streaming video quality measurements, you will need to install VLC 2.0.4 and Apple QuickTime 7.2 player on the computer, and to define streaming video settings in the Streaming Properties dialog. Both VLC and Apple QuickTime are available on the Nemo product DVD and Nemo User Club. Or you can download them from the product websites.
Making streaming video quality measurements:
1. Check that VLC and Apple QuickTime player are installed on the computer. 2. Define the video streaming settings in the Streaming Properties dialog. 3. Start recording by clicking the Start Recording button . From the Measurement menu, select All Devices | Start/Stop Data Transfer to start the data transfer with all test devices or <device name> | Start/Stop Data Transfer to start the data transfer with just one device. 4. You can view, for example, from a line graph some streaming parameters. Open a line graph (Data | Line Graph | New). Press the Add New Layer button and select Video Quality MOS in the Y field and click OK. The graph will now display the selected parameter. 5. From the Measurement menu, select Start/Stop Data Transfer to end the data transfer or wait until the entire video clip has been streamed.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
139
VOIP CALLS
With the optional VoIP module combined to Nemo Outdoor, a user is able to perform IP telephony measurements on the IP networks based on the established VoIP sessions. In order to be able to make VoIP call measurements, you will need to install a SIP server. Nemo Outdoor VoIP system is compatible with Asterisk SIP Server. To find more information on installing the Asterisk SIP server, login to http://www.asterisk.org/applications/pbx To start making VoIP call measurements, you will need to define some VoIP session settings in the SIP Server Settings and VoIP Call Configuration dialogs. Open the SIP Server Settings dialog by double-clicking the SIP Server item in the Devices view.
Domain defines the address of the SIP server, e.g. pbx.nemo.fi. Port defines the SIP port. The default SIP port is 5060. Username/Password defines the username that the user has registered to the server and the corresponding password. Connection timeout defines the timeout while trying to connect to the server. Registration duration defines the duration for which the SIP registration is valid. Automatic registration, when selected, automatically registers the user to the SIP server (as soon as Packet Session has been created). When selected, Use SIP proxy option enables the user to send outbound SIP messager via Proxy. Proxy address/port defines the proxy, through which SIP messages are sent.
140
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Open the VoIP Call Configuration dialog by double-clicking the VoIP Call item in the Devices view.
SIP callee address defines the SIP address of the call receiver. Audio codecs for the call can be selected from the list by selecting the box next to them. The order of the codecs is significant since the first codec is offered as the primary codec when making a call to a counterparty. For example, in the image above the primary codec offered for an outgoing call is G729/8000. In addition, only selected codecs are used while negotiating the codec in the case of an incoming call. Select the Voice quality option to enable voice quality measurements for VoIP calls. Please note that this option is available after you have selected the VoIP only option from the Device Configuration for Mobiles and Modems dialog. Reference sample filename refers to the file used as the reference sample in the voice quality measurements. Click the Browse button to select a file. Select the Save sample files option to save the received sample files on the laptop. With the Prefix for received sample files option you can define a prefex that will be added to the filename of all received sample files. With the Save only samples below threshold option you choose to save only those samples that are below a user-definable threshold (MOS score). Script settings defines the duration of the call and the call attempt timeout in seconds.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
141
Making VoIP measurements:
1. Define SIP Server Settings and VoIP Call Configurations. 2. To start packet session, click on the Measurement control button | Start Packet Session.
3. To register SIP server, click on the Measurement control button | Register SIP Server. 4. To start VoIP measurement, click on the Measurement control button | Start VoIP Call. 5. To end VoIP measurement, click on the Measurement control button | Stop VoIP Call. 6. Finally, to unregister SIP server, click on the Measurement control button | Unregister SIP Server (Note: This is not a mandatory step, a new call can be made without unregistering)
SKYPE CALLS
In order to be able to make Skype call measurements, you will need to set up a Skype account. Please note that you cannot use the same Skype account to log in to Skype and to Nemo Outdoor on the same computer. You can log in to Skype on a different device using the same account and use that account for receiving Skype test calls from Nemo Outdoor. To start making Skype call measurements, you will need to define some Skype settings in the Skype Account Settings and Skype Call Configuration dialogs. Open the Skype Settings dialog by double-clicking the Skype Account item in the Devices view. Please note that if the Skype Account and Skype Call items are not visible in the Devices view, your Nemo Outdoor license does not support Skype calls.
142
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
If you already have a Skype account, type in the Username and Password.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
143
The Privacy Settings button is activated after you have defined the account settings and logged in to the Skype server through Measurement control. In the Skype Privacy Settings dialog you can, for example, prevent people from contacting you through Skype. If you need to create a Skype account, click Create New Account. In the Create Skype Account dialog define the account information. Please fill in all fields.
Full name defines your name. This information is visible to all Skype users. Skype name refers to a Skype screen name. This information is visible to all Skype users. In the Password field type a password that contains 6-20 characters and at least one letter and one number. In the E-mail address field, define a valid e-mail address. Accept Skypes terms and conditions and finally click Create Account. After defining Skype account settings, return to the Devices view and double-click on Skype Call. In the Skype Call Configuration dialog, define the recipients Skype name and click OK.
144
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Making Skype call measurements:
1. Define Skype Account Settings and create a Skype account, if necessary. 2. Define the recipient in the Skype Call Configuration dialog. 3. To start packet session, click on the Measurement control button | Start Packet Session.
4. To login to the Skype server, click on the Measurement control button | Login to Skype Server. 5. To make a Skype call, click on the Measurement control button | Start Skype Call. 6. To end a Skype call, click on the Measurement control button | End Skype Call. 7. Finally, to log out from the Skype server, click on the Measurement control button | Logout from Skype Server (Note: This is not a mandatory step, a new call can be made without logging out).
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
145
SMS TESTING
SMS testing allows you to monitor how text messages are transferred in the network. Open the SMS Testing dialog by double-clicking the Short Messaging Service item in the Devices view.
Phone Number defines the number of the mobile where you are sending the test messages. Enter the number without spaces and with the international country code; for example, +3581234567. Service Center Address defines the message center number of the mobile from where the messages are sent. The number is found from the test mobile SMS settings. Timeout defines the time in seconds after which the SMS sending attempt is terminated. When the End-to-end message option is selected, a unique ID consisting of 42 characters is added to the beginning of the message text when the SMS is sent. When the measurement file is added to the Nemo Analyze database, Nemo Analyze is able to recognize the SMS and the time it took for it to reach its destination from the time of sending during post-processing. All handlers support sending and receiving concatenated SMS messages. Message refers to the user-defined test message that will be sent. The limit is set to 15000 characters.
146
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Making SMS testing measurements:
Note that with CDMA terminals, before carrying out SMS testing in Nemo Outdoor, you must send an SMS to the target phone number using the terminal's keypad. After that Nemo Outdoor can be used to send the same message again. 1. Define the Phone Number (with the international country code and without spaces) where you are sending the test SMS message. 2. Enter the Service Center Address of the test mobile from which you are sending the test SMS. The number can be found from your mobile SMS Settings. 3. Define the Timeout, i.e., the time in seconds after which the SMS sending attempt is terminated. 4. Type in the test message and click OK. 5. Start recording by clicking the Start Recording button . From the Measurement menu, select All Devices | Send SMS Message to send an SMS with all test devices or <device name> | Send SMS Message to send an SMS with just one device. Nemo Outdoor will send the test SMS. 6. You can view, for example, from a grid window if the test message was delivered successfully. Open an event grid (Data | Events Grid | New). Open the Grid Properties dialog (right-click on the grid and select Properties from the popup menu). Clear all selections and select the Short Message Service item and click OK. The grid will now display only the selected SMS testingrelated events.
SMS Testing with CDMA Terminals
SMS testing with CDMA does not require you to do any configurations prior to SMS testing for the terminal. The verified CDMA terminals supporting SMS testing are Huawei C7600 LG C680 LG C676 LG KX206 LG KX256 LG VX8100 LG VX8350 LG VX8360 Samsung SCH A870
The testing goes as follows. 1. Connect and add the terminal to Nemo Outdoor. 2. Prior to starting SMS testing in Nemo Outdoor, send an SMS to the target phone number from the phones keypad. 3. In the Devices view, click on the Measurement control button and select Send SMS Message. Nemo Outdoor sends the same message as was sent by the user from the actual phone interface by retrieving the text message from the phones Saved messages folder.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
147
MMS TESTING
MMS testing allows you to monitor how multimedia messages are transferred in the network. MMS messages can be sent manually and with scripts. In addition to successfully sent/received MMS messages, also sending/receiving attempts and sending/receiving failures are recorded enabling statistical success rate calculations. Nemo Outdoor measures total MMS sending delay. Also separate delays from Attach, PDP context activation, logging to MMSC, and message sending/receiving are recorded. In order to be able to make MMS measurements, you will need to define some MMS-related settings in the Packet Session Settings dialog. If you are using the Nokia 6630, 6680 or N80 mobile for MMS testing, please see chapter MMS Settings for Nokia 6630, 6680, and N80. Some special MMS settings are required. Please note that if you create a script for making MMS measurements, the script must not contain a PDP activation command.
148
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Packet Session Settings for MMS
Open the Packet Session Settings - MMS dialog by double-clicking the Multimedia Messaging Service item in the Devices view. The MMS tab is opened by default. Packet Session settings are needed to establish the packet switched data connection. All the parameters in the Packet Session and the Basic QoS and Extended QoS tabs are operator-specific. You must select the correct parameters to make the packet transfer function. Contact the operator of the network that you are measuring.
MMS
In the MMS tab, all the settings are required in order to make MMS measurements.
MMSC address defines the MMS Service Center address. This setting is operator-specific. MMSC username defines the MMS Service Center username. This setting is operator-specific. MMSC password defines the MMS Service Center password. This setting is operator-specific. WAP gateway host refers to the WAP gateway host. This setting is operator-specific. WAP gateway port refers to the port used by the WAP gateway. This setting is operator-specific. Connection timeout defines the time in seconds after which the connection attempt is terminated. Transfer timeout defines the time in seconds after which the MMS sending attempt is terminated. Message to be sent refers to the test MMS message used in the measurement. Message Editor button opens the MMS Editor dialog for editing and creating MMS messages.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
149
MMS Editor
Use the MMS Editor dialog to type and edit test messages. You can attach files to the test messages and save messages for later use.
New MMS Message saves the current changes and opens and empty MMS Editor. Open MMS Message opens an Open dialog where you can open premade MMS messages. Save MMS Message saves the current MMS message for later use. Save As saves the current MMS message with a different name for later use. Save Attachments saves the files attached to the test message to a selected location. Attachments field displays a list of attachments in the test message. Add opens an Open dialog for adding an attachment to the test message. Remove removes the selected attachment from the test message.
Making MMS Measurements
Follow these step-by-step instructions for making MMS measurements. You should have all the measurement devices connected and activated. If you are using the Nokia 6630, 6680 or N80 mobile for MMS testing, please see chapter MMS Settings for Nokia 6630, 6680, and N80. Some special MMS settings are required.
Making MMS measurements:
1. Define the MMS-related Packet Session Settings (see Packet Session Settings for MMS). 2. Edit the test message and add the media attachments in the MMS Editor.
150
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
3. If you want to make automated measurements, create a script for MMS measurements (see Making Script Files). 4. If you are making manual measurements, that is, not using a script, select Send MMS Message from the Measurement control menu or from the Measurement menu. Nemo Outdoor will send the test MMS. 5. If you are using a script, activate the script by clicking the Start/Stop Scripts button. This will start the measurement. 6. You can view, for example, from a grid window if the test message was delivered successfully. Open an event grid (Data | Events Grid | New). Open the Grid Properties dialog (right-click on the grid and select Properties from the popup menu). Clear all selections and select the Multimedia Message Service item and click OK. The grid will now display only the selected MMS testingrelated events.
MMS Settings for Nokia 6630, 6680, and N80
You need to make some MMS settings for the Nokia 6630, 6680, and N80 mobiles before you can use them in MMS testing with Nemo Outdoor.
Changing MMS settings for Nokia 6630, 6680, and N80:
1. On the phone main window, press Messag.
2. In the Messaging view, press Options.
3. From the menu, select Settings.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
151
4. From the Settings view, select Multimedia message.
5. Select the Access point in use option and change it to None.
6. Select the Recept. in home net. and change it to Off.
152
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
7. Select the Reception if roaming option and change it to Off.
8. Press Back and select Yes to confirm the changes. Finally switch the mobile on and off.
MMS Settings for Nokia N95, 6120, and 6121
You need to make some MMS settings for the Nokia N95, 6120, and 6121 mobiles before you can use them in MMS testing with Nemo Outdoor.
Changing MMS settings for Nokia N95, 6120, and 6121:
1. On the phone main window, press Messaging.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
153
2. In the Messaging view, press Options.
3. From the menu, select Settings.
4. From the Settings view, select Multimedia message.
154
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
5. Select the Access point in use option and change it to None.
6. Select Multimedia retrieval and change it to Off.
7. Select Allow anon. msgs. and change it to Off by pressing the navigation button on the phone, or by selecting Options| Change| No.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
155
8. Press on the navigation key to change the setting for Receive adverts from Yes to No.
9. Press the navigation button on the phone to change the Receive report setting from Yes to No.
10. Press Back and select Yes to confirm the changes. Finally switch the mobile off and on.
156
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
USSD TESTING
USSD testing allows you to monitor how USSD messages are transferred in the network. Open the USSD Message dialog by double-clicking the USSD Message item in the Devices view.
Timeout defines the time in seconds after which the USSD sending attempt is terminated. Message refers to the user-defined test message that will be sent. The limit for USSD messages is 182 characters.
Sending USSD messages:
1. Define the Timeout, i.e., the time in seconds after which the message sending attempt is terminated. 2. Type in the test message and click OK.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
157
3. Start recording by clicking the Start Recording button . In the Devices view, click the Measurement Control button and select Send USSD Message to send a USSD message with just one device. Nemo Outdoor will send the message.
4. You can view, for example, from a grid window if the test message was delivered successfully. Open an event grid (Data | Events Grid | New). Open the Grid Properties dialog (right-click on the grid and select Properties from the popup menu). Clear all selections and select the USSD item and click OK. The grid will now display only the selected USSD message testing-related events.
START EXTERNAL APPLICATION
This feature allows users to launch external applications from Nemo Outdoor as a part of the automatic measurement sequence. You can define the executable as well as the command-line parameters. With Nemo Invex, you can run external applications also on the measurement servers (UICs). The external application can be used to launch any proprietary or third-party applications that are not built into Nemo Outdoor. This enables, for example, the testing of data protocols that are not currently supported by Nemo Outdoor. You can then monitor the data throughputs from the PPP data throughput parameter. The external application feature can also be used to test web browsing. An APP event is written to the log file when a web browser is launched and closed. The user must set the cache size to minimum from the browser settings.
158
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
The Start External Application dialog is accessed through the Script Editor, Add menu. Select Start External Application from the menu.
Application Name defines the application that you want to run from Nemo Outdoor while making measurements. Define the path where the application .exe file is located on your computer. For example, C:\Program Files\Mozilla Firefox\firefox.exe. Please note that clicking the Browse button will only show the folders on the local computer. If you want to run an external application on a measurement server (Nemo Invex), check the path from that server, for example, with Remote Desktop and type in the path manually. If you select the Wait until completed option, the test script will be on hold until the external application is closed. Arguments defines what file or web page will be opened in the external application once it is started. For example, if you start Internet Explorer, define here a URL (http://www.anite.com/nemo). You can also leave the field empty. Note that there should be no spaces between the characters in the pathname or target file specified in the Arguments field. Working Folder refers to the folder that the application uses to open and save files. For example, C:\Temp.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
159
ICMP PING
The ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) Ping functionality allows you to perform ping measurements simultaneously with data transfers.
Host name refers to the IP address or URL that is being pinged, for example, www.anite.com. You can use Packet Data Tester or any IP server. Just make sure that the IP server used will respond to the ping. Packet size is the size of the ping packet that is used to measure ping time. The value determines the size of the packet sent to the server. In addition, it determines the size of the reply packet that the server uses to reply Nemo Outdoor. Timeout determines the maximum time that Nemo Outdoor waits for a reply packet from the server. If this time is exceeded, the ping measurement event will be created by using the timeout parameter (=-1). Delay defines the delay duration in milliseconds. In addition to the duration, also define where the delay will occur. The options are: Delay between requests which means the protocol will always wait for a reply before sending new request. If the delay is less than the ping delay, a new request is sent immediately after the reply. Delay from reply to request which means a new ping is sent after a reply is received.
Select the Repeat n times option if you would like to define the number of times the ping measurement is repeated. Select the Repeat until stopped option if you would like to continue the ping measurement until you stop it manually.
160
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Example 1. RTT time is 100ms and delay from reply to request is set to 1 s. New request is sent every 1.1s (100ms + 1000ms). If delay between request is selected, a new request is sent every 1000ms.
Example 2. RTT time is 100ms and delay from reply to request is set to 50ms. New request is sent every 150ms (100ms + 50ms). If delay between request is selected, a new request is sent every 100ms because the protocol always waits for a reply before sending a new request.
To make ping measurements:
1. Open the Ping Settings dialog by double-clicking the ICMP Ping item in the Devices view. 2. Define the required ping parameters and click OK. 3. Click the Start Recording button .
4. In the Devices view, click on the Measurement control button and select Start Packet Session. Wait until the status field in the Device Status window says PDP Context Activated. 5. From the Measurement control menu, select Start ICMP Ping. If you selected the Ping until stopped option in the Ping Settings dialog, select Stop ICMP Ping to stop the ping measurement. Otherwise, the ping will be repeated the user-defined number of times.
IP PACKET CAPTURING
Please note that IP packet capturing is not supported on 64-bit Windows. With IP packet capturing, network packets sent between IP addresses are stored in log files and can be post-processed with a third party application such as Ethereal. A separate log file is generated for each test terminal making data transfers. In order to use IP packet capturing in Nemo Outdoor, you must configure a dial-up connection (see the Dial-Up Networking Setup Guide for more information) and install the Network Monitor driver for the dial-up connection. After setting up the dial-up connection, go to Microsoft website at <http://www.microsoft.com/download/en/details.aspx?id=4865> to download the free Network Monitor installation package. Select the NM34_x86_setup.exe installation file and click on Download.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
161
1. Once the installation file is downloaded, double-click on it. The Microsoft Network Monitor 3.4 dialog appears. Click Yes to continue installation. 2. Click Next in the Welcome dialog. 3. In the End-User License Agreement dialog select I accept the terms in the License Agreement option, and click Next. 4. It is recommended to select the Use Microsoft Update when I check for updates (recommended) option. Click Next to continue with installation. 5. Select Typical in the Choose Setup Type dialog that appears. 6. Click Install in the Ready to install dialog. 7. Click Finish in the Completing the Setup Wizard dialog. 8. Start Nemo Outdoor, add a device, and go to the Measurement Properties, General page. Click the Advanced button. In the Advanced Properties dialog, select the Enable IP Capture option. Note that if the Enable IP Capture item is not on the list, the Network Monitor driver is not installed.
IP packet capture measurement option has four states: disabled, enabled, partial, and full. Disabled: IP packet monitoring is not performed at all Enabled: a separate .pcap file is not written but, for example, KPI, IP service access time is recorded Partial: only message headers are recorded Full: all messages are recorded
The IP packet data is stored in a separate file (.pcap) for each measurement terminal for which IP capturing is enabled.
162
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
To view data in Packet decoder grids during playback, you need to enable the packet decoding function prior to performing data measurements. Select Enabled in the Enable IP Capture field. A separate .pcap-file will be generated for the measurement. This file needs to accompany the measurement file in the same folder when viewing and decoding packet capture information in Packet Decoder grids in Nemo Outdoor.
Performing IP Packet Capturing:
1. Set up a dial-up connection (see Dial-Up Networking Setup Guide for instructions). 2. In Nemo Outdoor, enable IP capturing in the Advanced Properties dialog. 3. IP packet capturing data is stored in a separate file (.pcap) for each measurement terminal and the data can be analyzed with Ethereal.
MAKING SCRIPT FILES
Note that it is not possible to use scripts with scanners. The script file is an ASCII file containing the list of numbers that are to be called. The extension for all Script files is .nsf. You can edit the Script file configuration in the Script Editor dialog. You can access this dialog by selecting Measurement | Script Editor (Ctrl+E).
The table in the middle will show a list of all functions and parameters that will be executed during a measurement. Click the Add button to add commands in the script. Modify can be used to edit an existing script entry. Select a row from the table and click the button to change the settings for that function. Delete deletes the selected entry row. Move Up moves the selected entry row up by one row in the script. Move Down moves the selected entry down by one row in the script. Insert Script can be used to insert the contents of another script file into the current script.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
163
Repeat Script value defines how many times the script will be repeated during the measurements. The range of repeat script values is from 1 to 10,000. When the Use device settings for script commands option is selected, the settings that have been configured in the Measurement Properties dialog are used for the script settings. For example, if you have defined a Voice number in the Measurement Properties Configuration dialog, that number is used when you add a voice call in the script and the Voice Call Properties dialog does not appear. New clears the entry fields for inserting new script values. Open opens a dialog for selecting an existing script file to be modified or reviewed. Save saves the file with the existing name or if the script is a new one, opens a dialog for inserting the file name. Close exits the dialog. Notes about script functions: Scrambling code or removed scrambling code can be selected for conditional testing using the IF loop Examples of conditions: o Is different: If UMTS carrier RSSI is different than -70dBm Whenever the value is other than -70dBm, IF condition is triggered o Is changed: If UMTS carrier RSSI is changed Whenever the UMTS carrier RSSI value changes, the IF condition is triggered. The reference value is unknown, which means that when starting the measurement and when the first UMTS carrier RSSI value is received, the IF condition is triggered. The next trigger occurs when the carrier RSSI value is different from the previous value. For example, 1. Carrier RSSI value in the log file: -70dBm triggers the IF string 2. Carrier RSSI value -70dBm nothing happens 3. Carrier RSSI value -68dBm Triggers the IF string
164
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Script Transfer Stop Commands
With the forced stop command it is possible to abort a current script command. For example, a data transfer can be canceled if the serving system changes, instead of waiting for its completion. It is also possible to set a time duration for data transfers. If a data transfer is not completed during a userdefined time, the Nemo Outdoor application will abort the data transfer automatically. Please note that in this case the data disconnection status is written as Normal data disconnect.
The forced stop command, e.g., with voice calls, can be used in conjunction with conditional or wait commands as well. For example, if a call should be stopped when the system changes from GSM to UMTS, the forced stop command can be used to end the call immediately after the system changes. In the example below, the voice call is started only when the serving system is GSM. Call duration is set to 120 seconds. It should be noted that the actual call duration is set with line three, Wait until system is UMTS but at most 120s. After the call is connected, the script starts waiting for the system to be changed to UMTS, or at most 120 seconds. The call is ended with End a voice call (forced) with line 4 after 120 seconds, or when system changes to UMTS; whichever comes first.
GSM voice call example. Voice call is started only in GSM and aborted when system changes to UMTS.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
165
The forced stop command can be used also to stop active data transfers. In the example below the script waits until the system changes to UMTS. Once the system is in UMTS, the script waits 5 seconds before making a voice call followed by PDP context activation and FTP data transfer. The script stops, waiting until the system changes to GSM, but at most for 60 seconds. If the system changes to GSM before 60 seconds, the voice call is continued normally until a 60-second call duration is reached. FTP data transfer is aborted immediately when the system changes to GSM, or after 60 seconds, whichever comes first. If line eight were End a voice call (forced), the voice call would be stopped immediately after inter-RAT handover occurred.
In the following you will see a PS data and voice call example. The data transfer is aborted when the system changes to GSM, or after 60 seconds; voice call is continued. The call duration is 60 seconds.
166
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
In the following you will see another PS data and voice call example. The data transfer and voice call are aborted when the system changes to GSM, or after 60 seconds, whichever comes first.
The voice call is aborted when the system changes to GSM, or after 60 seconds, but data transfer is continued normally with the Stop FTP transfer (Normal) command.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
167
Add Menu
The Add menu contains all the items that can be used in a script. Selecting an item may open a dialog where you need to define some parameters and settings. See earlier chapters for more detailed information on the dialogs. The Start External Application item is described in more detail in chapter Start External Application. In the Script Editor, by clicking Add and selecting Send DTMF Characters you are able to send DTMF sequences. You can e.g. make calls to service numbers that work by using DTMF tones. This command can only be used during voice calls.
168
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Wait Settings
To add pauses in the script, select Wait. In the Wait Settings dialog you can define different conditions for the wait. You can also define custom conditions.
With the Wait until the time is option you can define a point in time after which the script continues. With the Wait for all scripts to be synchronized option you can place multiple synchronization points inside the script file. Nemo Outdoors script group functionality enables you to synchronize the script files and/or certain lines in the script file for certain devices. Both synchronization methods can be used together or separately depending on needs of the user. In the following example below both devices are doing PS data transfers. The idea is to start FTP download simultaneously. Script files for both devices are identical except that IP address is different. Wait for script synchronization command has been selected for both devices in the Wait settings dialog. The Wait for script synchronization is seen on line two for both devices.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
169
Both devices have been assigned for the same script group called PS data.
Script groups are useful especially if certain devices and when script files are needed to be synchronized. In this example, it is not necessary to use the script group. As many synchronization points as needed can be added to the script files. It should be noted that the number of synchronization points between script files used in the same script group should be equal. With the Current time option you can define a pause between items in the script. For example, you can set a 10 second pause after a voice call is finished and before the next call starts. With the Last notification option you can define a wait period after certain event notifications. For example, you can make the script pause for 60 seconds after a call attempt event. This will prevent the script from continuing before the call attempt has completed. Note that also custom-made notifications can be selected here. With the Next notification option you can make the script wait for a certain event notification to appear. For example, you can make the script wait until the system changes from GSM to UMTS. The until: Current system option enables you to define that the script file continues only when the system selected from the drop-down menu is in use. But at most value is the maximum wait time in seconds if the defined notification does not appear.
170
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
With the Custom condition option you can make the script wait for a custom condition. Click the Edit Rules button to access the Wait Custom Conditions dialog where you can define a wait condition. For example, you can define a specific parameter value.
Adding a pause in the script file:
1. First define the wait time in seconds. 2. Then define from which point onwards the wait time is calculated: from the current time or after a certain event notification, such as, call attempt. 3. If you selected the Last notification or Next notification option, define also the maximum wait time in seconds after which the script will continue.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
171
Advanced Script Settings
Conditional Blocks
By selecting Advanced | If/End If, you will enter the If Condition Settings dialog. Here you can define criteria which have to be met until a set of commands between the If - End If block in the script takes place. If the criteria set in this dialog are met, Outdoor will perform the set of commands within the If - End If block, and if the criteria are not met, this set of commands will be skipped altogether and the script resumes from the first item after the End If command.
Click on the Field tab to select a system and a parameter from the drop-down menu. In the Condition and Value fields you can define the value conditions for the parameter which have to be met for the commands inside the If-End If block to take place. In this example the serving system must be UMTS FDD. You can select the system in the Value drop-down menu. Click Add to list to add the condition to the list. If you want to remove the condition from the list, select it and click Remove. Click OK. Next, add commands to the script from the Add menu, and move them to their appropriate places with the Move Up and Move Down tabs. In the following example script, Serving sys.=5 on the fourth row in the Parameters field indicates the criteria that were set earlier. If the criteria are met, the commands between the If Condition and End If commands will be performed.
172
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Loops
You can add loops in the script files. By going to Add | Advanced | Loop/End Loop, you will enter the Loop Settings dialog.
You can select from the following loop options: Repeat the loop x times
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
173
Repeat the loop for x minutes Repeat the loop until the time is x Repeat the loop as long as the following criteria are met
With the Repeat the loop as long as the following criteria are met option you can set conditions for the loop to take place. Click the Field button to select a parameter. Then define the condition and value for the selected parameter. Finally click Add to list and OK to add the loop in the script. In the first example, the loop has been set to be repeated twice before continuing with the script. Click OK and add the wanted script commands in the script from the Add menu. You can move the commands to their appropriate places with the Move Up and Move Down tabs. In the example below the voice call within the loop will be repeated twice before continuing with the script.
174
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
The second loop option allows the user to define criteria which need to be met for the loop to be repeated. In the example below the system and parameter (UMTS | Ec/N0 (Active)) have been selected from the Field drop-down menu. The condition for the loop is that the parameter value needs to be greater or equal to -5. Click Add to list and OK. The commands inside the loop block will be performed only and as long as the Ec/N0 (Active) value is greater or equal to -5.
In the example below the script is set to start and continue making calls only when and as long as the call is connected to UMTS. As soon as there is a handover from UMTS to GSM, the call stops.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
175
Counters and Timers
Counters and timers can be used with If and Loop commands as conditions. With a counter you can define a number of instances and with a timer you can define a certain time in seconds. Click the Add button in the Script Editor and select Advanced | Counter or Advanced | Start Timer. Define a name for the counter/timer and click OK. The counter/timer can now be selected as a condition in the If and Loop Condition Settings dialogs.
176
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Below is an example of a script with both a timer and a counter. On row three there is a loop command with a counter condition called GSM calls and a timer condition called Duration. The loop is configured to repeat a voice call until one of the following conditions is met: number of calls in a GSM system is five or the loop has been running for 600 seconds.
Running Scripts
After you have created a script, it will be saved and you can load it for measurements later on.
To run the script file:
1. In the Measurement Properties, Scripts dialog, select the script in the Script File field. Note that you need to define the script for each device individually. The script can be different for each device. 2. Activate the Start/Stop Scripts (F8) button . Nemo Outdoor will start running the measurement according to the script file. Note that if you have selected the Start Scripts Automatically option in the User Interface Properties General dialog, Nemo Outdoor will start running the script when you click the Start Recording button. 3. The program will now conduct the measurement as defined in the script file. After the script is finished, you can stop the recording (Measurement | Stop or Stop button ).
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
177
MEASUREMENT LISTS
Measurement lists enable you to run automated measurements with several devices combining multiple scripts. You can use measurement lists with just one device to run several scripts one after another. Each measurement is recorded in a separate file. You can also use measurement lists in idle mode. In Online mode, select Measurement | Start Measurement List to open the Measurement List dialog.
Scheduled measurements displays a list of measurements that will be run when the measurement list is started. Each measurement will be recorded in its own file. Click Add New to add new measurements and Remove to delete selected measurements from the list. Click Load to load measurement lists and Save to save measurement lists. By default, measurement list files (*.nmix) are saved to Configuration files folder. Filename defines the filename format. The default format is %y%b%d %H%M%S (year-month-day hours-minutes-seconds, e.g., 06May31 165246) but you can use any combination of the items below. For example, "%y%b%d_%n means that the filename looks as follows: 06May31_1. The last number (%n) is the sequence number for measurement files recorded that day. %a %A %b Abbreviated weekday name Full weekday name Abbreviated month name
178
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
%B %d %H %I %j %m %M %n %N %p %S %U %w %W %y %Y %z
Full month name Day of month as decimal number (01 31) Hour in 24-hour format (00 23) Hour in 12-hour format (01 12) Day of year as decimal number (001 366) Month as decimal number (01 12) Minute as decimal number (00 59) Sequence number (1 ) Sequence number (1 ) Current locale's A.M./P.M. indicator for 12-hour clock Second as decimal number (00 59) Week of year as decimal number, with Sunday as first day of week (00 53) Weekday as decimal number (0 6; Sunday is 0) Week of year as decimal number, with Monday as first day of week (00 53) Year without century, as decimal number (00 99) Year with century, as decimal number Either the time zone name or time zone abbreviation, depending on registry settings; no characters if time zone is unknown Either the time zone name or time zone abbreviation, depending on registry settings; no characters if time zone is unknown
%Z
Select the Save statistics to file option to enable the CSV file writing. Measurement completion defines when the measurement list is finished. Select the When all scripts are completed option to finish once all scripts have finished running. Select the After recording duration option to finish after recording has been going on for a certain period of time. Define the time in hours and minutes (hh:mm). Select the At measurement size option to finish when the total size of the measurement files reaches a certain limit. Define the size in kilobits (KB).
Devices table displays a list of devices connected to Nemo Outdoor. Script file defines the script file used in the measurement. Click the Script Editor button to edit the selected script. Properties opens the Measurement Properties - Script dialog. Start runs the measurement list.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
179
Creating a measurement list:
1. Click the Add New button to add a new measurement. 2. Select a device from the Devices list. 3. Select a script from the Script File field. You can edit the selected script by clicking the Script Editor button. 4. Repeat the previous steps until you have a complete measurement list. 5. Select the When all scripts are completed option. Finally, click Start. 6. The measurement list is finished after all scripts have been completed. 7. To save the measurement list, click Save.
FORCING FUNCTIONS
Nemo Outdoor offers a set of forcing functions that are accessible through the Nemo Outdoor user interface. In addition to these, some terminals support more forcing features that are accessible via the mobile keypad. See the terminal-specific data sheets for more information on the forcing features available for each terminal.
Channel Locking
This functionality is available for GSM and UMTS mobiles only. You can lock GSM and UMTS test mobiles to a channel and/or scrambling code during the measurement process. Note that even though you are locking the mobile to a certain channel in idle mode, you are actually locking the mobile only to the base station supporting that channel at that moment if you make a call. As the base station can carry several channels simultaneously, the connection can be established or handed over to another channel but not to another base station. In other words, the channel used cannot be totally controlled by the mobile as the system will assign the channel.
To lock the Nemo Outdoor test mobile to a channel:
Note that when the channel lock is activated, the Neighbor Stations window displays only Serving Cell values. Note that if you are using the single mode, you must keep the test mobile connected to the power cord. If the mobile is not connected to the power cord and the program switches it off, you must switch the mobile on manually.
180
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
1. When you have connected the measurement device, select the device and click the Measurement settings button in the Devices view and select Channel Locking. You can also select Measurement | <device name> | Channel Locking. The Channel Locking dialog will appear on your screen.
2. Enter the system and channel number and/or scrambling code within the given limits (it must be a valid channel/scrambling code number) and click the Lock button. The button will remain pushed down indicating that channel lock is activated. A red indicator will appear in the Device Status view when a lock is activated.
3. Click the Unlock button in the Forcing functions | Channel locking dialog to release the channel lock.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
181
Band Locking
You can use band locking if you want to compare how the network functions with different bands and systems. Using the Band Locking dialog, you can force the mobile to use certain bands or system(s). You can open the Band Locking dialog by selecting the device and clicking the Measurement settings button in the Devices view and choosing Band Locking.
Choose the band(s) or system(s) from the list and click the Lock button. This will lock the mobile to the band/system you have chosen. Click Close to exit the dialog. A red indicator will appear in the Device Status view when a lock is activated.
To release the band lock, open the Band Locking dialog and click the Unlock button.
182
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Handover Control
This functionality is available only with certain Nokia terminals. Forcing handovers can be used to check that they work properly. You do not have to wait for the mobile to make handovers, as you can, for example, force a handover to every neighbor cell. Start a measurement and initiate a call (Measurement control button | Start Voice Call). Open the Handover Control dialog (Measurement settings button | Handover Control). Define the channel and handover type and click OK.
The BCCH ARFCN can be used to select the broadcast control channel (1-885) you want to force the handover to. The BSIC field defines the Base station identification code for the target cell. The user has three mode request commands, Normal mode, Handover forcing and Handover suppression. If the terminal accepts the command made by the user, the corresponding button will indicate this. If the command fails, the user is notified. It is also possible to send the same command several times without clicking other commands (i.e. send a new Handover Forcing command with different bias values or forced the terminal to different scr. code, or in GSM to a different channel without first deactivating HO forcing). For example, the device can be forced to scrambling code 6. Once the terminal is locked to scrambling code 6, the user can set a new target cell and press the Handover forcing button again. The Target cell settings and Non-Target cell settings fields enable the user to define 3G offsets, i.e. enhance target cell Ec/N0 and RSCP, and degrade non-target cell Ec/N0 and RSCP)
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
183
During Normal mode, forcing is disabled and the terminal performs 2G and 3G handovers normally.
The system field shown in the Target cell field shows in real time whether the serving system is GSM or WCDMA. When the serving system is GSM, the target cell and non-target cell settings are disabled. In case the current serving system is GSM, but the wanted target cell is in WCDMA, band locking can be used first to lock the terminal to WCDMA.
184
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Once target cell settings including biasing information are defined by the user, handover mode can be changed to Handover forcing mode by pressing the button. Handover forcing is done by biasing target and non-target cell Ec/N0 and RSCP values. Therefore it is also possible to bias the current active cell. For example, in the example below active set includes only one scrambling code. By pressing the Handover forcing button, the terminal reports biasing Ec/N0 and RSCP values as set by the user. When the mode is changed back to Normal mode the terminal reports unbiased values.
In the next example regarding Forced 3G handover and measurement report modification, the terminal active set includes scrambling code 63 with Ec/N0 value -7.6dB shown as a brown curve. Scrambling code 6 and 255 are seen in the monitored set with colors blue and green. Scrambling code 6 is selected to be a target cell.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
185
Once the button is pressed, scrambling code number 6 is added to active set with Ec/N0 value -4.7dB. Scrambling codes seen in the monitored set are decreased -10dB. Scrambling code 6 is seen with Ec/N0 value -18.2dB (brown) and scrambling code 255 (green) is removed from the monitored set.
This situation is active as long as forcing/biasing is enabled. The device sends measurement reports to the network with biased values.
Once the mode is changed back to normal, the terminal starts reporting unbiased values.
186
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
When the Handover suppression button is pressed, the terminal is not allowed to do handovers to other cells. It should be noted that target cell biasing can be done only with WCDMA. Biasing/ measurement report message modification is not possible with GSM at the moment. You can use this feature, for example, to find the edge of a cell by stopping the handovers from taking place when driving away from a base station.
Note that with scripts you can also perform handover forcing from one system to another. See chapter Making Script Files.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
187
Cell Barring
This functionality is available for Nokia 2G and Motorola 3G terminals.
During the measurement you can select if you wish to access only cells that are accessible to all end users (Accept), all cells; that is, also cells that are barred (Ignore), and only barred cells (Reverse). The Cell Barring dialog is accessed by selecting the device and clicking the Measurement settings button in the Devices view and choosing Cell Barring. You can also select Measurement | <device name> | Cell Barring.
Set Terminal Radio On/Off (Airplane Mode)
It is possible to set the terminal radio on and off by selecting the device and clicking the Measurement settings button in the Devices view and selecting Set Terminal Radio On/Off. You can also select Measurement | <device name> | Set Terminal Radio On/Off. The Device Status view will display a red indicator when the terminal radio is off.
188
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
CELL TESTING
The surrounding cells of a location can be tested through an automated list of test calls that are locked to a cell at a time. The Cell Testing dialog is accessed by selecting the device and clicking the Measurement settings button in the Devices view and choosing Cell Testing. You can also select Measurement | <device name> | Cell Testing.
Phone number defines the phone number that is called at the outset of the cell test. During the call the neighbor list which defines the cells to be tested is updated. This is necessary since if the cell from which the cell testing is performed is a strong one, without this call the neighbour list may remain empty. Test cases defines whether the user wishes to perform Voice call or Packet call testing or both by selecting Voice & Packet in the drop-down menu. If the user selects both, the test starts with a voice connection attempt, and after that the test continues with the attempt to create a PDP context with the cell. The choice of test case also affects the displayed fields in this dialog. For example, if Voice call is selected, no Packet call settings are displayed RX level threshold: if the cell to be tested is a GSM cell, only cells stronger than the value defined here will be included in the test Ec/N0 threshold: if the cell to be tested is a UMTS cell, only cells that are stronger than this value will be included in the test Maximum number of calls defines the maximum number of calls that are made in the test Voice call settings | Maximum number of retries defines the maximum number of retries to a cell if no voice connection is formed. After the maximum voice connection attempts Nemo Outdoor continues to the next cell or to packet call testing
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
189
Packet connection settings | Maximum number of retries defines the access point name for the packet connection and the maximum number of retries for the connection attempts to a cell. After the maximum voice connection attempts Nemo Outdoor continues to the next cell Save results to file defines whether the report is saved to a file Save results to clipboard defines whether the report is saved on the clipboard after testing. The Test results page shows the progress of the test. The green color indicates successful attempts, and the number the number of attempts.
MISSING NEIGHBOR DETECTION
Realtime missing neighbor detection can be performed with the possibility to detect both GSM/WCDMA and CDMA missing neighbors at the same time. Missing neighbor measurements are also supported on some Nokia terminals. You have three options in which to perform missing neighbor detection: 1. with a mobile terminal supporting missing neighbor detection, 2. a scanner, or 3. a scanner and a mobile. Each cell has list of neighboring intra-frequency, inter-frequency, and inter-system cells. A terminal sees/measures only cells in the neighbor list, whereas a scanner measures all available cells. Missing neighbor detection is based on comparing scanner measurements with the neighbor list of the mobile. Hence, a possible missing neighbor refers to a cell that is not in the neighbor list of the mobile at a given time, but is detected/measured by the scanner. In mobile only missing neighbor measurements, the mobile is able to detect also missing neighbors through the missing neighbor detection functionality.
190
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Missing Neighbor Detection with a Mobile
1. Connect your mobile phone to Nemo Outdoor. 2. In the Devices view, select the device and click the Measurement control button . Select Frequency Scanning Properties. Select BSIC decoding and Missing neighbor detection in the Frequency scanning view. Next, click on Select Channels.
Note that both BSIC decoding and Missing neighbor detection need to be selected and Top-N option deselected. 1. Select the channels for scanning in the Select Channels dialog. 2. Click OK and OK.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
191
3. Start the device by pressing on the work online button if you have not done this already, and select Measurement control | Start Single Shot Scanning or Start Continuous Scanning.
4. Once the selected scans have been performed, Nemo Outdoor compares the scanning results to the neighbor list of the serving cell before scanning was initiated and reports possible detected missing neighbors.
Missing Neighbor Detection with a Scanner/Scanner and Mobile
You will need a scanner or a scanner and a mobile. If you are performing missing neighbor detection with a scanner only, the scanner needs either of the following options enabled: GSM Layer 3 or GSM/WCDMA decoding. Note that missing neighbor detection using a scanner only is not available for CDMA/EVDO. A scanner scans all possible pilots whereas a mobile scans only channels that are on its neighbor list. Nemo Outdoor compares these two measurements and, based on the data, reports the neighbor channels that are seen by the scanner but are not in the mobile's neighbor list. You can observe the missing neighbors in a bar graph and also view some important network parameters, such as, difference to strongest, Ec/N0, and RSCP related to the missing neighbors. Connect a mobile and a scanner to Nemo Outdoor. Configure the devices so that they are measuring the same frequency and channels. From Measurement | <device name>, select Missing Neighbor to open the following dialog. The field displays the scanner(s) used. The user can also set a minimum RX level threshold for missing neighbor. If the measured RX level is below the threshold, the channel is not detected as a missing neighbor. Click on Enable to start the missing neighbor detection.
192
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
In GSM Missing Neighbor detection, the maximum number of missing neighbors is 32. However, note that it is recommended to use default values to prevent false missing neighbor detection results. Number of missing neighbors: Max. 32, default 3. RX level: -50- -110dBm, default -95dBm
Open a bar graph, for example, with a Missing Neighbor Ec/N0 layer (Data | Bar Graph | New, click the New Layer button and select the parameter in the Y box). The bar graph with the selected parameter will display the missing neighbor channel(s).
PILOT POLLUTION ANALYSIS
Available for UMTS, CDMA and EVDO networks, Pilot Pollution Analysis measurements can be performed in real time with Nemo Outdoor by using test terminals or a scanning receiver. In a pilot pollution situation there are more active/monitored pilots than a handset can measure, or there is no clear dominance for any pilots in the area. The pilot signal is used to distinguish cells in the network from one another. Pilot pollution analysis is done based on CELL MEASUREMENT events, and analysis is always active. The user can define thresholds for pilot pollution analysis via Nemo Outdoors UI. Pilot pollution is detected when all the criterias match. Right-click on the device in the Devices view and select Pilot Pollution Analysis.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
193
The user can define thresholds for pilot pollution analysis via Nemo Outdoor user interface. Ec/N0 active set best below threshold (dB) (for UMTS): The default value is set to -12dB. Pilot pollution analysis is done when the best reported active set Ec/N0 value is below -12dB. Ec/I0 active set best below threshold (dB) (for CDMA and EVDO): The default value is set to -12dB. Pilot pollution analysis is done when the best reported active set Ec/I0 value is below -12dB. RSCP active set best above threshold (dB) (for UMTS): The default value is set to -95dBm. Pilot pollution analysis is done when the reported active set best RSCP value is above -95dBm. RSCP (Ec) active set best above threshold (for CDMA and EVDO): The default value is set to 95dBm. Pilot pollution analysis is done when reported active set best RSCP value is above -95dBm Polluter level window from best active set cell (dB) (for UMTS): The default value is set to -6dB. Pilot pollution analysis is done when the Ec/N0 values of polluting pilots are within -6dB from the best active set Ec/N0 value. Polluter level window from best active set cell (for CDMA and EVDO): The default value is set to 6dB. Pilot pollution analysis is done when Ec/I0 values of polluting pilots are within -6dB from the best active set Ec/I0 value. Pilot count threshold (for UMTS): The default value is set to 3. The number of cells that are within the user-defined window from the Ec/N0 of active set best cell. The pilot count includes active and monitored sets. For example, pilot pollution analysis is performed when more than three pilots are detected within the user-defined window from the Ec/N0 of active set best cell. Pilot count threshold (for CDMA and EVDO): The default value is set to 3. The number of cells that are within the user-defined window from the Ec/I0 of active set best cell. Pilot count includes active and neighbor sets. For example, pilot pollution analysis is performed when more than three pilots are detected within the user-defined window from the Ec/I0 of active set best cell. Start recording by clicking on the Start recording button .
194
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
UMTS Pilot Pollution Analysis on Mobile Phone
Pilot pollution analysis results are written to a log file as an event of their own, called CELLPOLLUTION. The event includes the following information: Source system Source band Source channel number Pilot pollution scrambling code Pilot pollution Ec/N0 Pilot pollution RSCP Cell name of polluting pilot (if cell site file is used) Cell ID of polluting pilot (if cell site file is used)
NOTE! Cell site file (BTS file) is not used with scanning receivers with Nemo Outdoor at the moment.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
195
Note that pilot pollution analysis takes some time to happen, and the results are based on earlier cell measurement events.
UMTS Pilot Pollution Analysis Based on Scanner Measurements
Ec/N0 values for pilots are less than -12dB Ec/N0 values of the pilots are within -6dB from the best Ec/N0 value
CDMA/EVDO Pilot Pollution Analysis - Mobile Phones
Pilot pollution analysis results are written to a log file as an event of their own, called CELLPOLLUTION. The event includes the following information: Source system Source band Source channel number
196
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Pilot pollution scrambling code Pilot pollution Ec/I0 Pilot pollution RSCP Cell name of polluting pilot (if cell site file is used) Cell ID of polluting pilot (if cell site file is used)
Note that pilot pollution analysis takes some time to happen, and the results are based on earlier cell measurement events.
CDMA/EVDO Pilot Pollution Analysis - Scanners
Ec/I0 values for pilots are less than -12dB Ec/I0 values of the pilots are within -6dB from the best Ec/N0 value
GSM INTERFERENCE ANALYSIS
In GSM mobile communication networks, system capacity is often limited by co-channel interference. This is because of the surrounding cells using the same carrier frequency, or adjacent channel interference when surrounding cells use a channel too close to the serving cell used by a terminal. The GSM recommendations state that reference interference will be achieved at a minimum C/I margin of 9 dB for co-channel interference, and that the margin is -9 dB C/I for adjacent channel interference with voice. With packet switched data connection C/I margin should be much higher. Interference source can be a BCCH or TCH channel, or it can be also from out of band in some circumstances. ETSI 05.05 requirements for the interference rejection are: Co-channel channel interference: z = 9 dB 200 kHz adjacent channel: z = -9dB
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
197
400 kHz adjacent channel: z = -41dB 600 kHz adjacent channel: z = -49dB
GSM co-channel and adjacent channel analysis is done in real time during the measurement and playback with Nemo Outdoor. The user must enable interference analysis similarly, as with, e.g. missing neighbor detection. Interference detection is done based on GSM terminal and GSM scanner measurements and these measurements are combined together. GSM terminal continuously reports RX level, RX quality and C/I values. With RX level and RX quality, the sub values are used to make correct analysis in case DTX downlink is used. In idle mode C/I and RX level values are used to trigger interference analysis from the BCCH channel. A decent RX level with a simultaneous poor C/I value is a clear sign of an interference situation. Once triggering is done, the power of BCCH channel used by a terminal is measured also by a scanning receiver. BCCH decoding must be enabled with a scanning receiver to decode BSIC information. Power of adjacent channels are (+/ - 1) is also measured by the scanning receiver. It should be noted that the C/I value is not available with all test terminals in idle mode. Due to this limit interference analysis in idle mode cannot be performed with all GSM test terminals. During dedicated mode, RX level sub, RX quality sub and C/I reported by terminal are observed. C/I value measured by the terminal is not available all the time in dedicated mode. For example, when AMR speech codec is used, the terminal reports the LQE (Link Quality Estimate) value to the network. During this time the C/I value reported by the terminal is not valid. Please note that all test terminals do not report C/I value. Triggering points in dedicated mode are: RX level sub and RX quality sub, OR RX level sub and C/I
These two combinations are observed all the time during the measurement to trigger interference analysis. Analysis is based on TCH channel numbers if valid data is available, or BCCH if no TCH channel data is found. If frequency hopping is used, C/I average value is used. The user can define triggering limits via the Nemo Outdoor user interface. Default values are: RX Level Sub is above or equal user-defined threshold (default value -90 dBm) RX Quality Sub is above or equal user defined threshold (default value 4) Channel average C/I is below or equal user defined threshold (default value 10 dB)
The following data is extracted from the terminal and written to the terminal measurement file: Terminal serving channel number or TCH channels in case of frequency hopping
198
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Cell ID RX level sub RX quality sub C/I if available
For each terminal serving channel number X, the following data is extracted from scanner measurements and written to terminal measurement file: Channel number, RX level and BSIC for channel X Channel number, RX level and BSIC for channel (X-1) Channel number, RX level and BSIC for channel (X+1)
Results are written to IANALYSIS event and can be displayed in different views, for example, in a table grid and bar graph. If BTS file is used also cell names for the serving and interfering cells can be seen during the measurement and playback. Nemo Outdoor includes two predefined custom windows for GSM interference analysis. Table grid and bar graph.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
199
BAND SCAN
With the Nemo FSR1 scanner you can perform band scanning. All specified channels are scanned for the selected band and technology and the strongest measured identifiers (CDMA PN, EVDO PN, WCDMA SC, LTE Cell ID) for every valid channel of that technology type are reported. Signal strength and signal quality are reported for each identified channel. This feature is useful in areas where broadcasted technologies and bands are unknown. To start a band scan, right click the Nemo FSR1 item in the Devices view and select Band Scan.
Available technologies and bands supported by the scanner are shown under Scan settings. Please note that only licensed technologies (systems) are shown. Select the technologies and bands that you want to be scanned and define the threshold levels for the parameters available. Finally press the Start Scan button. With the default threshold values it takes approximately two minutes and 30 seconds to scan GSM 900, 1800 and WCDMA 2100 bands. The scanning rate can be increased by adjusting the threshold values.
200
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Scanning results are displayed on the Scan results page. It is possible to save the results to a text file (.csv).
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
201
TIMESLOT TESTING
This functionality is available for certain GSM and GSM/UMTS dual-mode mobiles only. With Nemo Outdoor, it is possible to test the timeslots of any particular channel. Select Measurement | <device name> | Timeslot Testing and the Timeslot Test Configuration dialog will be opened.
Phone Number Used for Testing defines the test call number. This must be a valid number. Run Test Until Completed option keeps the test running until all the timeslots have been tested. Note that if you select the Run Test Until Completed option, the test may continue indefinitely. Click the Stop Testing button to interrupt the timeslot test. The Specify call duration option enables you to define a time in seconds that the call will last.
202
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
In the Channel Settings | BCCH channel you define the Channel (BCCH) that you want to test. Timeslots used by BCCH refers to the timeslots that are used for system messaging and therefore cannot be accessed with mobiles. Click on the button to enter the Select Channel dialog.
Save results to file defines whether the report is saved to a file Save results to clipboard defines whether the report is saved on the clipboard after testing.
On the Test results page you can view the progress of the test. Selecting timeslots will exclude them from the test, for example, in the case they are already reserved for data testing. Green color indicates channels and their timeslots that have been called, and the number in the slot the number of calls made in the timeslot. In the table you can see a list of all the TCHs of the selected channel and their timeslots. There is a yellow frame around the timeslot that was accessed during the previous call. Those white timeslots that were not tested will turn red. This happens, for example, if the user stops the testing. The Number of Call Attempts field tells how many calls have been made so far. Click the Stop testing button to interrupt the timeslot test. When there are no more white slots left, i.e. all time slots except for the ones that were excluded from the test by selecting them (grey), the measurement will stop on its own.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
203
VIEWING GRAPHS
There are several types of graphs in Nemo Outdoor: line, scatter, spectrum, and bar graphs. There are some pre-made custom windows of each graph type that offer easy access to relevant network parameters. See chapter Custom Windows for opening custom windows. To open an empty graph, select Data | [graph type] | New. It is possible to view selected parameters in graphs by drag and dropping them in it. Click on a parameter in the Parameters view and drag and drop it on the graph.
204
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Parameters can also be opened for all devices at once and seen on different views. First, press down the Ctrl button and select the devices by clicking on them in the Parameter tree. After this, right-click on the wanted parameter from the parameter tree and select the graph type in which you want the parameter to be opened.
The Parameters view contents can be filtered using the Parameters and Windows buttons. Clear the Windows button, and all the custom windows will be hidden. Clear the Parameters button, and all parameters will be hidden. The options listed in the graph popup menu will be introduced next.
Graph Popup Menu
Right-click on the graph to open a popup menu with various tools for configuring the layout of the graph.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
205
Custom Window Properties
In the Custom Window Properties dialog you can define the custom window name and select groups for the custom windows. The custom window groups define which custom windows are available for each device. For example, if you select LTE FDD, the custom window will only be available when an LTE device is added to Nemo Outdoor or you are playing back an LTE measurement.
Save Custom Window Changes
Use the Save Custom Window Changes command to save changes made in the custom window.
Save as New Custom Window
Right-click on a graph window and select Save as New Custom Window from the popup menu. The Custom Window Properties dialog is opened (see above). Type a name for the custom window and define the custom window groups.
Save as Image
Use the Save as Image command to save the active view as a .jpg image.
Move View To
With the Move View To command you can move the active view to another view group. See chapter View Groups for more information on view groups.
206
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Graph Properties
Right-click on a graph window and choose Properties from the popup menu to open the Graph Properties dialog. You can also open it by clicking the Graph Properties dialog button . Please note that the contents of this dialog varies depending on the graph type (line, bar, scatter, spectrum).
Select Yes in the Show value labels field to view the parameter value as a numerical label above the bar in the graph. Axes define the parameter for the left and right axes in the bar graph. If you select Default, the axis changes depending on the active layer. You can also define different parameters for the axes. This is especially useful if you have two layers open and they have different scales. Automatic bar scale option is available for bar graphs. When the option is set to Yes, the X-scale automatically scales to the displayed data. Select Yes in the Hide panels in full screen mode if you want panels to disappear once you enter full screen mode.
Edit Parameters
By selecting the Edit Parameters item in the menu you will enter the Edit Parameters dialog. Select parameters in the Parameters tree and move them to the editing table with the right arrow button . Remove a parameter from the table by selecting it and clicking the left arrow button
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
207
You can also quickly find parameters through the filter field. Use the up to move the parameters in the editing field.
and down
arrow buttons
The parameters will be shown in the Values view in the Graph side panel. This functionality is particularly useful for viewing textual parameters.
Side Panel
Right-click on a graph window and choose Side Panel from the popup menu. You can also open it by clicking the Side Panel dialog button .
Layers
Select Layers in the popup menu to view the Layers view in the graph side panel.
Values
Select Values in the popup menu to view the Values view in the graph side panel.
Full Screen
Selecting the Full screen item in the popup menu will display Nemo Outdoor in full screen mode.
208
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Zoom - Scatter Graph
To zoom in on a scatter graph, drag your mouse diagonally from either corner with the green dot towards the corners with the red dots. To zoom out, do the same in reverse, dragging the mouse from a red dot to a green dot.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
209
Graph Side Panel - Layers
The layers can be dragged and dropped on some toolbar buttons. For example, a layer can be dragged and dropped on the Remove layer button to remove the layer. The order of the layers can also be changed by dragging them with the mouse.
The layer is now removed.
210
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
To create space in the graph side panel, you can also click on the X button in the right-hand corner of the Layers view. To reopen the view, right-click on the graph and select Layers in the popup menu. You can also change the order of the parameters in the graph by dragging them in the Layers view.
Right-click on the Layers view to view the Layers popup menu.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
211
Grouping Layers
The New Group, Rename Group, Remove Group, Move Group Up, Move Group Down and Group Similar Layers items are used in editing and organizing layer groups. Layer groups can be used to group parameters with the same unit and scale. Parameters in the same group will be displayed in the same scales and the different groups will be stacked in the graph.
The Layers view displays all parameters added in the graph.
212
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Righ-click on the view and select Group Similar Layers.
The parameters will be organized into groups based on the parameter unit.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
213
Groups can be removed, renamed and moved up and down. You can also create a new group and drag and drop parameters into the group.
New Layer
The New Layer command creates a new layer.
Select a parameter in the Y or X field. You can also assign the parameter into a layer group. Define the layer properties, such as, line style and color. See chapter Layer Properties for more detailed information. Click Add to add the new layer and Close to exit the dialog.
214
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Hide Layer
The Hide Layer button hides the selected layer.
Remove Layer
The Remove Layer button removes the selected layer.
Layer Properties
Click on the Layer Properties icon to enter the Layer Properties dialog. The dialog can also be accessed by double-clicking a layer in the panel. The Layer Properties dialog can be used to edit the selected layer.
Line width defines the line thickness in pixels Stairs defines whether the line is drawn connecting two points using two lines (giving a "stairs" appearance) or one straight line Sort(Y): Support for data sorting based on y-value in bar graph. Data can be sorted based on descending or ascending order Draw as area defines whether the area below the line is filled Area transparency defines transparency value used in filling the area (0 = totally opaque, 100 = totally transparent) Averaging refers to whether moving average is used in drawing the line There is an option to manually configure graph layer colors. This feature can be used with line and bar graphs. The Color field determines whether the graph line is colored with a Classic (algorithmic) or fixed color set, or whether a color set based on parameter values is used (see chapter Graph Layer Color Configuration).
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
215
Window size defines the number of values to be averaged Automatic scale the minimum and maximum values of the scale are defined automatically based on the minimum and maximum values visible on the screen Use value scale defaults: the minimum and maximum values of the scale can be defined by the user, so the maximum and minimum values are not dependent on the values that are displayed. Note that if you want to select No in the drop-down menu, Automatic scale also needs to be set to No. Minimum defines the minimum value of the scale, if Automatic scale is set to No. If Automatic scale is set to Yes, this is not used Maximum defines the maximum value of the scale if Automatic scale is set to No. If Automatic scale is set to Yes, this is not used Minimum and maximum threshold define the maximum and minimum values at which the userdefined limits for a measurement result is set. Horizontal lines help determine if the value goes below or above the minimum and maximum values. Depending on the parameter, it is possible to define various filters: Channel: list of channels whose measurement values are shown (Ch = ch1 or ch2 or ch 3 or AND Pilot 0 p1 or p2 or o3 or...). If the list is empty, no filtering is used Pilot: list of channels and pilots whose measurement values are shown (Ch = ch1 or ch2 or ch 3 or AND Pilot 0 p1 or p2 or o3 or...). If the list is empty, appropriate filtering is not used so that it is possible to filter only channels, only pilots or both Frequency: list of frequencies whose measurement values are shown (Freq = f1 or f2 or f3 or); if the list is empty, no filtering is used TopN: only N best measurement results are shown based on a defined parameter. If 0, no filtering is used TopN(Y): Support for best TOP-N filtering based on y-value in line and bar graphs. E.g., only the best two values can be seen in the line or bar graph BottomN(y): This can be done by selecting number of topN and select sorting order. E.g., below bottom three RX levels are shown. Some of the graph types support data tips. Hover the mouse cursor over the graph line or bar. The data tip will display information from that point of time. Parameters with instantaneous values display points instead of a line in a graph. Such parameters are, for example, RACH TX Power, RACH Preamble Step and RACH Preamble Count. Such graphs include also the following layer properties. Point style allows you to select among various icons such as a triangle or a cross to display the instantaneous values in the graph Point size defines the size of the points in pixels in the graph Point transparency defines the degree of point transparency.
216
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
In the following example three RACH parameters are shown in the graph, and each of them has a different point style.
Arrow Down/Up
The Arrow Down and Arrow Up icons will move the selected layer up or down in the graph panel. You can also change the order of the parameters in the graph by dragging them in the Layers view with the mouse.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
217
Layer Device Selection
The Device Selection dialog enables you to view and reorganize layers by device. Layers can be reorganized easily by simply dragging and dropping them from one device to another. The Device Selection dialog is a convenient way to change a device for several layers at once instead of using layer properties dialog for each layer separately.
Graph Side Panel Values & Parameter
The Values view shows the layer parameter values at a specific point during the measurement defined by the position of the cursor in the graph window. Select a layer in the Layers view, and double-click on any parameter in the Values view to view the parameter properties.
If a given parameter value consists of more than one value, a separate parameter window, an extended values list, appears.
218
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
In the example above, the Parameters view is organized into tabs to view more than one parameter and its values. In this example the Ec/N0 (active) parameter is selected. You can also drag and drop the Values and Parameter views inside, beside, above or below each other. For example, in the example below the parameter view is embedded in the Values view.
In the example below all views are separate. By clicking the maximize icon at the upper right-hand corner of a view it is possible to maximize the view. Click the exit icon at the top to close the view. You can reopen the view by right-clicking on the graph and selecting Values.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
219
By right-clicking on the Values view, you can access the Edit Parameters dialog.
Graph Layer Color Configuration
Nemo Outdoor offers an option to manually configure graph layer colors. This feature can be used with line and bar graphs, and is very useful when observing a certain parameter or parameters, as different colors can be assigned e.g., to different channels, scrambling codes, cell ID, etc. First, add parameters to the graph by dragging them from the parameter tree. Next, double-click on a layer in the Layers side panel to enter the Layer Properties dialog.
220
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
If you select the Classic (algorithmic) option for coloring the graph, Nemo Outdoor will pick up the color automatically.
If you choose Fixed color, click to enter the Colors dialog. Define the fixed color by selecting it in the Standard or Custom page, or define the RGB for the color. Click OK. The graph will be colored based on the fixed color you selected.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
221
Selecting Color set in the Color method drop-down menu will activate the Color set parameter and Color set fields.
Select a parameter in the Color set parameter drop-down menu, and a color set in the Color set drop-down menu. Note that only layer-specific parameters will be available in the Color set parameter menu.
222
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
To edit the color set in question, click on Edit Color Set.. button. It will lead you to the Color Set Properties dialog. Here you can edit the color set selected. See chapter Color Set Editor for more information.
The parameter will be colored based on its values in the graph.
In the picture below you will see a bar graph colored based on BSIC numbers. Each BSIC is presented with its own color; the channels without BSIC information appear in blue color.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
223
Similarly, the picture below presents a bar graph where bars are colored based on BSIC numbers. All channels with BSIC information appear in green color, and channels without BSIC information are shown with black color.
224
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
The example below shows a bar graph in which bars are colored based on channel numbers.
How to Read MIMO Parameters in Bar Graph Data View
In the bar below, graph CQI can be seen for both antenna ports. CQI for antenna port 0 is on the top and bottom CQI value (CQI2) is for the second antenna port. For example, in the example below three percentage of time (200ms) CQI value 6 has been used with antenna port 0 and CQI value 3 has been used for antenna port 1. Bars are colored based on CQI type to indentify used CQI type. CQI type A is shown in green and CQI type B is shown in red.
If more detailed information about the link adaptation is needed, it can be seen from the HSDPA link adaptation information table grid. Distribution is shown for both antenna ports from the last sample duration which is set to 200ms. E.g., four percentage of the time during the sample duration modulation for antenna port 0 has been 16QAM with transport block size 14411 bits and for the second antenna port 1 modulation was 16QAM with transport block size 12266 bits.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
225
VIEWING GRIDS
Along with the graph windows, the grid tables offer you useful information about measurement events, such as statistics from the current measurement, QoS parameters, Layer2 and Layer 3 messages (the selection depends on the technology measured), and packet capture data. All events can be decoded by double-clicking on the event row. The decoded message is displayed in a separate window. Alternatively, you can right-click on an event row and from the popup menu select Decode Message. To open several decoded message windows, select Decode Message in New Window option. To view data in Packet decoder grids during playback, you need to enable the packet decoding function in Device Settings Measurement Properties | General | Advanced prior to performing data measurements. Select Full or Partial in the Enable IP Capture field. A separate .pcap-file will be generated for the measurement, and this file needs to accompany the measurement file in the same folder when viewing and decoding packet capture information in Packet Decoder grids in Nemo Outdoor. This requires Microsoft Network Monitor to be installed. Please see chapter IP Packet Capturing for more information. An empty grid table is opened by selecting Data | [Grid Type] | New. If you select one of the readymade custom windows and you have multiple devices connected to Nemo Outdoor, you need to select which device(s) you would like to view in the grid from the Select Device(s) to View dialog. In most grids you only view one device in a grid at a time. Open several grid windows to view multiple devices at the same time. However, in the Parameters grids you can view several devices simultaneously as separate columns.
You can also drag and drop parameters from the parameter tree into grids. Click on the parameter and drag it in the grid. It will be added there. The options listed in the grid popup menu will be introduced next.
226
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Find Function in Signaling Grid Based on Decoded Message
You can use the Find functionality in signaling grids to find message(s) with a specific string in its decoded message. Select the grid view, press Ctrl + F, and type the search string in the Search string field in the Find dialog. Depending on whether Up or Down direction is selected in the Direction field, the event next in the time sequence will be highlighted in the grid.
Grid Popup Menu
Right-click on the grid to open a popup menu with various tools for configuring the layout of the grid. Note that the contents of the menu vary depending on the grid type.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
227
Save As Custom Window
Right-click on a grid table and choose Save As Custom Window from the popup menu. The dialog below is opened. You can also access this dialog from the Data menu.
You can use this dialog to save a custom window with a name. The new custom window is added under the User Interface, Custom Windows item in the Configuration Manager dialog. Right-click on the item to rename the custom window.
Save Changes
Use the Save Changes command to save changes made in the custom window; e.g., size, parameters displayed, and colors.
Move View To
With the Move View To command you can move the active view to another view group. See chapter View Groups for more information on view groups.
Automatic Scrolling
Select the Automatic Scrolling option in order to make the grid view scroll as the measurement progresses.
Grid Color Configuration in Events Grids
To make grids more clear, you can colorize certain events in a grid based on the event name or event ID. Right-click on a grid, and select Configure Colors from the popup menu, or click on the Configure Colors button in the Grid Properties dialog. The Grid Color Configuration dialog is opened. Note that not all events and parameters are available with all devices. In the events Grid Color Configuration dialog select the Event name column. You can set a text color and/or a background color for the selected events. If you want to colorize the background, select Call events (Event name) in the Background Color Set field and select (none) in the Text Color Set field. Alternatively, if you want to colorize only the text in the grid, select Call Events (Event name) in the Text Color Set field from the drop-down menu and select (none) in the Background Color Set field, as in the example below. Note that the contents of the Grid Color Configuration dialog depend on which columns have been selected in the Grid Properties dialog.
228
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Click Edit to view the Color Set Properties dialog. Make sure that the color set type is string. Here you can also add more strings to the color set through Add
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
229
In the String Properties dialog specify the name of the string in the Text field and select the color code for it. If you want, you can also write a description for the string text in the Description field.
Click OK in the String Properties and Color Set Properties dialogs. Finally, click OK in the Grid Color Configuration dialog. You can see color-coded events in the grid data view. Each color corresponds to a certain type of event, defined in the Color Set Properties dialog.
Grid Color Configuration Based on Decoded Message in Grids
Messages and Events grids can be color-coded based on a string in a messages decoded message. In this case, you need to create a new color set in the Color Set Editor. It is possible to color-code both the text in the grid and the background color. While you can choose to colorize only one of them, it is also possible to color-code both text and background. For example, you can have a message appear in white text and blue background color. However, in that case remember to create two new color sets for the same string, for example, Decoded Text_1 and Decoded Text_2. Below you will see an example of how to create a color set and set it for the background color. Click Add
230
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
In the Color Set Properties dialog type, for example, Decoded Text in the Name field. You can also create a short name for the new color set, or write a description for it. Select string as the color set type. Click Add In the String Properties dialog type in the string which will determine the messages to be colored with the new color set.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
231
Click OK, and Close in the Color Set Editor.
Right-click on the grid and select Configure Colors. You can colorize the text color in the grid and/or the background color. If you want to colorize only the text, select the new color set created above, Decoded Text, in the Text Color Set field and select (none) in the Background Color Set field. In this example the background will be color-coded, so (none) is selected in the Text Color Set field, and Decoded Text in the Background Color Set field. Click OK.
232
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
All messages with sysInfoType2 in its decoded message will be color-coded with the Decoded text color set.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
233
Grid Color Configuration in Events Grids Based on Message Name
Messages in Events grids can also be color-coded based on the message name. You can color-code the message text or the background color, or both. Color-coding a message based on its name is done in the same way as color-coding a message based on a specific string in its decoded message. However, when creating the new color set in the Color Set Editor | Color Set Properties | String Properties, you need to type the name of the message you want to color-code instead of the string in the decoded message. Below you will see an example of two color sets made for the same message name. Further, both the message text and background will be colorized. Click OK.
Also click OK in the Color Set Properties and Color Set Editor dialogs.
234
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Next, right-click on the messages grid and select Configure Colors, or select Configure Colors in the Grid Properties dialog. Select Message_2 in the Text Color Set field and Message in the Background Color Set field. Click OK.
All messages called SYSTEM_INFORMATION_BCH will be color-coded with the new color sets.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
235
Grid Color Configuration for Parameter Grids
Grids can be made clearer through colors. Open a parameters grid from Data | Parameters Grid.
Right-click on the grid and select Configure Colors. In the Grid Color Configuration dialog click Use Defaults if no default color sets are shown in the Color Set field. The Clear All button inactivates the default color sets. Note that not all parameters have default color sets assigned to them. You can choose a color set for a selected parameter in the Text Color Set and Background Color Set dropdown menus depending on whether you want to color the text/values or the background of the text/values in the grid. If you want to set a color set for both text and color for the same parameter, note that you need to use two different color sets for it.
236
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
You can also edit the default color sets by selecting a color set and clicking Edit In the Color Set Properties dialog you can change the default settings to the color set.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
237
Parameters with assigned color sets are colorized according to their value. In the example below a background of the parameter values has been color-coded. Click OK twice to exit the Grid Color Configuration dialog.
238
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Grid Color Configuration for Table Grids
Table grids have default color sets assigned to them. Go to Data | Table Grid | New. In the Grid Properties dialog select a device and a parameter set to be viewed in the table grid. Click OK.
The parameters are colorized according to their default color sets. You can also edit the default color sets. Right-click on the grid, select Configure Colors the parameter you wish to edit, and Edit The Color Set Properties dialog appears where you can change the color set settings. Click OK to exit the dialogs and go back to the table grid.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
239
You can also view cell name information for missing neighbors when a scanner and a mobile are used simultaneously.
Configure Filters/Quick Filter
Another method to organize Events grids is to use filters. By using filters, only the selected messages will be displayed. Right-click on a grid view and select Configure Filters from the popup menu
240
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
. The Grid Filter Configuration dialog is opened.
Select the Showing all option to display all events in the grid window as default. Select the Hiding all option from the drop-down menu to hide all events in the grid window as default. If you would like to view one or more messages of a selected type and hide others, select hiding all lines. If you would like to hide one or more messages of a selected type and view others, select showing all lines. You can add a filter rule for the grid by clicking on the plus you options based on which the grid filtering takes place. button. A conditional row appears giving
It is possible to set filtering rules for message name, subchannel and decoded text. In addition, you can select a parameter in the Select Parameter dialog which you can access through the Other Parameter item in the filter target popup menu.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
241
The contents of the condition menu vary depending on which item in the filter target menu is selected.
Note also that a separate, independent condition needs to be added from the plus icon at the top left-hand corner of the dialog. If a condition has two or more constituents, the plus icon next to the first constituent needs to be clicked. In this case the conditions are indented and combined with one another with the text and if, and both conditions need to be met for the filtering to take place. In the example above, a line is filtered out if a message contains a missing neighbor ec/n0 value that is less than -5. The second filtering rule states that if a message name contains the text SYSTEM_INFORMATION_BCH and if a message contains SysInfoType18, the message is filtered out from the grid.
242
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
The minus icon removes a row next to it from the list. Alternatively, you can delete all filters by rightclicking on a grid and selecting Quick Filter and Remove All Filters from the popup menu. The Quick Filter menu offers a shortcut to defining filter rules for messages. Right-click on a row in the grid and select Quick Filter from the popup menu.
You can now quickly define a filter for the selected layer message. You can choose to hide the respective message and all similar messages either according to the Event (Hide this Event), subchannel (Hide This Subchannel) or according to the message text (Hide This Message). All messages with the selected event, subchannel name or message text will be hidden. In the same way, you can choose to display messages of the selected type only. Select Remove All Filters to delete all filter rules. When filtering is enabled, the text Filtering will appear in the title bar.
Decode Message
This function will open the selected event row in a decoded form. You can also decode messages by double-clicking on the message row. In the message decoding grid you can use the Show Next Message and Show Previous Message grid toolbar buttons to move to the previous/next message. If you move forward or back in the message decoding grid, use the Go to Message button to move to the same message in the messages grid. Click the Copy to Clipboard button to copy the contents of the message decoding grid as text to clipboard. With certain events such as cell measurement (CELLMEAS), it is also possible to arrange the contents of the decoded message in three different ways.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
243
The Format as list arranges the contents of a grids measurement results in a list. The Format as horizontal table arranges the contents in the form of a horizontal table with columns, and the Format as vertical table arranges the contents in a vertical table. The search field in the decoded text window enables the user to find a string in the decoded message window.
Select a string of text in the decoded text, right-click on it and select Copy to copy the selected text as text to the clipboard. If no text is selected in the decoded text window, all text in it will be copied. This is the same as the Copy to Clipboard functionality.
244
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Decode Message in New Window
This function enables you to have several decoded message windows open at the same time.
Automatic Decode
The Automatic Decode function opens up a window which displays the currently selected or latest message in decoded form.
Save - Grid
The Save command allows you to save a selected event row as a text file (.txt). If you select the Decoded Text option, the decoded event text is saved in a text file. You can also save the entire grid window as an image file (.jpg). From Events grids, you can export data into a MapInfo Tab-File or into a CSV file.
MapInfo Tab-File Export
You can export measurement data into a MapInfo .tab file. In an Events grid, select Save | MapInfo Tab-File. The MapInfo Tab-File Export dialog displays a list of parameters that can be exported. Select the parameters that you would like to include in the .tab file. Also define a File name and Layer title for the exported .tab file.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
245
To change the symbol for each parameter, double-click the parameter or select a parameter and click the Change Symbol button. The symbol is used to draw the route in MapInfo. In the Symbol Style dialog, you can select the symbol and define some effects and background color for it. Finally click OK.
Click OK in the MapInfo Tab-File Export to save the .tab file.
CSV File Export
You can export measurement data into a CSV file. In an Events grid, select Save | CSV File..
246
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
The exporting is supported for a single file, and the column separator can be a comma, semicolon, tab or space. The file(s) can be opened with third-party applications. Indoor files are not supported at the moment. The user can select all events or only specific events from the grid for export.
Copy
The Copy command allows you to copy a selected event row and paste to another application as text or as decoded text. If you select the Decoded Text option, the decoded event text is copied on the clipboard. You can also copy the entire grid window as an image and paste to another application.
Select All
Through the Select All item you can select all events in an Events grid. This presents an easy and quick way to select all lines, for example, to be exported.
Find
The Find command allows you to search through the measurement file opened in the grid.
Type in the Search string field what you are looking for. Define if the search results should match case and if the search should be applied to whole words only. You can also limit the search to decoded messages only. The matches are highlighted in the grid one by one. To move down to the next match, press F3. To move up to the next match, press Shift+F3.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
247
The search field in the decoded text window enables the user to find a string in the decoded message window.
Below you will see a list of commands for the decoded text view. Ctrl + Shift + F = Go to search field in decoded text view Enter = Highlight next match in decoded text view (when search field is focused) Shift + Enter = Highlight previous match in decoded text view (when search field is focused) Esc = Clear search field in decoded text view (when search field is focused)
Add/Remove Separator
The Add/Remove Separator option is relevant only with parameters and Statistics grids. Right-click on a grid table and choose Add/Remove Separator from the popup menu. You can choose a statistic or a parameter and add an open space (a separator) above it by first clicking it and then choosing the Add Separator option from the popup menu. You can remove the separator by clicking the open space and choosing Remove Separator from the popup menu.
Full Screen
The Full Screen item enables you to view Nemo Outdoor in full screen mode.
Grid Properties
Right-click on a grid table and select Properties from the popup menu. The Grid Properties dialog is opened. Note that the appearance of the grid and the selection of parameters depend on the grid type and on the measurement device.
248
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
You can select the events, parameters, and statistics you would like to see in the grid table. The available parameters are organized by technology and call mode in the All tab. If you select, for example, the UMTS option, all the parameters under UMTS are selected. You can also select individual parameters. Expand the branch by double-clicking on the main item (GSM, UMTS, Voice, etc.). Select the parameters that you would like to view in the grid and click OK. In the Selected tab you can view which parameters you have selected and change their order using the arrow buttons. Click the Configure Colors button to access the Grid Color Configuration dialog.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
249
User Parameters
The User Parameters function allows you to specify parameters from layer messages that will be automatically decoded and the values displayed in the Device Status window or in graphs. Click the User Parameters button in the Parameters dialog to access the Layer Parameters dialog.
Click the Add button to define new parameters.
Parameter name and Short name refer to the long and short name of the parameter to be decoded. Search string is the string that is searched from the decoded layer messages, for example, Ordered MS power level. Layer defines the layer messages from where the string is searched. After you have defined all the parameters, click OK. The new parameter is added to the list in the Layer Parameters dialog. Click OK to exit the dialog. In the Parameters dialog, expand the User Parameters item. Select the parameter you just defined and click OK.
250
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
The list of user parameters that you have defined are saved in a file called Parameters.xml. User Parameters can be searched in messages grids. The user can also perform more complex searches where the search key is split across multiple rows of data. It is possible, for example, to search and display multiple results in a single Layer 3 message.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
251
Exporting/Importing User Parameters
Exporting user parameters
It is possible to export and import user parameters from and to Nemo Outdoor. 1. To export user parameters, go to File | Export Settings in Nemo Outdoor. Save the .aex file on your PC. The exported parameters will be saved on this file.
2. Next, the Export Settings dialog appears. Scroll to the User Parameters folder. The user parameters previously created are listed under the folder. Select the ones you wish to export, and click OK. You can also select other items to be exported in the dialog.
252
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
3. The selected user parameters and possible other items that you selected in the Export Settings dialog are now saved in the .aex file that you saved earlier.
Importing user parameters
1. To import user parameters, select File | Import Settings in Nemo Outdoor.
2. Select the user parameters you wish to import in the Import Settings dialog.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
253
3. Click OK. The user parameters are now saved and are shown in the Nemo Outdoor parameter tree under User Parameters. If there already is a user parameter with the same name saved, the imported user parameter will replace it.
VIEWING MAPS
Nemo Outdoor supports two types of outdoor maps: MapX and OpenStreetMap maps. Most of the functions are the same for both types but there are some differences. Please note that in order to use OpenStreetMap maps, the computer needs to be connected to the Internet or OpenStreetMap data must be downloaded on the computer. Open a map by selecting Data | Map | New MapX or New OpenStreetMap. If you open a new MapX map, Nemo Outdoor will open by default the map that you have entered in the Default Map field in the User Interface Properties dialog, Paths tab. If you open an OpenStreetMap map, the view will center on your current location. The map window specific commands can be accessed through toolbar buttons as well as from the popup menu when right-clicking on the map. See chapter Map Toolbar Buttons for a description of the Nemo Outdoor map toolbar buttons. Note that the Indoor map differs from the example below. For information on Indoor measurements, refer to chapter Viewing Indoor Maps.
254
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
It is possible to view selected parameters on a map by drag and dropping them in it. Click on a parameter in the Parameters view and drag and drop it on the map. Parameters can also be opened for all devices at once and seen on different views. First, press down the Ctrl button and select the devices by clicking on them in the parameter tree. After this, right-click on the parameter you wish to view from the parameter tree and select Open in Map from the drop-down menu.
If you have a GPS receiver connected to the test system, the current location of the test vehicle will be displayed on the map as a circle on the route. If there is no GPS connected to the system, you can define the current location manually with the Set Current Location tool. A new GPS event is created in the handler after which all location-specific data, such as BTS cell names are displayed using the specified location. You can observe the values of certain network parameters from the route coloring on the map. You can define which color refers to which parameter value. This way it is easy to spot the problem areas on a map. While viewing notifications on a map, hovering above the notification icons will display a tooltip with information such as cell name (if cell site file is used) and channel number.
Base Stations on a Map
If you select a BTS file (.nbf) for the measurement file, the base stations will be displayed. A line will be drawn from the test vehicle to the serving base station. Also, the distance to the serving base station is displayed in the status bar of the map window. Note that the BTS file is displayed only if a device is associated with the BTS file (BTS Properties Connected devices). The BTS icons display the antennas, the channel numbers for the antennas, and directions that the antennas point to. The antennas are drawn in one degree steps. Hover your mouse over the base station icon to see more information about the BTS.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
255
Note that if there are more than five cells in a BTS, the BTS name will be truncated with In this case, click on the BTS icon to view the rest of the cells.
Editing Base Station Files in Nemo Outdoor
It is possible to edit the locations of base station icons directly in Nemo Outdoor. Open a BTS file on a map. Right-click on a BTS icon and select Move. Then click on the new location and the BTS icon is moved there. You can also remove BTS sites from the BTS file. The changes are saved in the BTS file when you exit Nemo Outdoor.
Right-click on a BTS icon and select Edit or right-click on the map and select Add Site. In the BTS Editor you can edit the site and cell information. You can also add new sites, cells, and neighbor cells by clicking the Add button.
For sites, you must define the following information: site name, longitude, and latitude.
256
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Under sites you have cells. For cells there are some mandatory and optional settings.
The settings below are mandatory. System defines in which cellular system the cell belongs. Cell name defines a unique name for the cell.Antenna direction defines the direction of the antenna in degrees. Channel number defines the channel number. Cell ID/Cell ID 16-bit defines a unique cell ID for the cell. Radio network controller ID defines a unique radio network controller ID for the cell. Scrambling code defines a unique scrambling code for the cell. The settings below are optional. Antenna height defines the height of the antenna from the ground in meters. Antenna tilt defines the angle of the main beam of the antenna relative to the horizontal plane. Antenna beam width defines the width of the beam in degrees. Cell range defines the range of the cell in kilometers. For Cell type the options are undefined, normal, and repeater. Location area code defines in which location area the cell belongs. Routing area code defines in which routing area the cell belongs. UTRAN registration area defines in which UTRAN registration area the cell belongs.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
257
MapX Maps
You can customize the MapX map view using the MapX properties. The customized settings can be saved in a MapInfo Geoset file (.gst) and loaded later on. MapInfo Workspaces (*.wor file) cannot be directly opened with MapX, but can be saved as a .gst file in MapInfo Professional using the MapInfo MapX Geoset Utility tool (Geoset.mbx) that ships with version 5.x of MapInfo Professional. This file (.gst) can be directly opened by MapX in Nemo Outdoor. Each MapInfo raster map has two files: an image file (.tif. .gif, .jpg) and a .tab file When MapInfo raster maps are used, the image file is the actual map image file. The .tab file contains information about a map (such as location coordinates) and is used by Nemo Outdoor to refer to a particular map. When using vector data for MapInfo, there are three different files that need to be in the same directory, the .tab, .map, and the .id file. The corresponding image and .tab files for raster maps have to be in the same folder in order to view a MapInfo map. If you are using a large map (size over 1 Mb), updating the map window will slow down Nemo Outdoor functions. We recommend you minimize the map size by reducing the number of colors to 256 or 16, or turning the color map to black and white.
Map Side Panel
258
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
The contents of the map side panel depend on which items have been selected in the map popup menu. Right-click on a map and select Color Legend, Layers, and Waypoints in the popup menu to view the three items above. You can drag each view to different places on the map as well, or dock it to another side of the map window following the arrows that appear when you drag the window. When you double-click on the displaced view, it will resume its original position in the side panel. You can view three different kinds of items in the Layers view. The item indicates a devicespecific measurement route on the map, the item indicates a base station file connected to the measurement route, and the item indicates a route plan. Double-click on an item to access its Properties dialog (see Layer Properties). You can also access the Properties dialog by right-clicking on the item and selecting Properties in the popup menu. When you right-click on a layer, the following popup menu appears:
In the popup menu you can select whether or not you want to show or delete a layer. You can also clear the option next to the layer item if you do not want to view it, or click on the X button next to the option to delete the layer. Through the Properties item you can access the layers Properties dialog (see Layer Properties), and you can also add a new route or a new BTS file from the popup menu or directly from the Layers view. The Add route functionality is useful, for example, when a multi measurement is loaded, and you want to view all the routes in the Layers view and all the color legends in the Color legends view. The Color legends view shows the selected color set for a measurement route. If you have loaded a multi measurement and added multiple routes with assigned color sets on the map, the color legends will be shown next to one another in this view. See chapter Color Set Editor on how to create and edit color sets.
The Waypoints view is meant for controlling route plans. The Show next waypoint field is only activated when at least one device and one GPS receiver are attached to Nemo Outdoor in online or offline mode. This functionality is not active during measurement playback. See the Route Plans chapter below for more information on waypoints.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
259
Route Plans
Route plans are useful when you want to follow a certain route while performing a measurement. You can create route plans automatically from a measurement in playback mode, or you can manually create one with the Add waypoint functionality both during a measurement and during playback. In addition, you can alter the route plans at any point through the control buttons in the Waypoints view in the map side panel. You can save a route plan as a Route Plan File (.rpf), and if you have made any changes to the route plan properties in the map window, you can save them as a custom window for later use. The custom window will also contain changes made to the color set or Waypoints views. If you have previously created and saved a route plan (.rpf), you can open it through the Open Route Plan item in the map toolbar or by right-clicking on the map and selecting Open Route Plan from the popup menu. The route plan (.rpf) is now viewed on the map and in the map side panel, and is ready to be used in a measurement. By pressing Ctrl+A you can jump from one waypoint to the next.
Creating and Modifying Route Plans with Waypoints
Start Nemo Outdoor with at least one device and a GPS receiver attached to it in online or offline mode. You can select a ready workspace in the Nemo Outdoor Welcome page (see Configuration through Welcome page) as you start Nemo Outdoor and view a map window, or alternatively you can open a map manually from Data | Map.
260
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
You can create a route plan manually by clicking on the Add waypoint button in the map toolbar, or by selecting Add Waypoint in the map popup menu, and clicking on the map. The Add button at the bottom of the Waypoints view in the side panel is also activated. A new route plan (.rpf) is viewed in the Layers view, and the Waypoints view is enabled. You can save the route plan for later use by clicking on the Save Route Plan icon in the map toolbar or by selecting it in the map popup menu.
You can define waypoint-related settings in the Waypoint view in the side bar. The Show next waypoint option should be selected when you want to view the next waypoint on the map during a measurement. Note that the Show next waypoint functionality is only enabled in online or idle mode, not during playback. The next waypoint is shown on the route as a big circle. If you clear the Show next waypoint option, the Waypoint detection radius and Distance to next waypoint items will also be disabled.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
261
The Waypoint detection radius slide bar indicates at which distance (meters) the next waypoint is selected. As you approach the next waypoint during a measurement, the next waypoint is selected on the map when distance to it is smaller than the distance selected in the slide bar. The Distance to next waypoint field indicates how many meters there still are to the next waypoint from the current position on the route, so the figure decreases as you approach the next waypoint.
You can make changes to the route plan through the four buttons at the bottom of the Waypoints view. To select a waypoint on the map, click on the Select button in the Waypoints view, then select a waypoint on the map. This waypoint is shown as a bigger circle than the others, and the Distance to next waypoint field will display the appropriate distance in meters to the next waypoint. In addition, the delete functionality is only enabled when the Select button is selected. If you click on Delete, the selected waypoint on the route plan will be deleted, and the previous waypoint on the route will automatically be selected and shown as a bigger circle. If the deleted waypoint was the first waypoint on the route plan, the next waypoint on the route will be selected. Moreover, the Delete button is only enabled with the Select button if there is more than one waypoint on the map. Reclick on Select to clear the functionality.
262
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
You can move waypoints on the map by first clicking on Select, then selecting a specific waypoint on the map. Click on the Move button, and you will be able to move the selected waypoint on the map. The part of the route attached to the waypoint is moved with the waypoint. The Add button in the Waypoints view in the side panel is synchronized with the Add waypoint button in the map toolbar. If you click on either button when they are inactive, they will both be activated, and conversely if you click on either button when active, they will become inactive. When you select either, you are able to place new waypoints in the route plan.
Creating and Saving Route Plans from a Measurement
In addition to creating a route plan with waypoints, you can create a route plan from a measurement. Start Nemo Outdoor, load a measurement file and open a map window. Right-click on the map and select View Entire Route, or zoom in on the map to make sure the measurement contains GPS coordinates. Create a route plan by clicking the Create Route Plan toolbar icon, or select the option from the map popup menu. The route plan should now be visible on the map, the layer list should have a new layer (Untitled.rpf), and the control buttons on the Waypoints view should be enabled. The route plan should closely follow the route from which it was created. Save the route plan by clicking the Save Route Plan item in the toolbar, or by selecting it in the map popup menu.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
263
You can also modify the route plan with the Select, Move, Add and Delete buttons at the bottom of the Waypoints view in the side panel. Note that when you click on Select, you may need to zoom in on the map to view the discrete waypoints. The selected waypoint will show as a bigger circle among all the circles. See chapter Creating and Modifying Route Plans with Waypoints for more information on how to use the control buttons, and on how to read the waypoints on the route plan during a measurement.
Saving a Route Plan to a Custom Window
When you create a route plan and save it, the actual route plan will be saved as a Route Plan File (.rpf). However, if you have made changes to the default map window and to the layer-specific properties, and you want to save these changes, you need to save the map window as a custom window. When you open a measurement the next time, you can open the custom window by rightclicking on the gray space outside the map window, and select Map | [name of custom window]. You will also find the custom window in Data | Map | [name of custom window]. First, create or open a route plan, and save it. Next, double-click on the route plan in the map side panel to access the Route Plan Properties dialog, change the properties and click OK. Change the settings in the Waypoints view in the side panel, right-click on the map, and select Save As Custom Window in the map popup menu. Close the map and open the custom window you saved. When you open the properties dialog, the properties should be what you set them to.
264
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Map Popup Menu
Right-click on the map to open a popup menu with various tools for configuring the layout of the map. Please note that the contents of the menu depend on the map type (MapX or OpenStreetMap).
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
265
Custom Window Properties
In the Custom Window Properties dialog you can define the custom window name and select groups for the custom windows. The custom window groups define which custom windows are available for each device. For example, if you select LTE FDD, the custom window will only be available when an LTE device is added to Nemo Outdoor or you are playing back an LTE measurement.
Save Custom Window Changes
Use the Save Custom Window Changes command to save changes made in the custom window.
Save as New Custom Window
Right-click on a graph window and select Save as New Custom Window from the popup menu. The Custom Window Properties dialog is opened (see above). Type a name for the custom window and define the custom window groups.
Save as Image
Use the Save as Image command to save the active view as a .jpg image.
Save as MapInfo Tab-file
Use the Save as MapInfo Tab-file command to export the active view into MapInfo format.
Save as CSV File
Use the Save as Image command to export the active view into CSV format.
266
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Export to Google Earth
By clicking on the Export to Google Earth item you can export a map with measurement route, colors based on selected parameter, notifications, and base station information to Google Earth .kml file which can be viewed with the installed Google Earth application.
Move View To
With the Move View To command you can move the active view to another view group. See chapter View Groups for more information on view groups.
Open Map
By selecting the Open Map item, you can open existing map files (.tab).
Save Map
By selecting the Save Map item, you can open the Save As dialog that you can use for saving the map with another name.
Find Map at Position
When you right click on the map and select the Find Map at Position item, Nemo Outdoor will view a list of possibly more detailed maps of the same location from the directory you have specified in the View | User Interface Properties | Paths dialog. In this way you have the possibility to choose the most appropriate map for your purposes. You can also browse for a suitable map manually by clicking on the Browse button and browsing your local folders.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
267
Download Tiles
With the Download Tiles tool you can download OpenStreetMap data on your computer so you can use the OpenStreetMap maps even when you are not connected to the Internet.
Zoom levels defines the number of levels from which map data is downloaded. The more levels you choose, the more data is downloaded. Select the Reload existing tiles option to overwrite existing map data. Click the Select Area button to the select an area with your mouse from where map data will be downloaded.
Empty Disk Cache
Select the Empty Disk Cache option to delete all downloaded OpenStreetMap data. The tiles open on the map will not be deleted.
Create Route Plan
The Create Route Plan item creates a route plan from an open measurement in a map window.
Open Route Plan
Through the Open Route Plan item you can open saved route plans to be viewed on a map.
Save Route Plan
The Save Route Plan item will let you save the route plan as a Route Plan File (.rpf) for later use.
Add Waypoints
Activates the add waypoint functionality for creating route plans manually.
268
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Find Cell
With Find cell functionality you can search for a cell in a map window based on a parameter. Below a cell is searched based on its Cell ID number.
Tool
Tool pull-down menu offers a selection of settings for configuring the window setup. Arrow tool changes the cursor back to an arrow. Pan tool changes the cursor into a hand that can scroll the map. Center tool allows the map to be centered according to the cursor point. Zoom In and Zoom Out tools change the cursor into a magnifying glass. You can also zoom in and out using the mouse wheel and the + and - keyboard buttons. Clear Route tool removes the measurement route from the map. Note that this command is activated only during measurements. It cannot be used during playback. Set Current Location tool defines the current location when no GPS data is available. Note that this command is activated only during measurements and when no GPS is connected. It cannot be used during playback.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
269
Auto Center
The Auto Center tool pans the map so that the current location will stay on the visible area of the map. Note that you cannot use the Pan and Center tools when the Auto Center command is selected.
Auto Clear Route
The Auto Clear Route tool automatically removes the route from the map when measurement is stopped. If you wish to keep the route on the map when starting a new measurement, unselect the tool.
Previous View and View Entire Map
With the Previous View command, you can return to the previous map view, and the View Entire Map command displays the whole map.
View Entire Route
By selecting the View Entire Route item you will be able to view the whole route on the map.
Scale
The Scale appears in the window when the respective selection is activated.
Modify Route
With the Modify Route tool you can modify and reposition the measurement route in playback. This is especially useful if there is a gap in the measurement route, for example, because GPS fix was lost in a tunnel. Right-click on a map and select Modify Route from the popup menu.
270
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
The route will be displayed as dots.
Drag and drop the dots into their new positions. Please note that you should maintain the correct order of the dots. Otherwise the route will appear jagged.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
271
When you have finished modifying the route, right-click on the map and clear the Modify Route tool. The modified route is now displayed in normal mode.
Add Site
With the Add Site tool you can edit and add new BTS sites on the map. Please see chapter Editing Base Station Files in Nemo Outdoor for more information.
Textual Comments
With the Textual Comments tool you can add textual comments on the map. Select Add Textual Comment from the menu and type in the text box that appears on the map. The box can be repositioned by dragging it on the map. To remove or edit individual comments, right-click on the text box and select Remove or Edit. To remove all comments, right-click on the map and select Textual Comments | Remove All Textual Comments.
Color Legend
Color Legend displays the name of the selected Color Set on the map window.
Layers
By selecting the Layers item you will be able to view all the layers of the map in the map side panel.
Waypoints
The waypoints item will activate the free route planning functionality on the map. You can create and save a route plan for later use. See chapter Creating and Modifying Route Plans with Waypoints for more information.
272
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Measure Distance
Use the Measure Distance tool to measure the distance between multiple points on a map. Click the Measure Distance button to activate the tool and click the Add point button. Select the points on the map and the distance between these points is displayed on the map. The Total distance is displayed in the left-hand panel.
With the Draw distance circle tool you can draw a circle where the distance between the last two points is used as the radius.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
273
To remove points from the map, click the Remove latest point or Remove all points buttons. To hide the Measure Distance panel, click the Measure Distance button.
Side Panel
When Side Panel is selected, you will be able to view the side panel in the map window. The Color Legend, Layers and Waypoints items can only be viewed in the side panel, and if you activate any of these items, also the side panel will be shown along with the specific item. However, if you start by activating the side panel, all the three items will be shown in the side panel.
Full Screen
Selecting the Full screen item will display Nemo Outdoor in full screen mode.
Layer Properties
The dialog appearing when you click on the Layer Properties item depends on the layer selected in the map side panel. It is possible to view three different kinds of layers in the side panel: the devicespecific measurement route layer, the base station layer, and the route plan layer.
Route Properties
When a measurement route is selected in the side panel and you right-click on the map and select Layer Properties, the Route Properties dialog appears. You can also access this dialog by doubleclicking on the device-specific route layer in the side-panel.
In the case of multi measurements, you need to select a device in the drop-down menu on the Device page. Select the Show Device Label next to route option to display the device name at the starting point of the measurement route. By clicking on the MapX Properties button you will enter the MapX Properties dialog.
274
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
In the Route page you can define route line specific settings. The Line thickness field allows you to define the thickness of the route in pixels. The X offset and Y offset fields allow you to move the route on the map in x and y directions. With the Show parameter next to route option you can display a selected parameter value in numerical format next to the route. Select the parameter and define the text and background colors. Select the Show active cell information option to display active cell information and direction. The Draw as dots item enables you to view the measurement route in dots instead of a line. If the Draw as dots item is selected, the Dot size field appears and allows you to define the dot size in pixels. If you select the Draw thicker line when using high band option, the route will be drawn thicker when the device is using the 1800/1900 band. When the Draw during pause option is deselected, the route is not drawn during when measurement is in pause.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
275
On the Color page you can define route-specific line coloring. Use default color defines a single color for the measurement route. The entire route is drawn with the same color. If you would like to colorize the route based on parameter values, select the Use color set option. First, select the Parameter for which you would like to define colors. Then select a matching color set in the Color set field. Click the Edit Color Set button to access the Color Set Editor dialog. Please note that even if you are using a color set to colorize the measurement route, the route will be drawn with the default color if the selected parameter does not have valid values. Therefore it is best not to use the default color in the color set. If you are measuring with a scanner, click on Configure Filters to select specific channels or scrambling codes for which the parameter values are displayed.
276
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
To select scrambling codes, first select a channel by clicking the Select button under Selected channel numbers. Then select scrambling codes for the selected channel by clicking the Select button under Selected scrambling codes.
If you would like to use averaging in drawing the route, select the Trend line option and select from the Number of previous values field how many values will be included in the average value. When the Hide route line on invalid value is selected, the default color is not drawn. For example, if the route is colored based on Ec/No but the terminal is using GSM, the system route is not drawn while in GSM.
On the Notifications page select the Show notifications option to view notification icons on the map. You can also define the notification icon size in pixels.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
277
By selecting the Show Textual notes option on the Textual notes page, you will be able to view textual notes on a measurement route in the map window. You can select a text and background color for the note in the Text color and Background color fields.
The Base stations page displays information on the open BTS files on the map. Connected BTS File refers to the BTS file that is used in connection with the map. Select a BTS file by clicking the Add BTS File button in the map side panel. See chapter Side Panel for more information. Select the Draw line to active base station option to draw a line from the serving BTS to the test vehicle. Define also the line Thickness and Color. Select the Draw line(s) to neighbor cell(s) option to draw a line from the neighboring cells to the test vehicle. Define also the line Thickness and Color. Select the Draw only to active system cell(s) option, if you only want to draw a line from active system cell(s) to the test vehicle.
278
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Select the Draw line(s) to detected neighbor cell(s) option to draw a line from the detected neighboring cells to the test vehicle. Define also the line Thickness and Color. Select the Draw line(s) to missing neighbor cell(s) option to draw a line from the missing neighboring cells to the test vehicle. Define also the line Thickness and Color. Please note that lines to missing neighbor cell(s) are drawn only when measuring with a mobile and a scanner. If missing neighbor detection is performed using a scanner only, this information is not shown on the map. Instead, the missing neighbor information can be viewed in a table grid. Select the Draw line(s) to interferer cell(s) option to draw a line from interferer cells to the test vehicle. Define also the line Thickness and Color. Please note that a BTS file must be used with this feature. GSM interfering analysis results (IANALYSIS event) are written to the terminal output file and due to this reason, the interfering cells can be seen on a map only when a BTS file is used with the terminal. Click OK to exit the Route Properties dialog.
BTS Properties
When a base station file is selected in the map side panel, the BTS Properties dialog appears when Layer Properties is selected in the map popup menu. You can also view the dialog by double-clicking on the BTS file in the map side panel.
BTS file refers to the BTS file that is used on the map. If you have a BTS file that contains base stations from several systems (e.g., UMTS and GSM), select the Draw only active system base stations option to display only base stations from the active system, in other words, the system in which the test device is currently. The other base stations are hidden.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
279
Define also the size and color of the BTS icons. Note that you define a different color for active system base stations and for other base stations. The Selected BTS cell color refers to neighbor cells that can be highlighted on the map if neighbor information is defined in a BTS file. Neighboring cells are highlighted with the selected color and the selected cell is shown with the same color but also with a bolded outline. The tooltip shows neighbor cell names for the selected cell.
Select the Use color set to color BTS icons when you want to distinguish between different base stations through the use of existing and user-defined color sets. Select a parameter from the Parameter drop-down menu based on which you want to color base stations, and a color set in the Color set drop-down menu.
280
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Clicking on the Edit Color Set button will lead to the Color Set Editor dialog where you can edit existing color sets or create a new one to suit your needs.
See chapter Color Set Editor for more information on how to edit and create color sets. On the Cell info page you can choose what information is displayed from each base station.
Select the Show labels option to display a label or a description next to the selected cell information and define the Text color and Background color.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
281
In the example below, all cell information and the Show labels option are selected.
The Cell Range page enables you to view cell range on the map. Define the degree of cell range transparency in the Cell Range transparency slide bar.
282
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
The Connected Devices page displays a list of devices that you can connect to the base station sites. Note that the BTS sites will not be drawn if no device is selected.
Route Plan Properties
When a route plan is selected in the side panel and you right-click on the map and select Layer Properties, the Route Plan Properties dialog appears. You can also view the dialog by doubleclicking on the route plan in the map side panel.
Route plan file field defines the name of the route plan you selected in the map side panel. The Waypoint properties field allows you to define the color for the waypoint icon and the line attaching the icons together. You can also define the icon size and line thickness in pixels. The X offset and Y offset fields allow you to move the route plan on the map in x and y directions.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
283
MapX Properties
Click the MapX Properties button to define some MapX specific properties. Note that these settings differ according to the map provider. These settings can be saved in a MapInfo Geoset file by clicking the Save Map button in the Map window. To later open the .gst file, click the Open Map button, select MapInfo Geoset file in the Files of Type listbox, and select a file from the list.
If you are using MapInfo maps, you can define the appearance of the map even further by clicking the MapX Properties button in the Route Properties dialog. In the Layers tab the table shows a list of the current layers. The order on the list defines the order in which the layers are displayed on a map; for example, in this case the Route layer is on the top, Current Position layer is under that, and World map is at the bottom. This utility is useful if you want to have a bigger map on the bottom (e.g., a map of Europe) and a more detailed map of a smaller area (e.g., of Helsinki) on top of that. To add layers on the map click Add. An Open dialog is opened where you can choose the map you want to add as a layer. The map is added on the list and with the Up and Down you can change the maps position on the list. By selecting and clearing the Visible option you can decide whether or not to display the layer on the map. To remove layers from the map, select the layer from the list and click the Remove button.
284
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Color Set Editor
You can access the Color Set Editor by clicking the Edit Color Set button in the Route Properties | Color dialog. You can also access the Color Set Editor by selecting View | Color Set Editor.., or by double-clicking Color sets in the Configuration Manager (Ctrl+ M). With the Color Set Editor you can define and name color sets to be used in maps and grids. In the Color Set Editor dialog you will see a list of all existing color sets. You can sort the color sets by selecting the Type. You can also search for a color set by its name. To edit an existing color set, double-click on the color set.
In the Color Set Properties dialog you can edit the settings for each color set.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
285
Name and Short name identify the color set. You can also type a description of the color set in the Description field. Type defines what kind of data the color set is used with, numerical, gradient, string, or automatic. T The Groups and Type settings can be used to sort the color sets in the Color Set Editor dialog. Values table displays the different value ranges and the colors associated with them. Click the Add button to define the colors and limits. In the Range Properties dialog, select the color and then the upper and lower limits of the value range. You can also write a description for the value range. Finally click OK.
Click the Add Range button to quickly assign colors to parameter values. In the Add Range dialog, define the top and bottom values and the step, i.e., how many values are represented by the same color. Finally click OK and Nemo Outdoor will automatically assign colors for the parameter values.
286
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Map Example 1
In the map below, the measurement route is colored using the Active set size color set. In the Route Properties | Route dialog, Color page, select Number of TBF-s Uplink in the Parameter field, and Active set size in the Color Set field, and click OK. The Color Legend in the map side panel displays the color codes for the Active set size values.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
287
Map Example 2
In the map below, the measurement route is colored using the TX Power color set. In the Measurement's Route Properties dialog, Color page, select TX Power in the Parameter and Color Set fields and click OK. The Color Legend in the map side panel displays the color codes for the TX Power values. In this color set, green means a low TX Power level and red a high level.
288
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Map Example 3
In the map below, the measurement route is colored using the EcN0 color set. Base station icons are displayed and a red line is drawn to the serving base station and a blue line to the neighbor stations. In the Layer view in the map side panel, click on Add BTS File, or right-click on the measurement layer and select Add BTS File. Right-click on the measurement layer in the map side panel again, and select Properties | Base stations. Select the Draw line to active base station, and Draw line(s) to neighbor cell(s) options. On the Color page, select the Use color set option, select Ec/N0 (Active) in the Parameter field, and EcN0 in the Color set field. Click OK. The Color Legend in the side panel displays the color codes for the EcNo values.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
289
Map Example 4
In the map below, the same measurement route is drawn twice on the map. The route with the blue current location symbol is colored using the Ec/N0 color set, and the route with the black current location symbol is colored using the MS Power Level color set. In the Layers view click the Add Route button, or right-click on the existing measurement layer and select Add Route. Select a device from the Route Properties | Device page, and now there should be two measurements in the Layers view in the side panel. Right-click on the first measurement route and select Properties. On the Route Properties | Color page, select the Use color set option, and Ec/N0(active) in the Parameter field, and Ec/N0 in the Color set field. Click OK. Next, right-click on the second measurement in the Layers view, and select Properties. In the Route Properties | Color page, select the Use color set option, and MS Power Level in the Parameter field, and MS Power Level in the Color set field. Click OK. You will see the two adjacent routes colored with the above-mentioned color sets on the map. In addition, you will see the measurements in the Layers view, and their color sets in the Color legends view in the map side panel.
290
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Map Example 5
It is possible to export a map with measurement route, colors based on selected parameter, parameter values, notifications, and base station information to Google Earth .kml file. The Google Earth application needs to be installed for viewing the file. Click on the Export to Google Earth toolbar button in the map window.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
291
A Save As dialog appears. Select a destination for the saved .kml file in the Save in field, and type a name for the map to be exported in the File name field. Click Save.
Go to the file destination and double-click on the saved file to open it. Note that you must have Google Earth installed on your laptop to view the file.
The route and cell information are visible on the Google Earth map.
292
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Map Example 6
With scanner measurements, it is possible to view parameter values for a specific channel or scrambling code on a map. In this example we will view RX level values for a selected channel. First open a scanner measurement on a map.
Right-click on the route layer in the Layers view and select Properties.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
293
On the Route Properties, Color page, select Use color set. Select RX level in the Parameter field. The corresponding color set is selected automatically.
Click on Configure Filters. In the Select Channels dialog, first click Remove All and then select one channel by double-clicking on the channel in the Available list. Click OK and OK.
294
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
The route now displays the RX level values for the selected channel.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
295
VIEWING INDOOR MAPS
Open an indoor map by selecting Data | Indoor | New and click the Open Map button. The supported indoor map types are MapInfo, iBwave, and Google Earth maps (.kmz). Please refer to Google Earth documentation on how to create KMZ files. To view measurement data on KMZ maps, select Data | Indoor | New. Change the file type to Google Earth Files (.kmz). Select a map file and click Open. KMZ and MapInfo maps have the same functionalities. For more information on iBwave files, please see chapter iBwave Maps. It is possible to view selected parameters on an indoor map by drag and dropping them in it. Click on a parameter in the Parameters view and drag and drop it on the graph. Parameters can also be opened for all devices at once and seen on different views. First, press down the Ctrl button and select the devices by clicking on them in the parameter tree. After this, right-click on the parameter you wish to view from the parameter tree and select Open in Indoor from the drop-down menu.
296
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
To view a route on the floorplan you must have a marker file (.mrk) attached to the measurement file (.nmf). To move the markers on the map, select a marker in the Markers | Index field, click on Move and select a new destination for the marker.
On the map you can view, for example, a floorplan of the test site. While you are performing the measurement and walking around in the building, use the markers to draw the measurement route on the floor plan. If you are running Nemo Outdoor on the Microsoft XP Tablet PC Edition, click with the Tablet PC pen on the screen and the marker will be placed there. You can observe the values of certain network parameters from the route coloring on the map. You can define which color refers to which parameter value. This way it is easy to spot the problem areas on a map. Map layers can be saved to .gst file and also as a custom window.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
297
Floorplans and BTS Files
You can also use BTS files on indoor maps. Open a route on an indoor map. Click the Add BTS File button and browse for a BTS file.
After the BTS file is loaded, select a device that will be connected with the BTS file. Click OK.
298
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
The BTS icons will appear on the map and when the measurement file is played back, a line is drawn from the test device to the serving base station.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
299
Multiple Routes and Floorplans
You can also view more than one route on a floorplan. Click on Add Route in the Layers view in the side panel to add a route, and go through the steps mentioned above. The floorplan below has three routes, two with parameter-based coloring and one with a default color. When more than one route with parameter-based coloring exists, you can switch between the color legends in the Color legends side panel.
You can load multiple floorplans in the indoor map by clicking on the Add Floorplan button in the Layers view. This makes it possible for you to have, for example, indoor maps of different floors on the same building at once. You can switch between the different floorplans through the Go Downstairs and Go Upstairs buttons.
300
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Indoor Route Planning
Prior to conducting indoor measurements, you can plan the route in the indoor map window. You can create a route plan manually by clicking on the Add waypoint button in the map toolbar, and clicking on the map. The Add button at the bottom of the Waypoints view in the side panel is also activated. A new route plan (.rpf) is viewed in the Layers view. You can save the route plan for later use by clicking on the Save Route Plan icon in the map toolbar or by selecting it in the map popup menu.
The route planning functionality with indoor measurements works in the same way as with outdoor maps. See chapter Route Plans for more information.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
301
iBwave Maps
iBwave indoor maps can be viewed in Nemo Outdoor. Please refer to iBwave documentation on how to create iBwave maps that can be imported to Nemo Outdoor. To view measurement data on iBwave maps, select Data | Indoor | New. Change the file type to iBwave Design Files. Select an iBwave map file and click Open.
If the map file contains several building, choose one of them and click OK.
302
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
The map is opened. With the Go Downstairs and Go Upstairs buttons you can move the view between floors. From the Layers list you can hide and displays the different floors and the BTS files for each floor.
Nemo Outdoor will not automatically place the measurement route on the correct floor. Therefore, when making measurements on several floors, it is adviced to make a separate log file for each floor and, for example, include the floor number in the measurement file name. Alternatively, you can add a textual note in the log file identifying the floor number in question. This way you will be able to place the measurement route on the correct floor when playing back the log file.
BTS Files on iBwave Maps
You can also view BTS sites on iBwave maps. An iBwave map file contains, by default, BTS sites but you will also need a separate BTS file (.nbf) that has the same BTS sites with matching cell IDs than the iBwave file. Without the .nbf file, BTS cell information and antenna directions will not be displayed.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
303
First open an iBwave map and click the Add BTS File button to open the .nbf file.
Select the BTS file (.nbf) and then select the device connected with the map. Click OK.
304
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
The BTS file (.nbf) appears in the Layers panel but to make it appear on the map, you will need to associate it with the iBwave BTS file. To do this, right-click one of the iBwave BTS layers and select Properties.
On the Linked BTS page, select the .nbf file that you opened on the map and click OK.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
305
The BTS sites and cell information are now displayed on the map.
306
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Indoor Map Popup Menu
Right-click on the floorplan to open a popup menu with various tools for configuring the layout of the map.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
307
Custom Window Properties
In the Custom Window Properties dialog you can define the custom window name and select groups for the custom windows. The custom window groups define which custom windows are available for each device. For example, if you select LTE FDD, the custom window will only be available when an LTE device is added to Nemo Outdoor or you are playing back an LTE measurement.
Save Custom Window Changes
Use the Save Custom Window Changes command to save changes made in the custom window.
Save as New Custom Window
Right-click on a graph window and select Save as New Custom Window from the popup menu. The Custom Window Properties dialog is opened (see above). Type a name for the custom window and define the custom window groups.
Save as Image
Use the Save as Image command to save the active view as a .jpg image.
Save as MapInfo Tab-File
Use the Save as MapInfo Tab-File command to export the active view into MapInfo format. See chapter MapInfo Tab-File Export for more information.
Save as CSV File
Use the Save as Image command to export the active view into CSV format. See chapter CSV File Export for more information.
308
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Move View To
With the Move View To command you can move the active view to another view group. See chapter View Groups for more information on view groups.
Open Map
By selecting the Open Map item, you can open existing map files (.tab).
Save Map
By selecting the Save Map item, you can open the Save As dialog that you can use for saving the map with another name.
Import Map
You can import your own bitmap files to Nemo Outdoor and use them as maps. Click the Import Map button in the map toolbar or select Import Map from the popup menu. The Map Import Parameters dialog is opened.
In order for the map and route drawing to function correctly, you must define some map settings. Either define the dimensions in meters of the area visible on the map or define the GPS coordinates of the upper left corner and the lower right corner of the map area.
Create Route Plan
The Create Route Plan item creates a route plan from an open measurement in an indoor map window, after which you can save the route plan.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
309
Open Route Plan
Through the Open Route Plan item you can open saved route plans to be viewed on an indoor map.
Save Route Plan
The Save Route Plan item will let you save the route plan as a Route Plan File (.rpf) for later use.
Add Waypoints
Activates the add waypoint functionality for creating route plans manually.
Tool
The Tool pull-down menu offers a selection of settings for configuring the window setup. With the Add Marker command you can add markers in the measurement file. The Arrow selection changes the cursor back to an arrow. The Pan selection changes the cursor into a hand that can scroll the map. The Center selection allows the map to be centered according to the cursor point. The Zoom In and Zoom Out selections change the cursor into a magnifying glass. You can also zoom in and out using the mouse wheel. The Clear Route command removes the measurement route from the map. Note that this command is activated only during measurements. It cannot be used during playback.
Center on New Marker
The Center on New Marker option defines whether the indoor view is centered on a marker when it is inserted.
Auto Center
The Auto Center tool for MapInfo pans the map so that the current location will stay on the visible area of the map. Note that you cannot use the Pan and Center tools when the Auto Center command is selected.
View Entire Map
The View Entire Map command displays the whole map.
View Entire Route
The View Entire Route command displays the whole route.
Textual Comments
With the Textual Comments tool you can add textual comments on the map. Select Add Textual Comment from the menu and type in the text box that appears on the map. The box can be repositioned by dragging it on the map. To remove or edit individual comments, right-click on the text box and select Remove or Edit. To remove all comments, right-click on the map and select Textual Comments | Remove All Textual Comments.
310
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Show Minimap
With the Show Minimap command you can view and hide the Minimap in the Indoor window. Minimap displays a miniature version of the map and the current location is highlighted with a red square.
Show Marker Info
Show marker info hides or displays markers inserted into the measurement file.
Show Waypoints
The waypoints item will activate the free route planning functionality on the map. You can create and save a route plan for later use. See chapter Creating and Modifying Route Plans with Waypoints for more information.
Color Legend
Color Legend displays the name of the selected Color Set on the map window.
Show Markers
Show Markers hides or displays markers on a map.
Show Layers
Selecting the Show Layers item in the popup menu will display the Layers view in the side panel.
Full Screen
Full Screen switches the Indoor map view to full screen. Close the full screen view by clicking on Close Full Screen in the popup window that appears.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
311
Route Properties Indoor Map
In the Route Properties dialog, you can define map-related settings.
Device defines the device that is being viewed on the map. Click the MapX Properties button to define some MapX specific properties. Note that these settings differ according to the map provider. These settings can be saved in a MapInfo Geoset file by clicking the Save Map button in the Map window.
In the Route page you can define route line specific settings.
312
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
The Line thickness field allows you to define the thickness of the route in pixels. The X offset and Y offset fields allow you to move the route on the map in x and y directions. With the Show parameter next to route option you can display a selected parameter value in numerical format next to the route. Select the parameter and define the text and background colors. Select the Show active cell information option to display active cell information and direction. The Draw as dots item enables you to view the measurement route in dots instead of a line. If the Draw as dots item is selected, the Dot size field appears and allows you to define the dot size in pixels. When the Draw during pause option is deselected, the route is not drawn when measurement is paused.
Use default color defines a single color for the measurement route. The entire route is drawn with the same color. If you would like to colorize the route based on parameter values, select the Use color set button. First, select the Parameter for which you would like to define colors. Then select a matching color set in the Color set field. Click the Edit Color Set button to access the Color Set Editor dialog. See chapter Color Set Editor for more information on defining color sets. If you would like to use averaging in drawing the route, select the Trend line option and select from the Number of previous values field how many values will be included in the average value. When the Hide route line on invalid value is selected, the default color is not drawn. For example, if the route is colored based Ec/No but the terminal is using GSM, the route is not drawn while in GSM. Please note that even if you are using a color set to colorize the measurement route, the route will be drawn with the default color if the selected parameter does not have valid values. Therefore it is best not to use the default color in the color set.
D URI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
313
Selecting the Show notifications option will view notifications on the indoor map. You can define the size of the notifications in pixels in the Size field.
314
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
ENDING MEASUREMENTS
The measurement is being recorded when a REC text appears in the upper right corner of the main window. Follow these instructions to stop the measurement.
To end the measurements:
1. If you are using a script to perform the measurement, you can either wait until the script file has been executed or interrupt the script either by selecting Measurement | Stop Script or by clicking the Stop button on the toolbar. 2. If you are performing measurements manually, the measurement process is terminated either by selecting Measurement | Stop or by clicking the Stop button on the toolbar. All the ongoing calls will be stopped and scanning will be terminated. Data transfers will be stopped, PDP context will be deactivated, and GPRS detach will be performed. 3. Nemo Outdoor will display a report window with some call statistics. At this point, you can choose if you would like to save this file or delete it. You can also start a playback of this file. 4. If you wish to exit Nemo Outdoor, select File | Exit or click the cross in the upper right corner of the Nemo Outdoor main window. When carrying out measurements using a script, stopping the measurement is not recommended while a test call is on. Always wait until the end of the call, then select Measurement | Stop Script or click the Stop button to end the measurement. If the measurement is stopped while the test call is on, it may affect the Quality Survey Report values. The Call Length from the TCH assignment percentage in this report might indicate calls to be shorter than they actually were.
E NDI NG M EAS UREM E NTS
315
MEASUREMENT REPORT
The Measurement Report dialog is displayed when recording is stopped. The dialog displays some statistics from the measurement. Select the Save statistics to file option to save the statistics to a separate Excel .csv file. The filename is the same as for the actual measurement file and the file is located in the Results folder. If you do not want this dialog to appear, select the Do not show this dialog again option. To save the measurement file under another name, click the Rename button and type a new file name in the field that appears. To delete the file without saving, click the Delete button. To export the measurement, click the Export button (see Exporting Measurements). Click the Playback button to playback the measurement file immediately. To save the file, click Save. Note that if you press Esc on your computers keyboard, or click on the button on the dialog, you will save the measurement file just as if you had clicked on the Save button. Click the Export button the access the Export Measurements dialog (see Exporting Measurements). Click the Analyze button to open the measurement file for analysis in Nemo Analyze. Note that this requires that you have Nemo Analyze installed on the same computer where Nemo Outdoor is installed.
316
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
In the Analyze Measurement dialog, select a workbook where the data is opened and/or a report template that is used for creating a report from the data. If you do not select a workbook or a report, the measurement file is added to the Nemo Analyze database without starting Nemo Analyze. Finally click Upload.
USE R I NT ERF ACE
317
MEASUREMENT RESULTS
This section guides you on viewing and analyzing the measurement results produced by Nemo Outdoor, and explains how measurement files are uploaded to an FTP server. The measurement process produces one or more output files at a time, depending on whether you have been using a mobile and a scanner at the same time or just one device at a time. The file name can be user defined but Nemo Outdoor always decides the extension part. If you change the file name manually, the file name format should be xxxx.1.nmf where the number refers to the device number.
ANALYZING MEASUREMENT RESULTS
The measurement results produced by Nemo Outdoor can be viewed and analyzed, for example, with: Nemo Outdoor Playback functions Nemo Analyze Text editor Spreadsheet software such as Microsoft Excel Mapping software via conversion utilities provided by Anite Finland Ltd.
PLAYING BACK MEASUREMENT FILES
Playback is a handy tool for making a quick analysis of measurements. You can playback files anytime and anywhere immediately after the measurement has been finished or later on.
Selecting Playback Files
When you open a file for playback, Nemo Outdoor will deactivate all connected devices. Nemo Outdoor will ask if you would like to save the current device. If you answer Yes, Nemo Outdoor will save the current configuration and reactivate the devices that you had connected before the playback when you close the playback file(s). The following file types can be opened by dragging and dropping them from Windows Explorer: Measurements files (.nmf) Workspaces (.worx) Hardware configurations (.hwcx) Maps (.tab, .gst)
318
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
To open files for playback, select File Open Measurement. This will open up the following dialog.
In the dialog, you can look for a file by clicking the button. The File Header box displays the measurement file header. If you have selected a multi measurement, you can still clear some of the files from playback.
During Playback
The Playback commands can be executed with a set of toolbar buttons. The same commands can be found in the Playback menu. The Play button starts the playback. The Pause button pauses the playback. The Stop button stops the playback. With the Add Textual Note button you can add written remarks in the measurement file. The status bar at the bottom of the main window displays the progress of the playback; that is, the starting, ending, and current time. There is also a time slider which you can use to jump into certain points in the measurement.
USE R I NT ERF ACE
319
Viewing and Moving Markers
You can use the grid window to view the markers you have inserted in a measurement file during measurements. After a file has been loaded, select the Play command from the Playback menu or click the Play button on the tool bar. Open a marker grid from Data | Events Grid | User Markers.
The grid window will display all the markers that you have inserted in the file during measurements. Click on any of the markers in the grid window, and all the other open windows will display the same point of time.
320
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Markers are also displayed on the Indoor map along with the marker number. You can move the markers by selecting a marker from the list (click the index number) and pressing the Move button. Place the red pin to the new location on the map. The new longitude and latitude information is saved in the marker file.
Closing Playback Files
After playback, you need to close the playback file. Select File | Close Measurement. If you saved the current device configuration when you started the playback, Nemo Outdoor will ask if you would like to load the same device(s).
USE R I NT ERF ACE
321
UPLOADING MEASUREMENT FILES TO AN FTP SERVER
You can upload measurement files from Nemo Outdoor to an FTP server when a measurement is stopped, or at any later point via the Nemo Outdoor user interface. Note that it is recommended to stop all measurements before uploading files. Select File | Send Measurement to FTP Server. Select one or more measurements in the Send Measurement to FTP Server dialog.
Click on the FTP Options button.
Under FTP Server you can define the FTP server address in the Server address field, and the name of the folder to which the measurement files are sent on the FTP server in the Remote folder field. The Username and Password fields will grant you permission to access the server.
322
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Select the Use SFTP protocol option to send the measurement files using SFTP protocol. Select the Use passive mode option to send the measurement files using passive mode. When the Move local files to Sent folder after upload option is selected, the measurement files are moved to the Sent folder in the C:\Nemo Tools directory on your computer after the transfer. You can also change this default destination in User Interface Properties | Paths | Measurements. The file transfer can be performed using a default Internet connection or via a user-selected dial-up connection. When you select the Use a Proxy Server option, the Proxy address, Username and Password fields will become active. After configuring the FTP settings, click OK. The Measurement file(s) are sent to the FTP server.
EXPORTING MEASUREMENTS
With the Export Measurements functionality it is possible to export measurement files from Nemo File Format to MapInfo or .csv formats. Close all measurements and select File | Export Measurements. You can also export individual measurements through the Measurement Report dialog when you are ending measurements.
USE R I NT ERF ACE
323
The Export Measurements dialog is opened.
Template contains a predefined set of parameters and parameter rules for export. To create a new template, select New in the Template field and type a name for the template. Then select the parameters that will be exported and define parameter rules. When you export the parameters, the settings are saved. The saved template will be available in the Template field the next time you open the Export Measurements dialog. With the Add Measurement and Add Folder buttons you can add individual measurement files or entire folders containing measurement files to be exported. Export format defines the format in which the files are stored. The options are MapInfo TAB file and CSV file. Export interval defines at what rate (in seconds) parameter values are sampled from the measurement data for export. If you select all, all data is exported. Number of values per parameter defines the maximum number of values exported for parameters that can have multiple values. By default, multiple values of the same parameter are exported in a single column. To create a separate column for each value, select the Separate values to columns option. With the Export files to folder option, the individual files will be saved in a folder. Also define the Target folder.
324
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
With the Export to single file option, the selected files will be stored in a single .tab file. Click the Select Parameters button to define which parameters will be included in the export.
Select a parameter from the list of available parameters and with the arrow button move it to the right. The selected parameters will be exported. You can also make more rules for selecting parameter values for export. Only those parameter values that meet the rule will be exported. Click the Edit Rules button.
Select a parameter from the field in the middle. Then define the condition and value for the parameter and click Add to List. You can define as many rules as you wish. Finally click OK. When you have selected all parameters to be exported, click OK.
USE R I NT ERF ACE
325
326
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
USER INTERFACE
This section presents the Nemo Outdoor user interface. You will find general descriptions on all the commands and windows. The functions and dialogs related to the commands are described in detail in the following sections. The Nemo Outdoor user interface is compatible with common Windows standards. If you are not familiar with these standards, refer to your Microsoft Windows Documentation.
VIEW GROUPS
View Groups is a function that allows you to organize measurement windows into different tabs for easier viewing. This is especially useful if you have several graphs and maps open at the same time and you have to overlap them to fit them all in the Nemo Outdoor main window. Now you can create view groups and organize the measurement windows into several groups. Each view group appears at the bottom of the main window as a tab that you can view by clicking the tab.
When you start Nemo Outdoor for the first time, you will have one default view group. To rename the default view group, right-click on the tab and select Rename.
Enter a name for the view group and click OK.
To create a new view group, right-click on the empty area next to the existing view groups, and select Create New. Enter a name for the view group and click OK. The new view group appears as another tab.
To organize measurement windows into the view groups, open a view group, for example, Maps, and open the windows that you would like to have in this particular view group. Then go to another view group by clicking on the respective tab, for example, Graphs and open measurement windows there. The windows are automatically saved in the view groups and will be opened the next time you start Nemo Outdoor. To copy the contents of an existing view group to a new view group, right-click on the view group label and select Copy to New View Group. Type a name for the new view group and select the device for which the data is displayed.
USE R I NT ERF ACE
327
If you need to change the device for which the views in a particular view group are displaying data, right-click the view group label and select Select Device. Select the device from the list. All the views in the view group will be updated to display data from the selected device.
MENU BAR
The menu bar contains all Nemo Outdoor commands. The commands are arranged in menus. Some commands execute their respective operations immediately, while others will first display a dialog with options for you to select from. A command ending in three dots () will open a dialog. Note that you can use shortcut keys to carry out some of the commands. The shortcut keys are presented on the menus next to the menu commands.
TOOLBAR
You can use the toolbar with the mouse for quick access to frequently used commands. In the View menu, you can choose to hide the toolbar; this will bring more space to the other objects in the main window. The Nemo Outdoor toolbar comprises of a set of buttons that allow you to perform common tasks quickly. For example, to start the measurement, just click the Start Recording button on the toolbar. See chapter Toolbar Buttons for more information on the Nemo Outdoor toolbar buttons.
STATUS BAR
The status bar at the bottom of the Nemo Outdoor window gives you variable information depending on the operations you are performing. For example, when you are pointing to a toolbar button with the mouse (without clicking), the status bar will show a description of the corresponding function. You can also see a brief description of the same function in a help box that appears next to the button when you hold the mouse over the button long enough. There is also a time slider which you can use to jump into certain points in the measurement. In the View menu, you can select to hide the status bar; this will bring more space to the other objects in the main window.
328
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
NEMO OUTDOOR MENUS
The menus in the Nemo Outdoor software are introduced next.
File Menu
The File menu allows you to open and save Workspace files and Device Configurations. Measurement files for playback are also opened through the File menu. By selecting the Save Workspace on Exit option, the current configuration is saved in a file and opened automatically the next time the program is started. The Work Offline item activates and deactivates the offline mode. The Send Measurement to FTP Server enables you to send measurement files to an FTP server (see chapter Uploading Measurement Files to an FTP Server). With the Export Measurements tool you can export measurement files from Nemo File Format to MapInfo or .csv formats (see chapter Exporting Measurements). With the Export and Import Settings items you can export and import settings into an .aex file. The following items are stored in the .aex file: Scripts Color sets Custom views Device configurations Notification settings Route plans Workspaces
You can also export measurements. Note that measurement needs to be closed before export.
USE R I NT ERF ACE
329
The Recent Workspaces, Recent Device Configurations, and Recent Measurements items display the recently used workspaces and device configurations and recently viewed playback files, respectively. With the Exit command you can close the program.
Edit Menu
In the Edit menu, you can copy and save as images selected items from the Nemo Outdoor program. It is also possible to export data views as images and open them in MS Word or PowerPoint. Please note that playback needs to be idle or paused and measurement must be paused when exporting views. The Find command allows you to search through the measurement file opened in the grid.
View Menu
330
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
In the View menu, you can select, hide and display items of the main window, such as the standard toolbar, custom window toolbar, status indicator, output, and device status, those you wish to see on the screen. Through quick windows you have easy access to custom windows defined by the user. You can also access the Configuration Manager, Color Set Editor, Notification Manager, User Parameters and the User Interface Properties dialogs. Through the View Groups item you can create new view groups or switch between existing View Groups. The Active View Properties will open a properties dialog for the currently active window.
Measurement Menu
Through the Measurement menu, you can control the measurement process and add, autodetect and remove devices. The Start Scripts command starts and stops a user-defined script file. These same commands can be executed by clicking the Start/Stop Scripts button in the toolbar. In the Script Editor you can edit script files. You can also add markers and textual notes in the measurement file. The Clear Buffers command will empty the event history buffer. This does not affect the measurement file. Through the All Devices item you can control several devices at once. For example, you can make a voice call or send an SMS with all test mobiles connected to Nemo Outdoor.
USE R I NT ERF ACE
331
Below All Devices are listed individually all measurement devices connected to the system. Through these items you can control and configure the individual test terminals.
Measurement Properties General, Measurement Properties Measurement Settings, Measurement Properties Frequency Scanning with Mobiles, Measurement Properties Pilot Scanning with Mobiles, and Measurement Properties - Script dialogs can be accessed through this menu. By selecting the Reset command, you can reset the Devices window, for example, if you want to reconnect and activate a device after disconnecting it. The menu also offers access to various actions that can be performed during manual measurements. If you are using scripts to run measurements, you will not need these commands. Please note that the menu displays only those functions that are supported by the device. Note that you cannot use scripts with scanners.
332
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Playback Menu
The Playback menu offers you commands for the playback of measurement data. The same commands can also be executed by means of toolbar buttons. With the Play, Pause, and Stop commands you can control the playback. You can also add markers and textual notes in the playback file.
Data Menu
Through the Data menu you can open different views for observing a measurement. You can also access the Open Custom Window dialog (see chapter Custom Windows).
Under each type you will find a selection of premade custom windows of the selected type. If you select New, Nemo Outdoor will open an empty graph of the selected type. By right-clicking the Spectrum Graph item you are able to see the static line graph displaying spectrum scanning results. By adding markers (vertical lines) on top of the window, it is possible to see the RX level for certain frequencies shown on the side panel. Markers can be also edited, added or removed via edit marker window.
USE R I NT ERF ACE
333
The Grid items offer a selection of grid types. Events grids list, by default, all measurement events but the user can configure the view so that only events that are of special interest are displayed. Parameters grids display selected network parameters. Statistics grids list various statistics, such as, the number of PDP context activation attempts, successes, and failures from the measurement. Messages grids are used for observing layer 2 and 3, RLC/MAC, and LLC messages. Table grids provide an easy way of simultaneously displaying the same parameter values for multiple instances. For example, the neighbor list of a serving cell can be displayed in a table grid so that each row represents one neighbor and each column represents a parameter value (e.g., system, carrier, scrambling code, etc.). The Packet Decoder Grid offers a chance to display and decode packet capture files in playback mode. The Indoor item opens a floorplan (see chapter Viewing Indoor Maps). The Map item opens a map window (see chapter Viewing Maps).
334
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
The Save as Custom Window item offers a quick way to save your own custom windows. The custom windows are presented in chapter Custom Windows. The Save Changes option saves changes to measurement windows. For example, if you resize the windows, Nemo Outdoor will open the window in the same size the next time you start the program.
Window Menu
The Window menu provides you with a list of all open windows on the main window. You can switch the focus between these windows and arrange them with the Cascade, Tile Horizontally, Tile Vertically, and Arrange Icons commands. With the Close All command you can close all windows at once. The active window is marked with a check mark .
Help Menu
The Help menu offers you quick access to all the most important help topics. By selecting the License Information item, you can check the current license status for your Nemo Outdoor version. From the About dialog you can also receive further information on the Nemo Outdoor application, including the contact information and the application version number.
USE R I NT ERF ACE
335
CUSTOMIZING MENUS AND TOOLBARS
Nemo Outdoor menus and toolbars are fully customizable. To edit the contents of menus, to add new menus, or edit the toolbars, right-click on the menu bar or toolbar at the top of the main window and select Customize.
In the Toolbars page hide and display the default toolbars by clearing and selecting the corresponding options. Click the New button to create a new toolbar. In the New Toolbar dialog, type a name for the new toolbar and click OK.
336
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
The new toolbar is added to the Customize dialog. Delete the toolbar by selecting it and clicking the Delete button.
In the Commands page you will find all available commands sorted under categories. Drag commands from the list to a toolbar or menu.
USE R I NT ERF ACE
337
To remove commands from a toolbar or menu, drag and drop the command outside the toolbar or menu. If you want to restore the original toolbar and menu content, open the Customize dialog (rightclick on main toolbar and select Customize) and in the Toolbars page, select the toolbar or menu bar you want to restore and click the Reset button.
338
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
In the Options page you can further personalize the appearance of toolbars and menus. For example, you can activate large icons for toolbars for easier viewing or change the menu animations.
You can also change the icon for each toolbar button. Open the Customize dialog, right-click on a button, and select Change Button Image.
USE R I NT ERF ACE
339
NEMO OUTDOOR WINDOWS
The windows in Nemo Outdoor are highly user configurable. Different network parameters and events can be viewed as line graphs, bars, and dots. To make the measuring process easier for first-time users, Nemo Outdoor offers some ready-made custom windows that include some essential windows for specific types of measuring. The users are also able to make their own custom windows and save them for later use.
Custom Windows
Nemo Outdoor offers a selection of premade graphs and grids which can be quickly accessed through the Data menu or the Custom window tool bar if selected in the View menu. They are also accessible through the parameter tree. The custom windows are grouped under the corresponding graph and grid types. You can also browse for the existing custom windows through the Open Custom Window dialog (Data | Open Custom Window).
You can view the existing custom windows sorted by type (graph, grid, map, indoor view) or by technology (AMPS, CDMA, GSM, UMTS, etc.). Select the custom window you would like to open from the table on the right and click Open.
340
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
You can also save your own custom windows. When you have set up a graph view that you would like to use later on, activate the window that you would like to save and select Data | Save as Custom Window. Nemo Outdoor will ask you to type a name for the new custom window. After clicking OK, the window is added to the custom windows list. If you want to remove some custom windows, select the custom window that you want to remove and click the Delete button. The Quick Windows bar (go to View, and select Quick Windows) in Nemo Outdoor main window offers quick access to custom windows. Click on one of the quick windows, and select a custom window from the list. Click OK. The next time you click on the same quick window button, that selected custom window will appear.
Parameter Tree Search Functionality
A user-specified search string can be used to search parameters, parameter short names and possible alias names. In addition, the string matching supports multiple search substrings separated by spaces i.e. HSDPA BLER search string matches, for example, HSDPA MAC-hs BLER and HSDPA HARQ process BLER.
USE R I NT ERF ACE
341
Devices View
The Devices view offers easy access to the most common commands and configuration dialogs. The view displays all devices connected to Nemo Outdoor and the device-specific commands. By doubleclicking the various items in the view, you can access the related configuration dialogs. For example, double-click the FTP item to access the FTP Transfer Properties dialog.
342
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
It is also possible to select multiple devices (Ctrl+left-click) and define settings that will be applied to all selected devices. For example, if the same APN is used with several devices, you can select the devices and define the APN for all devices at one go. When you have selected multiple devices, you can only edit settings that are supported by all the selected devices. From the Supported Data Protocols list, select the data protocol (FTP, SMTP, TCP/UDP, etc.) used in the measurements. Measurement servers button opens the Measurement Servers dialog (see Nemo Invex Device Set-Up) where you can connect to Nemo Invex servers. Note that this button is activated only if your Nemo Outdoor license includes the Nemo Invex option. Add or remove devices button opens a menu where you can choose to add a new device or remove the selected device. Measurement control button offers access to some commands that are supported by the selected device, such as, start/stop voice call, GPRS attach/detach, SMS/MMS message sending. Measurement settings button offers access to configuration and properties dialogs. The selection is device-specific. Device connection settings button opens the Device Configuration dialog (see Devices). Device measurement settings button opens the Measurement Properties Measurement Settings page for the selected device. Device notification settings button opens the Measurement Properties - Notifications page (see Notifications) for the selected device. Device script settings button opens the Measurement Properties - Script page for the selected device. Group devices by type/server button organizes the devices in the view.
USE R I NT ERF ACE
343
Device Status View
The Device Status view displays the device status. The green light at the upper left corner is blinking whenever the device is active and connected.
344
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Right-click on the Device Status view and select Toggle Status Window Docking Area to dock the Status view to the top of the main view.
Right-click on the Device Status view and select Reorder Devices to change the order of the devices in the Device Status and Devices views. Drag and drop the devices in the correct order and finally click OK.
USE R I NT ERF ACE
345
Server Status View
The Server Status view is available only with Nemo Invex.
The Server Status view displays the server status and some information about the server hardware. Right-click on the Device Status view and select Toggle Status Window Docking Area to dock the Status view to the top of the main view. Right-click on a server in the Device Status view and select Add New Device to Measurement Server to open the Add New Device dialog. Right-click on the Device Status view and select Measurement Servers to access a list of measurement servers connected to the system. You can connect and disconnect the servers. Right-click on a server in the Device Status view and select Restart All VQ Modules to access a list of measurement servers connected to the system. You can connect and disconnect the servers.
346
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Output Window
The Output window displays program messages and textual notifications. Icons ( ) next to the timestamps clarify the type of message or notification in question. For example, the speech bubble indicates a normal message, the orange flag a warning, the red flag an error message, and the exclamation mark a notification. The window can be opened by choosing View | Output. You can clear the Output window by right-clicking on the window and selecting Clear Window from the popup menu.
Script Status Window
Note that since you cannot use scripts with scanners, this window is also not available when making scanner measurements. From the Script Status window you can follow the progress of the script file used in the current measurement.
Controlling Windows
You can have several windows open at the same time. The minimizing, maximizing, and closing functions for individual windows operate in the same way as in all Windows applications. The active window is indicated through a color specified in the Windows Control Panel to indicate an active window (see your Microsoft Windows Documentation). You can drag windows outside the Nemo Outdoor desktop area to make more space on the main window.
Cascade Windows
The Cascade command in the Window menu organizes the windows in an overlapping array. You can bring any window to the top by selecting it from the Window menu or by clicking any visible part of that window (except for the Minimize, Maximize, and Close buttons in the top right corner). You can also bring the next window to the top by selecting the Next command from the window-specific menu (top left corner of the window).
USE R I NT ERF ACE
347
Tile Windows
The Tile command in the Window menu organizes the windows side by side, filling the whole space so that all windows are visible at the same time. The windows can be tiled horizontally or vertically.
Arrange Icons
The windows that have been minimized to icons can be arranged evenly in a row at the bottom of the main window, starting from the left side. To do this, select the Arrange Icons command in the Window menu.
Close All
The Close All command in the Window menu can be used to close all measurement windows in the Nemo Outdoor main window.
Saving Window Settings
If you wish to retain the same settings on your main window the next time you use Nemo Outdoor, activate the Save Workspace on Exit command in the File menu. Clicking the command will result on a check mark ; the second click will remove the mark.
348
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
TROUBLESHOOTING
This section describes some of the possible problem situations that may occur in Nemo Outdoor.
LOW THROUGHPUT
In case lower data throughputs are received with Nemo Outdoor compared to third party applications, read this chapter for troubleshooting throughput problems with various TCP based protocols. In case low throughput values are monitored with Nemo Outdoor and also with third party applications, the issue can most likely be seen by observing link adaptation parameters. For example, low average CQI and high MAC-HS 3rd retransmission rate indicate an area of bad coverage or high interference. Low HS-SCCH usage rate (= high HSDPA DTX percentage ratio) points to capacity, server or transmission problems. In LTE networks, observe physical resource block allocation (PRB) and signal to noise ratio (SNR). PRB affects throughput directly. Values less than maximum may indicate other users in the cell, a bottleneck in the transmission network or not enough data to be sent (application does not need all the available bandwidth). Requested throughput much higher than the actual measured throughput may indicate that there are other users sharing the radio resources of the cell or some other bottleneck in the network that prevents the mobile from getting the maximum achievable throughput. High PUSCH TX power values indicate a lack of uplink coverage. When operating in the dynamic range of link adaptation, average BLER (PDSCH BLER) should be higher than 0, typically 10-20%, in order to achieve the gain of HARQ retransmission scheme Residual BLER after all HARQ retransmissions should be 0%. Higher values indicate that the radio link is about to drop. Observe the MAC downlink/uplink residual BLER (%) values. Other things that could help troubleshooting: Disable any firewall and/or antivirus software that could reduce the throughput. Some HSPA USB interfaces may also install their own software which may affect to window size settings in registry. Disable IP capturing from the Advanced Properties. Try another FTP server for comparison. Command prompt FTP throughput. This comparison is recommended because command prompt FTP does not use any multithreading or other non-standard methods. For better results, keep Nemo Outdoor at the background measuring the mobile network while making the transfers. Also try different servers. For Nemo Outdoor 5.60 and older versions: Run a script with simultaneous FTP transfers to see if the throughput increases. Does not work manually, script is always needed. For Nemo Outdoor 5.70 and later versions: Use the multithread feature of the FTP protocol to test simultaneous transfers. Works also manually.
TRO UBLE S HO O TI NG
349
All Windows Versions
How to check the TCP window size from packet logs:
Using Wireshark: 1. Check the .pcap file and look at the (non FTP-DATA) TCP traffic in the middle of the transfer. Window size value tells the current TCP window size used.
Using Nemo Outdoor: 1. Open a packet grid window in Nemo Outdoor. 2. Look at the TCP traffic in the middle of an FTP transfer with PayloadLen=0:
3. Double click the frame to get detailed frame info. Look at the Tcp tree. Window shows the current value.
Using debug logs (for developers, help desk, etc.): 1. Look for the GetWindowSizeFromRegistry() function. TCP Window size set to n = Value found from registry. TCP Window size set to default: n = Value not found from registry. Set to default. TCP Auto-Tuning detected. Window size not set. = Windows Vista/7 is using auto-tuning TCP window.
2. A measurement file (.nmf) does not save window size info. Packet log and/or debug log is always needed.
350
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Windows XP
Check registry value of HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\TcpipParameters\TcpWindowSize. Windows and Nemo Outdoor both use it if it exists. The value can be changed manually or by using TcpOptimizer software. If the registry value is missing, Nemo Outdoor will use its default window size which is 256 KB.
Windows Vista/Windows7
Windows Vista/7 does not use static window sizes from the registry. They rely on dynamic window size which is handled by TCP auto tuning feature. However, if the same registry value that XP uses is set, Outdoor reads it and adjusts the manual window size based on this value. In most cases, the registry has been edited by a third party software or a USB mobile interface driver/software. This registry entry can be removed. If TCP auto-tuning is disabled, Nemo Outdoor will use its default window size 256 KB. Outdoor 5.40 and later checks the auto-tuning state and does not change any window sizes if auto-tuning is enabled.
How to check TCP auto-tuning state:
1. Open command prompt by typing CMD to Search programs and files field.
2. Type netsh interface tcp show global
3. Receive Window Auto-Tuning Level shows the current state. Please note that administrator rights are required to change auto-tuning settings.
TRO UBLE S HO O TI NG
351
4. Open command prompt by typing CMD to Search programs and files field. Right-click and select Run as administrator.
5. To disable auto-tuning type netsh interface tcp set global autotuning=disabled. This limits the TCP window size to 64KB. However, Outdoor sets its own default 256KB when auto-tuning is disabled. 6. To increase the maximum TCP window size that auto-tuning uses, type netsh interface tcp set global autotuning=highlyrestricted. 7. Below are all the values of auto-tuning level with explanations: disabled: Uses a fixed value for the TCP receive window. Limits to 64 KB (65535). highlyrestricted: Recommended. Allows the receive window to grow beyond its default value, very conservatively. restricted: Recommended. Somewhat restricted growth of the TCP receive window beyond its default value. normal: Default value. Allows the receive window to grow to accommodate most conditions. experimental: Allows the receive window to grow to accommodate extreme scenarios (not recommended, it can degrade performance in common scenarios, only intended for research purposes). It enables receive window values of over 16 MB.
352
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
DEVICE STATUS VIEW
The Device Status view displays the device status.
If a green light is blinking, it means that the device is properly connected to Nemo Outdoor and is functioning normally. If a red light is blinking, it means that the device has been disconnected. Connect the device, rightclick on the device in the Devices view and select Reset.
CANNOT ADD DEVICES
If the Add button is deactivated in the Configuration Manager window when you start Nemo Outdoor, your version of Nemo Outdoor is an unlicensed evaluation version. Please, see chapter Copy Protection for more information on copy protection. If the copy protection dongle is plugged in and the Add button is deactivated, check that recording is not on. Also, playback should be stopped and playback files closed (File | Close Measurement).
TRO UBLE S HO O TI NG
353
CANNOT MAKE CALLS/PACKET TRANSFERS
If the commands are inactive in the Measurement control menu , check that you have devices online. The Work offline or online button should be unselected.
PROBLEMS WITH GPS RECEIVERS
The Windows XP and Vista operating systems sometimes confuse a GPS receiver with the computers mouse. When this occurs, the mouse stops working correctly. In this case, follow the steps below. 1. Select Start | Settings | Control Panel. Double-click on System. 2. Go to the Hardware tab and click the Device Manager button. 3. Double-click on Mice and other pointing devices. A Microsoft Serial BallPoint device should appear. 4. Right click on the Microsoft Serial BallPoint device and select Disable from the popup menu. 5. Confirm the disabling by clicking Yes in the message box. 6. The mouse device is now disabled and the GPS device can be reconnected.
MEASUREMENT FILE CHECKSUM NOTIFICATION
Measurement file has a checksum that detects modifications to the measurement file after the measurement is stopped. The checksum is validated when loading measurement files for playback. The user is notified by the Nemo Outdoor user interface when opening a measurement file where modification is detected. However, measurement files are still opened normally. The last line in the measurement file is HASH events including time stamp and checksum information.
#HASH,14:46:49.262,1,"0360D938749FFE82B15545D3E55B75C0" Measurement files made with Nemo Outdoor 5.4 or earlier do not include checksum information and the notification is always prompted when such a file is opened with Nemo Outdoor version 5.50 or later.
354
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
NEMO OUTDOOR BUTTONS
TOOLBAR BUTTONS
These are the buttons available in the Nemo Outdoor toolbar. Title Open Playback File(s) Button Description Opens an existing measurement for playback Opens an existing workspace file. Saves the current workspace configuration. Opens the Configuration Manager dialog. Switches the offline mode on and off. Nemo Outdoor starts writing a file of the current measurement. Starts the playback with the selected files. Pauses the playback/recording. Stops the playback/recording. Switches a script on/off. Adds a marker in the measurement file or on the Indoor map. Adds a textual note in the measurement file. Opens the Open Custom Window dialog. Saves the active window as a new custom window. Saves changes to the active custom window. Saves the active window as an image file (.jpg).
Open Workspace Save Workspace Configuration Manager Work Offline Start Recording
Start Playback Pause Stop Start/Stop Scripts Add Marker
Add Textual Note Open Custom Window Save As New Custom Window Save Changes to Custom Window Save As Image
NEM O O UTDO O R B UT TO NS
355
DIALOG BUTTONS
These are the dialog buttons used in Nemo Outdoor. Title Expand Device Info Window Device notification settings Button Description Displays the selected device info parameters in the Device Info window. Opens the Notifications dialog where you can select the events of which Nemo Outdoor will display or play a notification. Through the Device Commands button you have access to various mobile specific functions. Offers access to several dialogs. Automatically detects devices connected to Nemo Outdoor. Updates information in the Configuration Manager. Opens a Properties dialog for the selected item in the Configuration Manager. Adds a new device, event trigger, or script depending on the item selected in the Configuration Manager. Removes the selected device, event trigger, or script from the Configuration Manager.
Device Commands
Device Settings Autodetect Devices Refresh
Properties
Add
Remove
356
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
GRAPH TOOLBAR BUTTONS
These are the toolbar buttons available when using graphs. Title Hide Layer Button Description Hides the selected layer in the graph
Remove Layer
Removes the selected layer
New Layer
Opens the New Layer dialog where you can configure a new layer to be added in the active graph. Opens the Layer Properties dialog where you can edit an existing layer. Moves the selected layer down in the layer view Moves the selected layer up in the layer view If there are two or more layers in a graph, you can view them in stacked mode; that is, in separate graphs. When the button is pressed down, the graph is scrolling automatically as the measurement proceeds. Displays the info panel with numerical values on the right side of the graph.
Layer Properties
Move Layer Down Move Layer Up Set Stacked Mode
Autoscroll
Show Panels
NEM O O UTDO O R B UT TO NS
357
MAP TOOLBAR BUTTONS
These are the toolbar buttons available when using maps. Title Open Map Save Map Button Description Opens the Open dialog for selecting a map file. Saves the current map layers and settings into a MapInfo Geoset file (.gst). Opens the Map Import Parameters dialog for importing bitmap images as floorplans. Available only in the Indoor map. Opens the selected layer's Properties dialog where you can configure the layer properties. With the automatic map find feature the user can easily locate all maps from same location. Creates a route plan from an open measurement. Through this item you can open saved route plans. Allows you to save the route plan as a Route Plan File (.rpf). Activates the add waypoint functionality for creating route plans manually. Changes the cursor into an arrow, which you can use for selecting items. Changes the cursor into a hand, which you can use for dragging the map to a different position. Place the hand on the map. Keep the left mouse button pressed down and move the map. Changes the cursor into the center tool, which you can use for selecting a point on the map on which the map view will be centered. Changes the cursor into a magnifying glass, which you can use for zooming in on the map. Changes the cursor into a magnifying glass, which you can use for zooming out on the map. Clears the measurement route from the map. This button is active only during measurements. It cannot be used during playback. Set Current Location tool defines the current location when no GPS data is available. That this command is activated only during measurements and when no GPS is connected. It cannot be used during playback.
Import Map
Layer Properties Find Map at Position Create Route Plan Open Route Plan Save Route Plan Add Waypoint
Arrow
Pan
Center
Zoom In
Zoom Out
Clear Route
Set Current Location
358
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Auto Center
With the Auto Center tool activated, the map view will always center on the test vehicle. This requires that a GPS receiver is used. The Auto center sensitivity slider defines in percentages the sensitivity of the activated Auto Center tool. The higher the percentage, the sooner the map is centered on the test vehicle when it moves around on the route. Click the Previous View button to return to the previous map view, for example, if you have moved the map with the Pan tool. Click the Entire Map button to display the entire map after zooming in. With the Entire Route button you can view the whole route on the map.
Auto Center Sensitivity
Previous View
Entire Map
Entire Route
Scale Bar
Activate the Scale Bar button to view a scale bar in the map window. With the Measure Distance tool you can measure the distance on the map in kilometers between multiple points. Activate the Side Panel button to view the side panel in the map window.
Measure Distance
Side Panel
S HO RTC UT KEY S
359
SHORTCUT KEYS
This is a complete list of the shortcut keys available in Nemo Outdoor. This window can be displayed by pressing down the F2 key when using Nemo Outdoor.
360
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
NOTIFICATION SYMBOLS
Below are described the default notification symbols. Attach Attempt Attach Failed Attach Success MMS Receiving Attempt MMS Receiving Failed MMS Receiving Success MMS Sending Attempt Call Alerting Call Answered Call Attempt Call Connected Call Disconnect Call Dropped Call Failed Call Received Packet Call Attempt Packet Call Connected Packet Call Disconnected Packet Call Failed Packet Technology Changed to HSDPA Packet Technology Changed to UMTS Cell Change Attempt Cell Change Failed Cell Change Success Cell Reselection Cell Reselection (3G) GSM/UMTS Cell Reselection (2G) UMTS/GSM RX Level Low/Bad Routing Area Update Attempt Routing Area Update Failed Context Activation Attempt Context Activation Failed Context Activation Success Context Deactivation Semiduplex Call Attempt Service Lost Routing Area Update Success PTT Idle PTT Receiving PTT Transmitting MMS Sending Failed MMS Sending Success
NO TI FI CA TI O N SY M BO LS
361
Service Received Data Call Attempt Data Connection Attempt Data Connection Failed Data Connection Success Data Disconnect Data Transfer Attempt Data Transfer Success Data Transfer Failed Soft Handover Failure Soft Handover Success SMS/USSD Received SMS/USSD Receiving Attempt SMS/USSD Receiving Failed SMS/USSD Sending Completed
Dead Reckoning in Use Detach Differential GPS in Use Duplex Call Attempt FER High
TX Power High/UL Power Up High
Video Call Attempt Voice Call Attempt/Voice Call Attempt (ETSI) Voice Call Connected (ETSI) Voice Call Disconnected (ETSI)
GPS Fix Lost GPS Fix Received HS-DSCH Serving Cell Changed
Voice Call Dropped (ETSI)
Star Thumb Down
Handover Attempt Handover Failed Handover Success
Thumb Up
Location Area Update Attempt Location Area Update Failed Location Area Update Success
362
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Marker Markov Call Attempt Measurement Error
NEM O O UTDO O R S UP PO RT
363
NEMO OUTDOOR SUPPORT
If you have questions on or beyond this documentation about Nemo Outdoor, please contact our Nemo Outdoor technical support service at nemosupport@anite.com or call +358 50 395 7800. Note that for full support you need to have the Maintenance Agreement.
INTERNET SUPPORT
At our web site http://www.anite.com/nemo, you can find all the frequently asked questions about Nemo Outdoor, among other information.
USER CLUB
The Nemo User Club offers several new ways to benefit from Nemo products. You can find it at our WWW site http://www.anite.com/nemo. Access to the Nemo User Club is restricted to customers with SW maintenance and Technical Support agreements or partner agreements. If you are an existing Anite Finland customer with SW maintenance and Technical Support agreements, but you are without access to the user club, please complete an on-line registration form. After submitting the requested information, you will receive a personal access key and password by email in a few days time. Once you are registered with our User Club, you will automatically receive e-mails informing you each time a new version of software for your Nemo Product is released. It is fast, easy, and it is available to you seven days a week, 24 hours a day. If you have questions relating to the Nemo User Club, please e-mail us at nemosupport@anite.com.
PHONE, EMAIL, AND FAX SUPPORT
During the warranty period, the phone and fax support related to potential software errors is free of additional charge. Registered users with a valid Maintenance Agreement are entitled to full support. When faxing or emailing, please let us know the number of your Software Maintenance and Support Agreement.
364
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Please contact us at the following locations:
Global Email Tel. Fax Address
nemosupport@anite.com
+358 50 395 7800 +358 8 551 6182 Anite Finland Ltd Kiviharjunlenkki 1 D 90220 Oulu Finland
Americas Email Mobile Fax Address
nemosupport@anite.com
+1 469 951 9105 +1 469 774 4608 (En espaol e portugus) +1 972 462 1640 Anite Inc. 6225 N. State Hwy 161 Suite 425 Irving, TX 75038 USA
APAC Email Tel. Fax Address
nemosupport@anite.com
+65 9746 2431 +65 6254 9885 Anite Singapore Pte. Ltd. 101 Thomson Road, #20-05 United Square Singapore 307591
P.R. China Email Tel. Fax Address
nemosupport@anite.com
+86 10 6567 8528 +86 10 6567 8521 Anite Wireless Trading (Beijing) Limited. Room 2109, 21st Floor The Exchange Beijing, No. Yi 118, Jianguo Road Chaoyang District, Beijing 100022 China
When contacting us for problem reporting, please supply/inform us of: Your Windows version number (e.g., Windows XP), see Windows Control Panel | System Your computer brand model (e.g., Lenovo) Your test mobile types (e.g., Nokia 6720) GPS receiver type (e.g., Garmin GPS II Plus) Your Nemo Outdoor version and build (e.g., Version 6.31.x), see Help | About Device handler versions Your description of the problem Whether you were able to repeat the problem The corresponding measurement results file (as email attachment or on disc)
APPE NDI C ES
365
APPENDIX 1
MAKING MAPINFO RASTER MAPS
Using raster image files, you can bring paper maps, photographs, and other graphic images into MapInfo. You can scan paper maps and then use paper maps as the foundation for the maps you create in MapInfo. After scanning the paper map into a raster image file, you can display it in a map window. Nemo Outdoor and Nemo Analyze support .TIF, .GIF, and .JPG formats. MapInfo can read the following types of raster images: - filename.TIF - filename.GIF - filename.JPG - filename.PCX - filename.BMP - filename.BIL Color options are: Monochrome images: each pixel in a map image can be black or white. Gray scale images: each pixel in a gray scale image can be black, white, or a shade of gray. Color images: each pixel can be of any color from a palette of available colors. MapInfo supports 256 colors. When using Nemo Outdoor and Nemo Analyze, we recommend using gray scale images. By doing this, the measurement route can be discerned better than with color map images.
Registering a Raster Map with MapInfo SW
If you want to overlay vector data on top of a raster image, then you must register the raster map image so that MapInfo can position it properly in a Map window. You do this in the Image Registration Dialog. You must identify control point coordinates and the projection of the raster image map. It is important to provide accurate control point information when registering a raster map image. Choose control points that can be easily identified and selected, such as street intersections or use the coordinates (latitude and longitude grid) for the selected point from a paper map.
To register a raster map:
1. Start the MapInfo software. Choose File | Open Table and Raster Image File Format. Select your raster map image file (.TIF, .GIF, .JPG) and open it. The Image Registration Dialog is displayed. A preview of the raster map image appears on the screen. 2. Select the Projection button to specify the projection of the raster image map. If you do not know the right projection, the default value is Longitude/ Latitude.
366
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
3. Start adding control points. Click on a location in the preview (raster image map). The Add Control Point Dialog is displayed showing the location of the point in pixels. Add Map X and Map Y coordinates in decimal formats. For example, to specify the coordinates 65 degrees, 30 minutes, enter 65.5 degrees. Use negative numbers when specifying west and south coordinates. If you want to register a raster map that does not use longitude and latitude coordinates, specify the appropriate projection in the Image Registration Dialog. Enter your coordinates in the native units of the coordinate system. For example, if you are registering a UTM map image, enter coordinates in meters. Using the MapBasic program, you can convert d/m/s coordinates into decimal degrees format, or the conversion from d/m/s to decimal degrees is as follows: degrees+(minutes/60)+(seconds/3600)=decimal degrees 4. You must choose at least three control points. Select points that can be easily identified and selected in the map window. 5. After all control points have been defined, click OK in the Image Registration dialog. The raster map will be displayed in the map window. 6. Move filename.tab and filename.tif/gif/jpg files to the map directory of Nemo Outdoor or Nemo Analyze. 7. Open filename.tab in Nemo Outdoor or Nemo Analyze.
APPE NDI C ES
367
APPENDIX 2
CDMA SETTINGS AND PRL EDITING IN NEMO OUTDOOR
You can access CDMA Settings and the PRL editing dialog in Nemo Outdoor through Device Settings .
In the NV items page you are able to read and write nonvolatile memory items.
You need to know your SPC before you can program any of the following settings. A known SPC can also be overwritten by this plugin. Directory number defines a phone number
368
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
MIN1 defines a seven-digit phone number of the terminal MIN2 defines a three-digit area code SPC defines the service programming code IMSI = IMSI_MCC + IMSI_11_12 + MIN1 + MIN2
On the PRL page you can read and write PRL items. This can be used to load any previously saved PRLs onto any Qualcomm-based mobile. You can also use this feature to save a PRL from a connected phone and then use this later to load the same PRL onto a new mobile.
On the DIP Switch page you are able to enable/disable the listed features.
APPE NDI C ES
369
Should you need to manually edit a PRL, you can use the Presto tool which can be downloaded from CDG.org. The download page can be accessed by searching for prl using the search tool on the main page.
1. Click on the prltools.asp link to get to the downloads page.
2. From there you can download the toolbar suite and the tutorial for it. Install the suite when launched. This will add a tool bar called Presto to MS Excel.
370
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
3. Run the Setup.exe file. Click Install in the dialog that appears.
4. Click Next in the PRL Toolbar Suite dialog that appears.
5. Click Next in the Welcome window. 6. Select I Agree in the License Agreement dialog, and click Next. 7. Click Next to confirm installation. 8. Click Close to exit the Installation Finished dialog. 9. Next, open Presto by going to Start | All Programs | QUALCOMM PRL Toolbar Suite | PRESTO. It should look as follows in Excel:
APPE NDI C ES
371
APPENDIX 3 - TROUBLESHOOTING DATA TRANSFER ISSUES
PS CONNECTION WORKS BUT NO DATA
UAC Settings
If UAC (User Account Control) is set to always notify, it might cause issues with data testing. A PS connection can be established but data transfers cannot be made. It is recommended that the UAC settings are changed to Never notify. This can be done via User Account Control Settings.
Antivirus Filtering
Disable the antivirus application and Windows firewall. If the data transfer still does not work properly, please do the following: 1. Activate PS connection (activate PDP context). 2. Go to Network Settings and choose the appropriate connection assigned for the device. 3. Go to Connection Properties and check that antivirus NDIS filtering is unchecked.
Low Data Throughputs
In case lower data throughputs are received with Nemo Outdoor compared to third party applications, read this document for troubleshooting throughput problems with various TCP based protocols. In case low throughput values are monitored with Nemo Outdoor and also with third party applications, the issue can most likely be seen by observing link adaptation parameters.
372
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
For example, low average CQI and high MAC-HS 3rd retransmission rate indicate an area of bad coverage or high interference. Low HS-SCCH usage rate (= high HSDPA DTX percentage ratio) points to capacity, server or transmission problems. In LTE networks, observe physical resource block allocation (PRB) and signal to noise ratio (SNR). PRB affects throughput directly. Values less than maximum may indicate other users in the cell, a bottleneck in the transmission network or not enough data to be sent (application does not need all the available bandwidth). Requested throughput much higher than the actual measured throughput may indicate that there are other users sharing the radio resources of the cell or some other bottleneck in the network that prevents the mobile from getting the maximum achievable throughput. High PUSCH TX power values indicate a lack of uplink coverage. When operating in the dynamic range of link adaptation, average BLER (PDSCH BLER) should be higher than 0, typically 10-20%, in order to achieve the gain of HARQ retransmission scheme Residual BLER after all HARQ retransmissions should be 0%. Higher values indicate that the radio link is about to drop. Observe the MAC downlink/uplink residual BLER (%) values. Other things that could help troubleshooting: Disable any firewall and/or antivirus software that could reduce the throughput. Some HSPA USB interfaces may also install their own software which may affect to window size settings in registry. Try another FTP server for comparison. Command prompt FTP throughput. This comparison is recommended because command prompt FTP does not use any multithreading or other non-standard methods. For better results, keep Nemo Outdoor at the background measuring the mobile network while making the transfers. Also try different servers. For Nemo Outdoor 5.60 and older versions: Run a script with simultaneous FTP transfers to see if the throughput increases. Does not work manually, script is always needed. For Nemo Outdoor 5.70 and later versions: Use the multithread feature of the FTP protocol to test simultaneous transfers. Works also manually. Make a comparison test between Nemo Outdoor and the connection manager used with the device. When configuring a device with Nemo Outdoor, only the trace port should be defined. The modem port and dial-up connection must be left blank. As ports are left blank it is not possible to perform a manual PDP context activation or data transfer via Nemo Outdoor. However, a script file with data connection commands can be used. Script files should include only data transfer commands, not Attach/detach or PDP context activation or deactivation commands. Start a data transfer and observe the application data throughput value. Make the same test again but this time make a connection using Nemo Outdoor.
All Windows Versions
How to check the TCP window size from packet logs: Using Wireshark:
1. Check the .pcap file and look at the (non FTP-DATA) TCP traffic in the middle of the transfer. Window size value tells the current TCP window size used.
APPE NDI C ES
373
Using Nemo Outdoor:
1. Open a packet grid window in Nemo Outdoor.
2. Look at the TCP traffic in the middle of an FTP transfer with PayloadLen=0:
3.
Double click the frame to get detailed frame info. Look at the Tcp tree. Window shows the current value.
Using debug logs (for developers, help desk, etc.):
1. Look for the GetWindowSizeFromRegistry() function.
TCP Window size set to n = Value found from registry. TCP Window size set to default: n = Value not found from registry. Set to default. TCP Auto-Tuning detected. Window size not set. = Windows Vista/7 is using auto-tuning TCP window. A measurement file (.nmf) does not save window size info. Packet log and/or debug log is always needed.
Windows XP
Check registry value of HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\TcpipParameters\TcpWindowSize. Windows and Nemo Outdoor both use it if it exists. The value can be changed manually or by using TcpOptimizer software. If the registry value is missing, Nemo Outdoor will use its default window size which is 256 KB.
374
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
Windows Vista/Windows7
Windows Vista/7 does not use static window sizes from the registry. They rely on dynamic window size which is handled by TCP auto tuning feature. However, if the same registry value that XP uses is set, Outdoor reads it and adjusts the manual window size based on this value. In most cases, the registry has been edited by a third party software or a USB mobile interface driver/software. This registry entry can be removed. If the TCP auto-tuning is disabled Nemo Outdoor will use its default window size 256 KB. Outdoor 5.40 and newer checks the auto-tuning state and does not change any window sizes if auto-tuning is enabled.
How to check TCP auto-tuning state:
1. Open command prompt by typing CMD to Search programs and files field.
2.
Type netsh interface tcp show global
3.
Receive Window Auto-Tuning Level shows the current state.
Please note that administrator rights are required to change auto-tuning settings. 4. Open command prompt by typing CMD to Search programs and files field. Right-click and select Run as administrator.
APPE NDI C ES
375
5.
To disable auto-tuning type netsh interface tcp set global autotuning=disabled. This limits the TCP window size to 64KB. However, Outdoor sets its own default 256KB when auto-tuning is disabled.
6. To increase the maximum TCP window size that auto-tuning uses, type netsh interface tcp set global autotuning=highlyrestricted. 7. Below are all the values of auto-tuning level with explanations: disabled: Uses a fixed value for the TCP receive window. Limits to 64 KB (65535). highlyrestricted: Recommended. Allows the receive window to grow beyond its default value, very conservatively. restricted: Recommended. Somewhat restricted growth of the TCP receive window beyond its default value. normal: Default value. Allows the receive window to grow to accommodate most conditions. experimental: Allows the receive window to grow to accommodate extreme scenarios (not recommended, it can degrade performance in common scenarios, only intended for research purposes). It enables receive window values of over 16 MB.
8. Windows XP fix KB943198 (http://support.microsoft.com/kb/943198) is needed when using HSDPA category 6 or higher data transfer speeds with Nokia test terminals.
376
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
APPENDIX 4
END-USER LICENSE AGREEMENT
IMPORTANT - READ CAREFULLY: This End-User License Agreement ("EULA") is a legal agreement between you (either an individual or a single entity) and Anite Finland Ltd for the Anite Finland Ltd software product(s), in whatever form, identified above ("Software Product" or "Software"). The Software Product includes computer software, the associated media, any printed materials, and any "online" or electronic documentation. By installing, copying or otherwise using the Software Product, you agree to be bound by the terms of this EULA. If you do not agree to the terms of this EULA, Anite Finland Ltd is unwilling to license the Software Product to you. In such event, you may not use or copy the Software Product, and you should promptly return the unused product(s) in their original packaging to the place of purchase within thirty days of the date of original purchase. SOFTWARE PRODUCT LICENSE The Software Product is protected by copyright laws and international copyright treaties, as well as other intellectual property laws and treaties. The Software Product is licensed, not sold. 1. GRANT OF LICENSE. This EULA grants you the following rights: Software. You agree that the Software product is licensed to you to be used with the mobile phone(s) and software protection key designated by Anite Finland Ltd for such use ("Designated Hardware"). You also agree that you shall not have more than one copy of the Software Product in use at a time for any Designated Hardware in which the Software Product is to be used or to be distributed except as expressly provided for in this EULA. You may use one copy of the Software Product in binary code form only on one computer at a time in order to conduct system measurements using the Designated Hardware at various locations to the extent necessary for the permitted operation of the application software but may not duplicate the Software Product. Storage/Network/Single Use. You may also store or install a copy of the Software Product in binary code form only over an internal network, and distribute the Software Product to your other computers over an internal network. However, you must acquire and dedicate a license for the Software Product for each Designated Hardware on which the Software Product is used or to which it is distributed. A license for the Software Product may not be shared or used concurrently on different computers. 2. DESCRIPTION OF OTHER RIGHTS AND LIMITATIONS. Limitations on Reverse Engineering, Decompilation and Disassembly. Removal, emulation, or reverse engineering of all or any part of this product or its protection constitutes an unauthorized modification to the product and is specifically prohibited. Nothing in this license statement permits you to derive the source or assembly code of files provided to you in executable or object formats. Limitations on Modifications, Adaptations and Other Changes. You may not modify, adapt or otherwise make any changes to the Software Product except and only to the extent you are expressly permitted to do so under the applicable mandatory law notwithstanding this limitation or by Anite Finland Ltd's prior written consent. Separation of Components. The Software Product is licensed as a single product. Its component parts may not be separated for use on more than one Designated Hardware and computer as designated above.
APPE NDI C ES
377
Not for Resale. This Software Product is Not for Resale" or "NFR" and your license only permits personal use and you may not sell or otherwise transfer the Software Product for value except as specified below. Rental. You may not rent, lease or lend the Software Product to any person or entity. Software Transfer. You may not otherwise give or permanently transfer any or all of your rights under this EULA without the express prior written consent of Anite Finland Ltd which such consent shall not be unreasonably withheld. Duration and Termination. This EULA is effective from the day you open the sealed media package or download and continues until termination. You may terminate this EULA at any time. Without prejudice to any other rights, Anite Finland Ltd may terminate this EULA if you fail to comply with the terms and conditions of this EULA. In either event, you must destroy all copies of the Software Product and all associated media, printed materials, updates and component parts and verify to Anite Finland Ltd in writing that such has been done. 3. SUPPORT SERVICES. Anite Finland Ltd may provide you with support services related to the Software Product ("Support Services"). Any supplemental software code provided to you as part of the Support Services shall be considered part of the Software Product and subject to the terms and conditions of this EULA. With respect to technical information you provide to Anite Finland Ltd as part of the Support Services, Anite Finland Ltd may use such information for its business purpose, including for product updates and development. 4. COPYRIGHT AND TRADEMARKS. All title and copyrights in and to the Software Product (including but not limited to any images, photographs, animations, video, audio, music, text and "applets", incorporated into the Software Product), the accompanying printed materials, and any copies of the Software Product, are owned by Anite Finland Ltd or its suppliers. The Software Product is protected by copyright laws and international treaty provisions. You may not copy the printed materials accompanying the Software Product. You may not remove, modify or alter any Anite Finland Ltd copyright or trademark from any part of the Software Product, including but not limited to any such notices contained in the physical and/or electronic media or documentation, in the Anite Finland Ltd Setup Wizard dialogue or 'about' boxes, in any of the runtime resources and/or in any web-presence or web-enabled notices, code or other embodiments originally contained in or dynamically or otherwise created by the Software Product. Portions based on WinWAP technology. Copyright Slob-Trot Software Oy Ab 2004. http://www.winwap.com Perceptual Objective Listening Quality Analysis (POLQA) according to ITU-T Recommendation P. 863 included in this product is protected by copyright and by European, US and other International patents and patent applications and isprovided under license from OPTICOM Dipl.-Ing. M. Keyhl GmbH, Erlangen, Germany, 2011 www.opticom.de POLQA is a registered trademark of OPTICOM GmbH. Used by permission. 2011 by the POLQA Coalition of OPTICOM GmbH, Germany - SwissQual AG, Switzerland - KPN, The Netherlands - TNO, The Netherlands. www.polqa.info This software uses Libresample library distributed under LGPL license. For detailed license information, see libresample-license.txt, gpl-license.txt and lgpl-license.txt located in the Nemo Outdoor installation directory.
378
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
This software uses libVLC library distributed under LGPL license. For detailed license information, see lgpl-license.txt located in the Nemo Outdoor installation directory. Iperf copyright Copyright (c) 1999-2006, The Board of Trustees of the University of Illinois All Rights Reserved. Iperf performance test Mark Gates Ajay Tirumala Jim Ferguson Jon Dugan Feng Qin Kevin Gibbs John Estabrook National Laboratory for Applied Network Research National Center for Supercomputing Applications University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign http://www.ncsa.uiuc.edu Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software (Iperf) and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions: Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimers. Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimers in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution. Neither the names of the University of Illinois, NCSA, nor the names of its contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from this Software without specific prior written permission. THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE CONTIBUTORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE. 5. DUAL-MEDIA SOFTWARE. You may receive the Software Product in more than one medium. Regardless of the type or size of medium you receive, you may use only that one medium that is appropriate for the systems you use to operate the Software Product. You may not use or install the other medium on any system. You may not loan, rent, lease or otherwise transfer the other medium to another user, except as part of the permanent transfer (as provided above) of the Software Product.
APPE NDI C ES
379
6. CONFIDENTIALITY AND NON-DISCLOSURE. You agree to keep in confidence and not to disclose in any manner or form to any third party nor publish any such data or information related to the Software Product. You agree to protect all information and data provided to you by Anite Finland Ltd related to the Software Product with the same degree of care that you use to protect your own like data and information, but with not less than that due care exercised by a reasonably prudent person under the same or similar circumstances. 7. U.S. GOVERNMENTAL RESTRICTED RIGHTS. The Software Product and documentation are provided with Restricted Rights. Use, duplication, or disclosure by the Government is subject to restrictions as set forth in subparagraph (c)(1)(ii) of the Rights in Technical Data and Computer Software clause at DFARS 252.277-7013 or subparagraphs (c)(1) and (2) of the Commercial Computer Software - Restricted Rights at 48 CFR 52-227-19, as applicable. 8. LIMITED WARRANTY. Anite Finland Ltd warrants that (a) the Software Product will perform substantially in accordance with the accompanying written materials for a period of three (3) months from the date of receipt, and (b) any third party hardware accompanying the Software Products will be free from defects in materials and workmanship under normal use and service for a period of one (1) year from the date of receipt. To the extent that implied warranties are disclaimable, they are disclaimed in paragraph 10. Some states/jurisdictions do not allow disclaimers of or limitations on duration of an implied warranty, so the above limitation may not apply to you. Any implied warranties on the Software Product and, as applicable, third party hardware that is not disclaimable are limited to three (3) months and one (1) year respectively. 9. CUSTOMER REMEDIES. Anite Finland Ltd and its suppliers' entire liability and your exclusive remedy shall be, at Anite Finland Ltd option, either (a) return of the price paid, or (b) repair or replacement of the software or hardware that does not meet the Limited Warranty contained in this EULA and which is returned to Anite Finland Ltd. The Limited Warranty contained herein is void if failure of the software or third party hardware has resulted from accident, abuse, misapplication or events beyond the control of Anite Finland Ltd including, but not limited to Acts of God, acts of nature or acts of war. Any replacement Software Products or hardware will be warranted for the remainder of the original warranty period or thirty (30) days, whichever is longer. Anite Finland Ltd is not responsible for ensuring adequate backup and storage for your data or records. 10. NO OTHER WARRANTIES. To the maximum extent permitted by applicable law, Anite Finland Ltd disclaims all other warranties, either express or implied, including but not limited to implied warranties of merchantability, fitness for a particular purpose, and non-infringement of third-party rights, with regard to the Software Product, the accompanying written materials, and any accompanying hardware. This limited warranty gives you specific legal rights. You may have others which vary from state/jurisdiction to state/jurisdiction.
380
Ne mo O ut door User M anua l
11. NO LIABILITY FOR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES. To the maximum extent permitted by applicable law, in no event shall Anite Finland Ltd or its suppliers be liable for any damages whatsoever (including without limitation, special, incidental, consequential, punitive or indirect damages for personal injury, loss of business profits, business interruption, loss of business information, or any other pecuniary loss) arising out of the use of or inability to use this Software Product, even if Anite Finland Ltd has been advised of the possibility of such damages. In any case, Anite Finland Ltd and its suppliers' entire liability under any provision of this EULA shall be limited to the amount actually paid by you for the Software Product and/or third party hardware accompanying the Software Product. The Limitations of Liability contained in this Section apply to claims of every kind, whether based on contract law, tort law or otherwise, even if these limitations have the effect of exculpating a party from responsibility for its negligence, fault or other conduct. Because some states/jurisdictions do not allow the exclusion or limitation of liability for consequential or incidental damages, the above limitation may not apply to you.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Nemo Outdoor 7.20 ManualDocument371 paginiNemo Outdoor 7.20 ManualViswanaath Subramanian100% (5)
- Nemo File Format 2.25Document642 paginiNemo File Format 2.25Daneil RadcliffeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nemo Handy A Manual 2 61Document17 paginiNemo Handy A Manual 2 61cspkerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nemo Outdoor TrainingDocument51 paginiNemo Outdoor TrainingDragon0909Încă nu există evaluări
- GENEX Probe Operation GuideDocument82 paginiGENEX Probe Operation GuideAtok Enteng DigzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nemo Outdoor User ManualDocument353 paginiNemo Outdoor User Manualrubenpat83% (6)
- Nemo Outdoor TrainingDocument51 paginiNemo Outdoor Trainingdwahjoedi3984Încă nu există evaluări
- 45 Nemo Analyze and OutdoorDocument4 pagini45 Nemo Analyze and OutdoorikkaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Xcal MPM4 1Document2 pagini1 Xcal MPM4 1Mom RothnyÎncă nu există evaluări
- ANDREW Installation AccessoriesDocument48 paginiANDREW Installation AccessoriesRichard Radcliff100% (1)
- Nemo Outdoor Config PDFDocument138 paginiNemo Outdoor Config PDFbinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- XCALDocument7 paginiXCALshohobiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To GENEX ProbeDocument68 paginiIntroduction To GENEX ProbeAmaruch BenaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- TEMS Pocket 21.3 - Device SpecificationDocument45 paginiTEMS Pocket 21.3 - Device Specificationhanhdk100% (1)
- LTE SIG Data Collection Based On The WebNICDocument15 paginiLTE SIG Data Collection Based On The WebNICSemihOzerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Huawei LTE Drive Test Guide for Genex ProbeDocument35 paginiHuawei LTE Drive Test Guide for Genex Probesayfull46100% (2)
- Introduction To GENEX AssistantDocument55 paginiIntroduction To GENEX AssistantAbd el rahman essamÎncă nu există evaluări
- TEMS Discovery Device 10.0 - Technical Product DescriptionDocument51 paginiTEMS Discovery Device 10.0 - Technical Product Descriptiontuanvuanh200777Încă nu există evaluări
- ReleaseNotes AnalyzerUpdate 2015 03 March PDFDocument8 paginiReleaseNotes AnalyzerUpdate 2015 03 March PDFdang_dung_44Încă nu există evaluări
- Comparison of Atoll Planet For LTEDocument16 paginiComparison of Atoll Planet For LTElahyouhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Huawei U8500 Software Upgrade GuideDocument6 paginiHuawei U8500 Software Upgrade Guide1LanistaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Procedure For Binning Using XcalDocument13 paginiProcedure For Binning Using XcalHazamir HamzahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atoll 3.2.0 User ManualDocument10 paginiAtoll 3.2.0 User ManualPhong TaÎncă nu există evaluări
- TEMS Pocket 13.2 - Release NoteDocument18 paginiTEMS Pocket 13.2 - Release NoteOthman EssamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Huawei GENEX Series Drive Test System GuideDocument111 paginiHuawei GENEX Series Drive Test System GuideRafael Andres Rodriguez MarulandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nemo Outdoor Training 2013Document247 paginiNemo Outdoor Training 2013Rehan RaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- White Paper For CDMA2000 1xEV-DO Rev.B Network Planning V1.3 (20100112)Document42 paginiWhite Paper For CDMA2000 1xEV-DO Rev.B Network Planning V1.3 (20100112)cyclicprefixÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mentum Planet Release Notes PDFDocument36 paginiMentum Planet Release Notes PDFnurys77Încă nu există evaluări
- M2000Document19 paginiM2000naveedalishaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial Mapinfo ProfessionalDocument12 paginiTutorial Mapinfo Professionalsalman, STÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tems InvestigationDocument13 paginiTems InvestigationLuis Von MatterhornÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atoll 2.8.2 Technical Reference Guide E0Document698 paginiAtoll 2.8.2 Technical Reference Guide E0nmtien1985Încă nu există evaluări
- U2000 Trace Server Lte MDT Data Northbound File Interface Developer Guid CompressDocument102 paginiU2000 Trace Server Lte MDT Data Northbound File Interface Developer Guid CompressJacob JacobÎncă nu există evaluări
- NEMO Outdoor8.20 Compatible DevicesDocument9 paginiNEMO Outdoor8.20 Compatible DevicesemilsonacruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- MDT Operation GuideDocument18 paginiMDT Operation GuideHamid Raza100% (1)
- 13 GSM BSS Network KPI (Network Interference) Optimiza - Buscar Con GoogleDocument11 pagini13 GSM BSS Network KPI (Network Interference) Optimiza - Buscar Con GoogleCarlos Paz0% (1)
- Introduction To GENEX ProbeDocument68 paginiIntroduction To GENEX ProbeDawood Khan100% (1)
- TEMS Discovery 21.2.3 Release NoteDocument35 paginiTEMS Discovery 21.2.3 Release Notehenry457Încă nu există evaluări
- Netact Documentation NSN Netact Oss5.1Document15 paginiNetact Documentation NSN Netact Oss5.1ICCB2006Încă nu există evaluări
- Huawei Ep 820 821Document3 paginiHuawei Ep 820 821Subditbinkom DithubadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mejtpg Infill Site: Nodeb Scanning GuideDocument10 paginiMejtpg Infill Site: Nodeb Scanning GuideMayank MohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tems Discovery HelpDocument17 paginiTems Discovery Helprf telecomÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample CV For - NOCDocument4 paginiSample CV For - NOCAzeemuddin KhajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scanner and Xcal Comperative Analysis v2Document22 paginiScanner and Xcal Comperative Analysis v2Ziya2009Încă nu există evaluări
- MP501 Mentum Planet 5.7 CoreDocument116 paginiMP501 Mentum Planet 5.7 CoreAnonymous iAYcAh100% (1)
- Genex Assistant Operation Guide LteDocument47 paginiGenex Assistant Operation Guide LteMustaf MohamedÎncă nu există evaluări
- LTE Optimization Tool PresentationDocument12 paginiLTE Optimization Tool PresentationAhmed Mansour SereerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Free Software Defined Radio GNU RadioDocument19 paginiFree Software Defined Radio GNU RadioNishant1234_2014Încă nu există evaluări
- Detecting Swapped Sectors Using Mobility StatisticsDocument4 paginiDetecting Swapped Sectors Using Mobility StatisticsFelix J. Alvarez HerreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Making Telecoms Work: From Technical Innovation to Commercial SuccessDe la EverandMaking Telecoms Work: From Technical Innovation to Commercial SuccessÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cross-Layer Resource Allocation in Wireless Communications: Techniques and Models from PHY and MAC Layer InteractionDe la EverandCross-Layer Resource Allocation in Wireless Communications: Techniques and Models from PHY and MAC Layer InteractionÎncă nu există evaluări
- VoLTE and ViLTE: Voice and Conversational Video Services over the 4G Mobile NetworkDe la EverandVoLTE and ViLTE: Voice and Conversational Video Services over the 4G Mobile NetworkÎncă nu există evaluări
- EasyRET Single-Band Antenna Specs and DetailsDocument2 paginiEasyRET Single-Band Antenna Specs and DetailsPunky HeroÎncă nu există evaluări
- FiberHome HXPLDX0B0020033DXTHF SpecificationDocument2 paginiFiberHome HXPLDX0B0020033DXTHF SpecificationPunky HeroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Powerwave 5755.00Document1 paginăPowerwave 5755.00Punky HeroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atr 451709 Datasheet PDFDocument2 paginiAtr 451709 Datasheet PDFCash Pappy0% (1)
- 18 DBi - Dual Band - 4 Port - MB900&3F-65-16.5&17.5DE-THDocument1 pagină18 DBi - Dual Band - 4 Port - MB900&3F-65-16.5&17.5DE-THPunky Hero100% (2)
- 5NPX1006F-634159Document1 pagină5NPX1006F-634159Punky HeroÎncă nu există evaluări
- AAU3940 Description Draft A (20150105)Document17 paginiAAU3940 Description Draft A (20150105)Punky Hero100% (2)
- HBX 6519DS T0MDocument2 paginiHBX 6519DS T0MSantiago CoderlioÎncă nu există evaluări
- OMF000001 Um Interface and Radio Channels ISSUE2.1Document43 paginiOMF000001 Um Interface and Radio Channels ISSUE2.1Abdelrahman Abdelkarim MansourÎncă nu există evaluări
- MB3F 30 21de10 THDocument2 paginiMB3F 30 21de10 THPunky HeroÎncă nu există evaluări
- 200d New AmplifileDocument6 pagini200d New AmplifilePunky Hero100% (1)
- MB3F 65 21de10 THDocument2 paginiMB3F 65 21de10 THPunky HeroÎncă nu există evaluări
- FiberHome HXPLDX0B0020033DXTHF Specification PDFDocument2 paginiFiberHome HXPLDX0B0020033DXTHF Specification PDFPunky Hero100% (1)
- BSNL BSS Technical PresentationDocument23 paginiBSNL BSS Technical Presentationneil02adamÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSM/GPRS TutorialDocument5 paginiGSM/GPRS TutorialWale OgunniranÎncă nu există evaluări
- RAN14.0 Capacity Monitoring GuideDocument44 paginiRAN14.0 Capacity Monitoring GuideRami DahhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Huawei 3G IntroductionDocument57 paginiHuawei 3G IntroductionSiêu Nhân100% (2)
- BSSPAR1: Chapter 1 Introduction To Parameter Planning: 1 © Nokia Siemens NetworksDocument13 paginiBSSPAR1: Chapter 1 Introduction To Parameter Planning: 1 © Nokia Siemens NetworksPunky HeroÎncă nu există evaluări
- BSC6900+GSM+Technical+Description (V900R012C01 03)Document113 paginiBSC6900+GSM+Technical+Description (V900R012C01 03)Jessica BrenesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Access Failures Troubleshooting WorkshopDocument30 paginiAccess Failures Troubleshooting Workshopsyedusama100% (2)
- T-Mobile Frequency Planning GuidelinesDocument26 paginiT-Mobile Frequency Planning Guidelinesasif_835527Încă nu există evaluări
- FrequencyPlanning Ed05 DR02Document69 paginiFrequencyPlanning Ed05 DR02Hasnain MuhammadÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02 GSM BSS Network KPI (SDCCH Call Drop Rate) Optimization ManualDocument26 pagini02 GSM BSS Network KPI (SDCCH Call Drop Rate) Optimization ManualMistero_H100% (3)
- OMF007001 GSM Frequency Planning ISSUE2 0Document60 paginiOMF007001 GSM Frequency Planning ISSUE2 0Punky HeroÎncă nu există evaluări
- WCDMA Radio Network Optimization GuideDocument79 paginiWCDMA Radio Network Optimization GuideAsh Shiddiqi100% (4)
- RF Optimization GuideDocument51 paginiRF Optimization GuideCoro MontyÎncă nu există evaluări
- HSPA +, Exploring The Potential of Mobile Broadband World: ZTE HSPA Evolution SolutionDocument78 paginiHSPA +, Exploring The Potential of Mobile Broadband World: ZTE HSPA Evolution SolutionPunky HeroÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.1.1. HSDPA Low Throughput AnalysisDocument15 pagini1.1.1. HSDPA Low Throughput AnalysisPhang KokHong100% (1)
- Mobile Broadband Review 2014H1Document26 paginiMobile Broadband Review 2014H1Punky HeroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pic16f877a Phpapp02Document35 paginiPic16f877a Phpapp02firdaus_n9Încă nu există evaluări
- Electro Pneumatics StudentDocument24 paginiElectro Pneumatics StudentbooÎncă nu există evaluări
- AzLM Installation GuideDocument54 paginiAzLM Installation GuideBhavna Kaushik Bajpai67% (6)
- ATmega16(L) Microcontroller Speed, Packaging and Ordering OptionsDocument1 paginăATmega16(L) Microcontroller Speed, Packaging and Ordering OptionsСтанислав ШевченкоÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cypress USB-Sunkoerial API DocumentationDocument56 paginiCypress USB-Sunkoerial API Documentationhoge100% (2)
- Sony Kdl-32ex729 Kdl-40ex729 Kdl-46ex729 Chassis Az2-FDocument56 paginiSony Kdl-32ex729 Kdl-40ex729 Kdl-46ex729 Chassis Az2-FNathan BleedÎncă nu există evaluări
- GM06NW ProtocolDocument19 paginiGM06NW ProtocolBery PujakesumaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dynamic Power Sharing Between LTE Carriers (ERAN16.1 - 03)Document52 paginiDynamic Power Sharing Between LTE Carriers (ERAN16.1 - 03)VVLÎncă nu există evaluări
- E8xx ManualDocument30 paginiE8xx ManualGlenn-anthony Sending-State HortonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jadual Peperiksaan Akhir Sem Ii Sesi 20192020Document3 paginiJadual Peperiksaan Akhir Sem Ii Sesi 20192020awankilatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course Description: Adama Science and Technology UniversityDocument7 paginiCourse Description: Adama Science and Technology UniversityTesfaye OlanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Buy APC 0.6-84 (KVA-VAH) Interactive UPS Online - GeMDocument4 paginiBuy APC 0.6-84 (KVA-VAH) Interactive UPS Online - GeMArun Chand C VÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASPIRS REVISED AgainDocument78 paginiASPIRS REVISED AgainShaena VillaluzÎncă nu există evaluări
- EC6703 Embedded Real Time Systems Course OutlineDocument2 paginiEC6703 Embedded Real Time Systems Course OutlineSuresh Kumar100% (1)
- Digital System Desgin Study AssignmentDocument5 paginiDigital System Desgin Study AssignmentZohaib AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- BC 107Document6 paginiBC 107Harry HasibuanÎncă nu există evaluări
- COHERENT D5 1 v6.0Document76 paginiCOHERENT D5 1 v6.0gkoutÎncă nu există evaluări
- NAD 3240PE Integrated AmplifierDocument2 paginiNAD 3240PE Integrated Amplifierpascalb41100% (1)
- WD TV® Live Hub ManualDocument196 paginiWD TV® Live Hub ManualhungwayloÎncă nu există evaluări
- PCS-974A-G X Instruction Manual en Domestic General X R1.10Document194 paginiPCS-974A-G X Instruction Manual en Domestic General X R1.10Hikari DewiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Current Status and Future Applications For DMD - Based Projection DisplaysDocument4 paginiCurrent Status and Future Applications For DMD - Based Projection Displaysgangwar_neeteshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Features Certified Protection: Motor Protection and Control RelayDocument2 paginiAdvanced Features Certified Protection: Motor Protection and Control RelayEliasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fishermen Rescue System With LoRa ModuleDocument5 paginiFishermen Rescue System With LoRa ModuleInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Time TableDocument29 paginiTime TableTijo ThomasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical LabDocument17 paginiElectrical LabBlack HeartÎncă nu există evaluări
- Salus RT500RF ManualDocument28 paginiSalus RT500RF ManualAmiablePCÎncă nu există evaluări
- Led Lighting Power Controller: Features ApplicationsDocument36 paginiLed Lighting Power Controller: Features ApplicationsVaibhavÎncă nu există evaluări
- AN-3004 PDFCN PDFDocument11 paginiAN-3004 PDFCN PDFgspolettoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Best Bluetooth HeadphonesDocument9 paginiBest Bluetooth Headphonesketan kathaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Codigos de Diodos SMDDocument14 paginiCodigos de Diodos SMDJorge RuizÎncă nu există evaluări